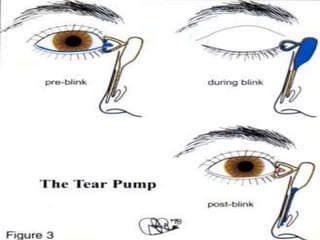
This document defines and describes the anatomy and physiology of the lacrimal apparatus, which is responsible for tear formation and drainage in the eye. It discusses how lacrimal syringing is used to test the structural integrity of the lacrimal drainage system by passing fluid through the puncta and observing for any blockages or abnormalities. The document also outlines the equipment needed for lacrimal syringing and provides interpretations of different results that could indicate where in the drainage system a blockage may be located.