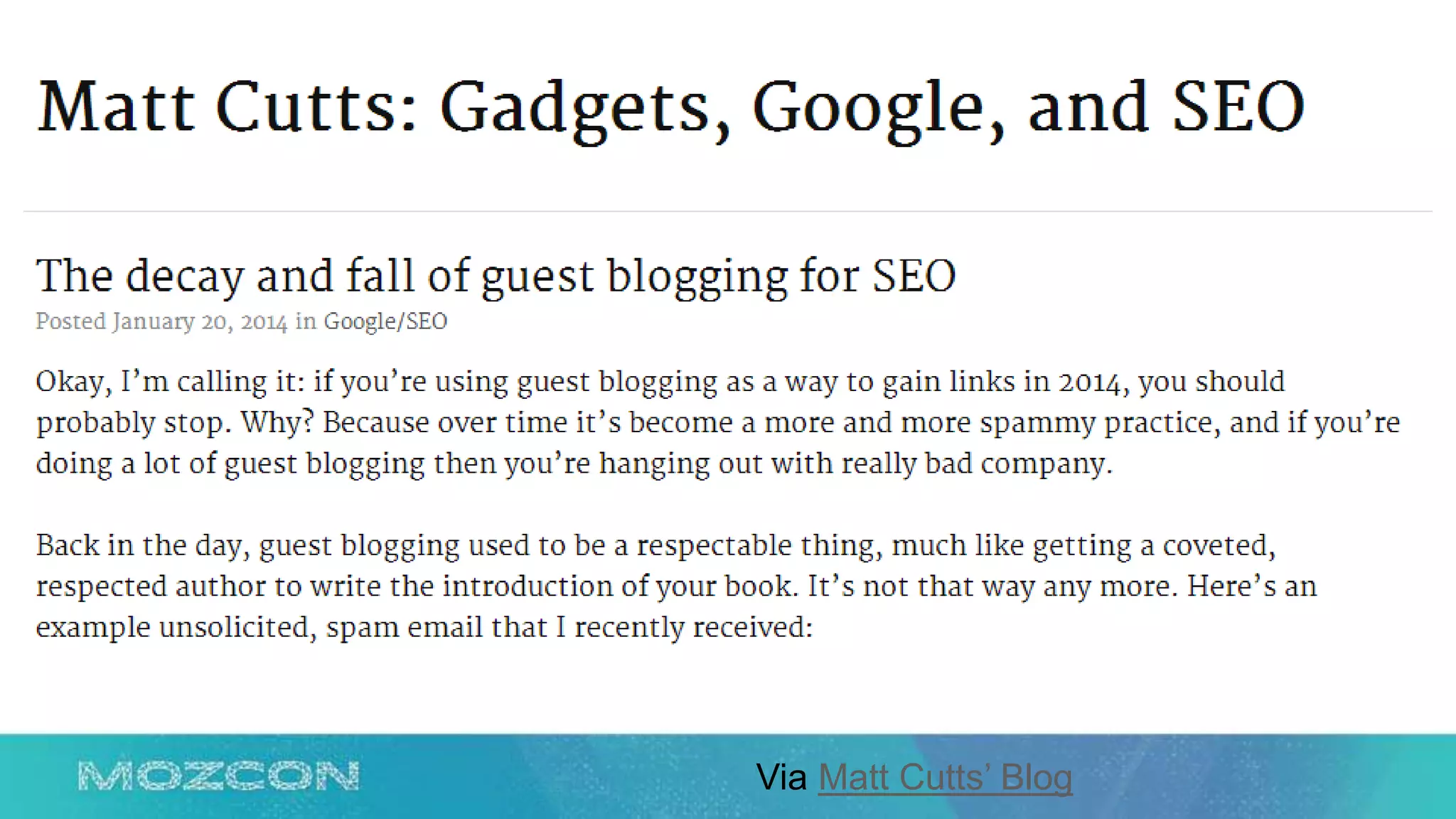
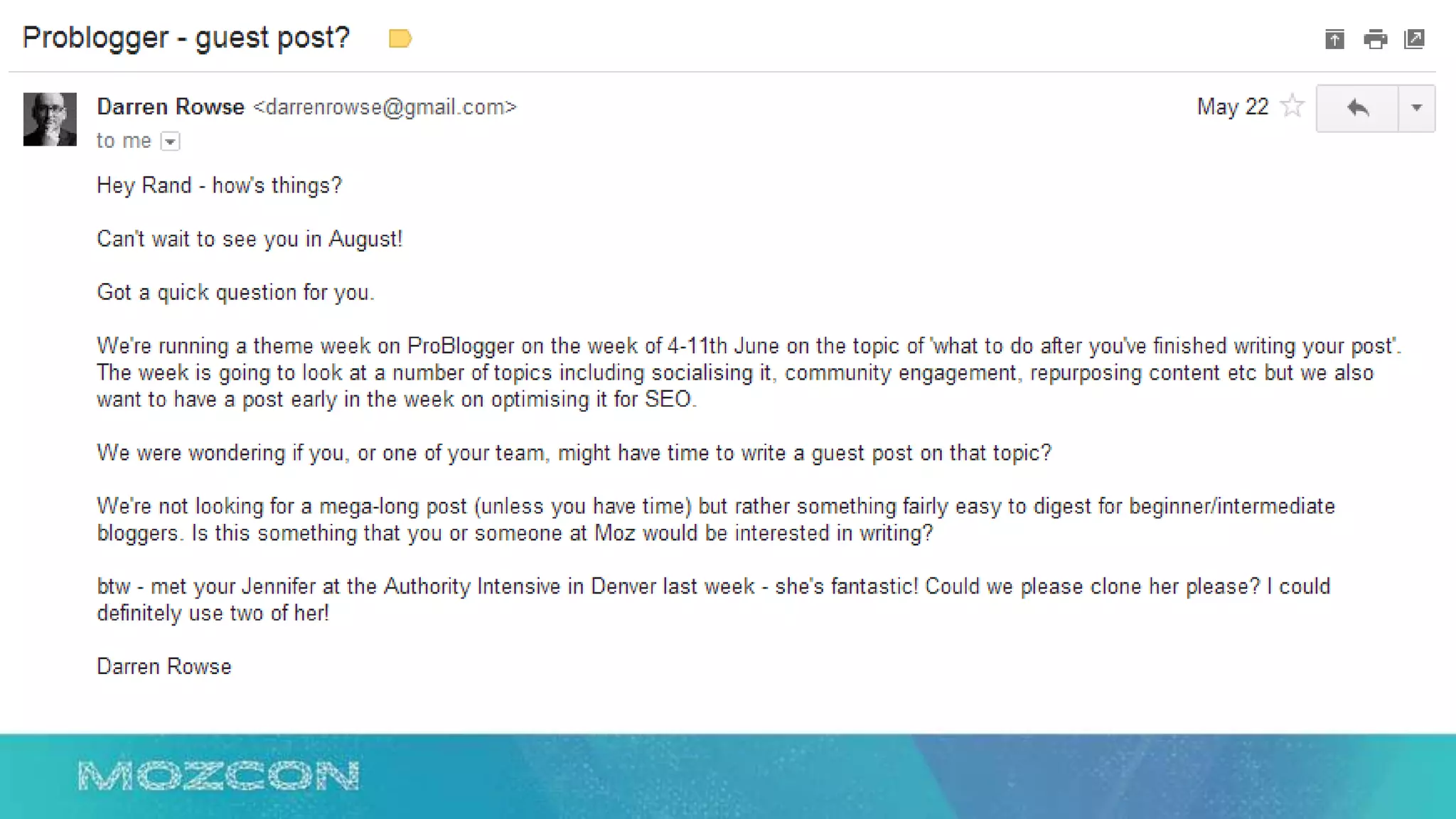
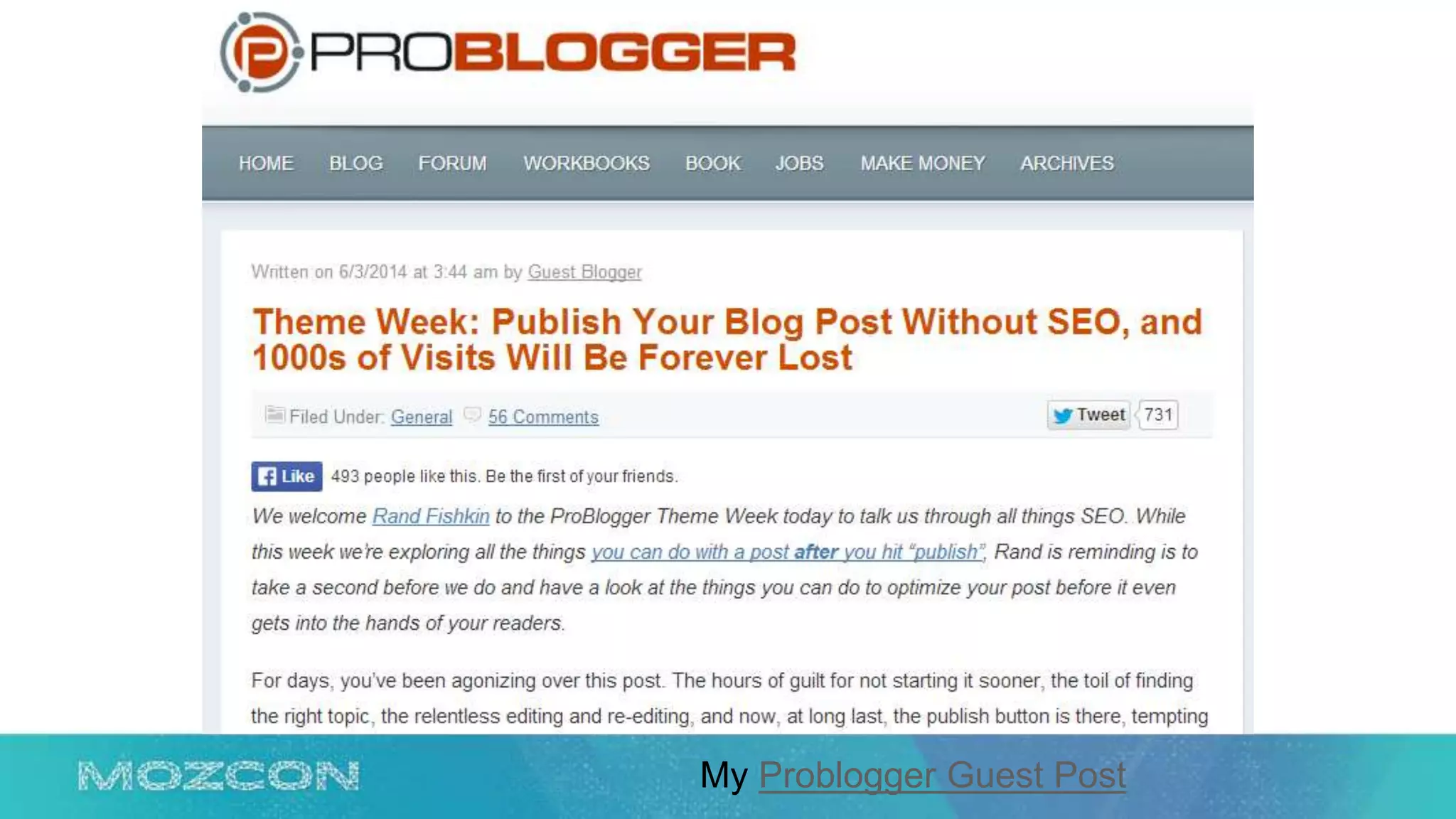
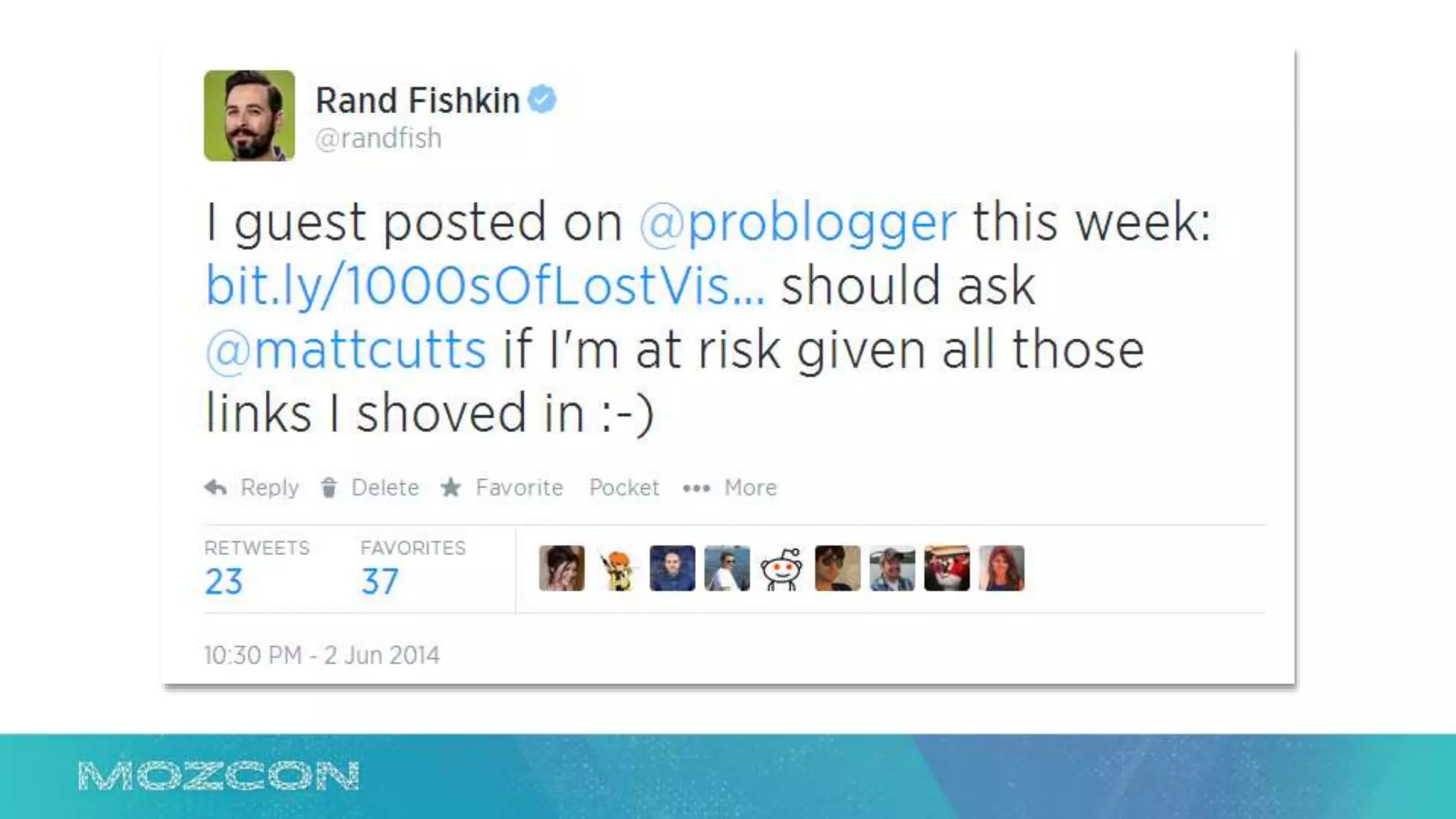
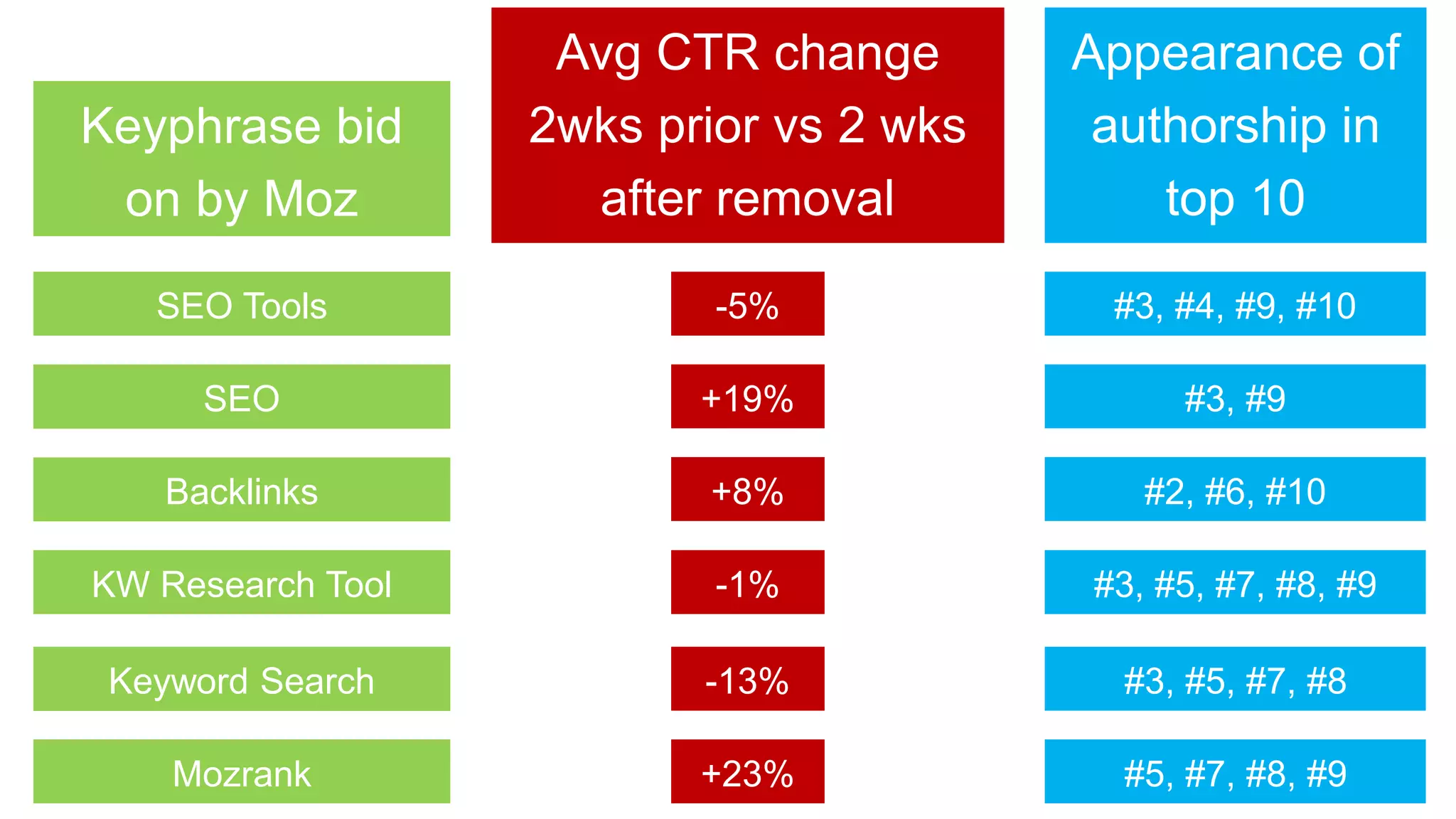
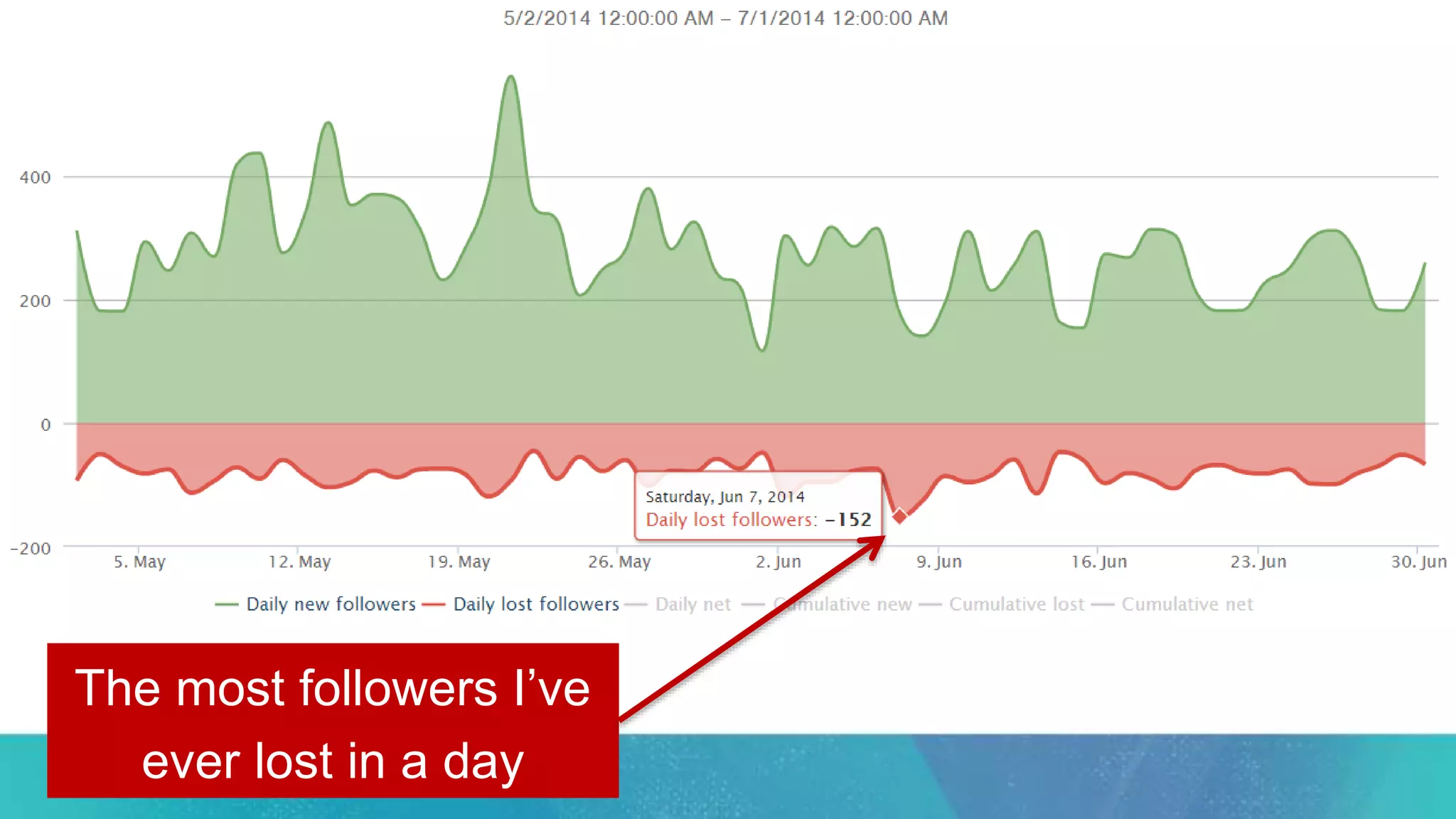
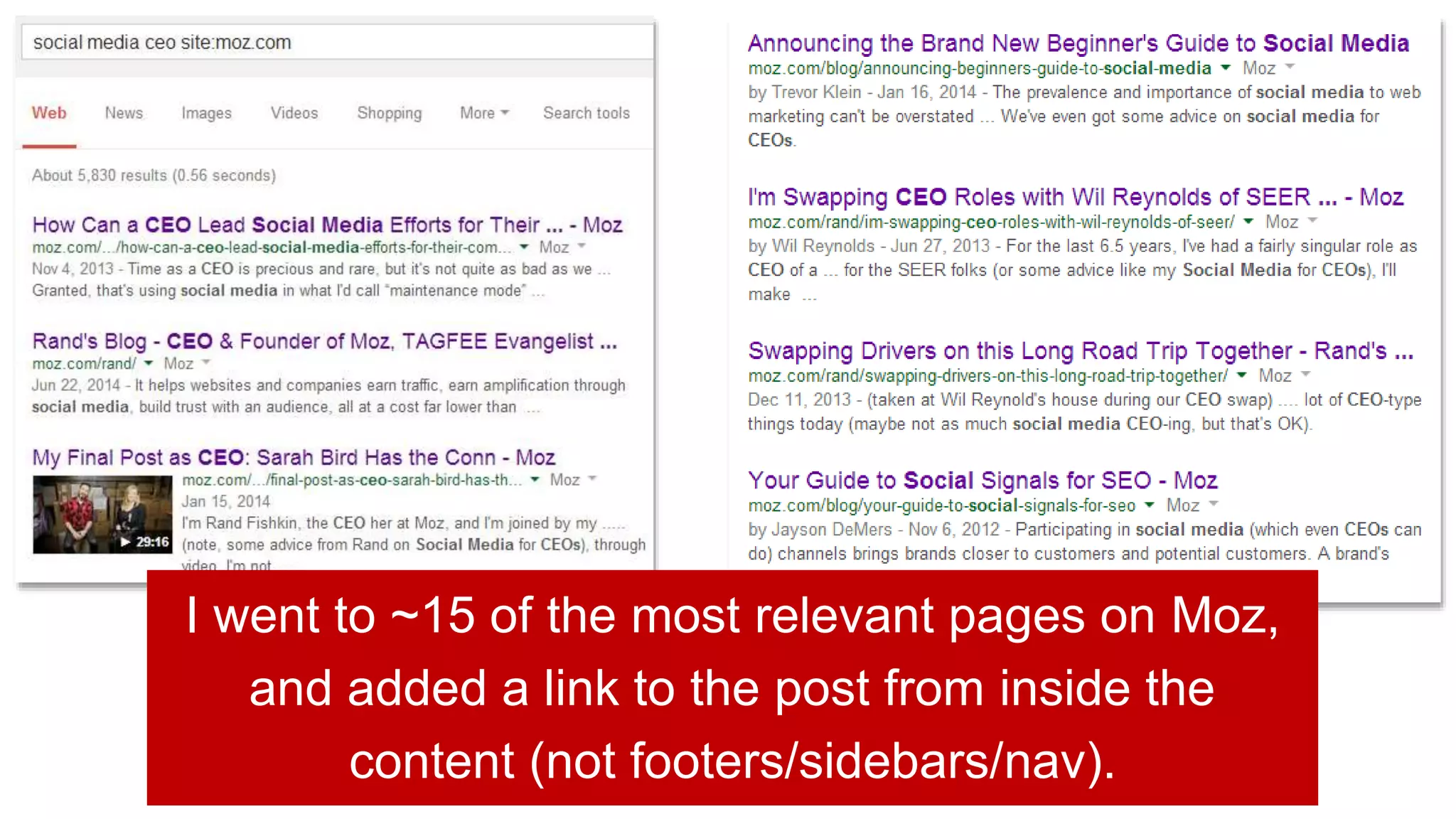
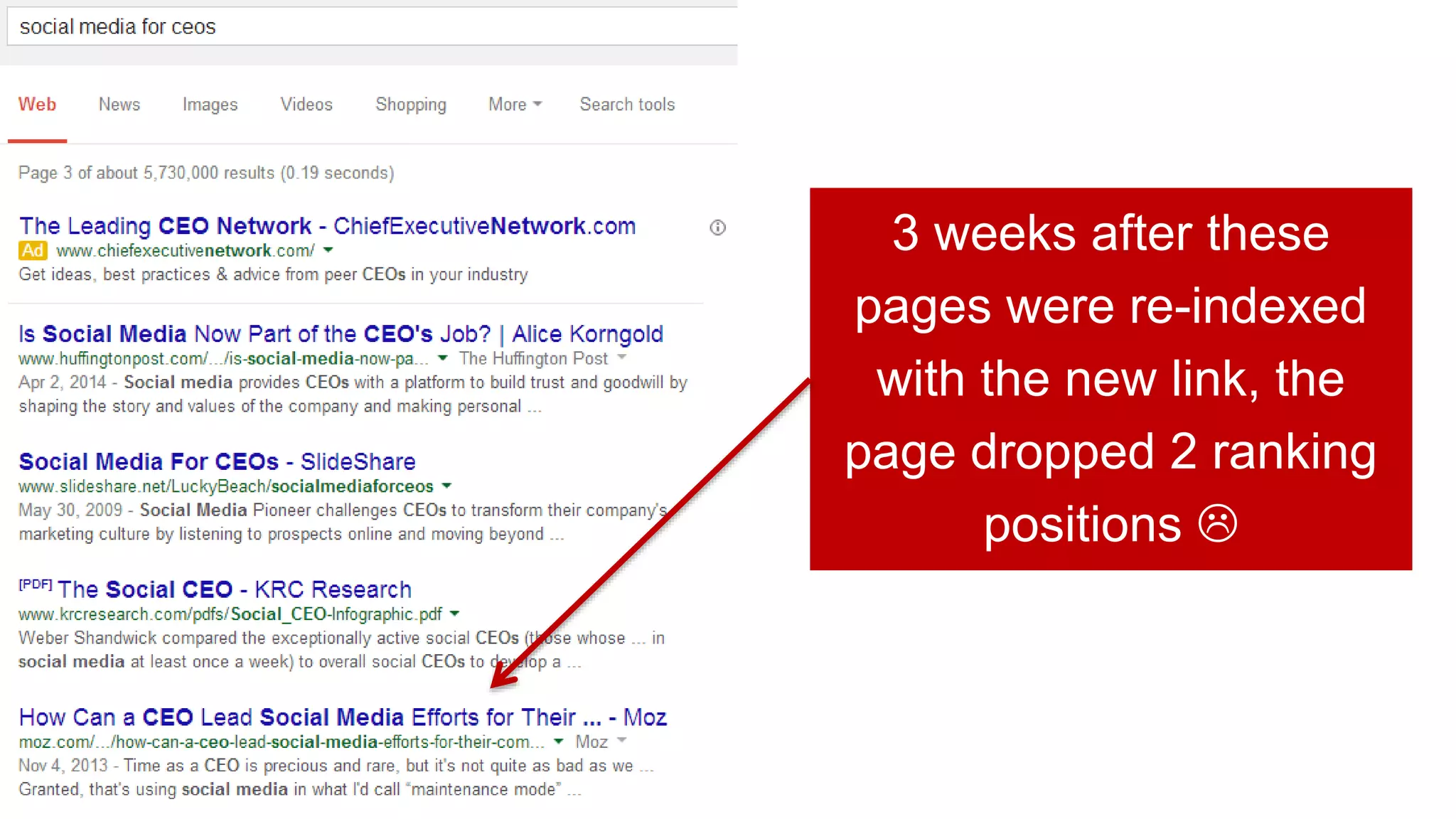
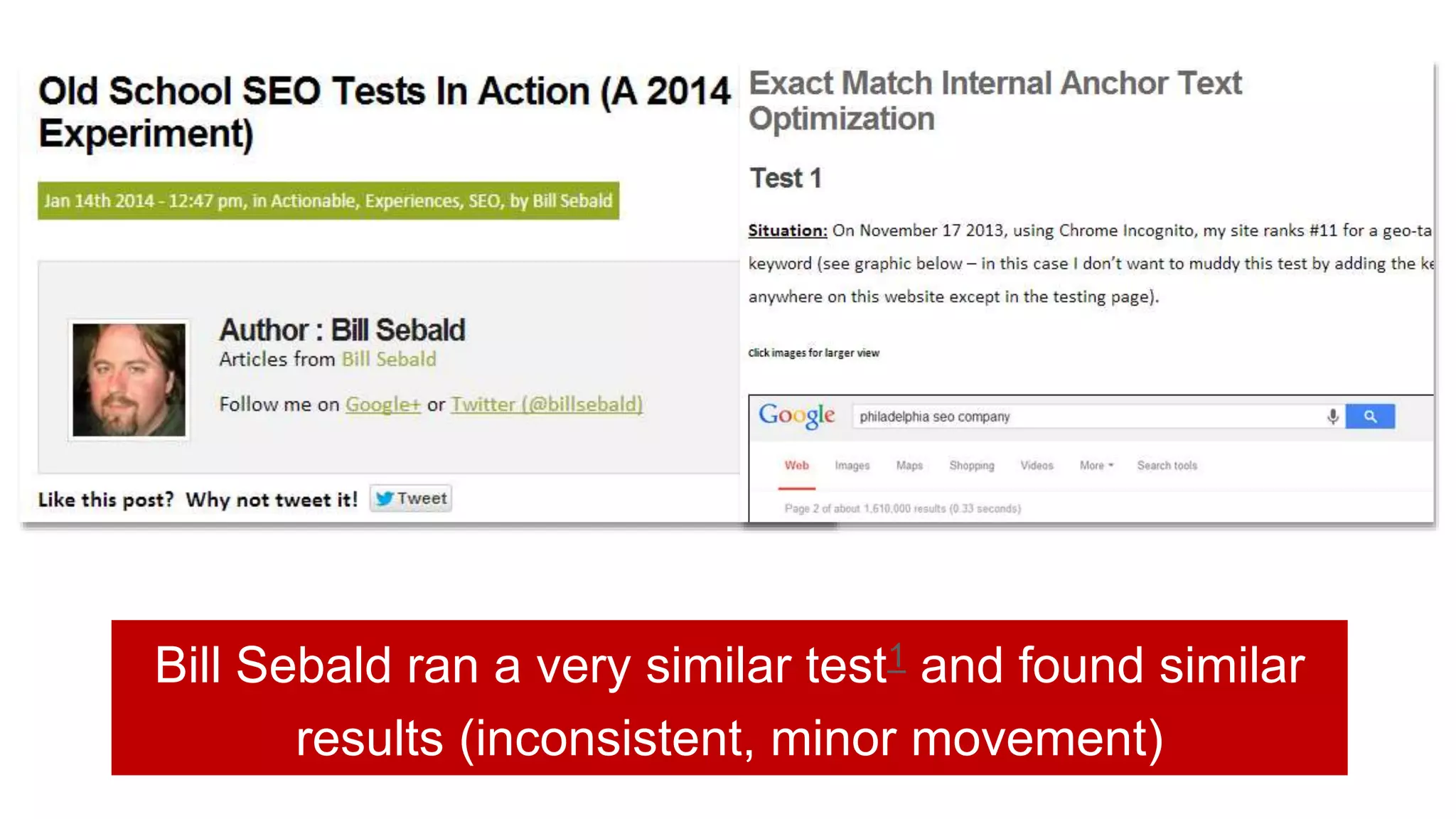
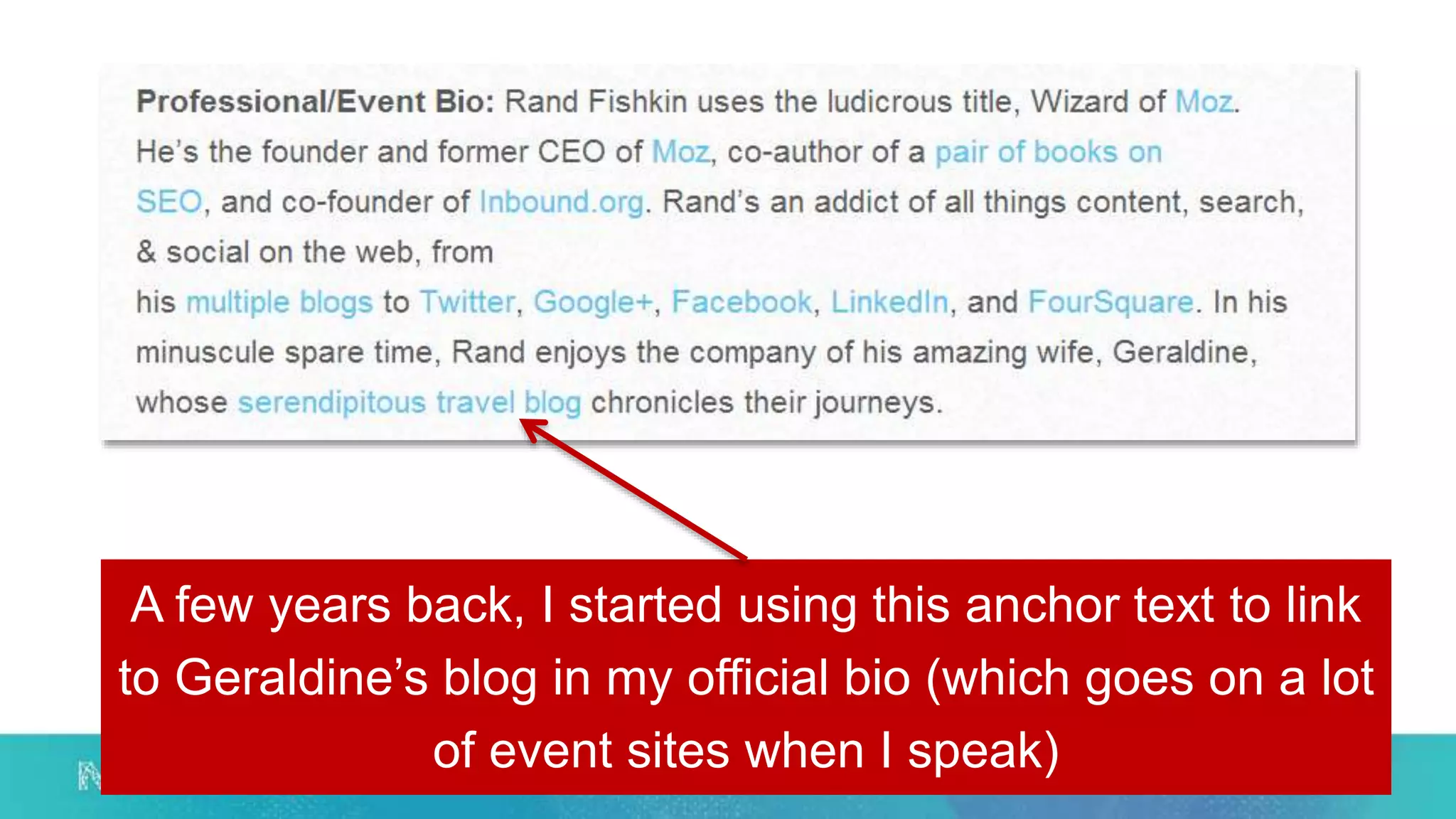
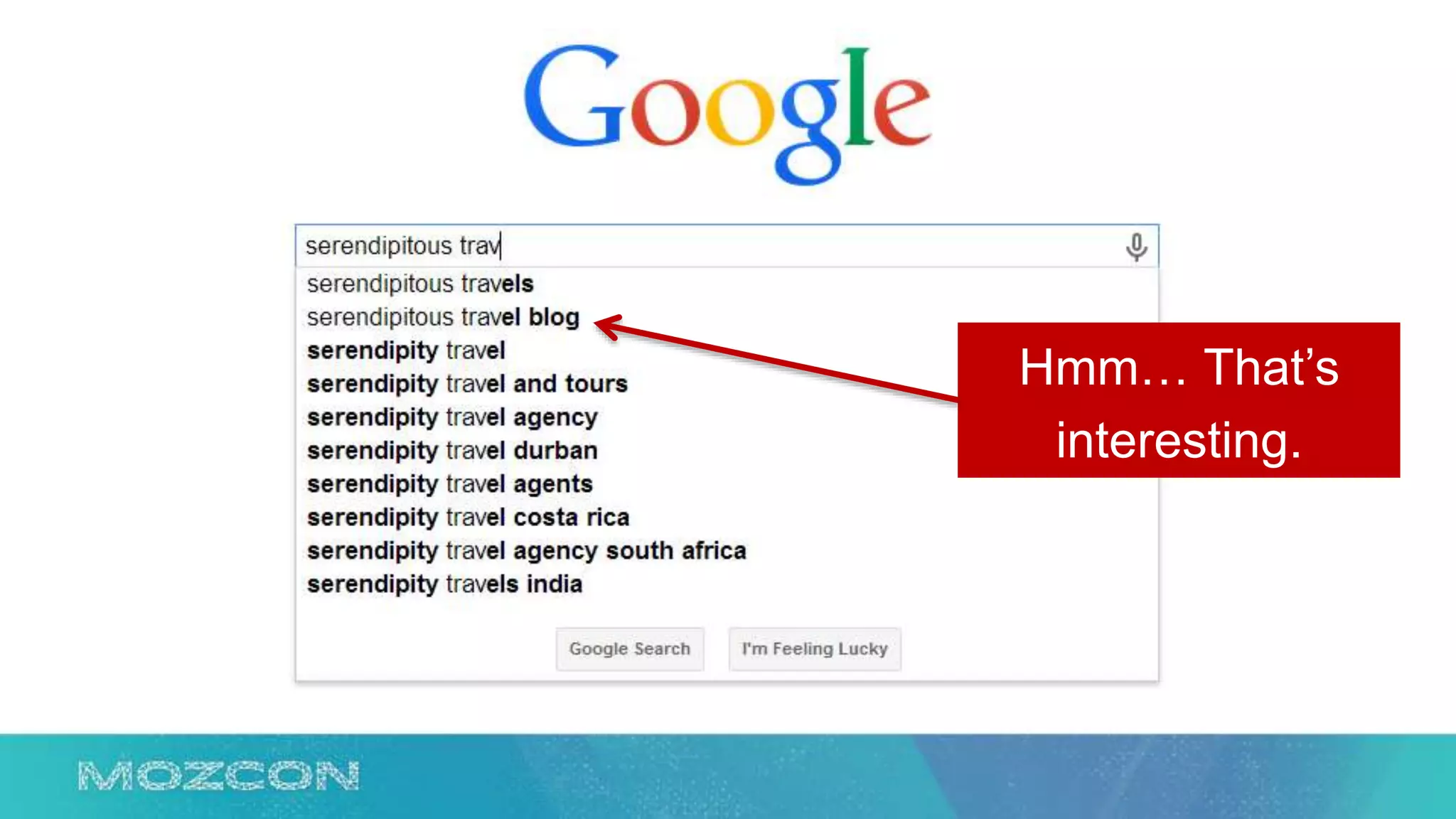
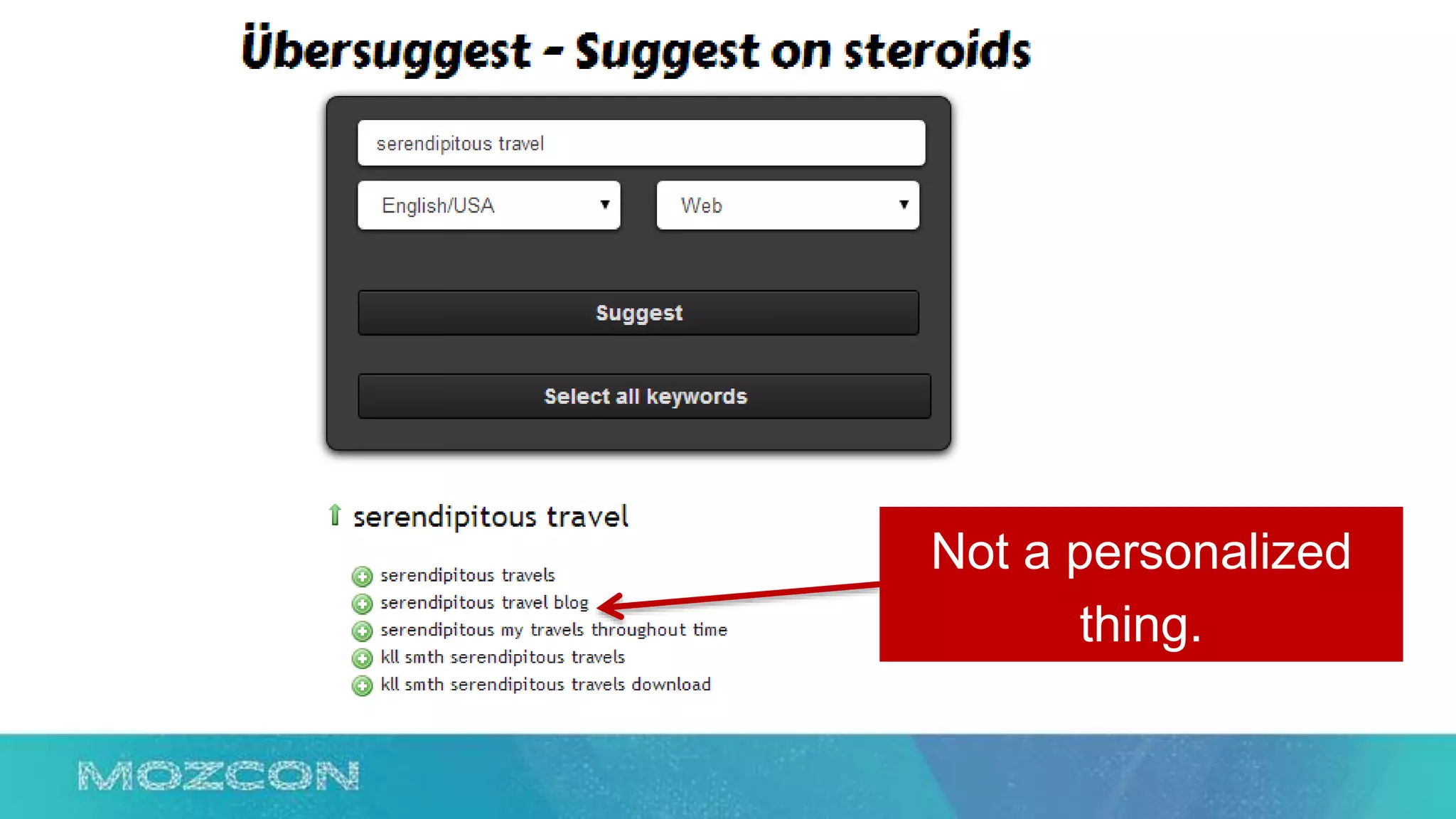
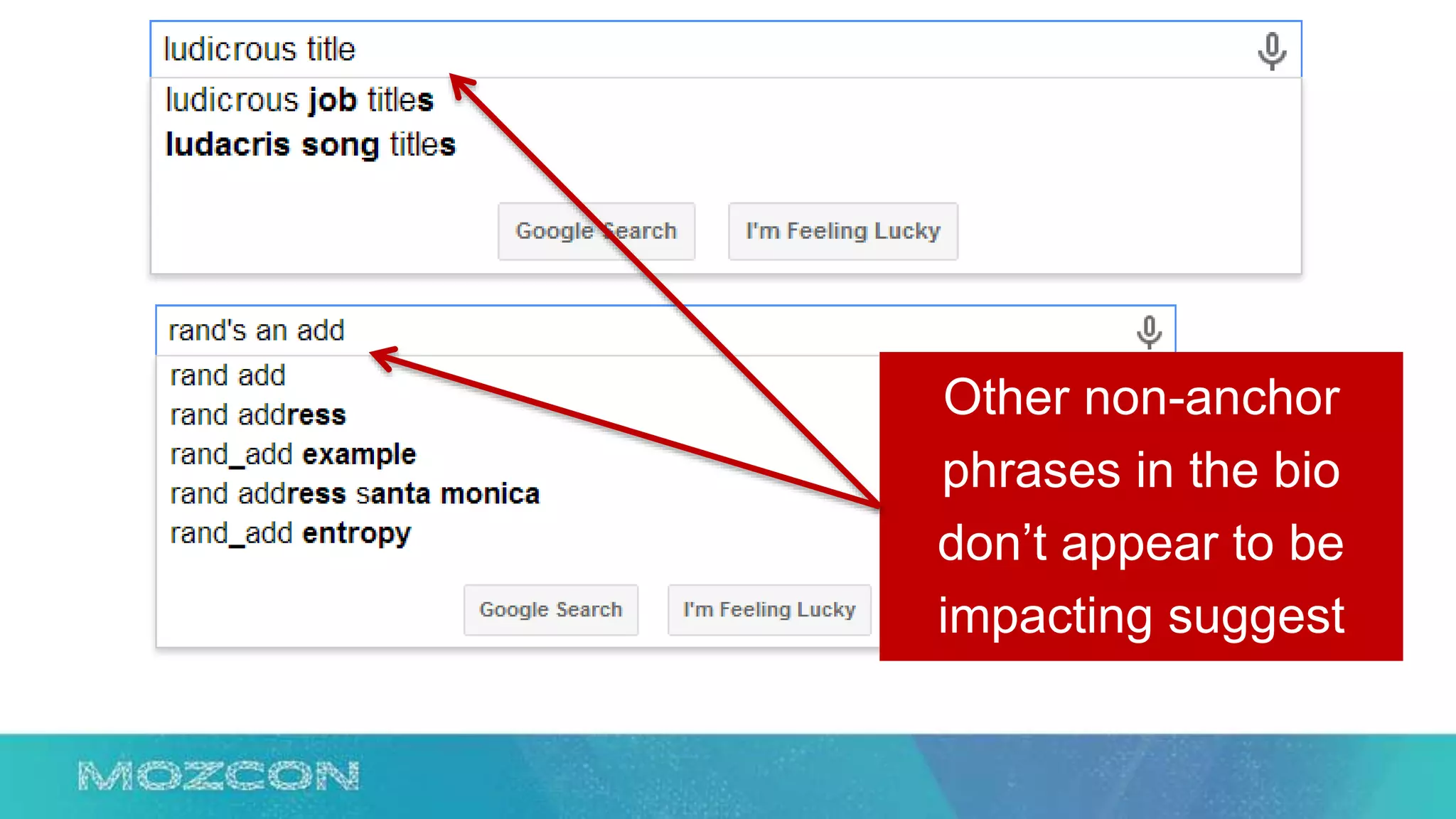
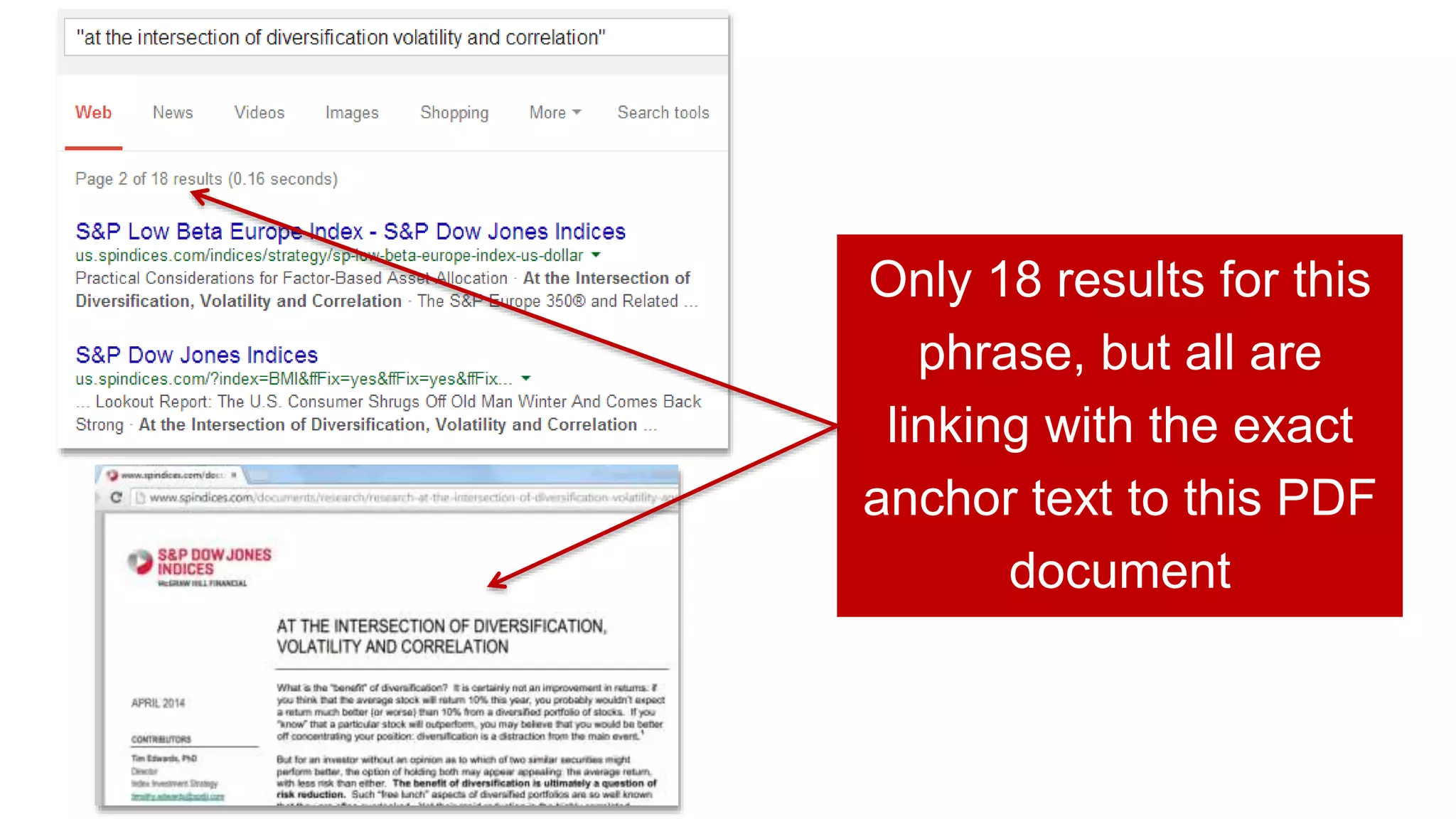
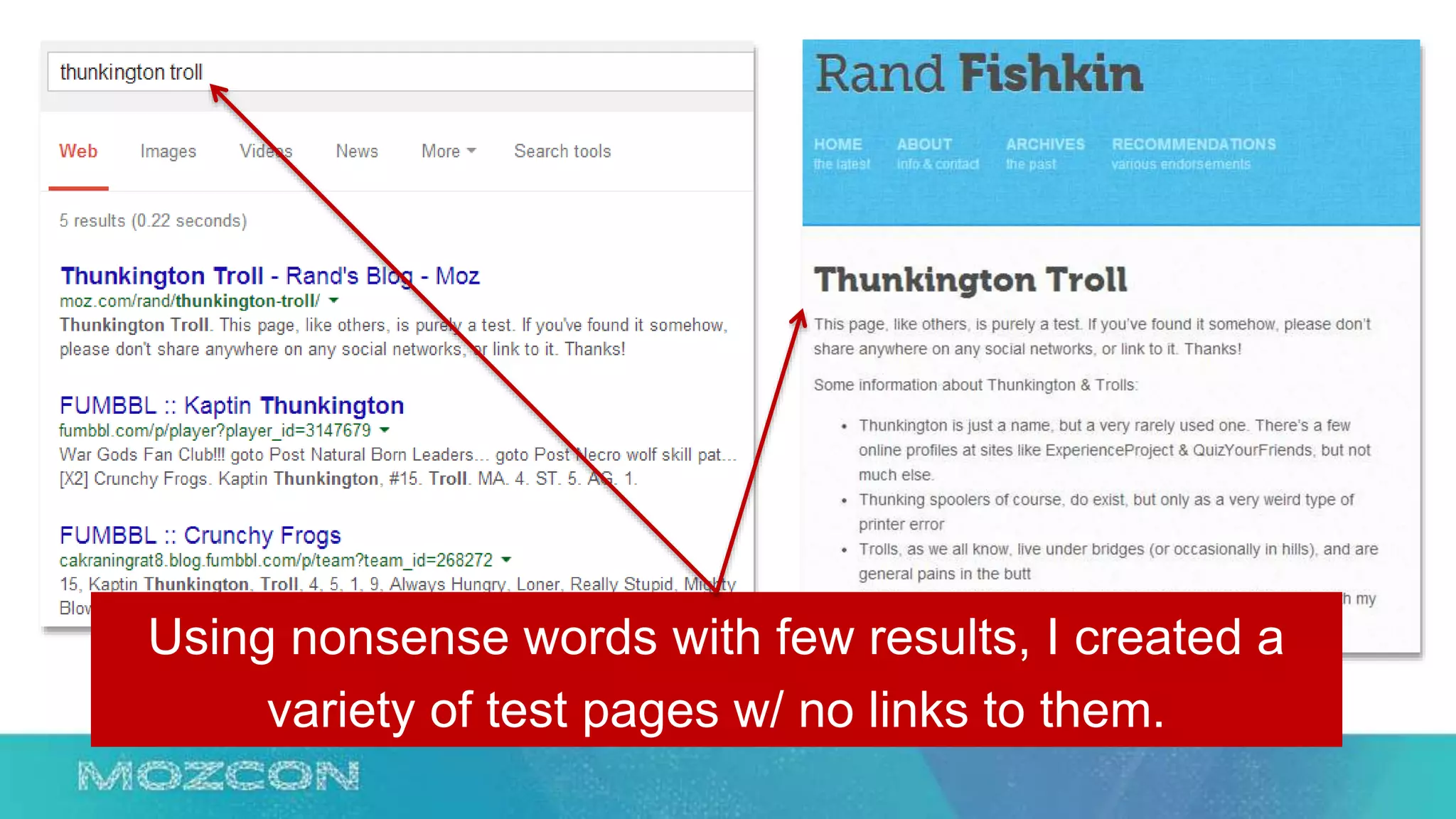
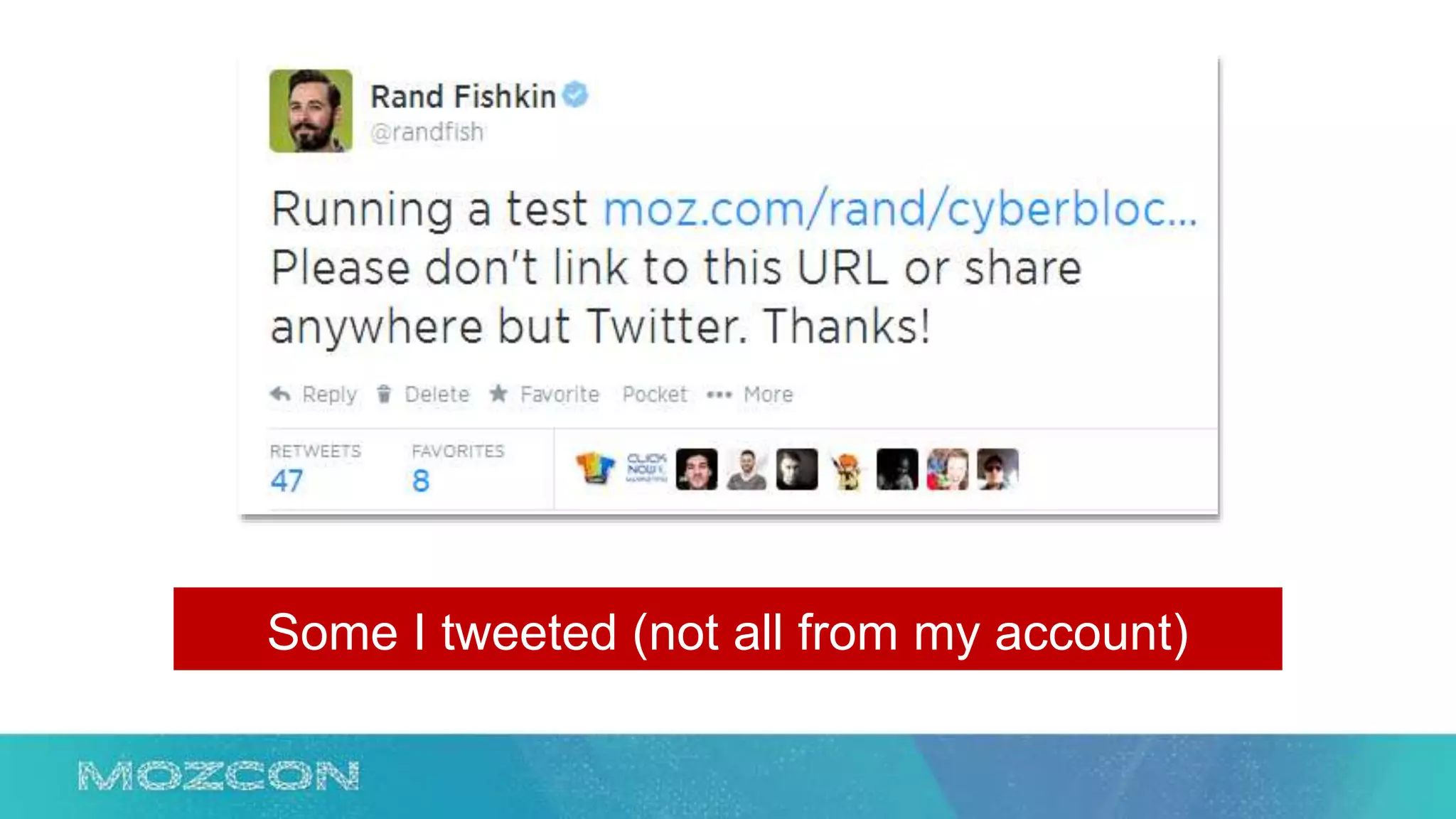
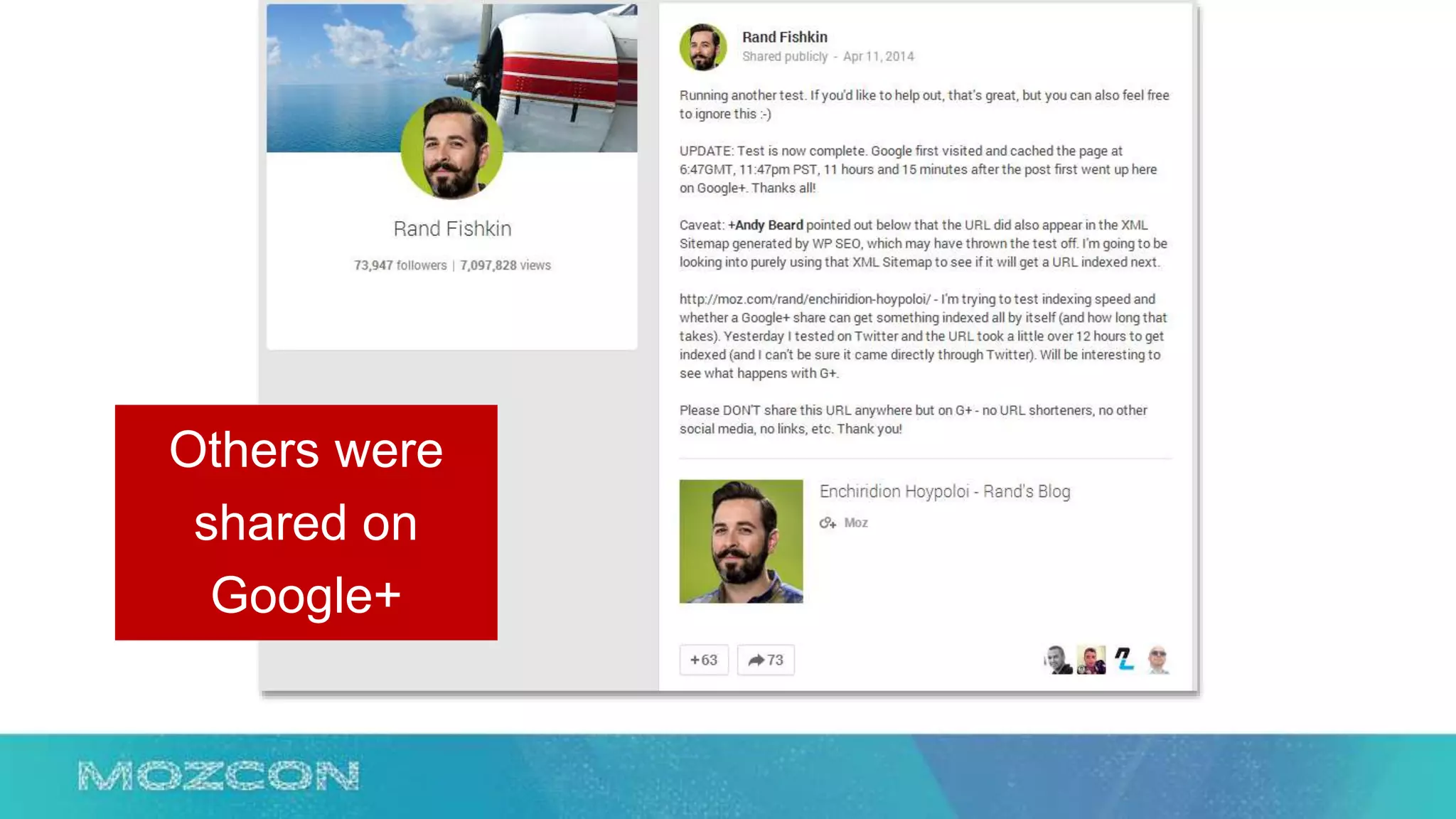
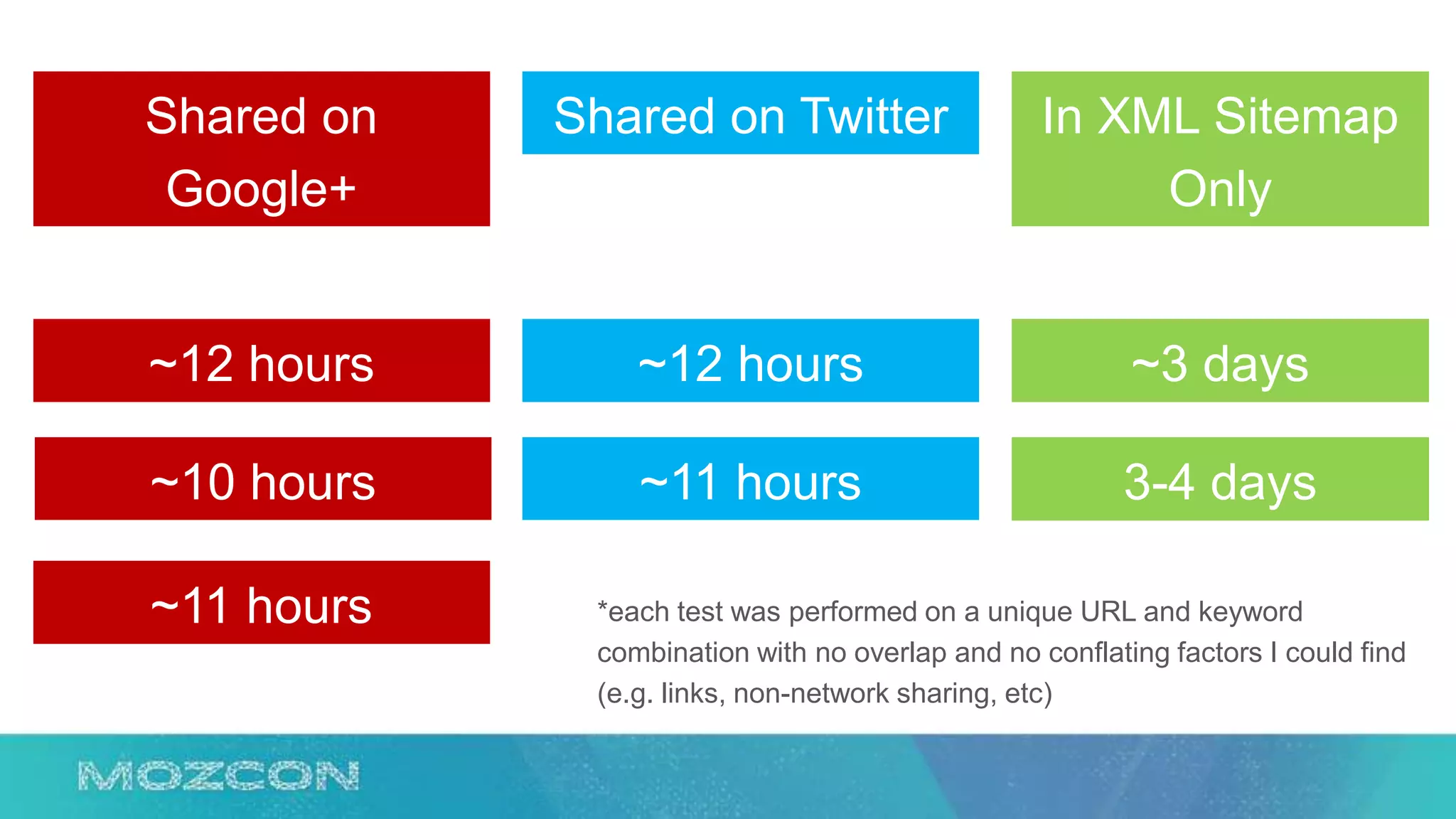
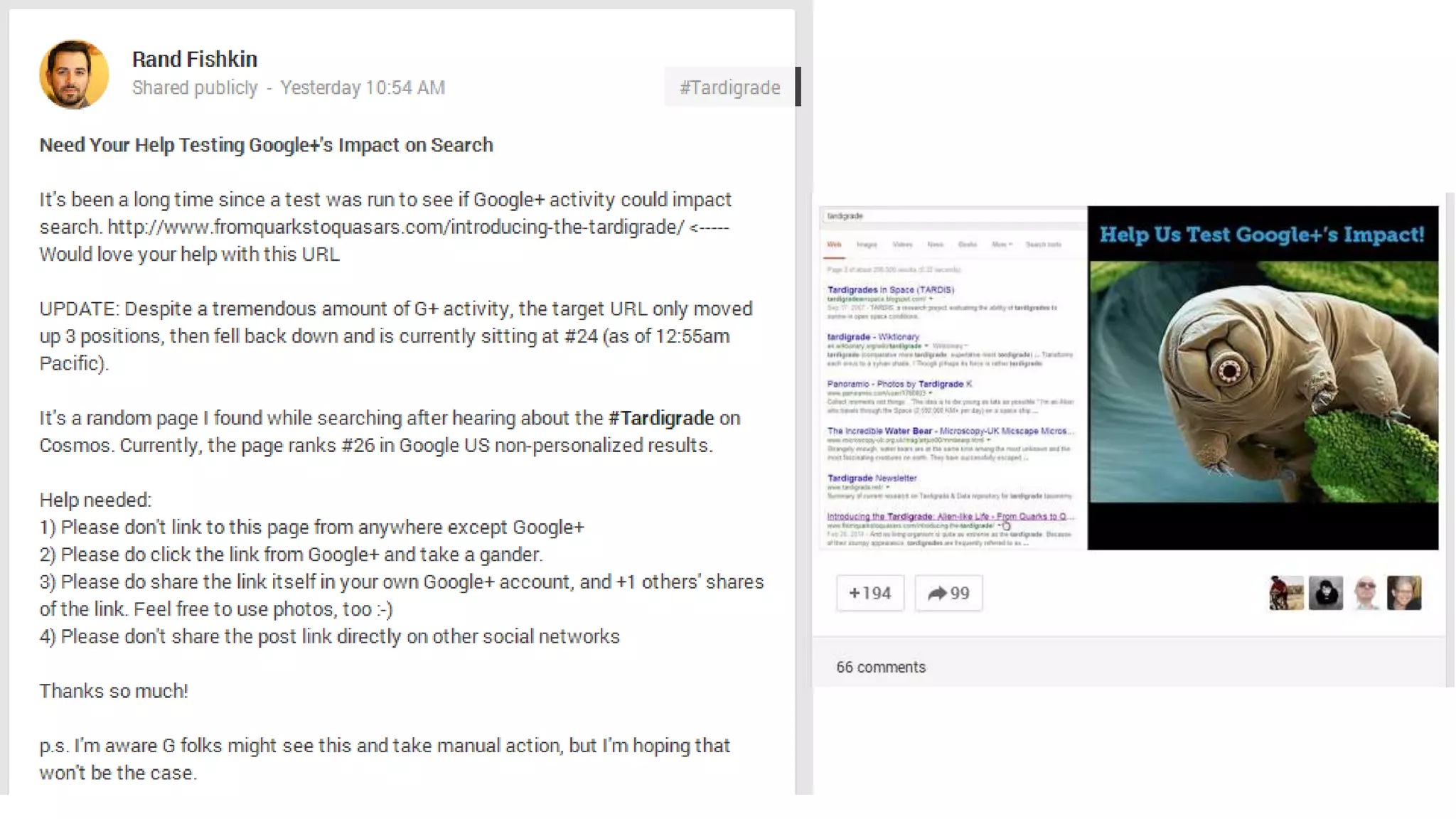
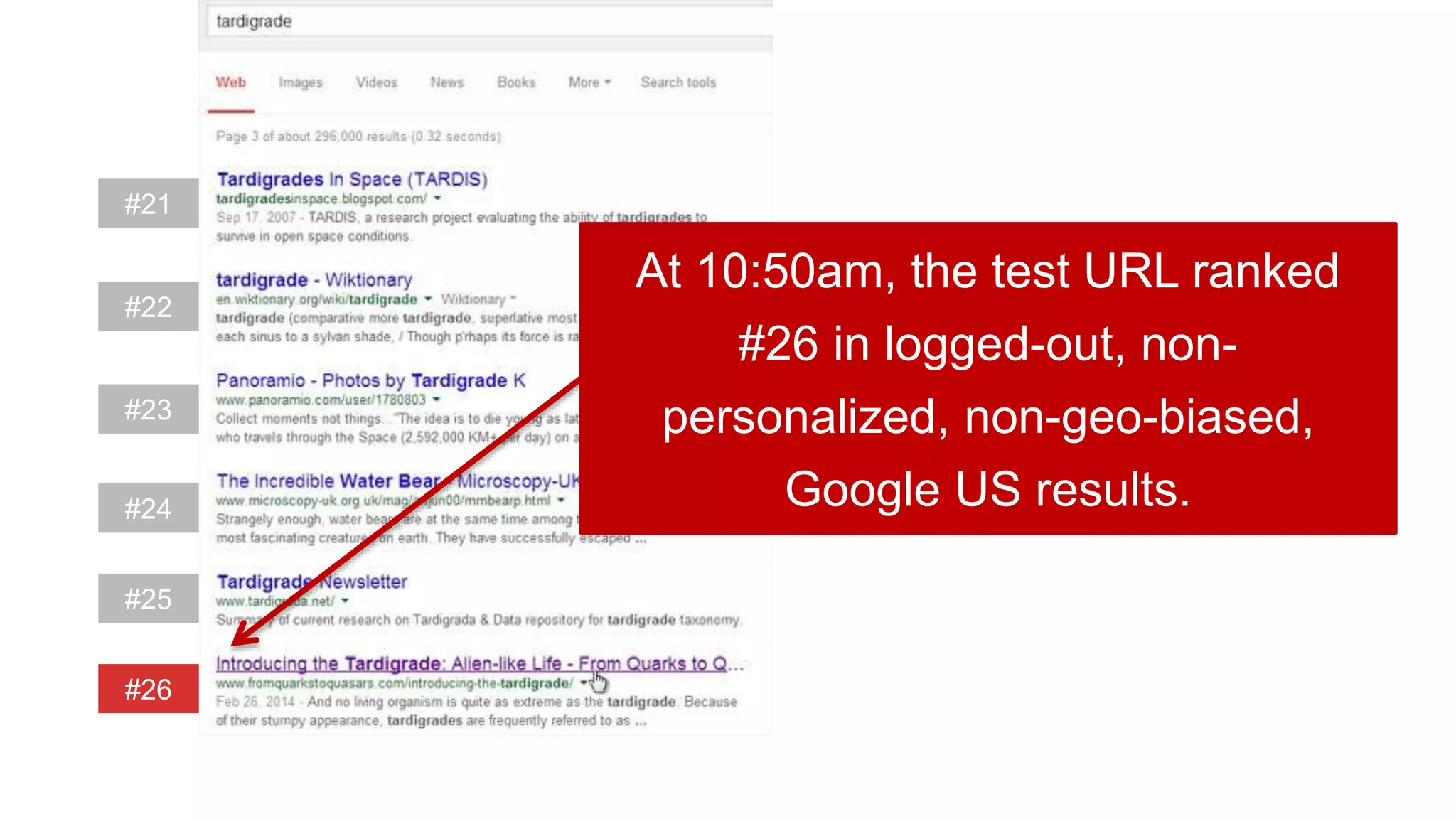
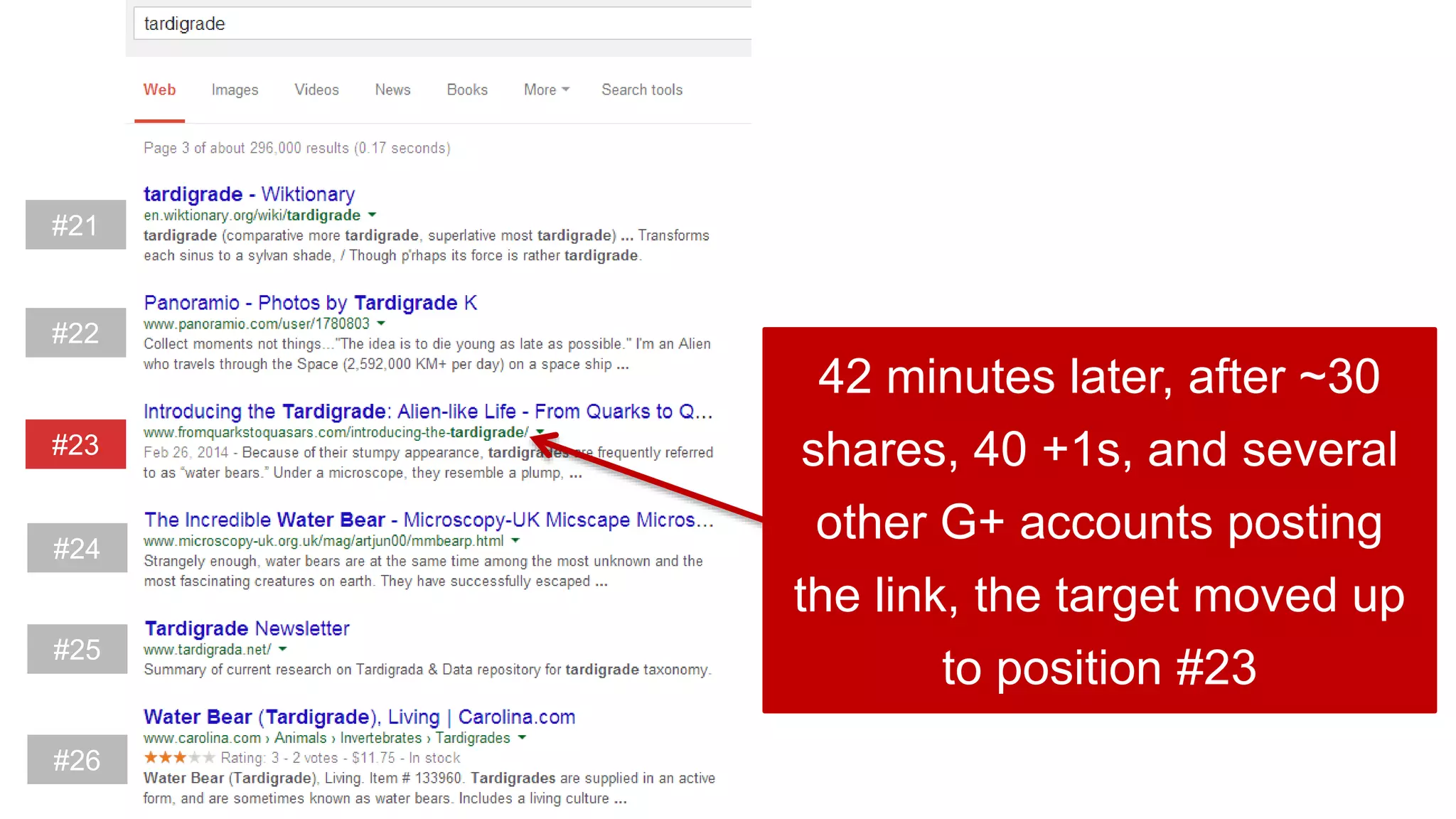
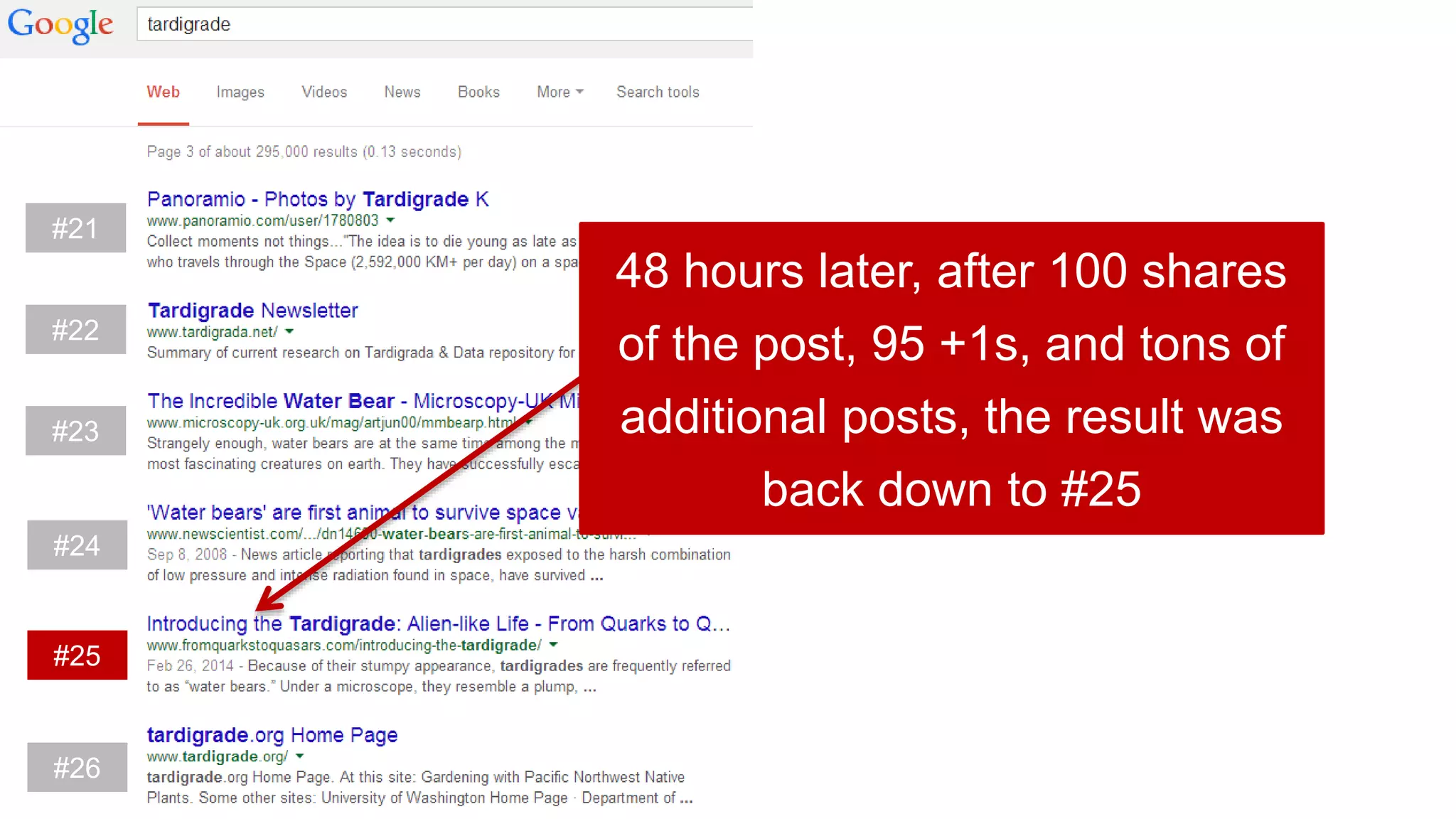
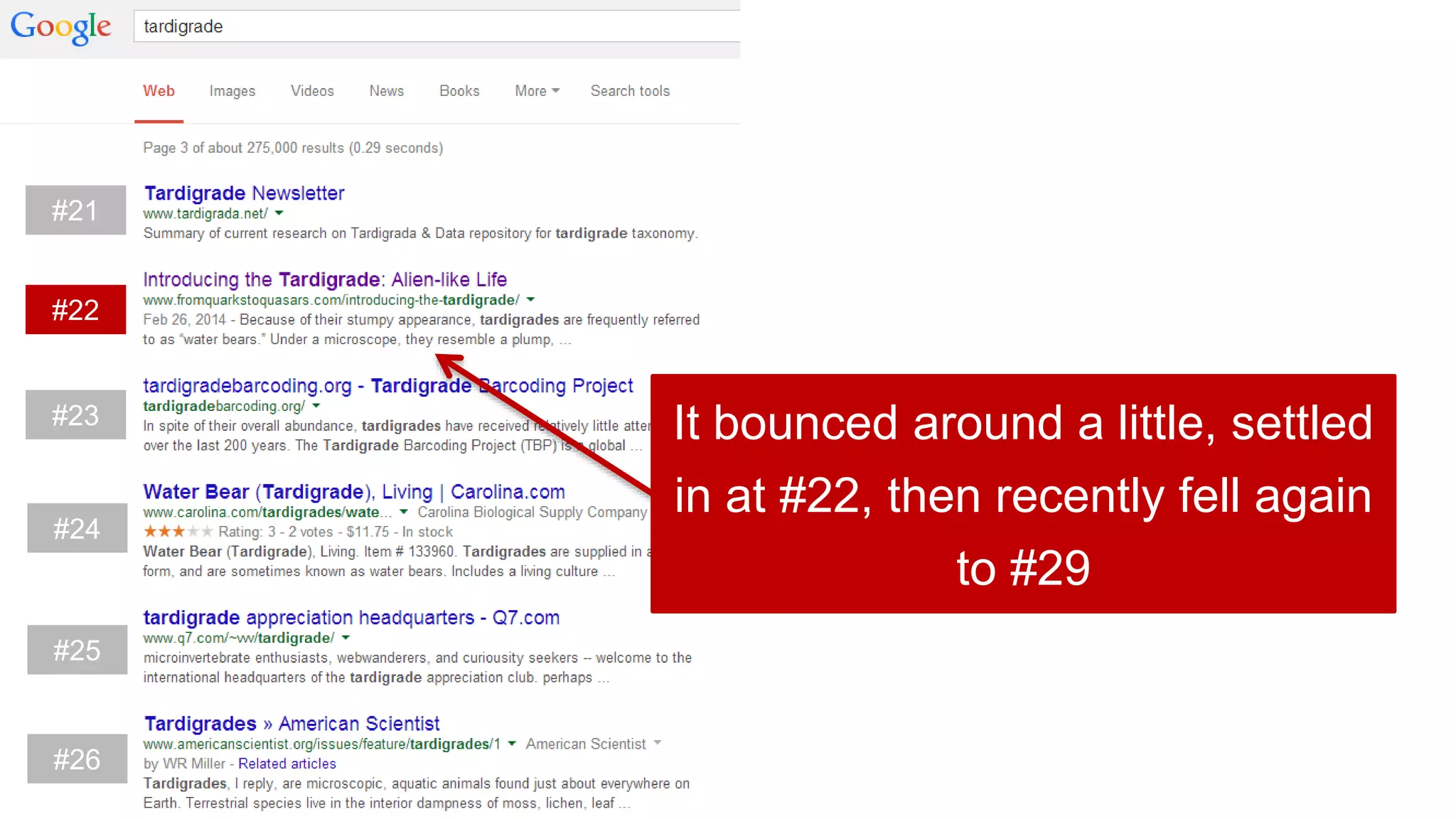
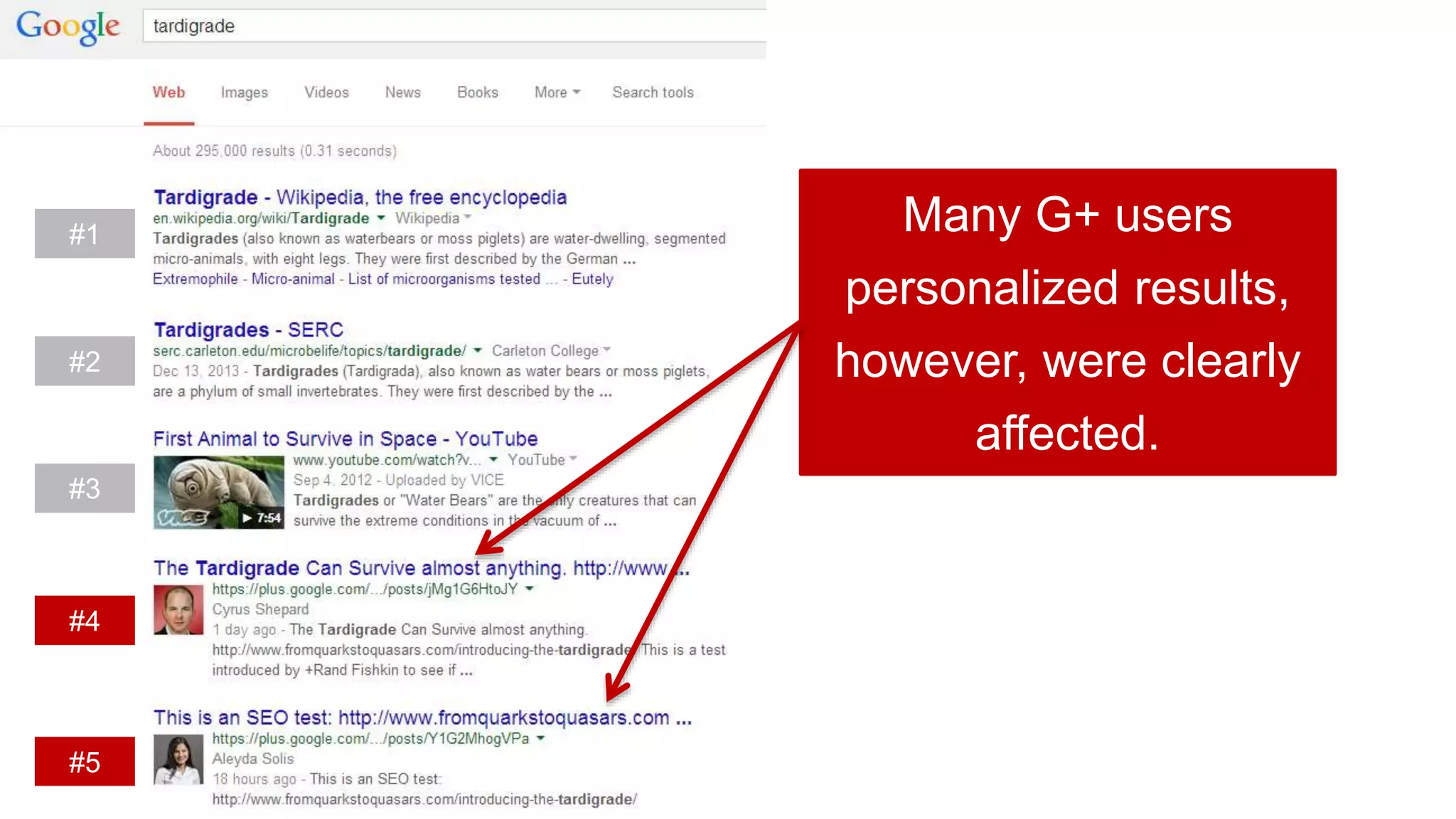
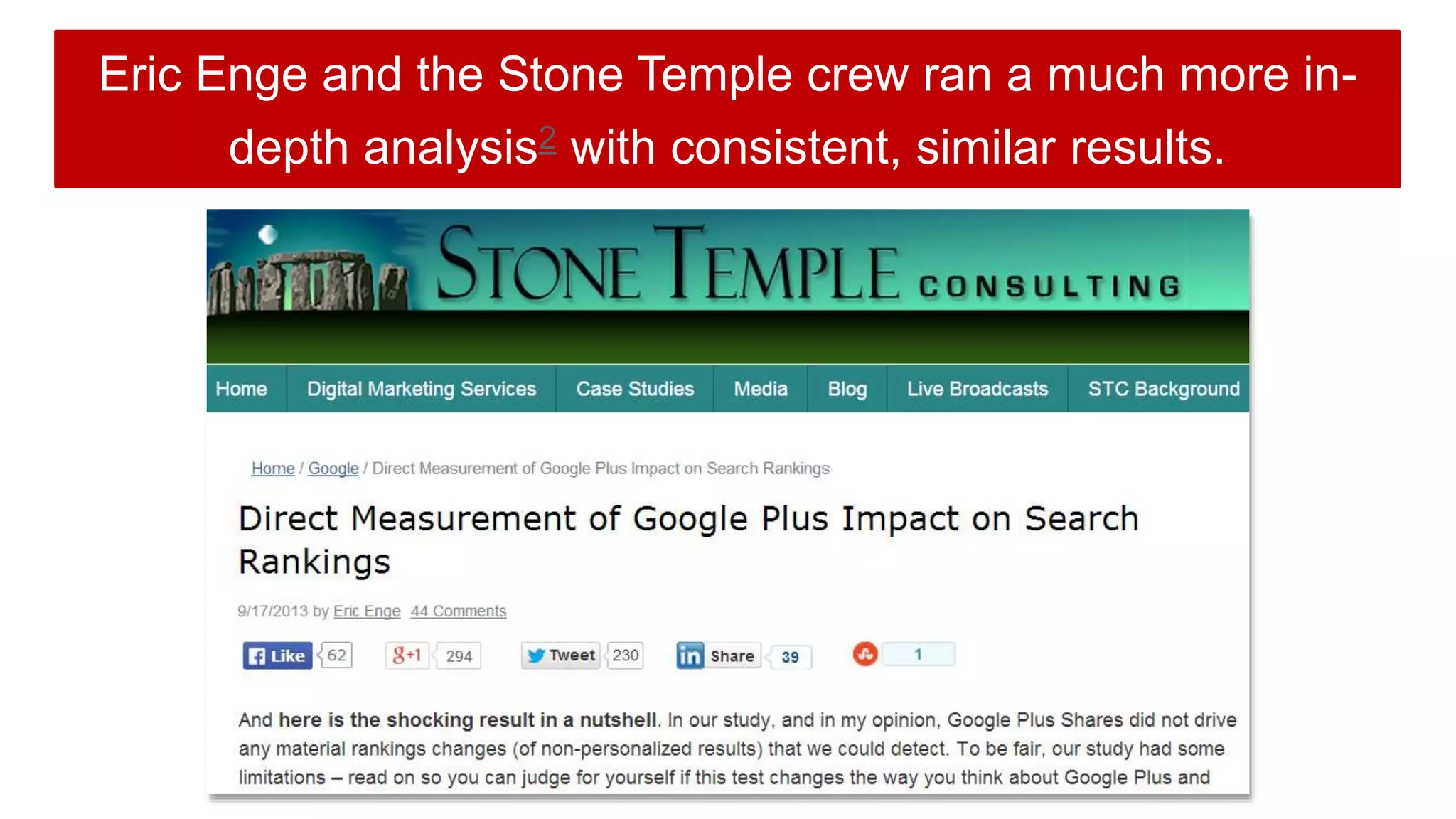
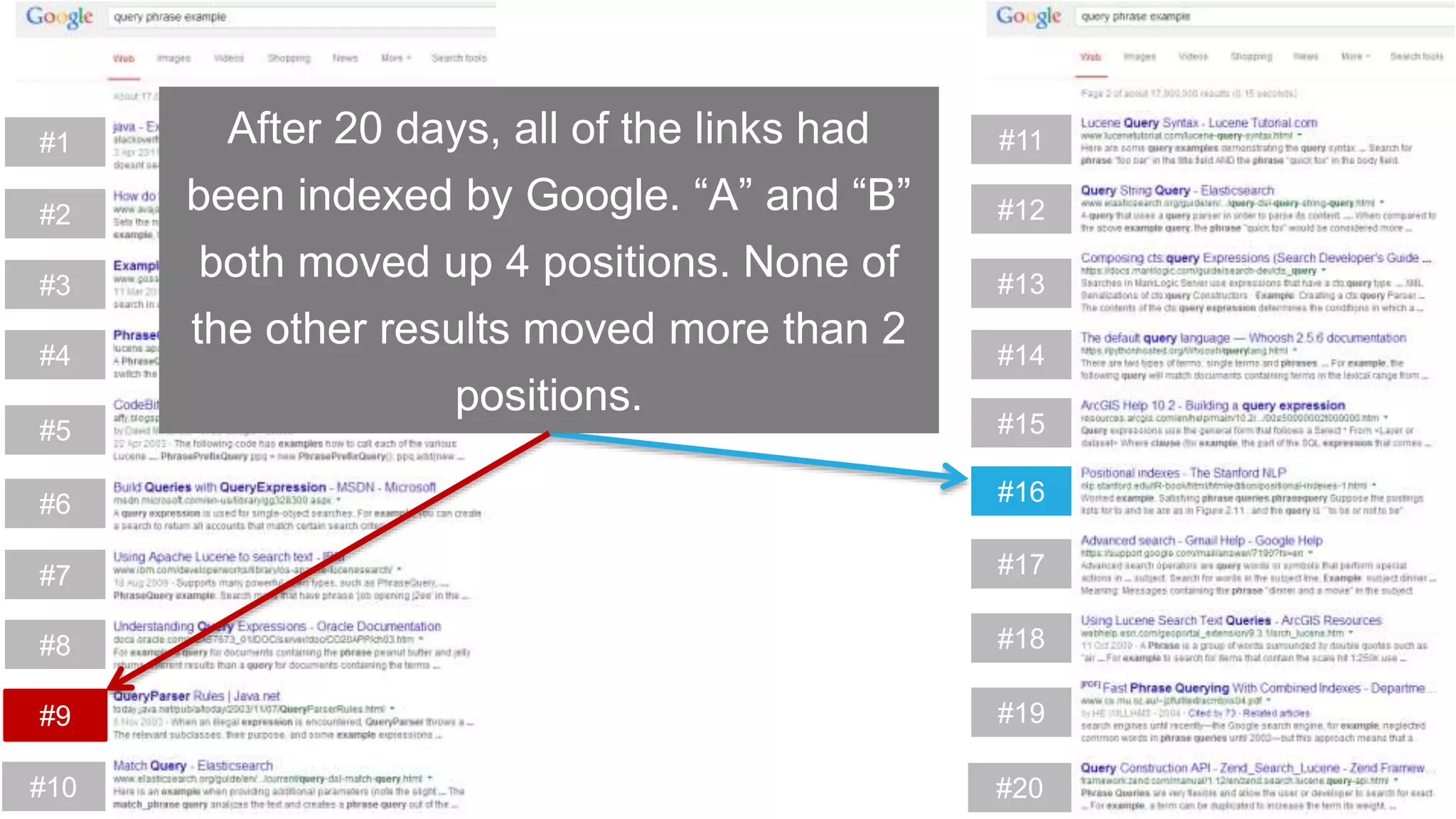
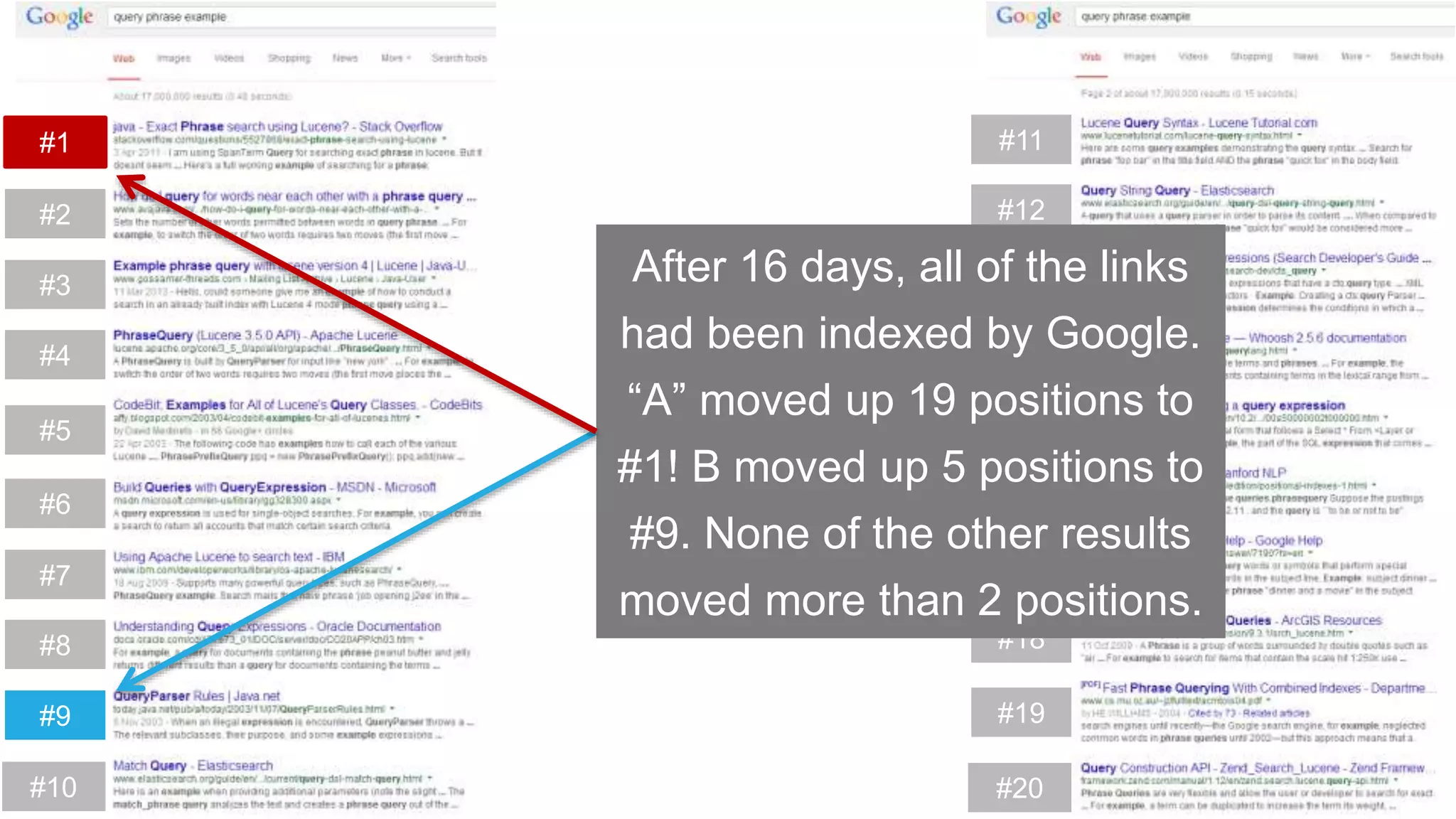
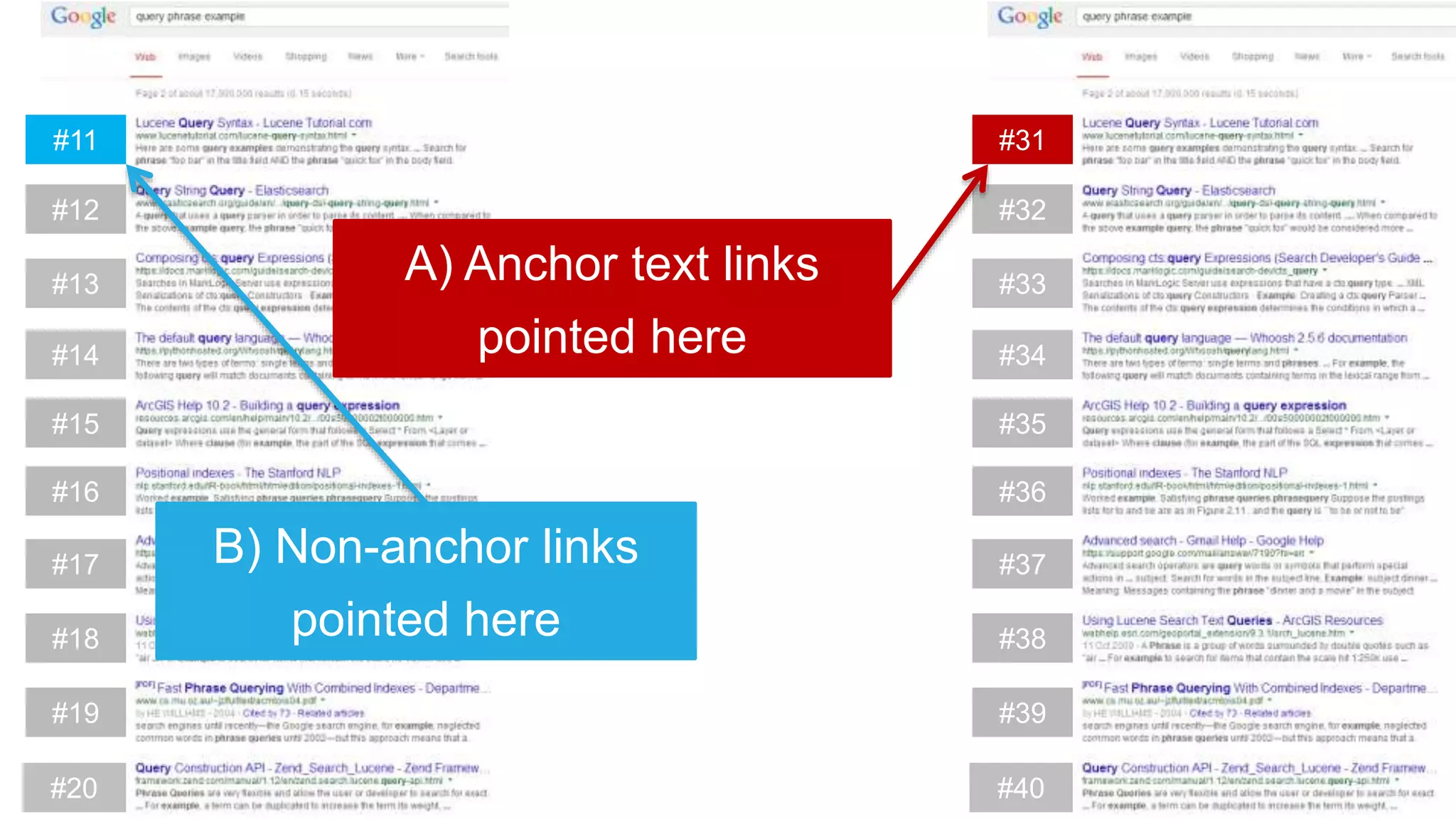
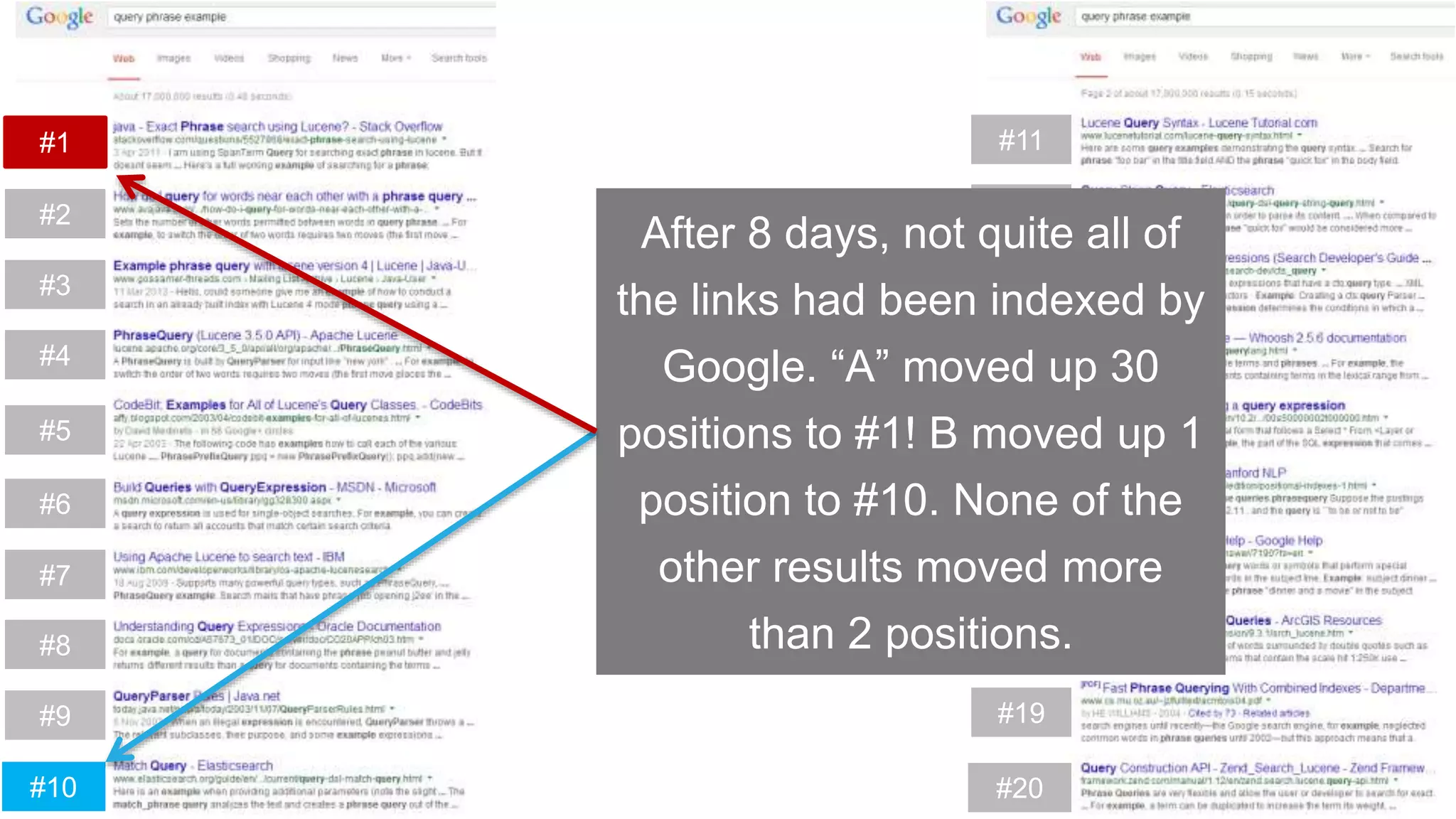
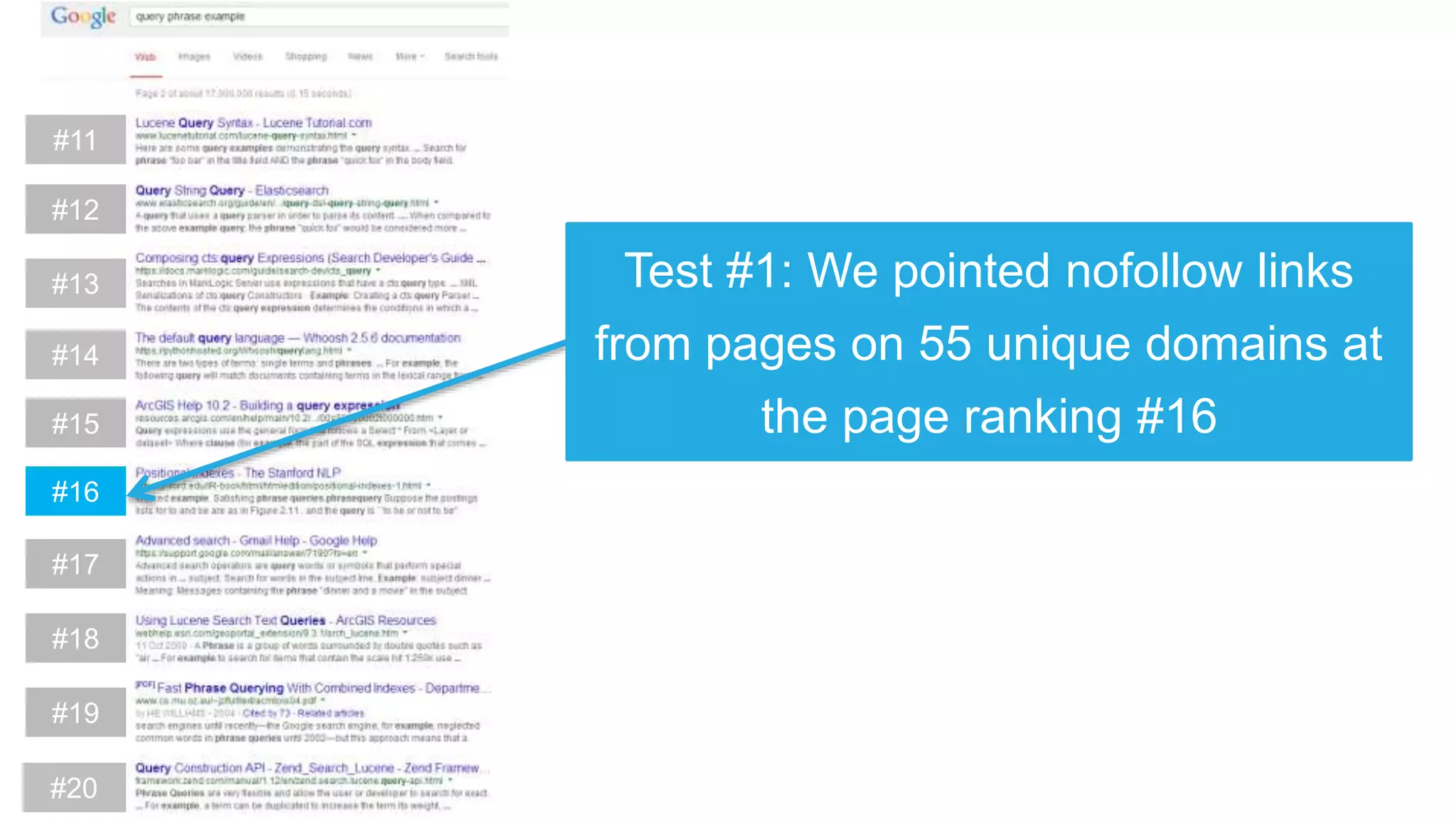
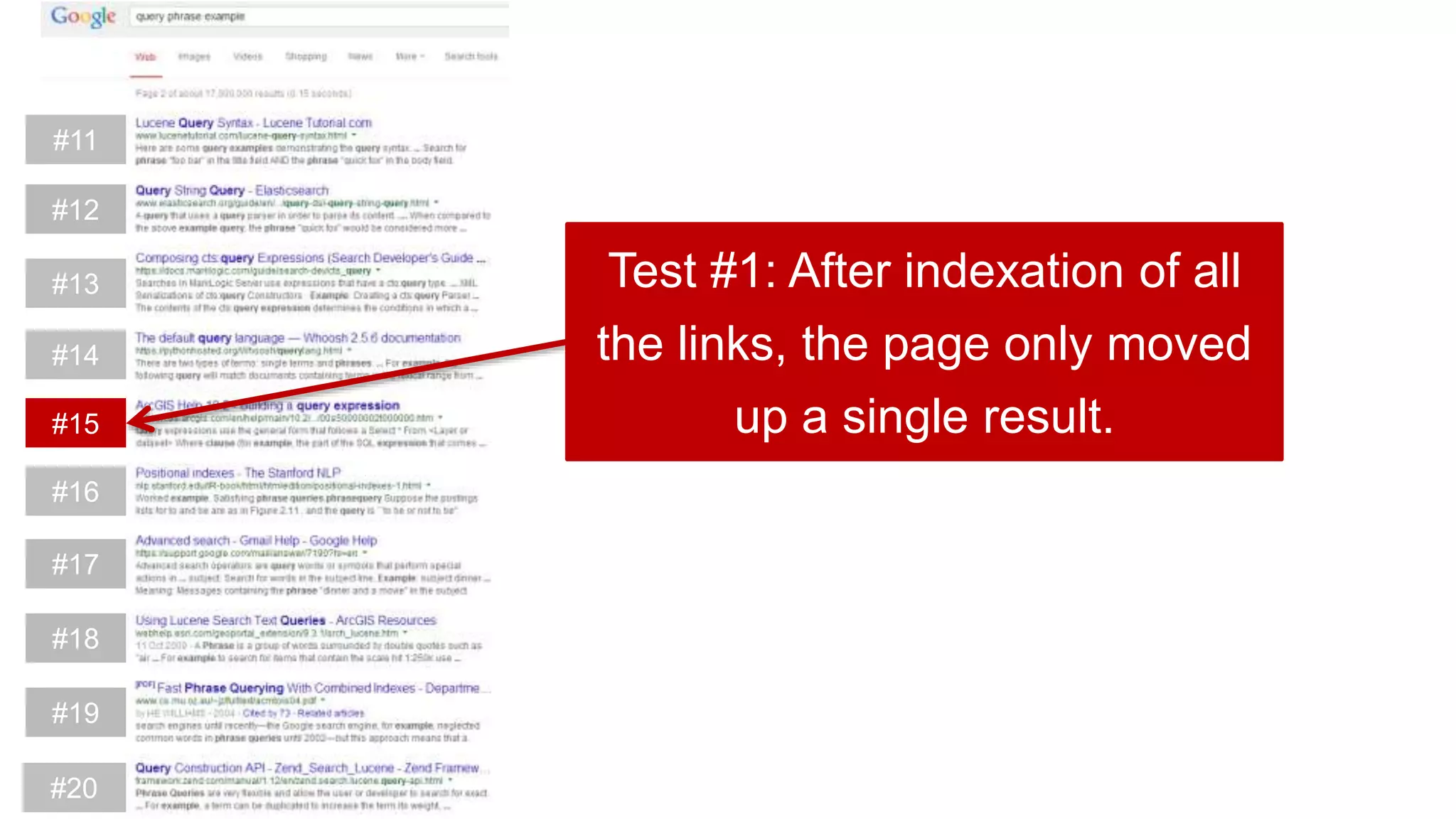
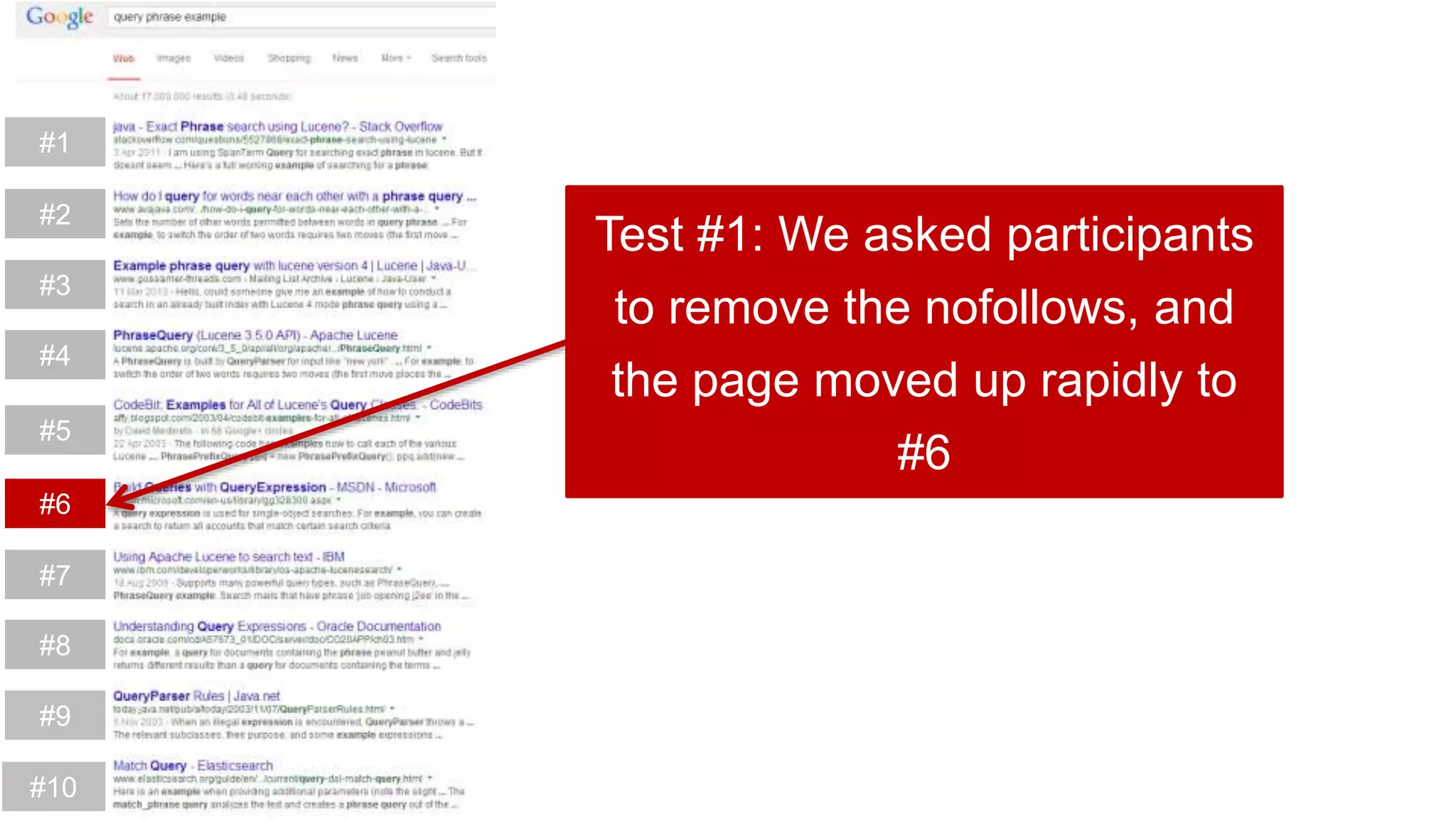
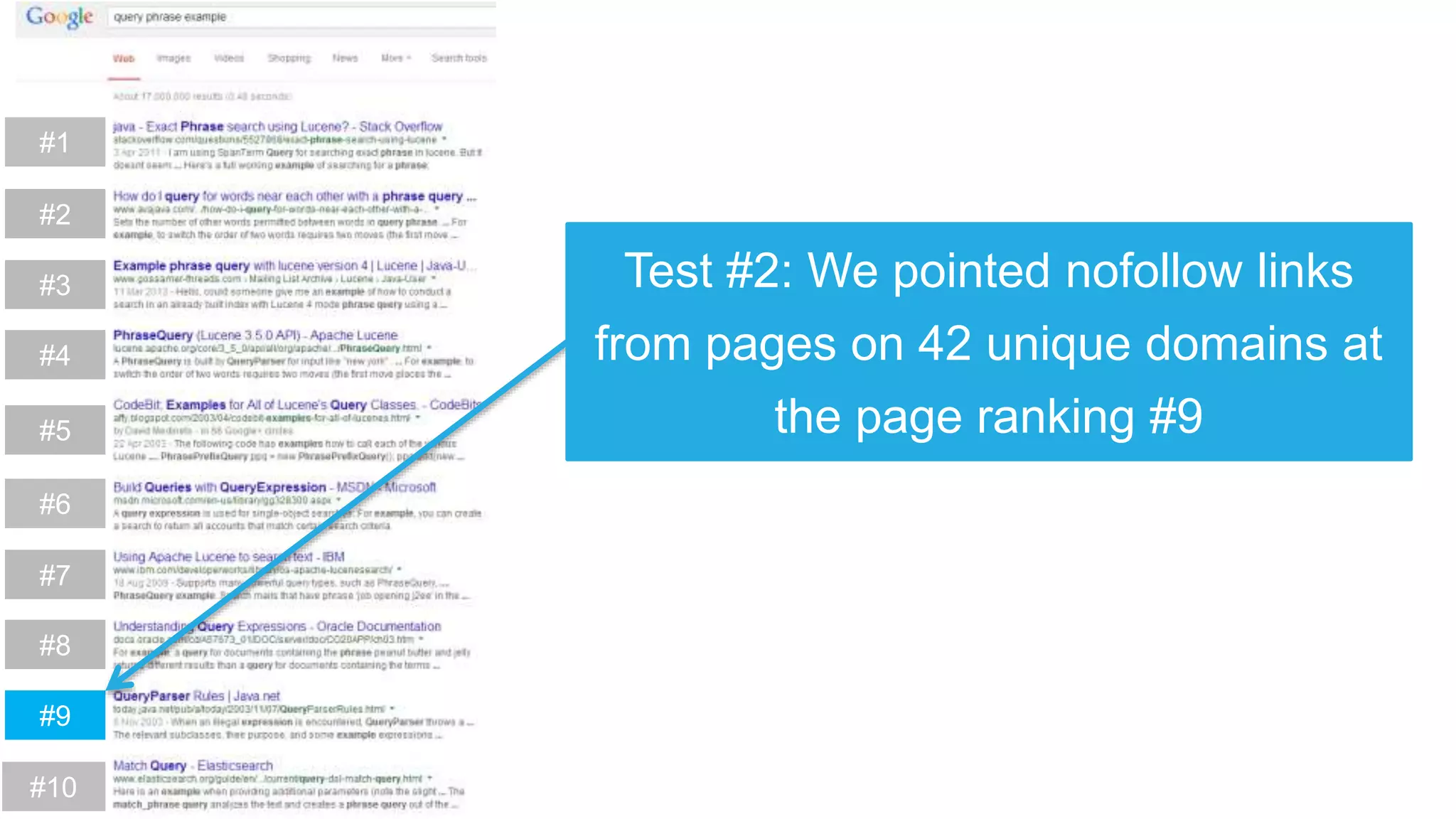
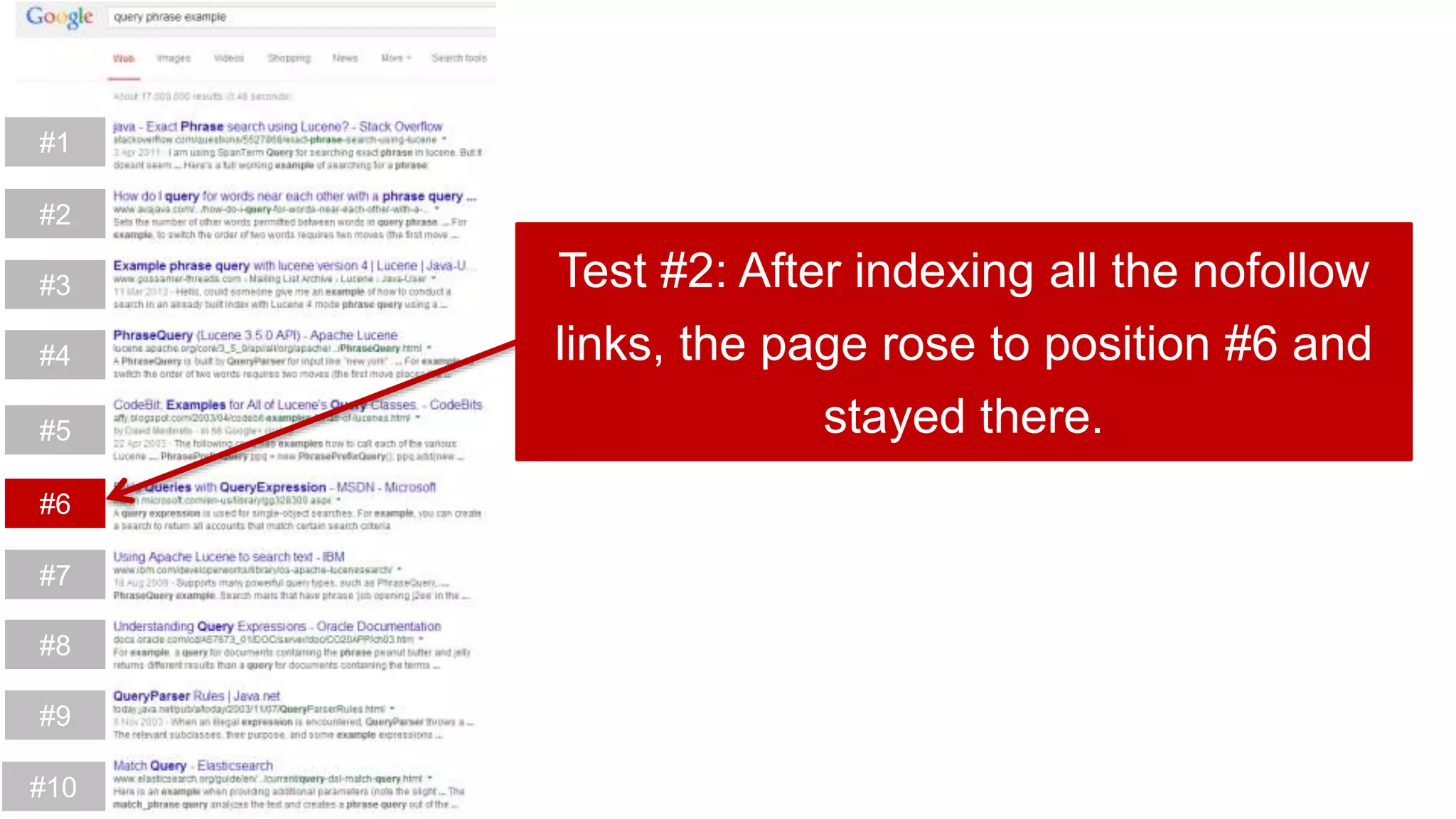
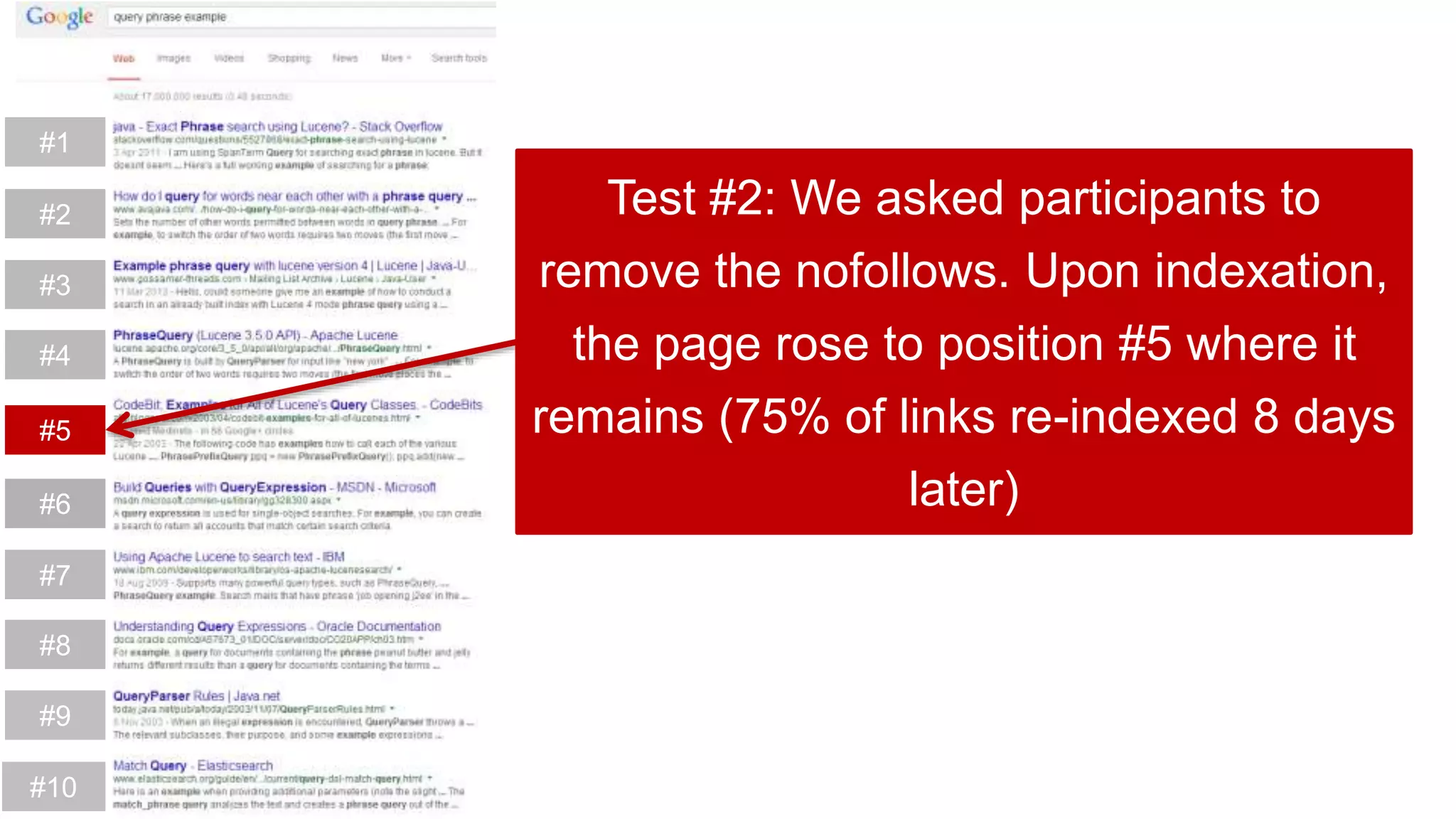
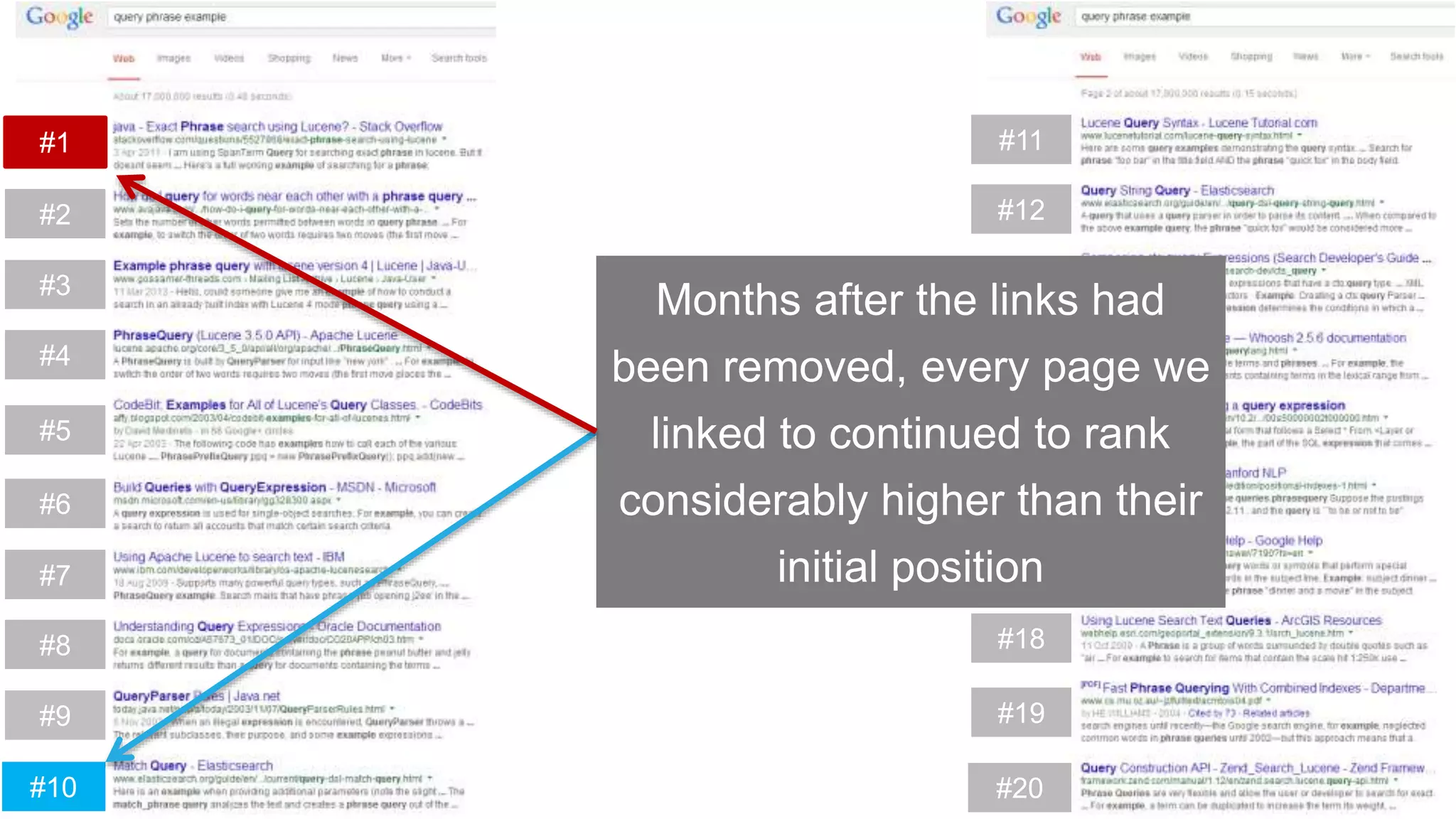
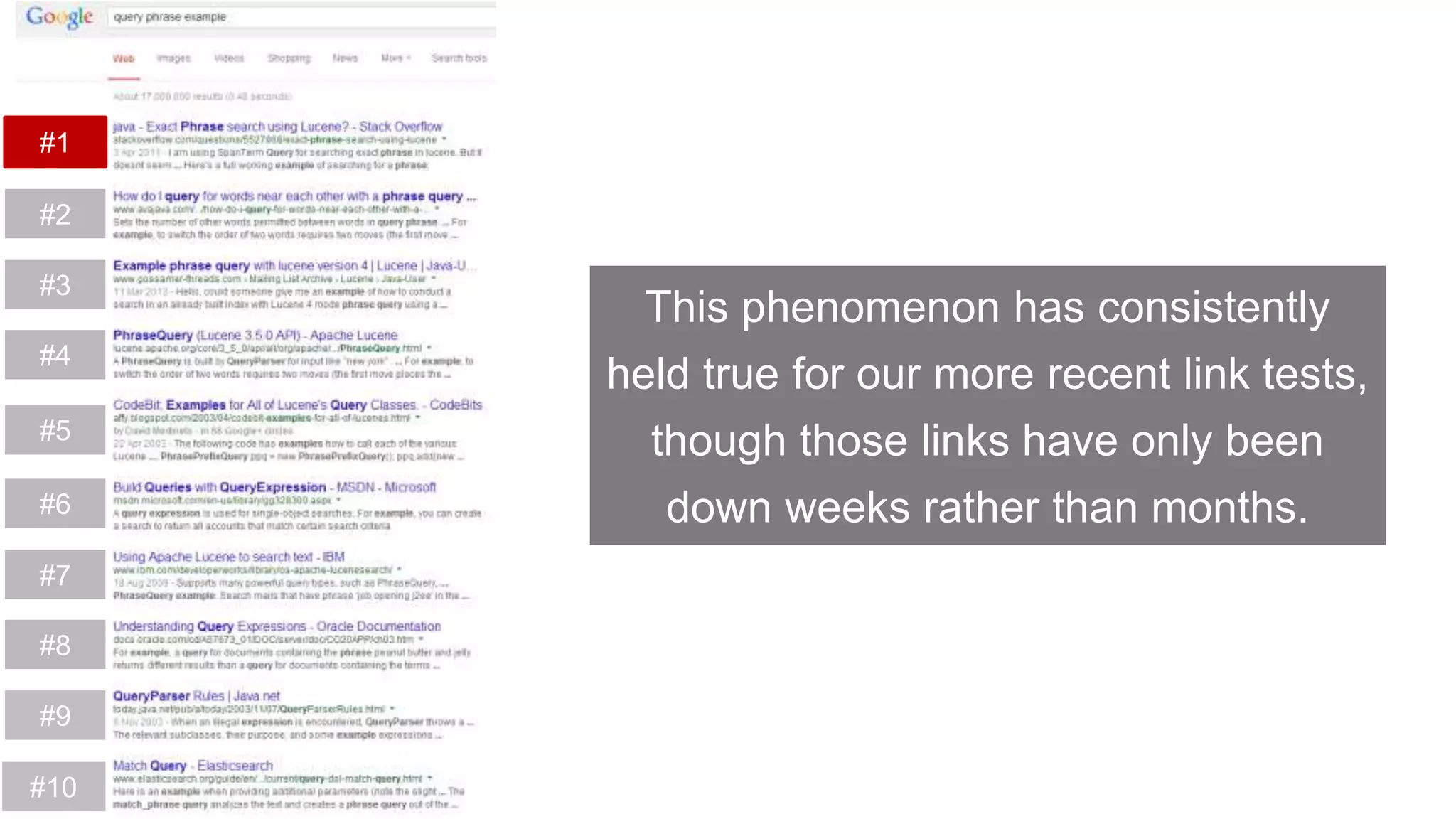
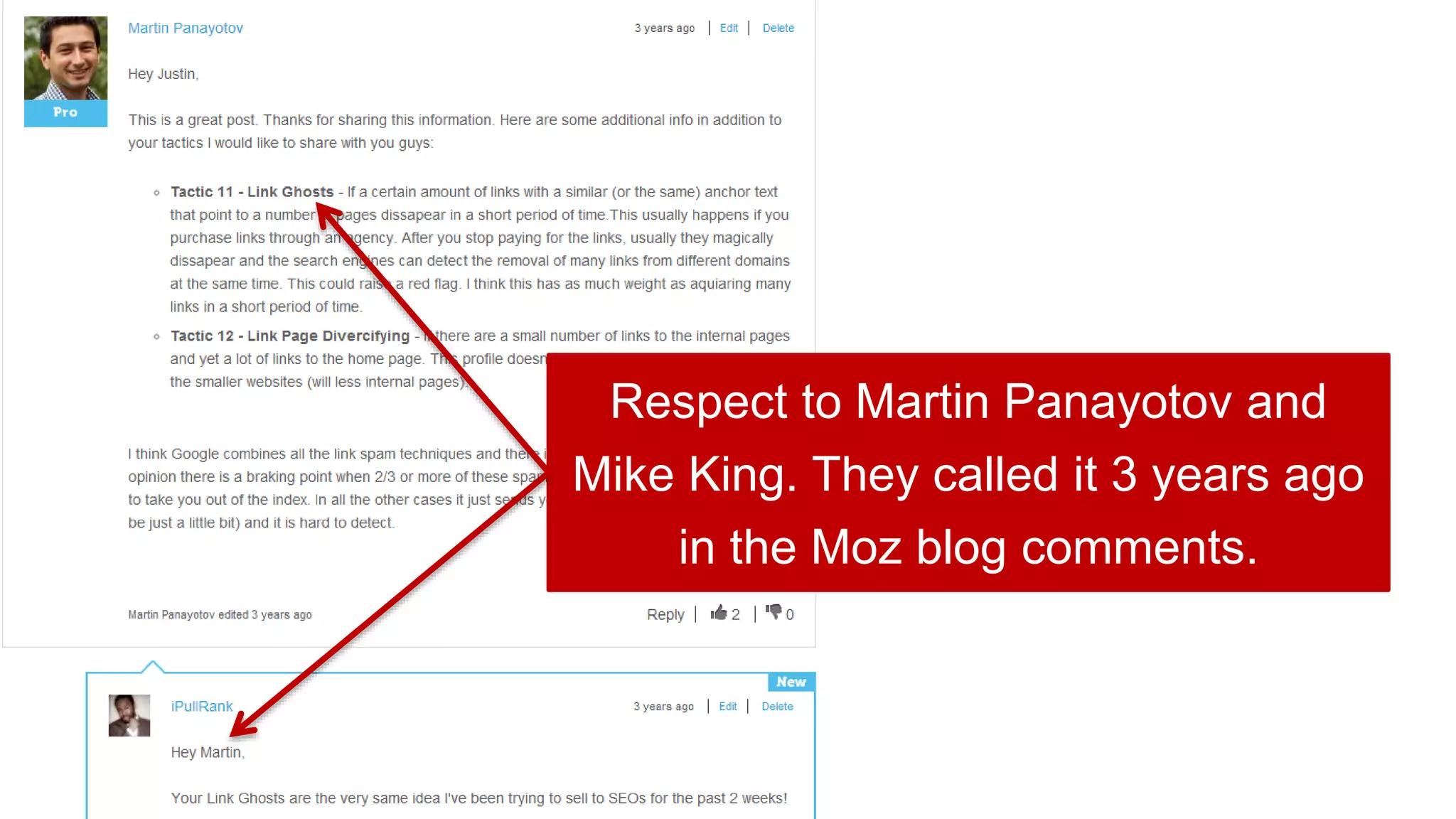
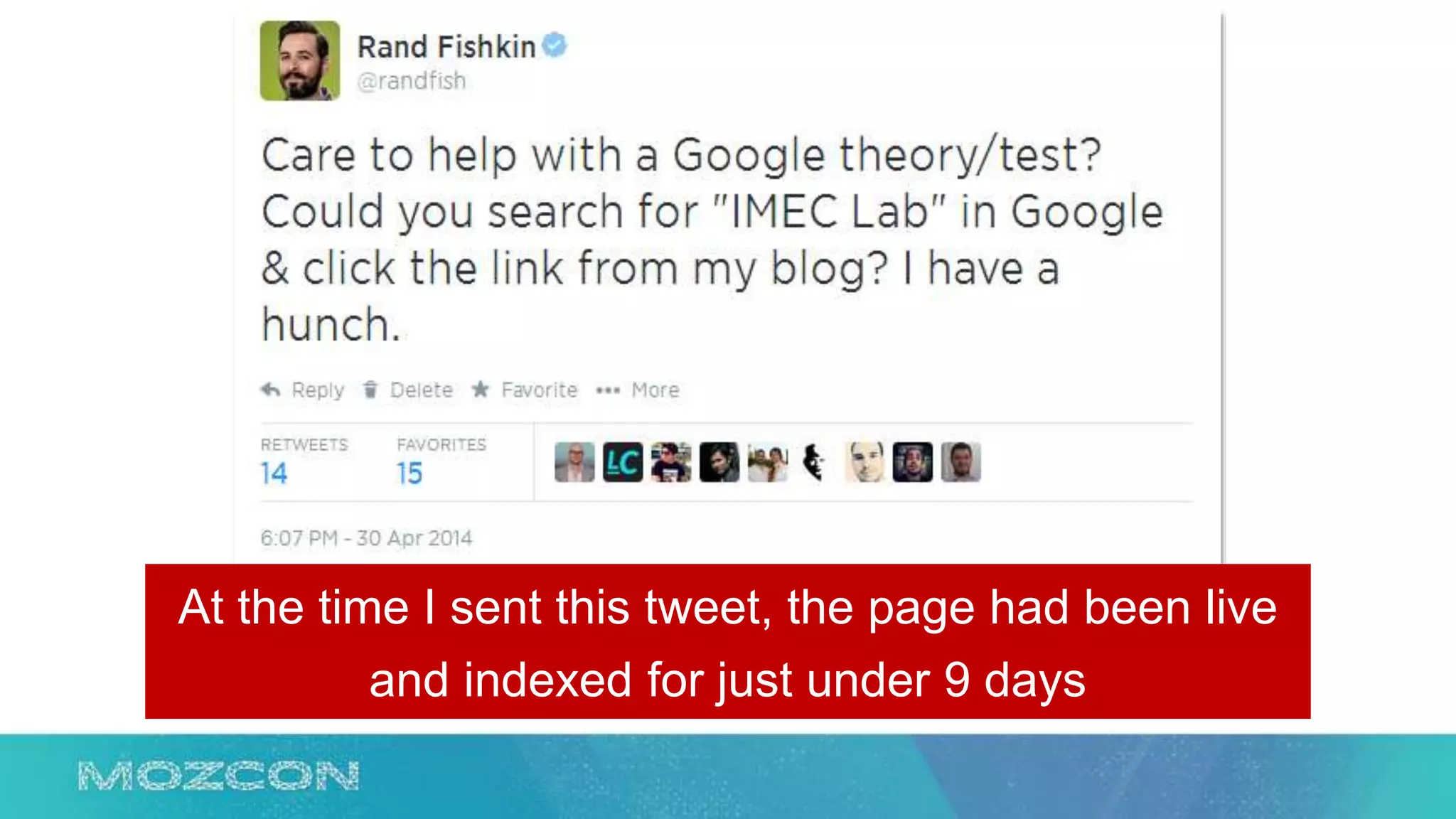
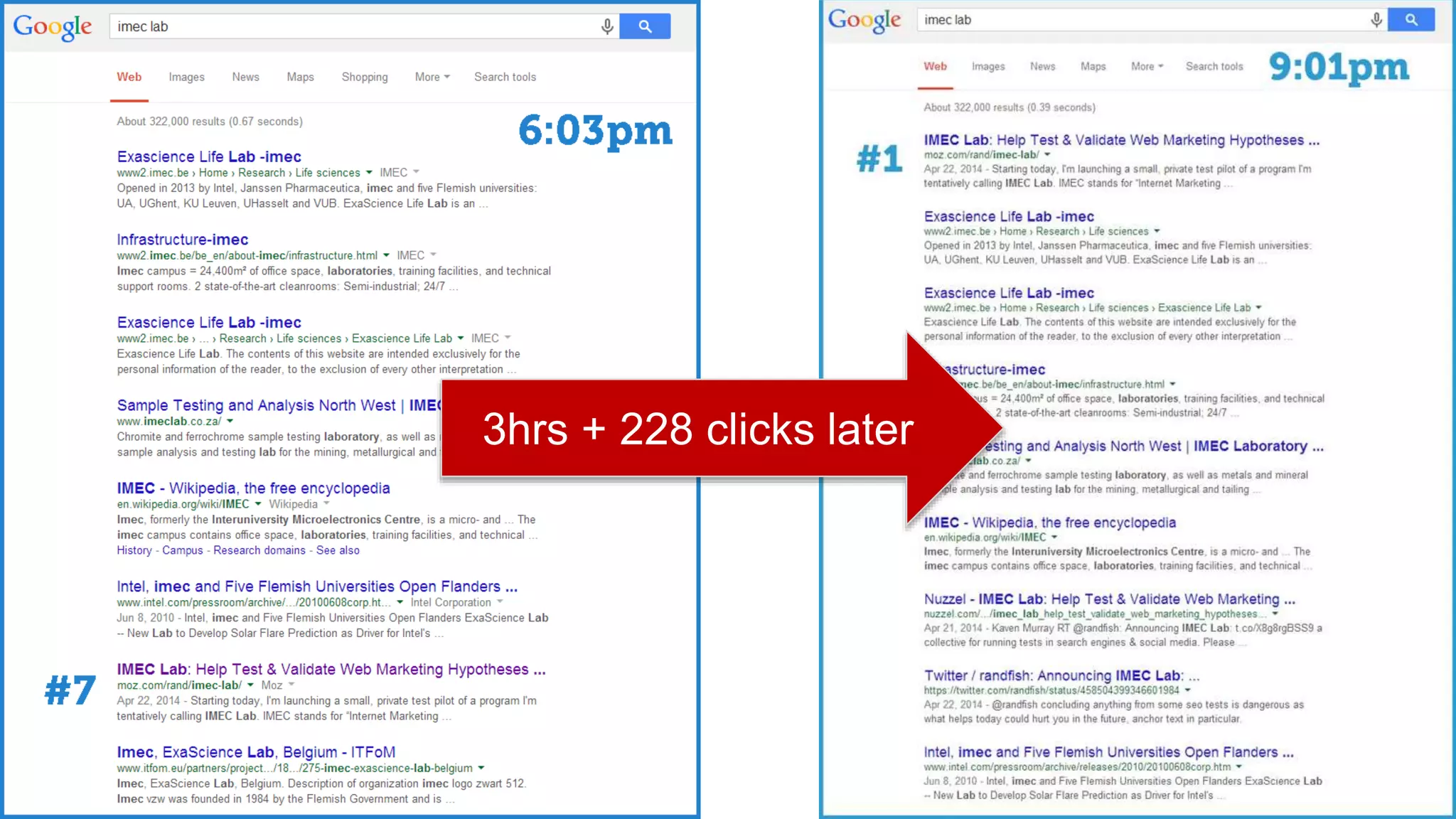
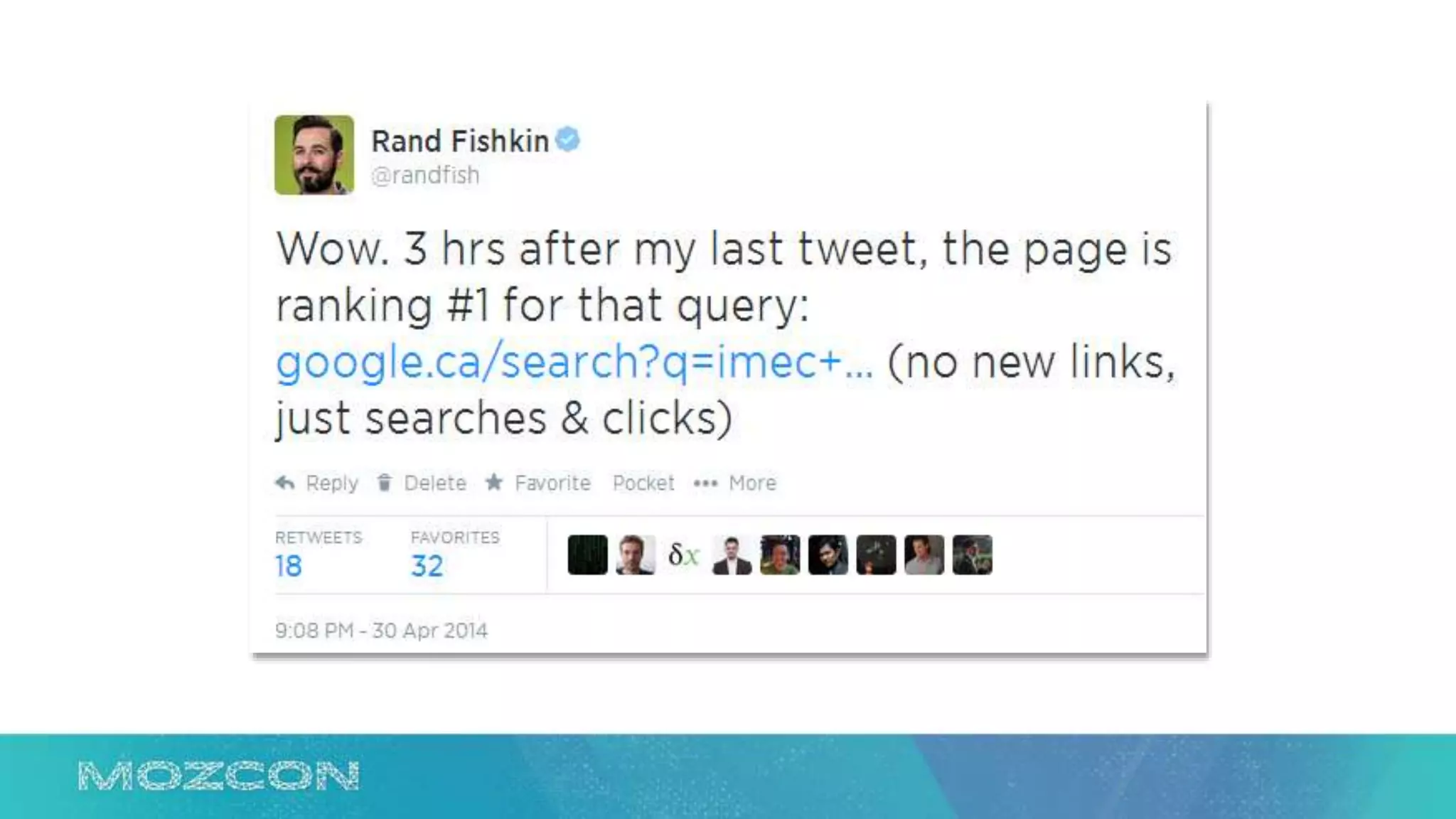
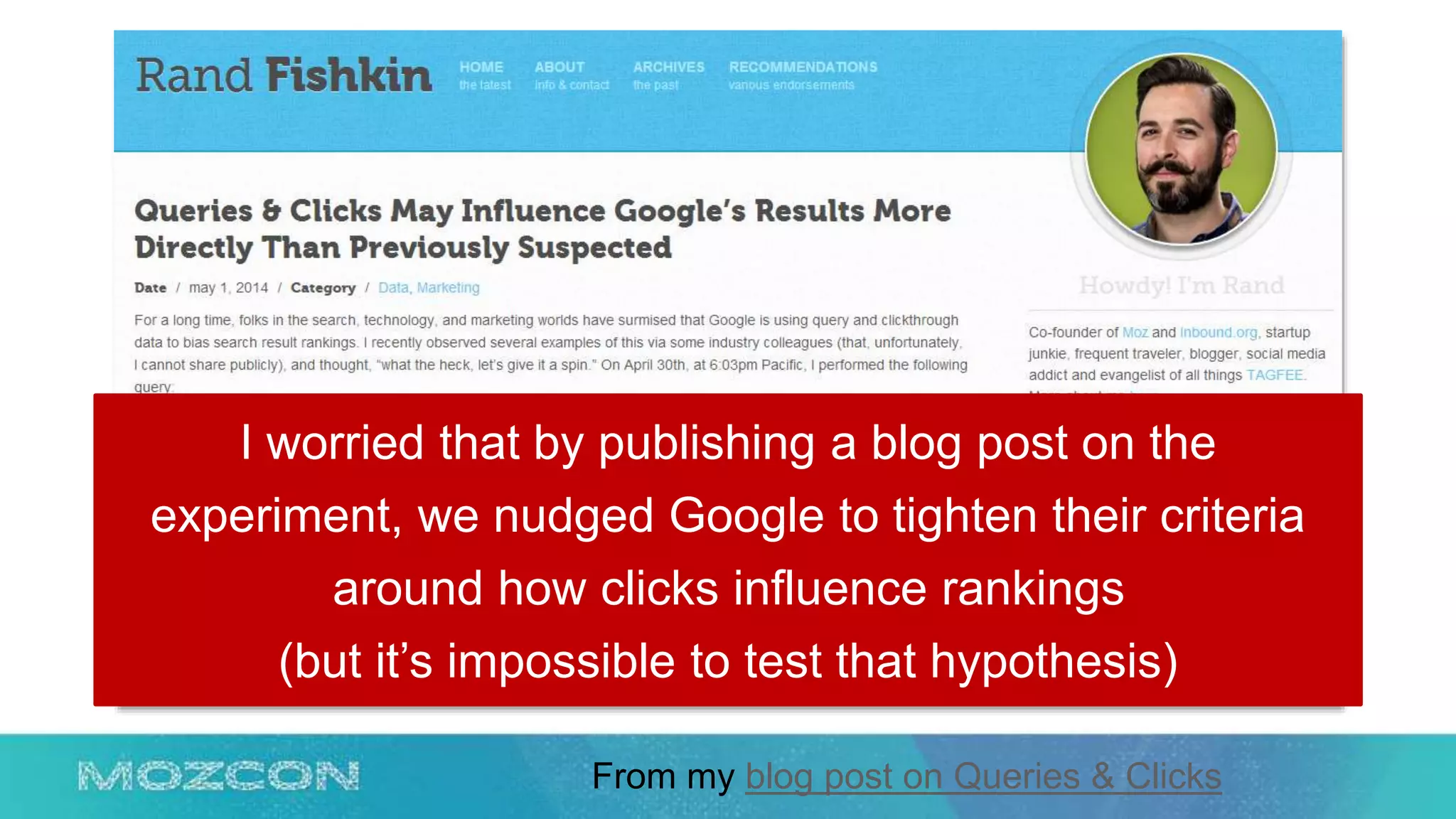
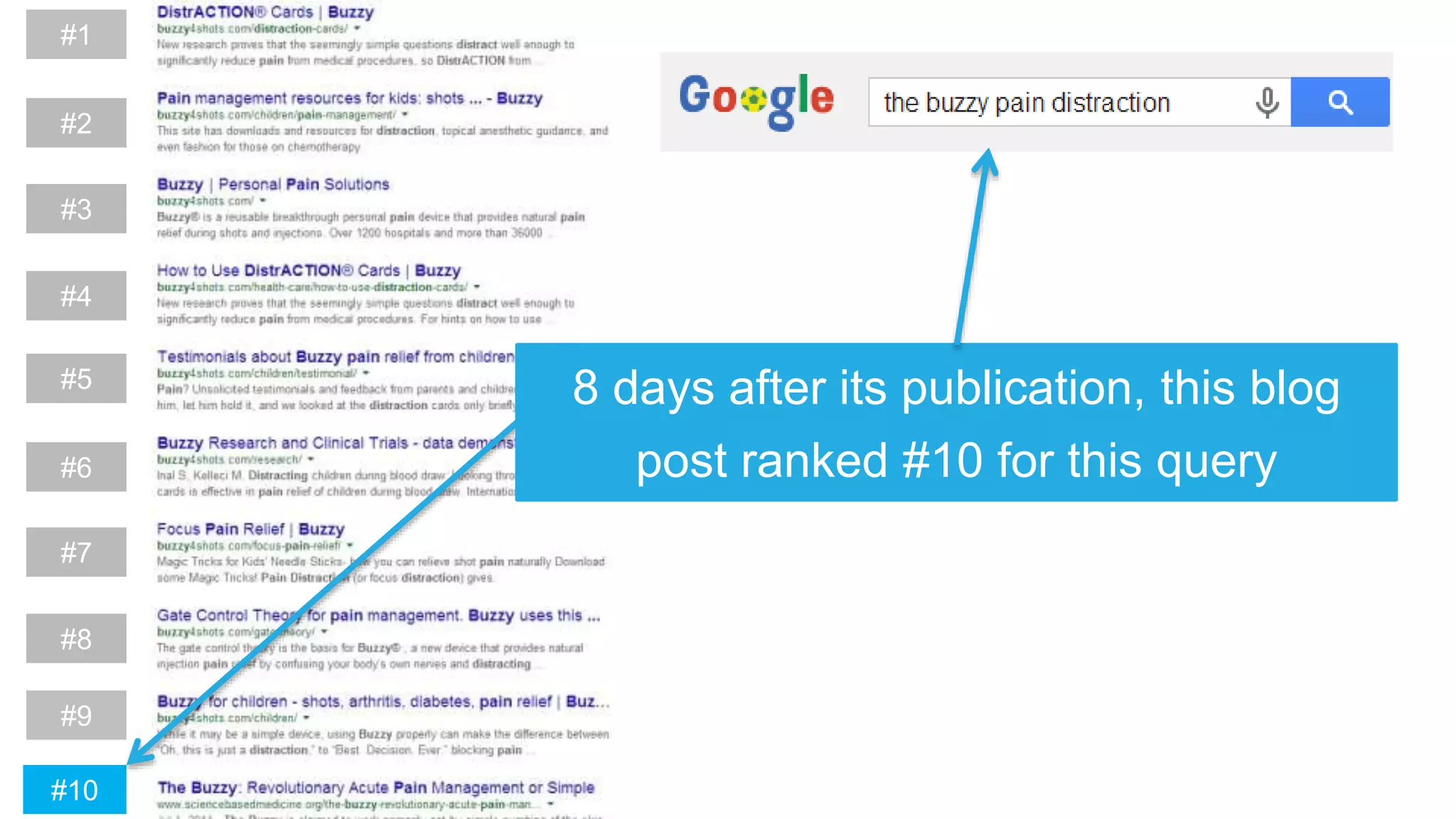
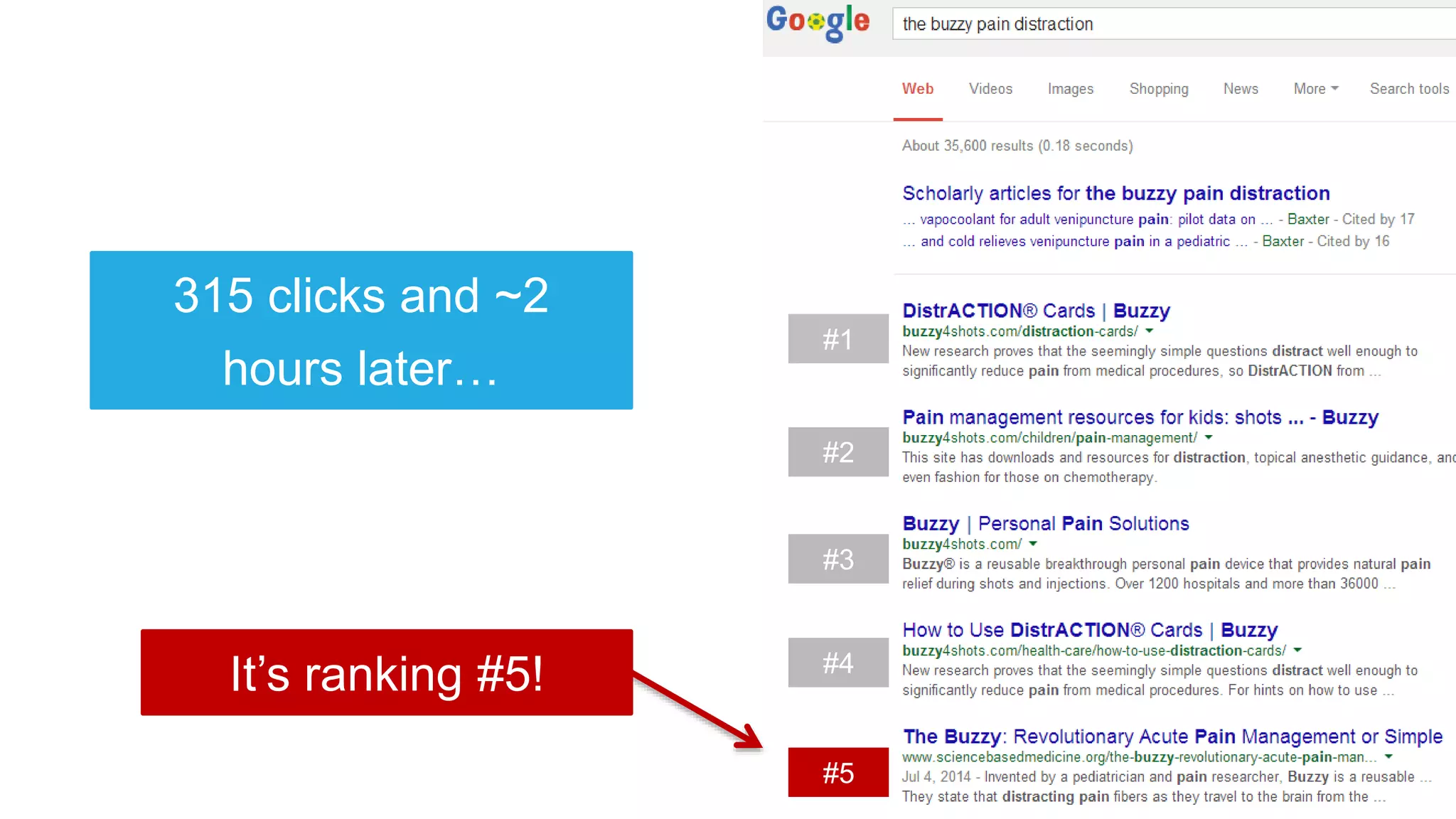
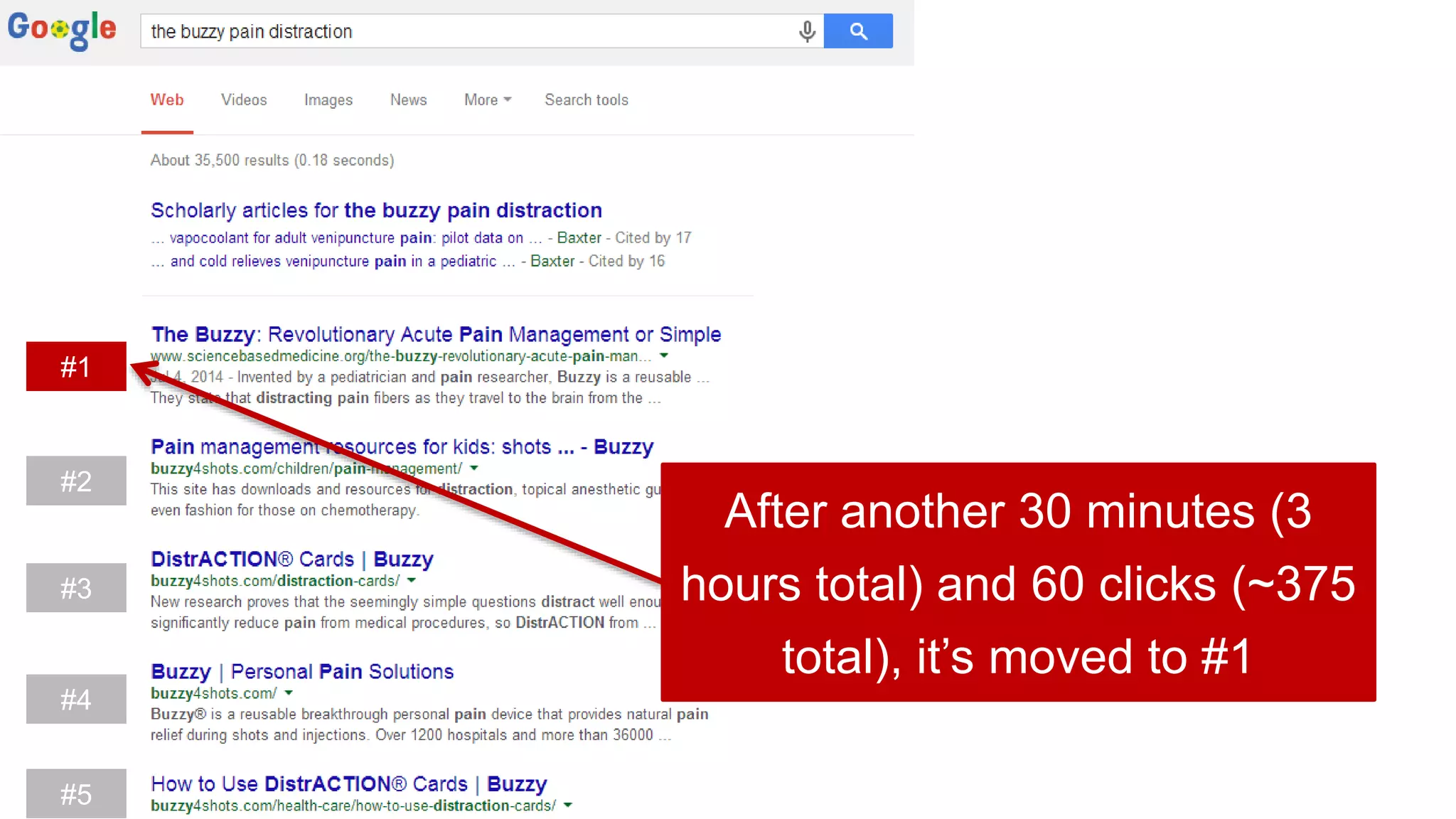
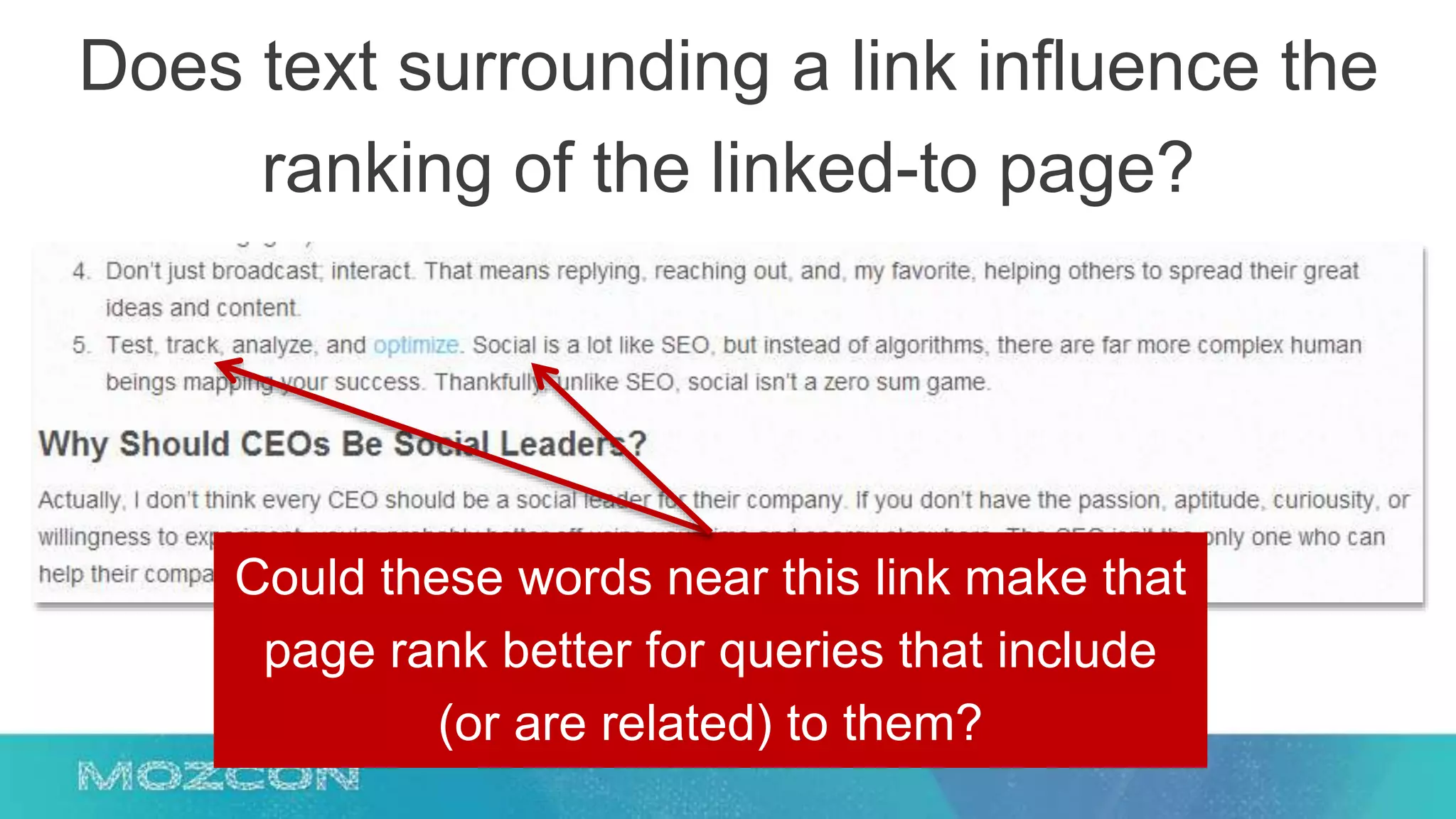
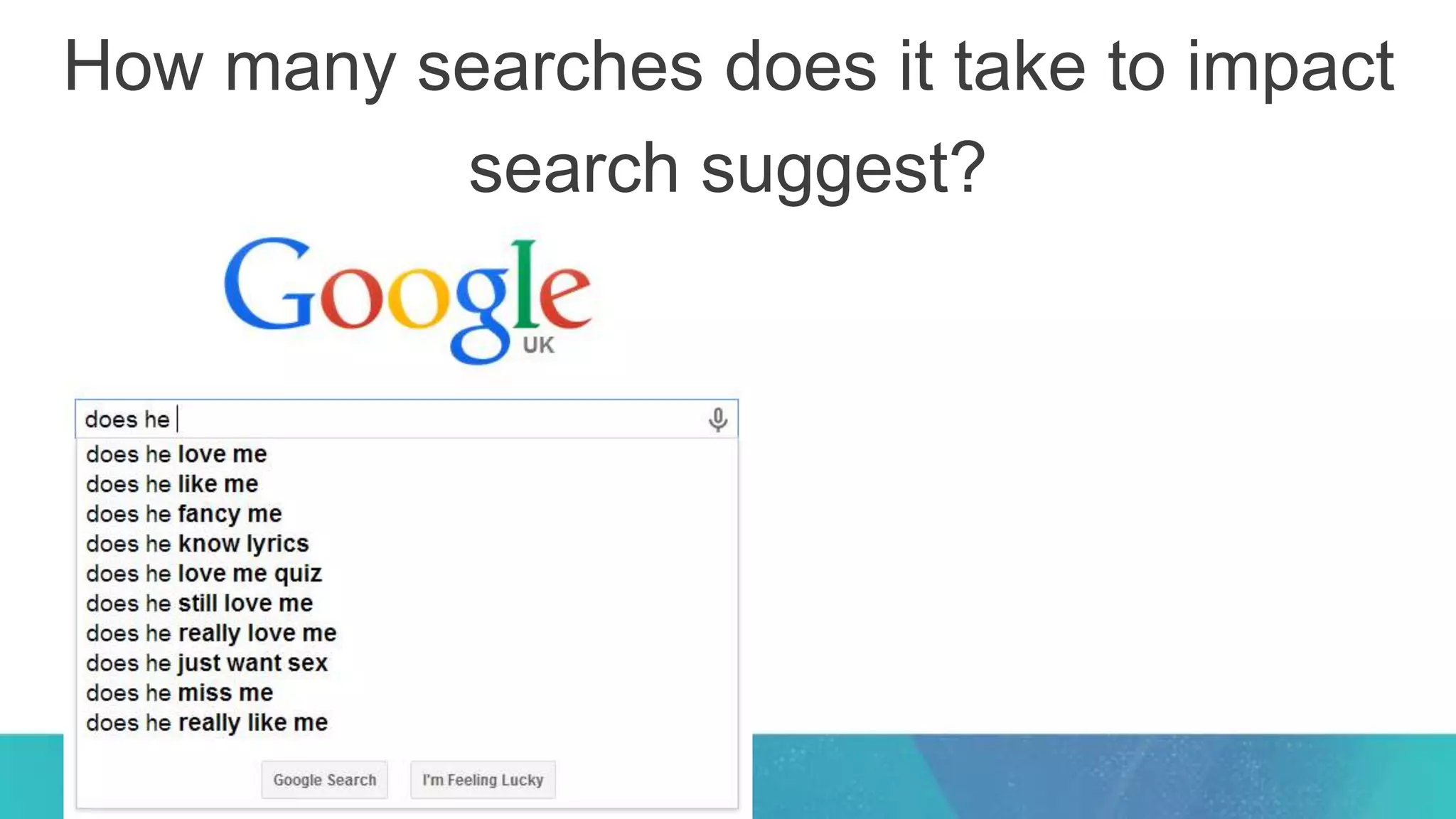
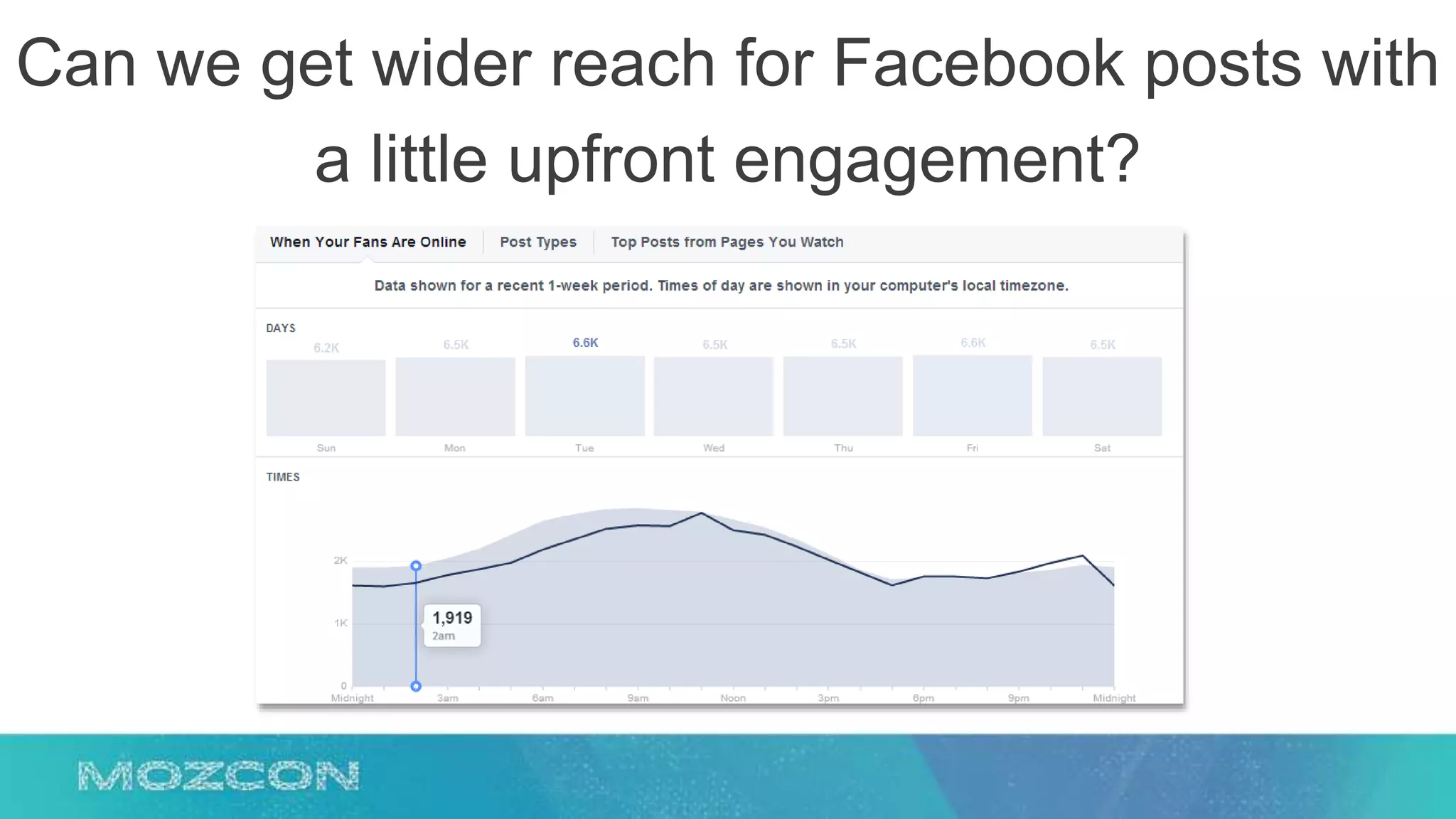
This document summarizes Rand Fishkin's experiments with search engine optimization (SEO) and social media. It discusses experiments testing how factors like anchor text, links, social sharing, queries, and clicks may impact search engine rankings. Some key findings include that anchor text remains powerful, link ghosts have lasting effects on rankings, and queries/clicks can sometimes influence rankings, especially with high volumes. The document advocates repeating experiments to obtain more conclusive results and calls for others to join future IMEC Lab testing.