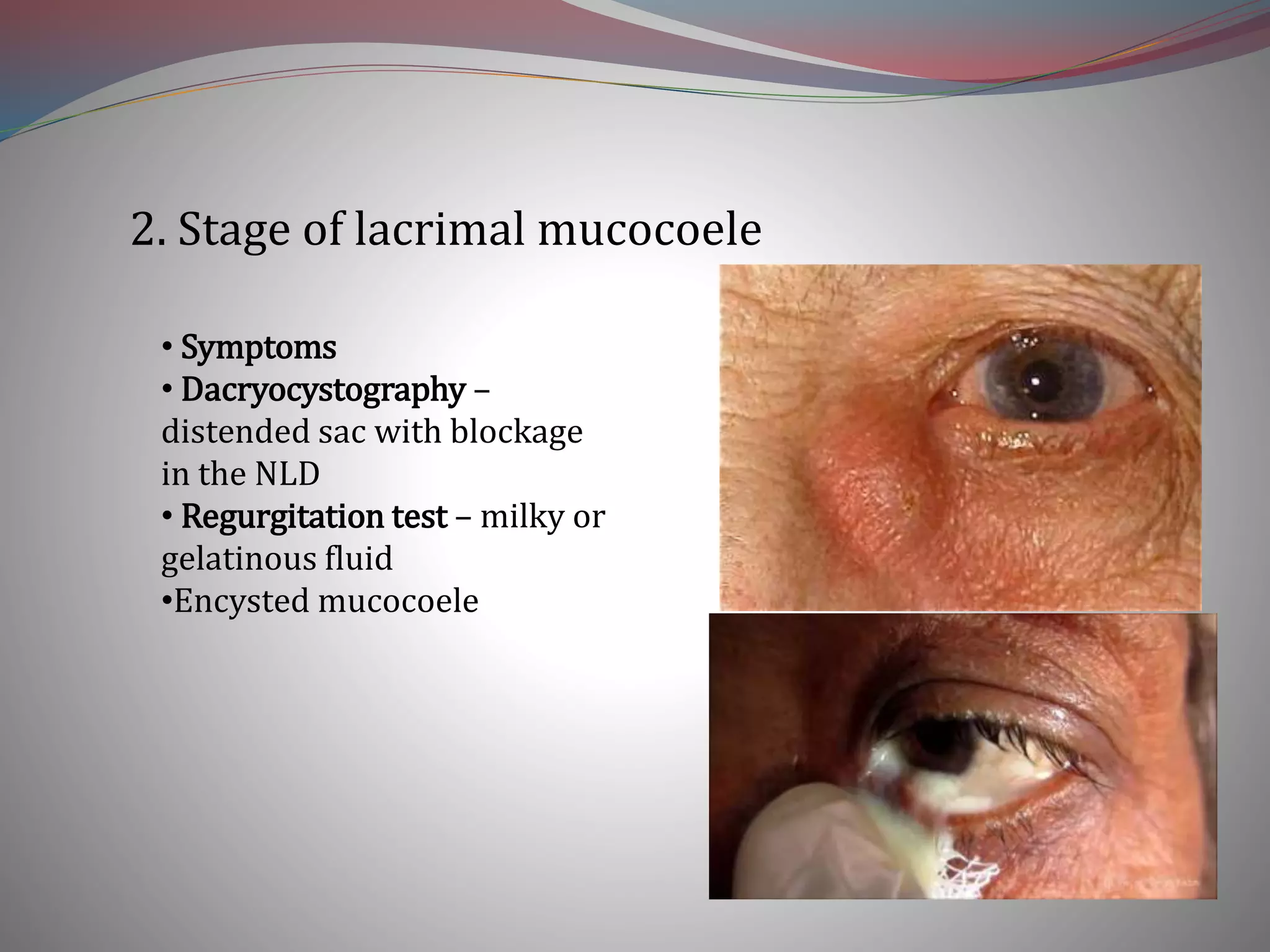
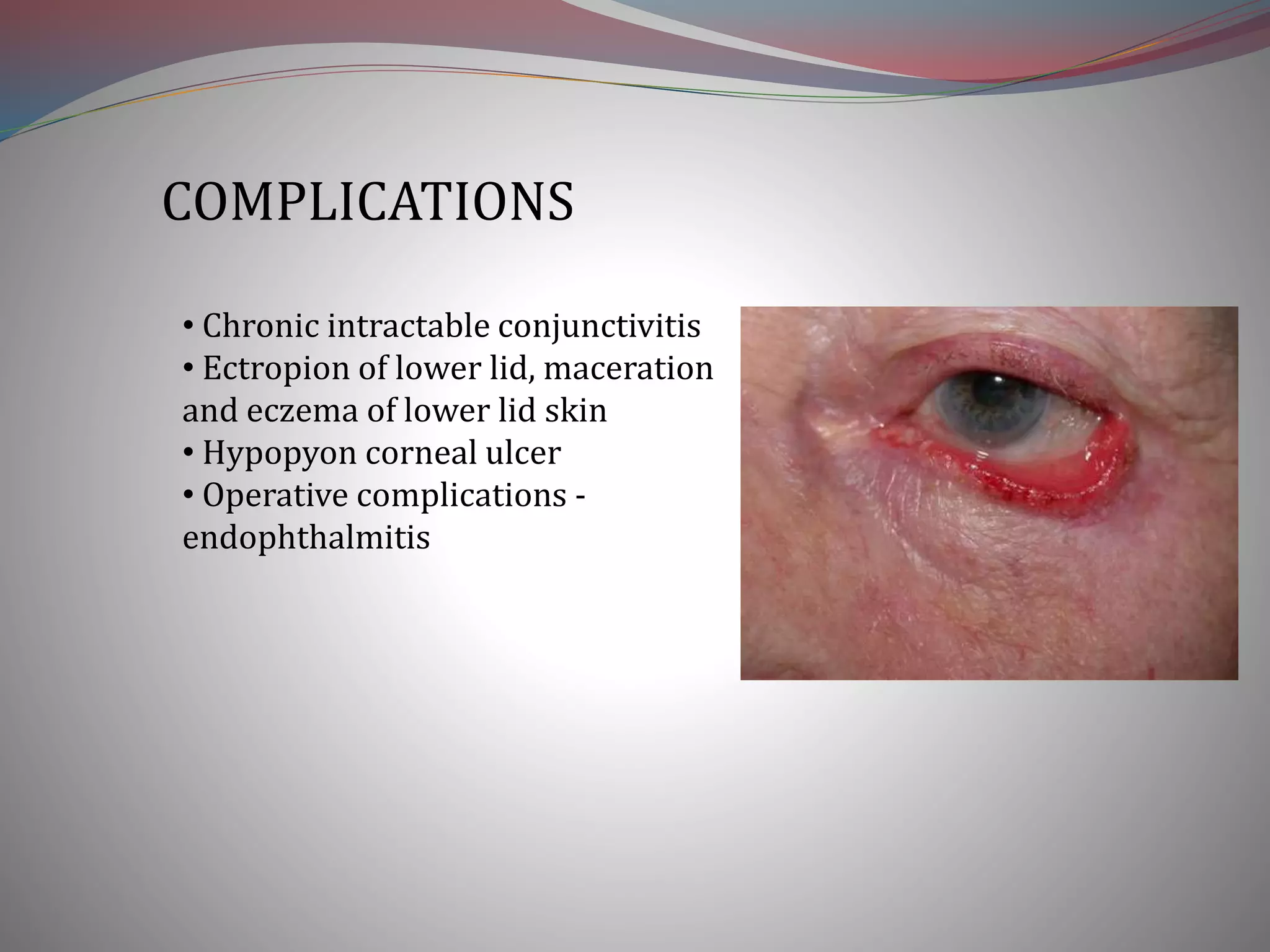
This document discusses chronic dacryocystitis, an inflammation of the lacrimal sac caused by blockage and infection. It identifies potential predisposing factors and causes, including age, anatomy, foreign bodies, and common infectious organisms like Staphylococci. The condition progresses through stages from chronic catarrhal dacryocystitis to lacrimal mucocoele and chronic suppurative or fibrotic sac stages. Potential complications include conjunctivitis, ectropion, and corneal ulcers. Treatment options include lacrimal syringing, balloon dilation, dacryocystorhinostomy surgery, or dacryocystectomy if other options are contraindicated.