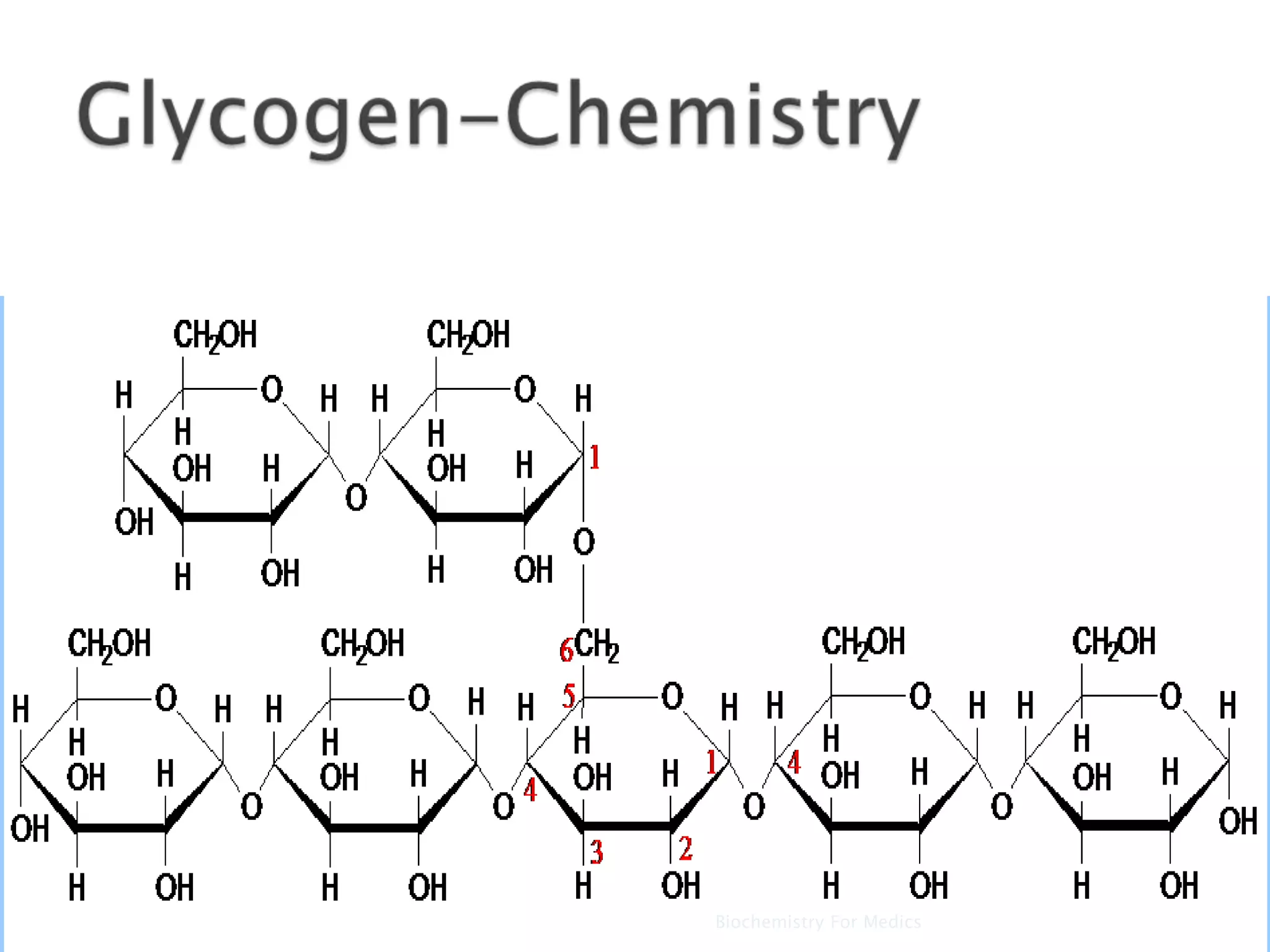
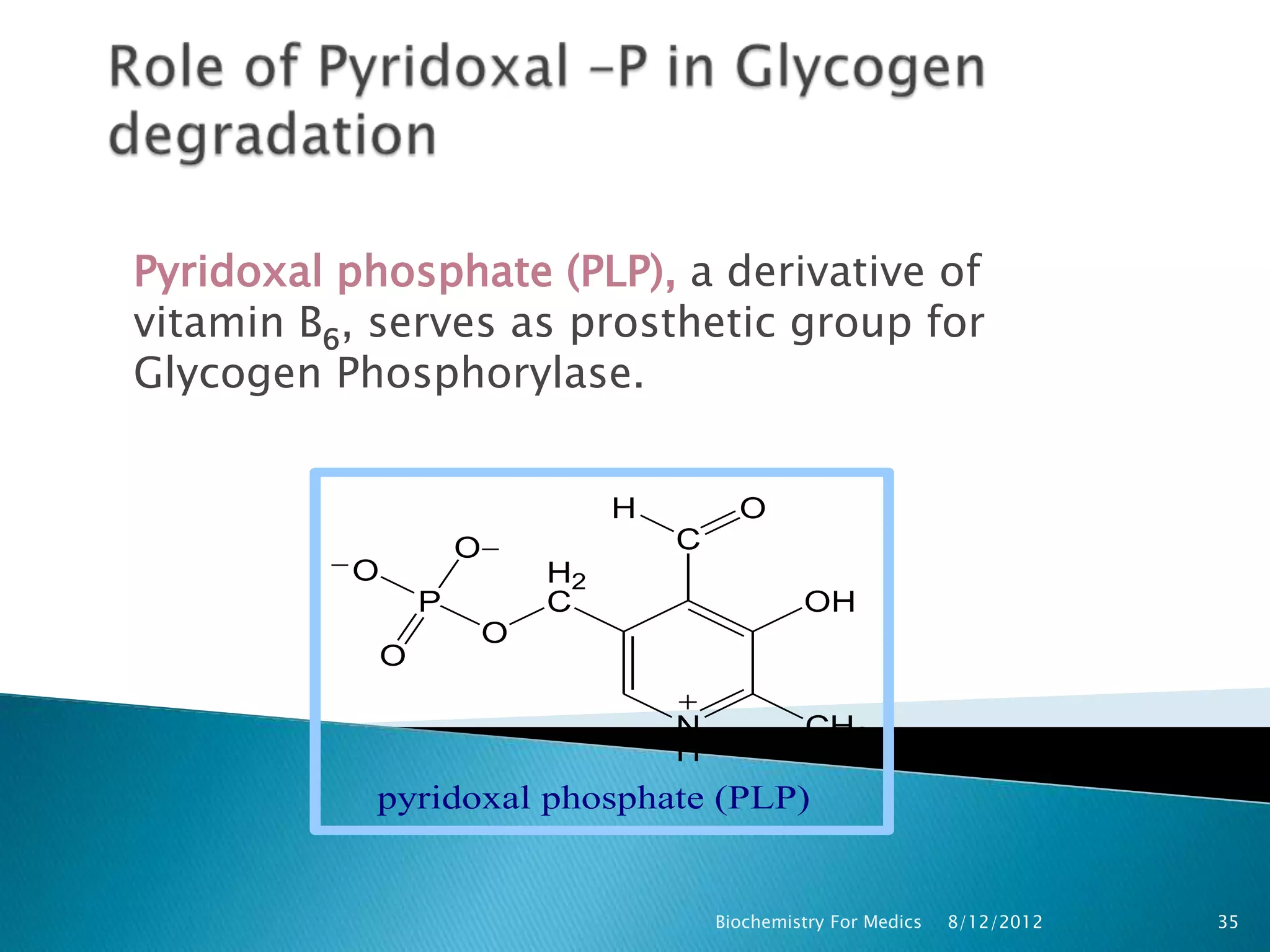
Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose residues that serves as a storage form of glucose. It is composed mainly of α-1,4 glycosidic linkages with branches every tenth residue by α-1,6 linkages. Glycogen is found primarily in liver and muscle cells bound in granules and provides a readily available source of glucose through breakdown. Glycogen synthesis utilizes UDP-glucose and glycogenin to initiate polymer formation, while breakdown is catalyzed by phosphorylase releasing glucose-1-phosphate and other enzymes are needed to further process the glucose for energy production.