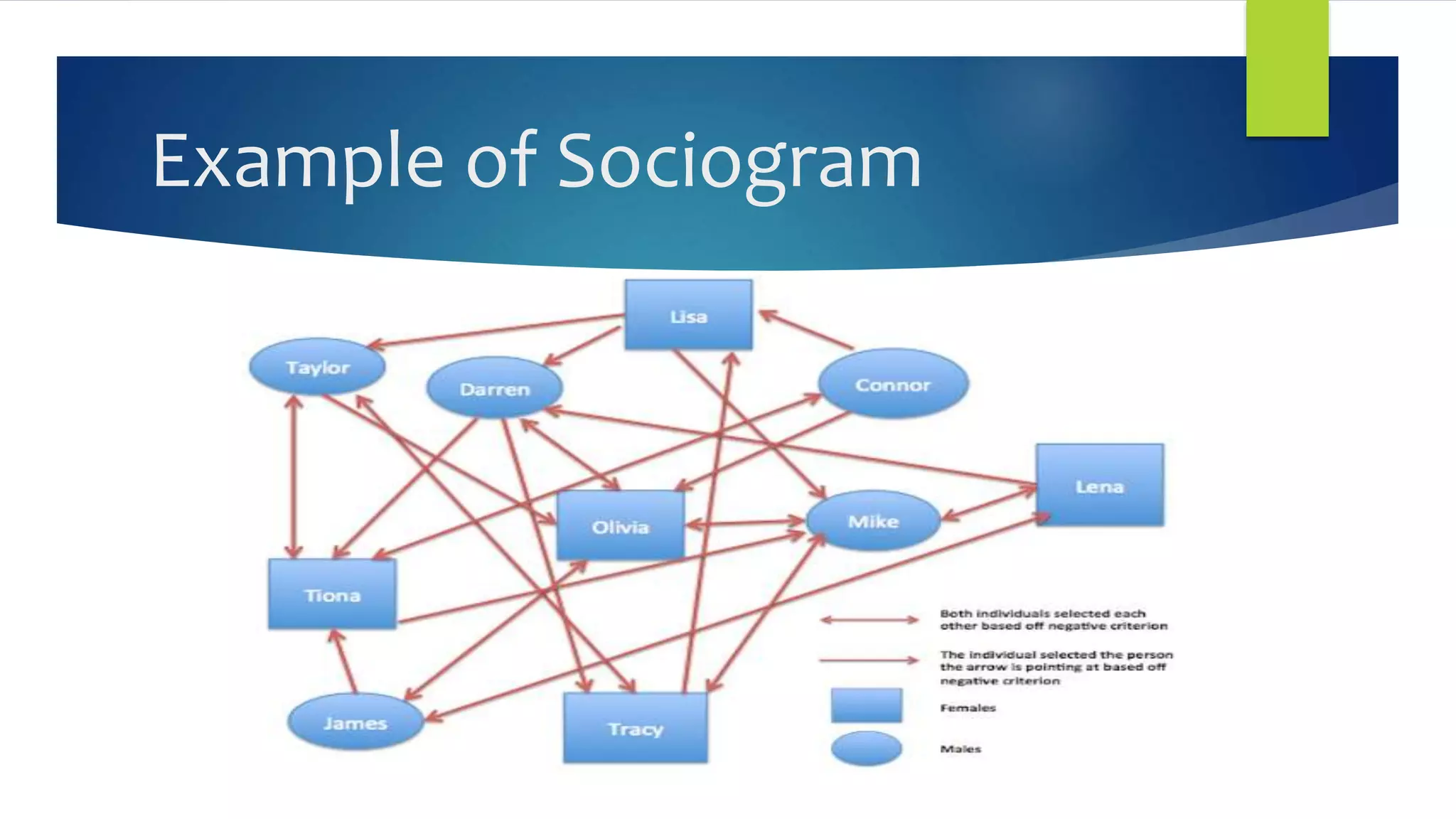
This document discusses sociograms, which are graphic representations of social relationships within a group. Sociograms are constructed by having students respond to a question about their social preferences, such as who they would invite to a birthday party. Their responses are then tabulated and diagrammed to determine how popular or unpopular each student is based on how many times they were selected. This can help teachers identify students who are socially isolated or well-connected. However, sociograms only provide limited insights and their results depend on the specific questions asked. To be more valid, sociograms should be administered multiple times using different questions and scenarios.