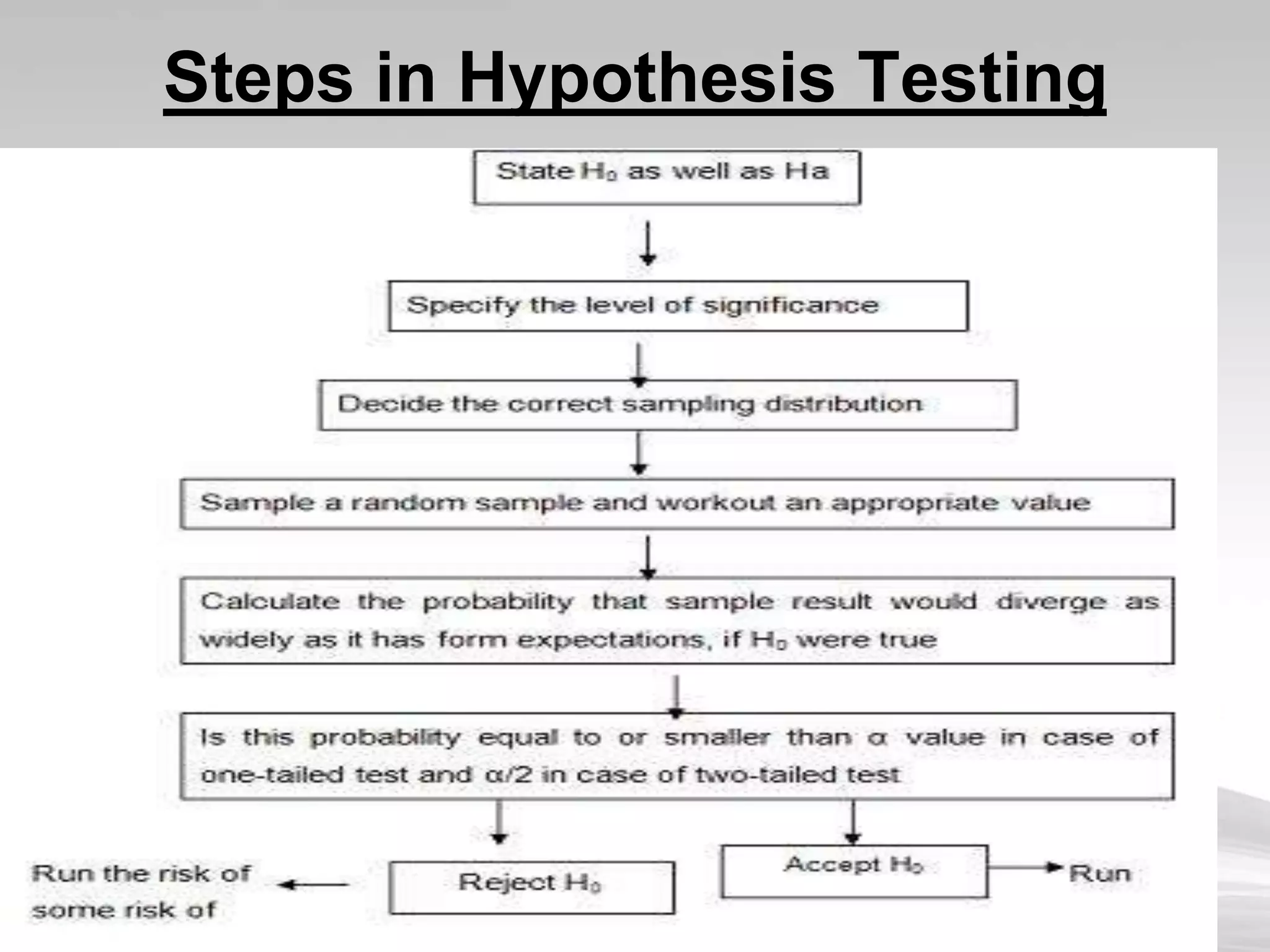
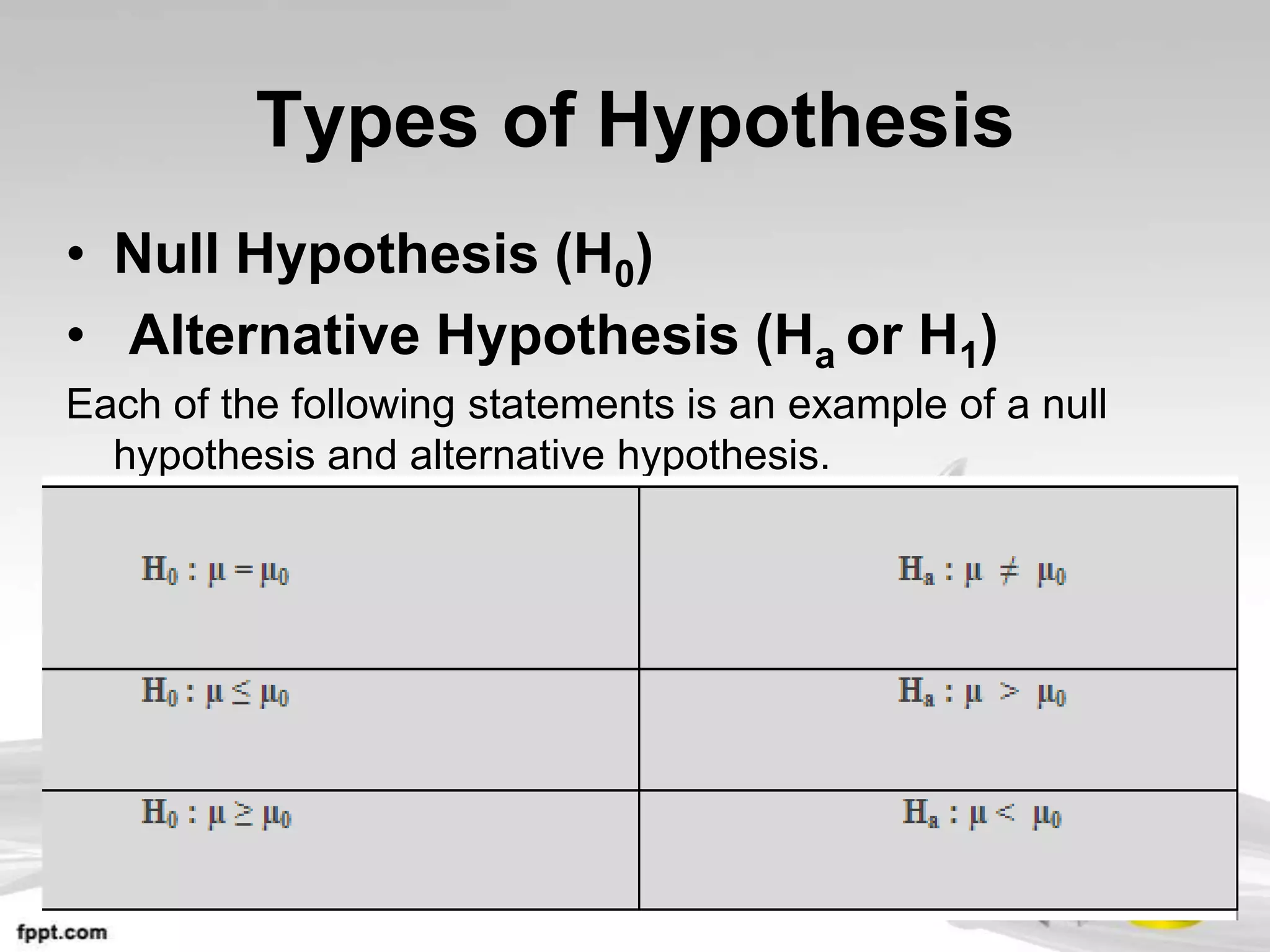
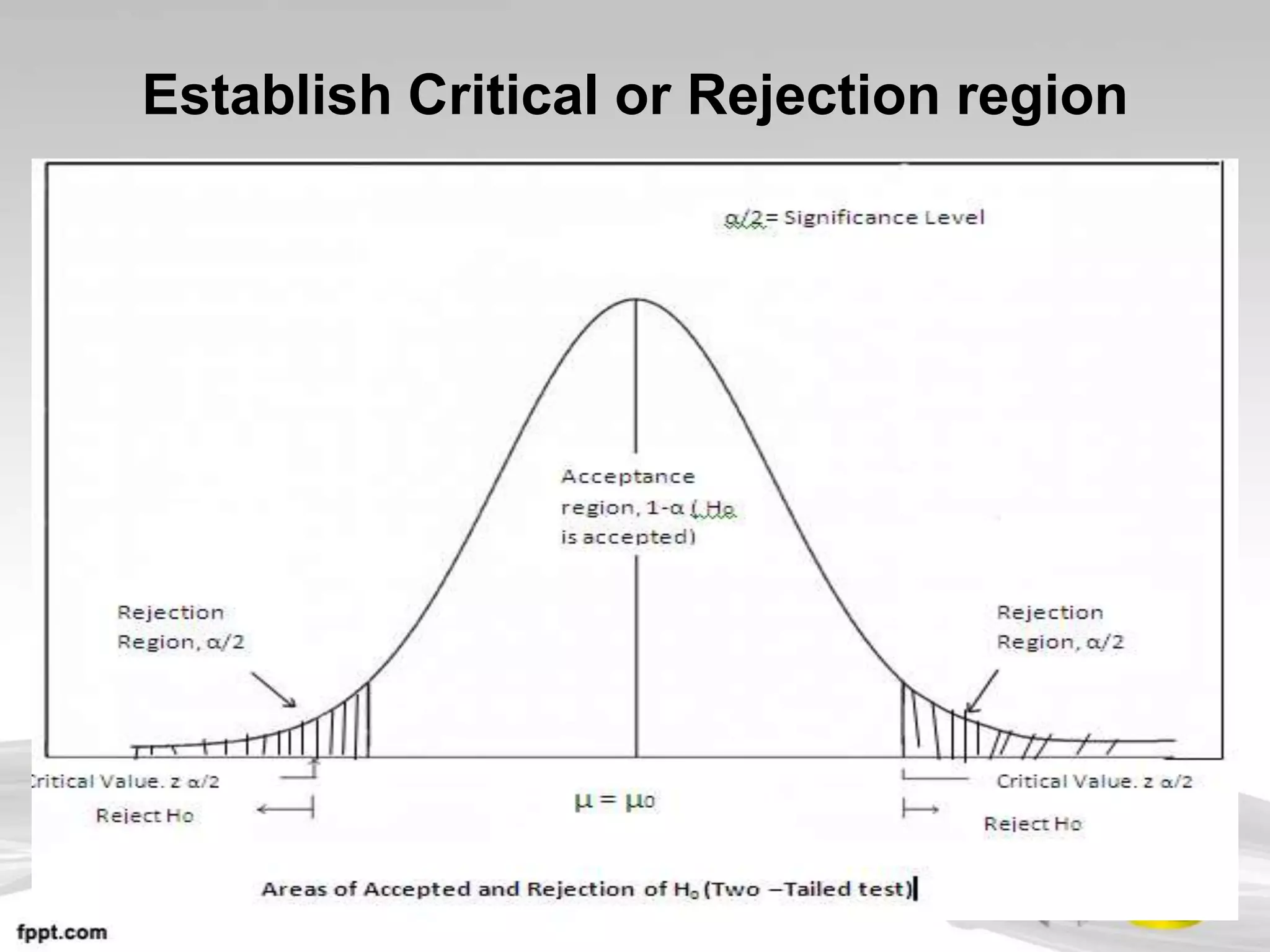
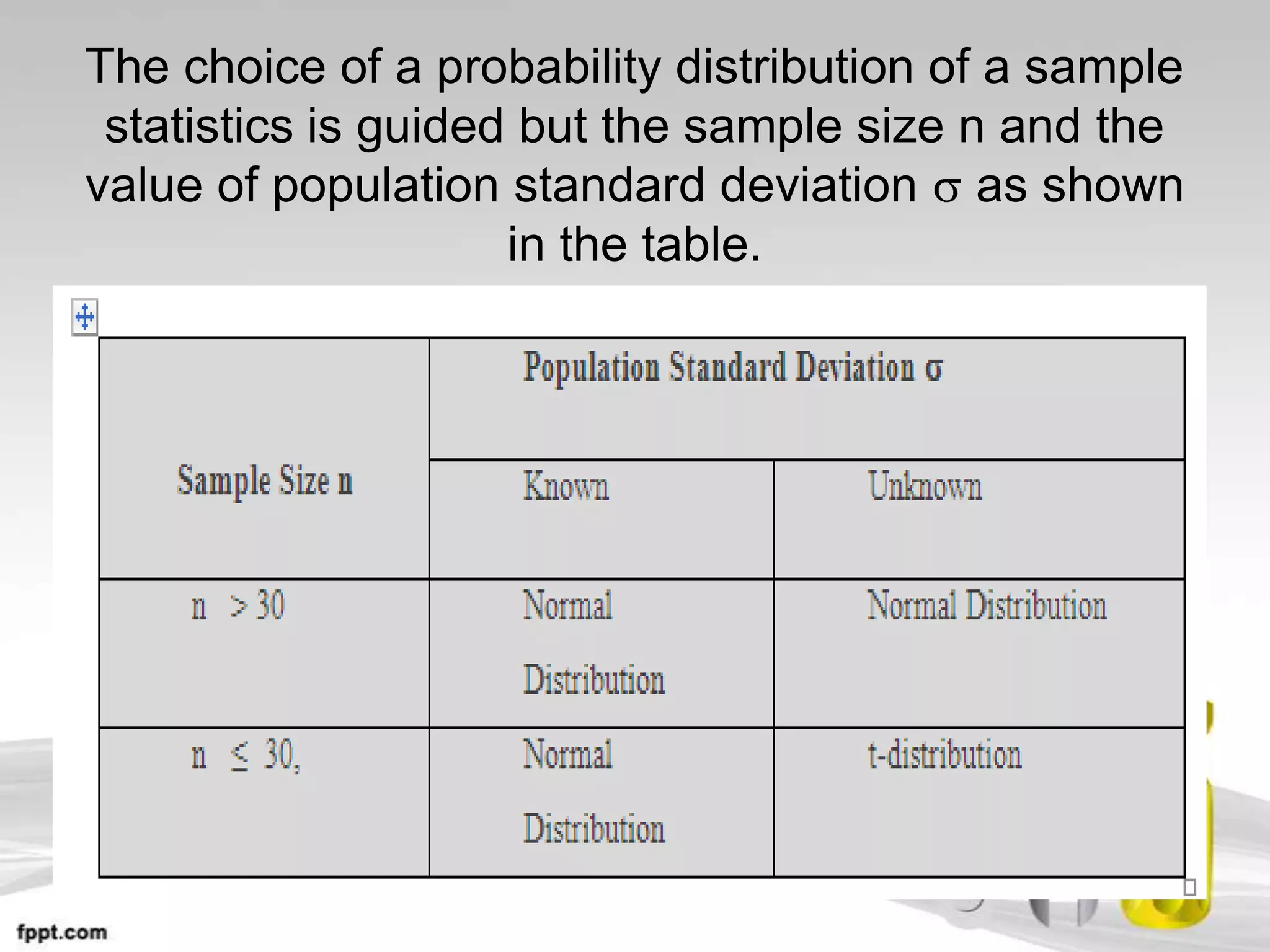
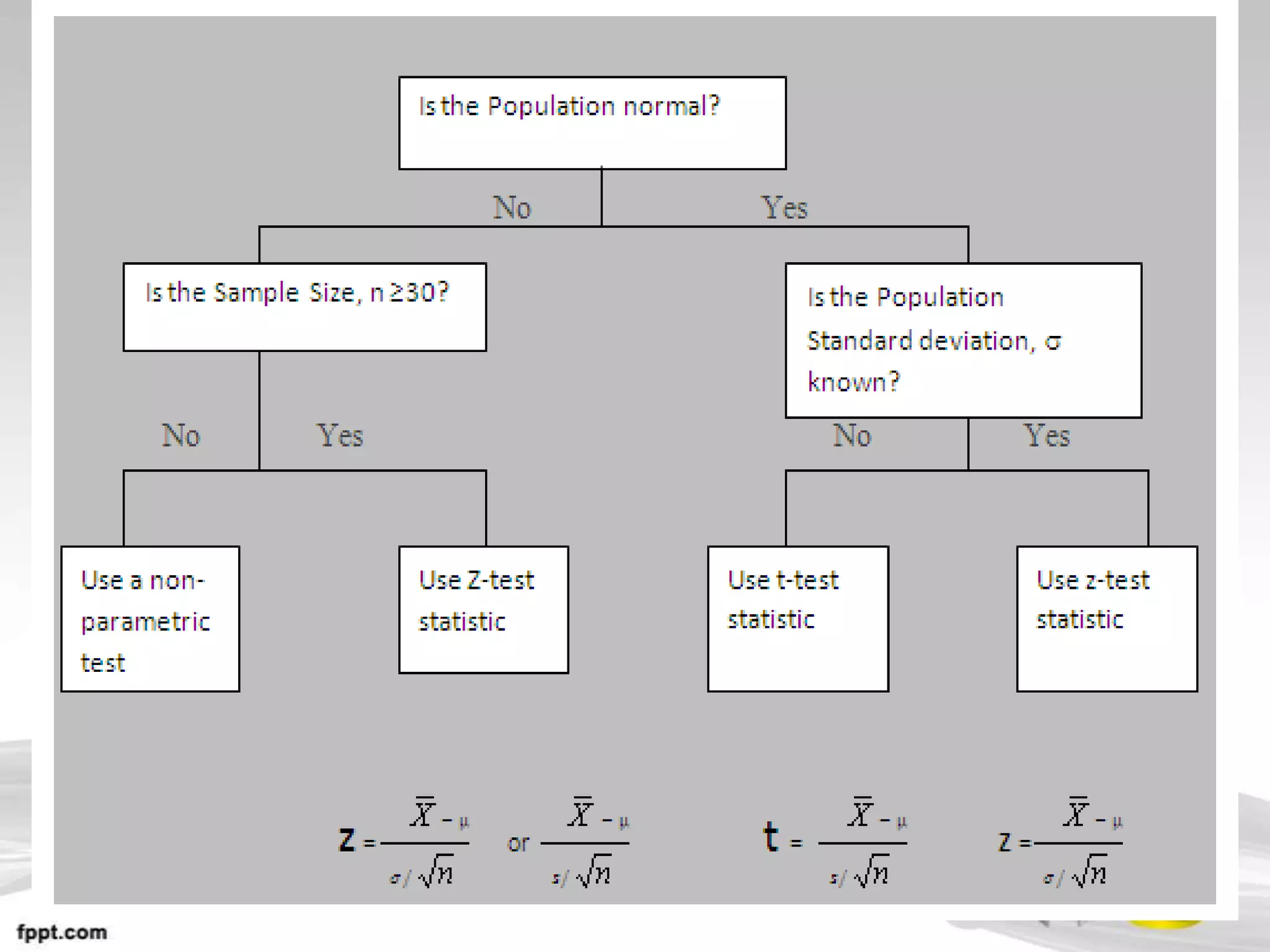
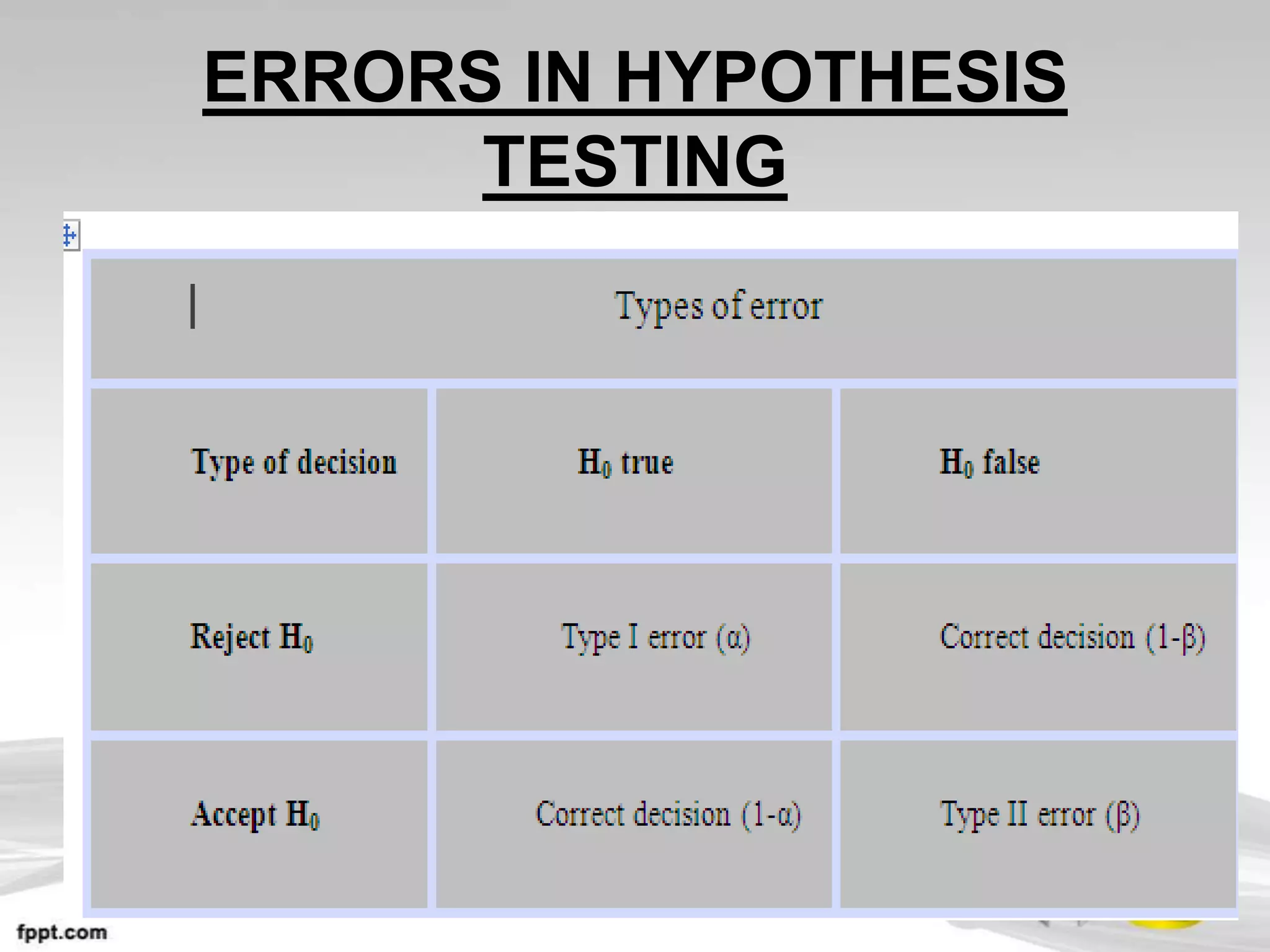
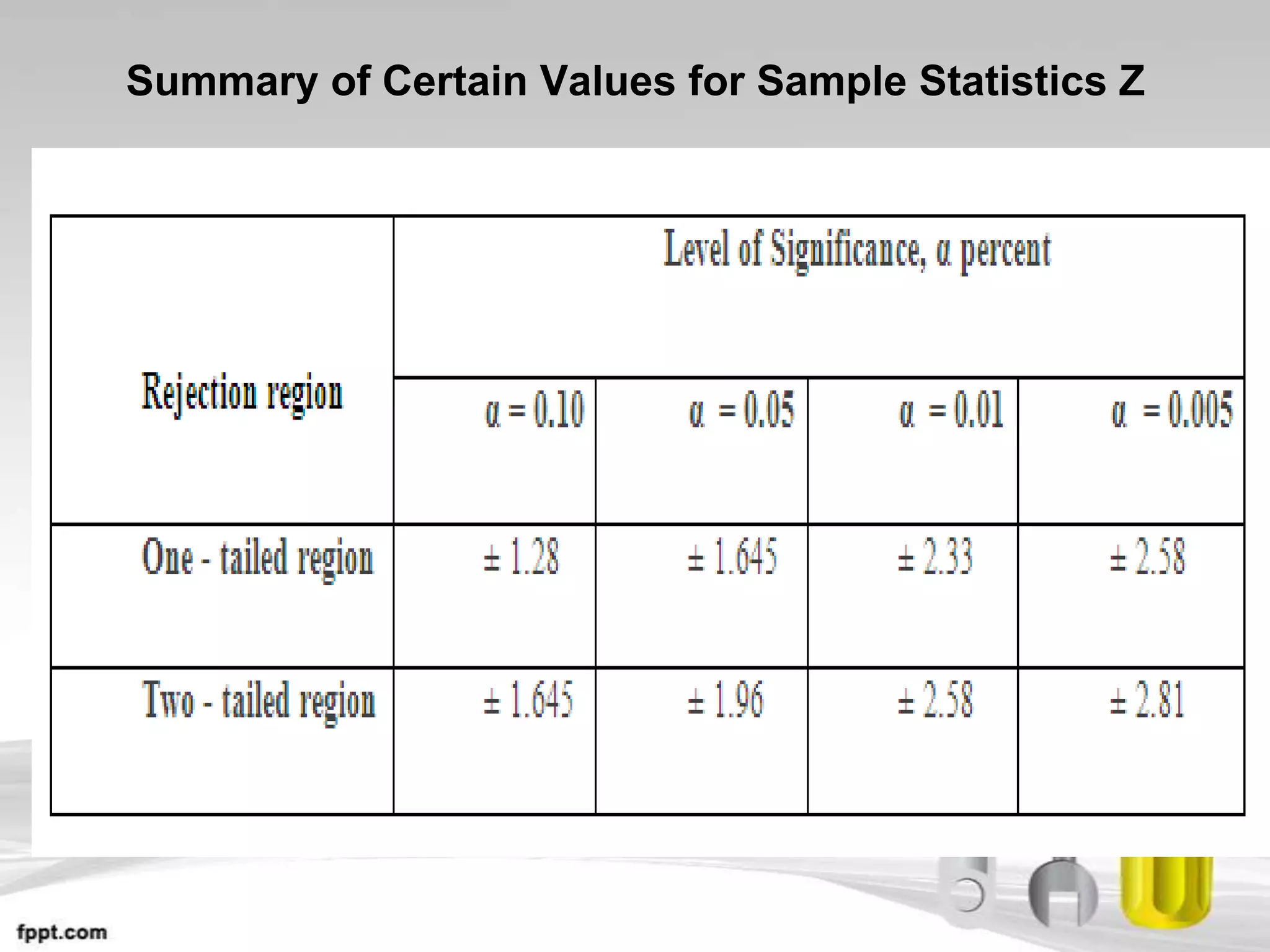
This document provides an overview of hypothesis testing in inferential statistics. It defines a hypothesis as a statement or assumption about relationships between variables or tentative explanations for events. There are two main types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis (H0), which is the default position that is tested, and the alternative hypothesis (Ha or H1). Steps in hypothesis testing include establishing the null and alternative hypotheses, selecting a suitable test of significance or test statistic based on sample characteristics, formulating a decision rule to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on where the test statistic value falls, and understanding the potential for errors. Key criteria for constructing hypotheses and selecting appropriate statistical tests are also outlined.