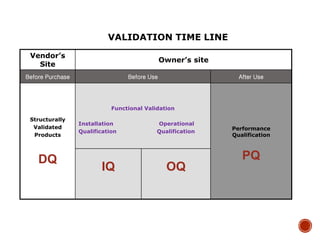
The document outlines the validation and qualification processes essential for ensuring compliance in production and testing, including steps such as design qualification, installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification. It highlights the purpose of documentation in preventing errors, ensuring quality, and achieving conformity. Each qualification step is detailed, emphasizing the verification of requirements, installation adherence, operational capability, and performance compliance under actual conditions.