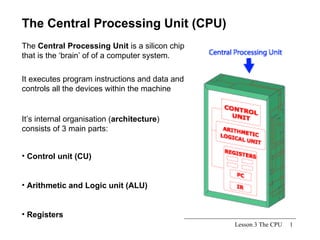
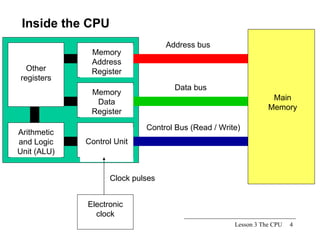
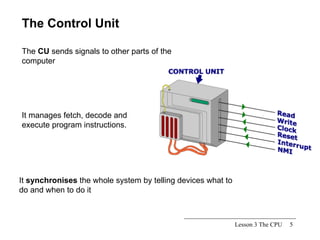
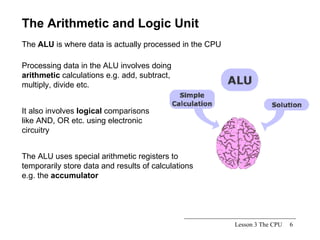
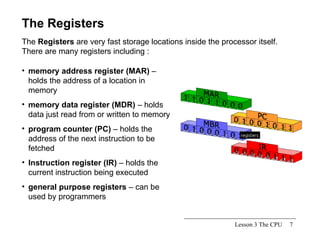
The CPU is the central processing unit that acts as the brain of the computer system. It has three main parts: the control unit that manages fetching and executing instructions, the arithmetic logic unit that performs calculations and logical operations, and registers for temporary storage of data and results. The CPU processes instructions and data to control all devices in the computer.