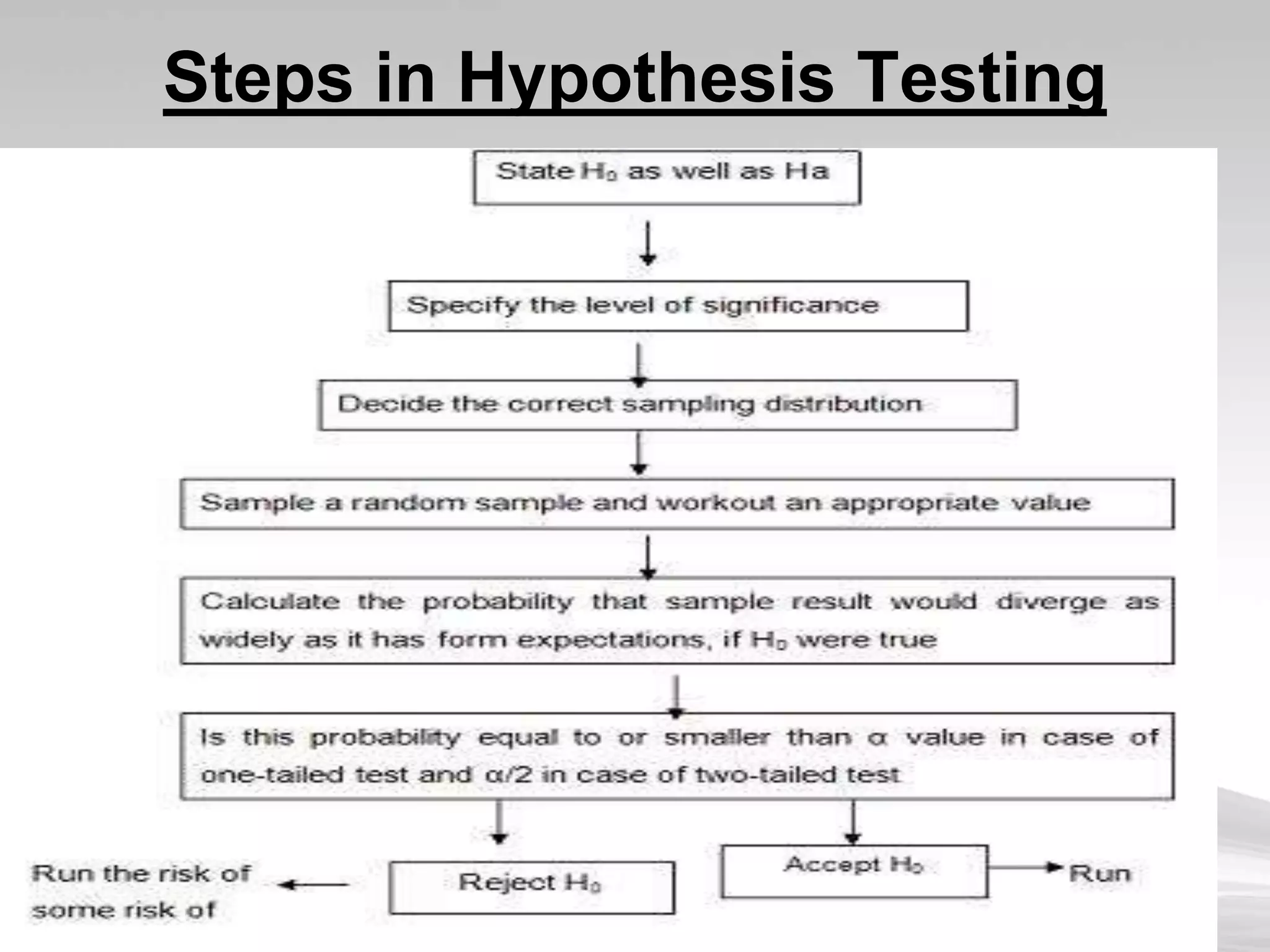
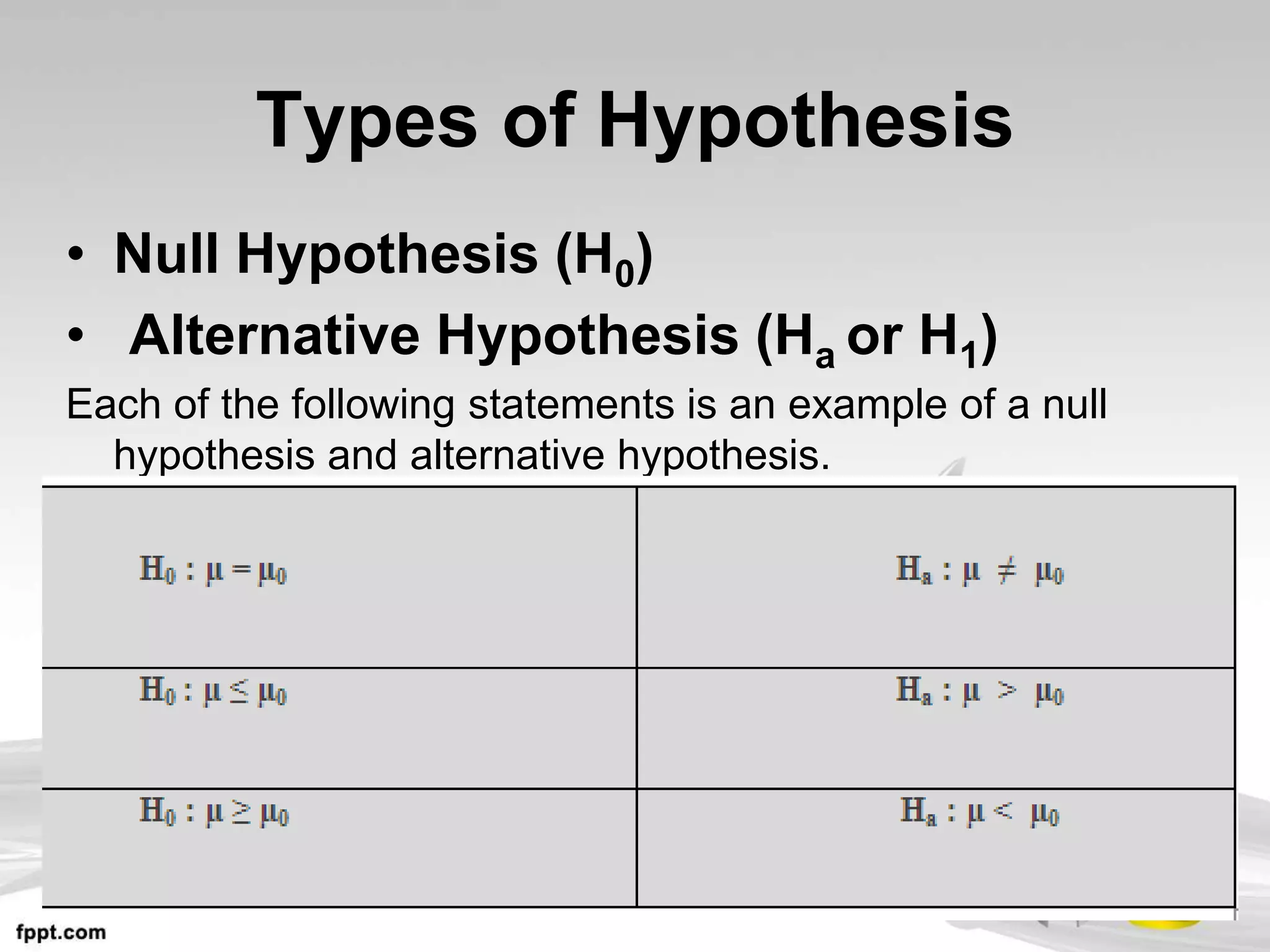
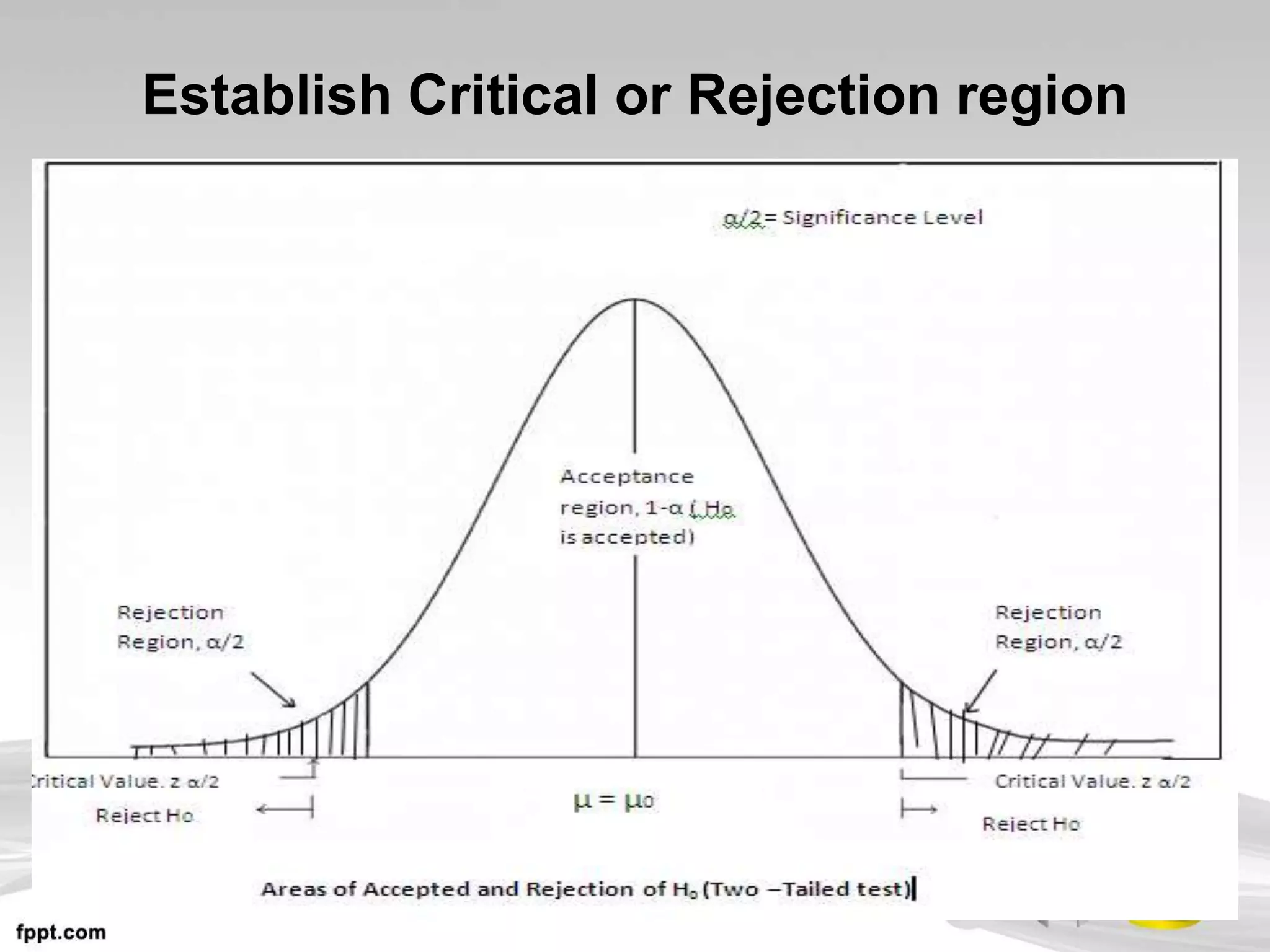
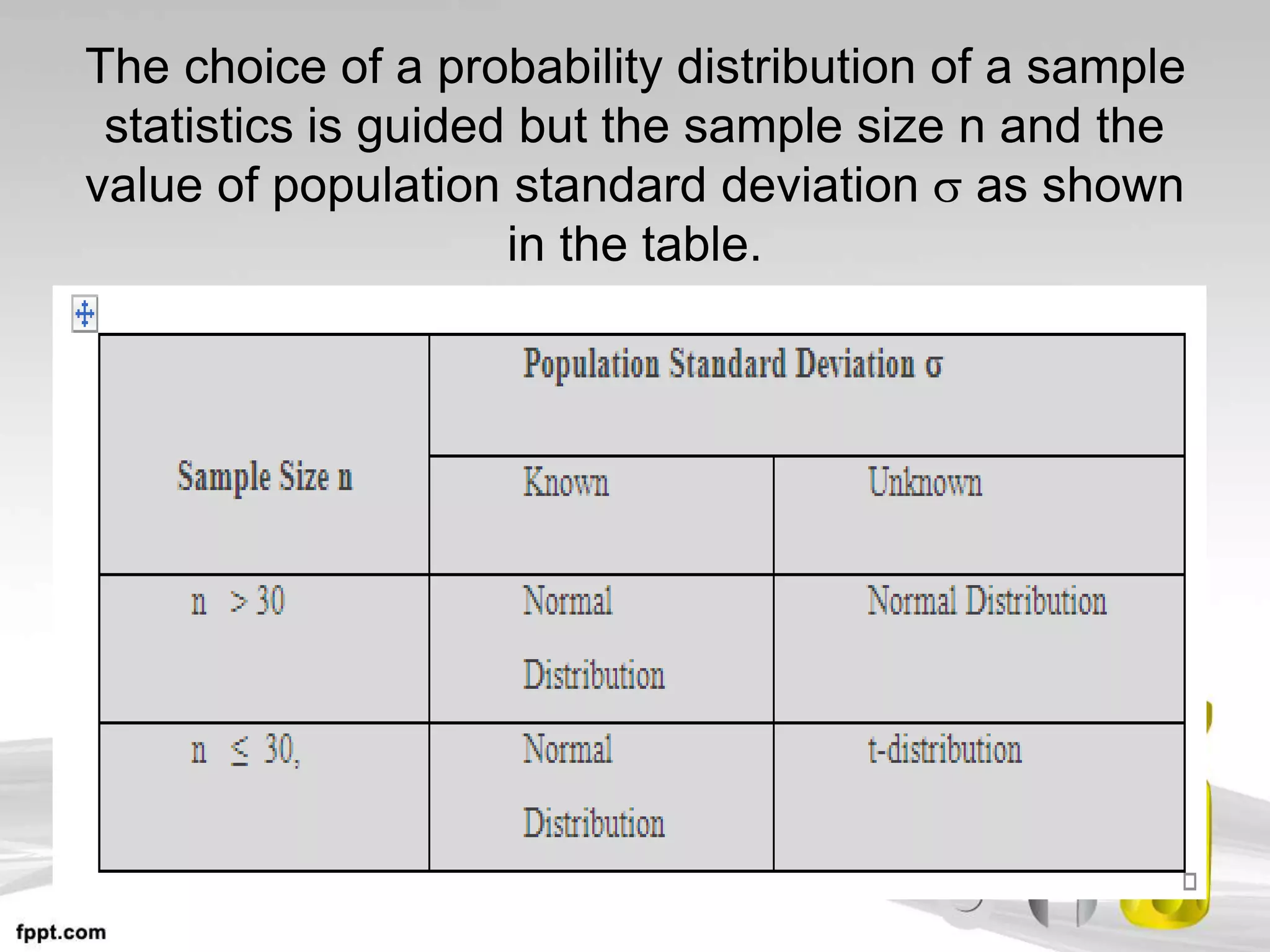
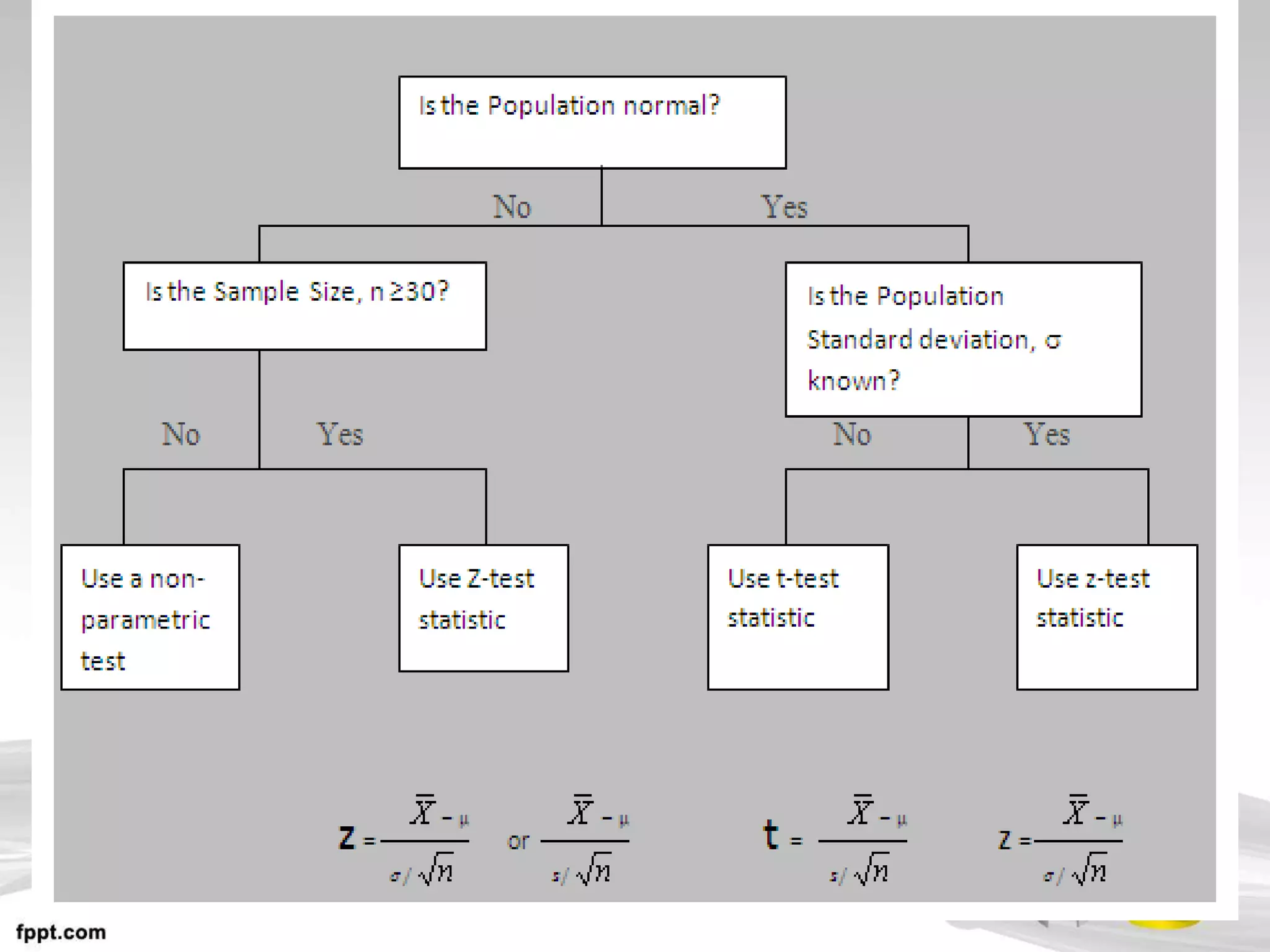
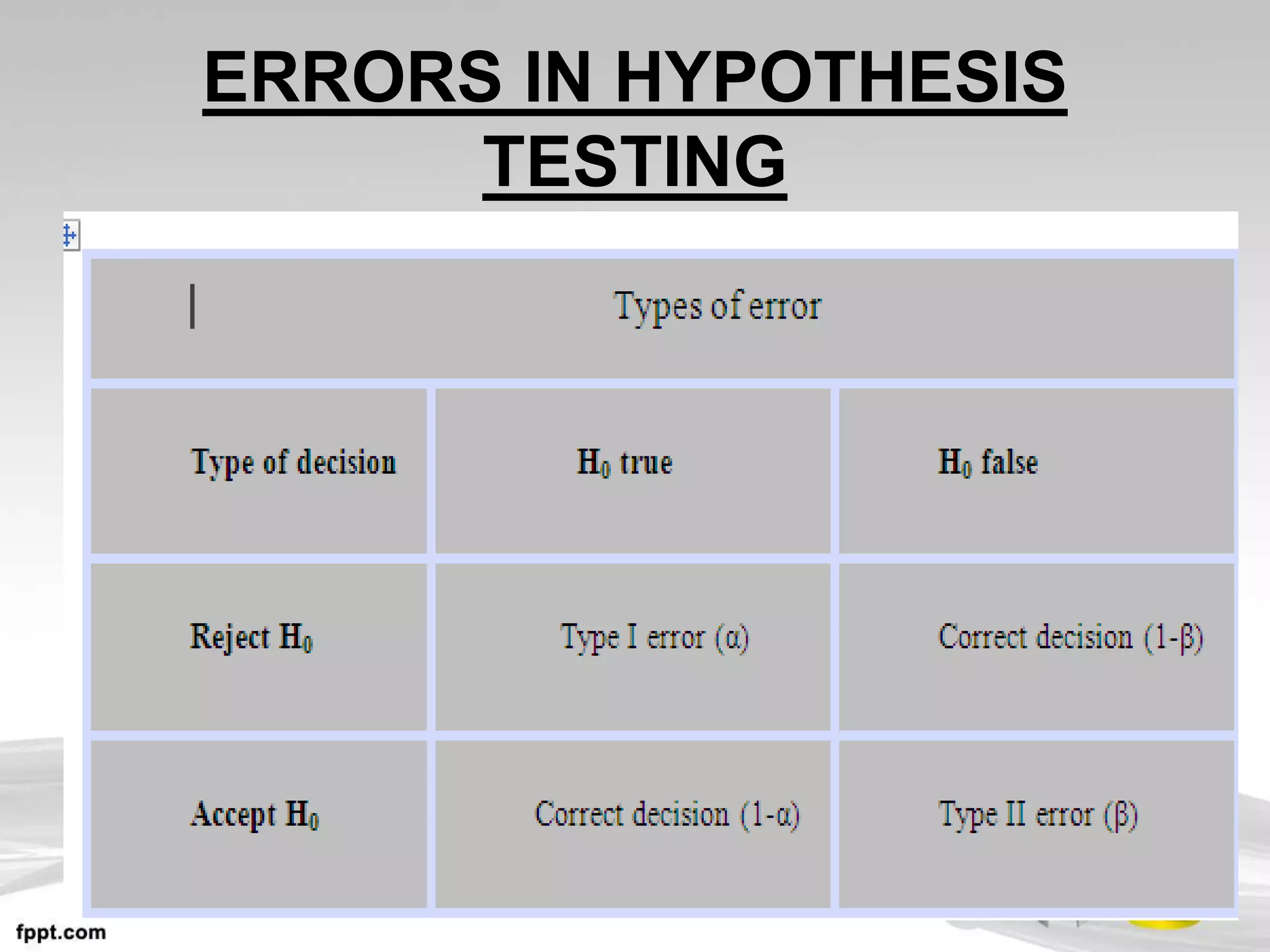
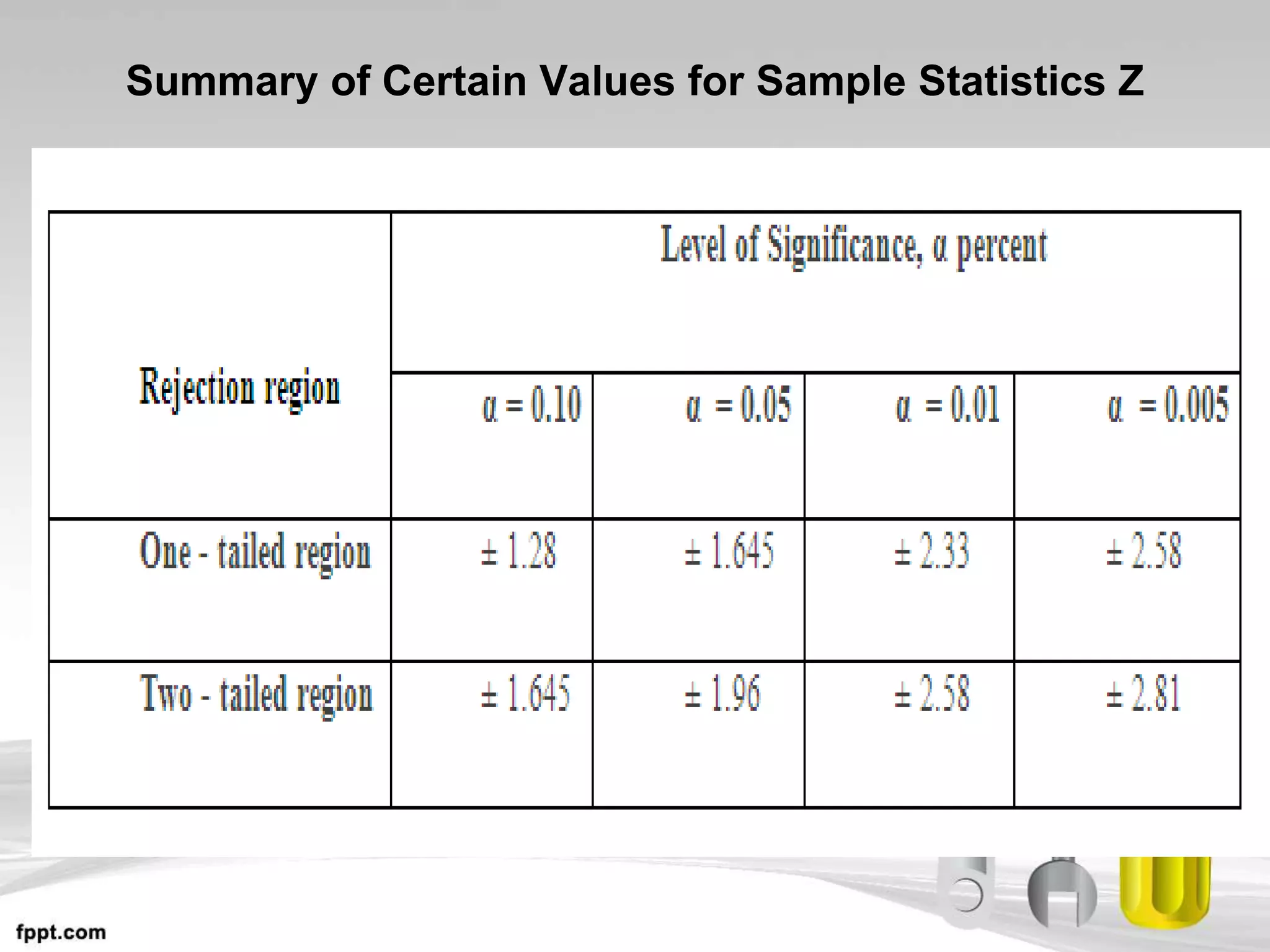
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which uses inferential statistics to determine the probability that an observed difference between groups occurred by chance. There are two main methods in inferential statistics: estimation and hypothesis testing. A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between variables. The steps in hypothesis testing are to establish the null and alternative hypotheses, determine the critical region, select an appropriate test statistic based on sample size and scale of measurement, calculate the test statistic value, and make a decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis based on where the value falls. Types of hypotheses include the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.