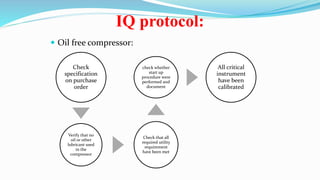
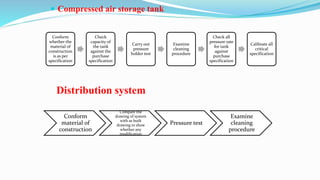
This document discusses the validation of critical utility systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. It covers the validation of HVAC systems, water systems, steam systems, compressed air systems, and nitrogen gas systems. For each system, it provides an overview and discusses the user requirements, design qualification, installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification protocols. The validation aims to ensure these utility systems meet quality standards and specifications to support the manufacturing of safe and effective pharmaceutical products.