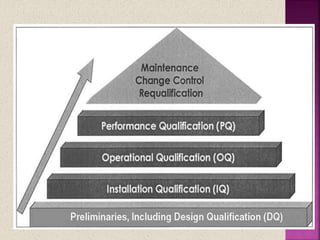
The document discusses validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It defines validation and equipment qualification, which includes design qualification, installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification. The goals of equipment qualification are to ensure equipment works correctly and produces accurate results through documentation and control of any changes. Specific validation processes for an autoclave used in stem sterilization are also outlined.