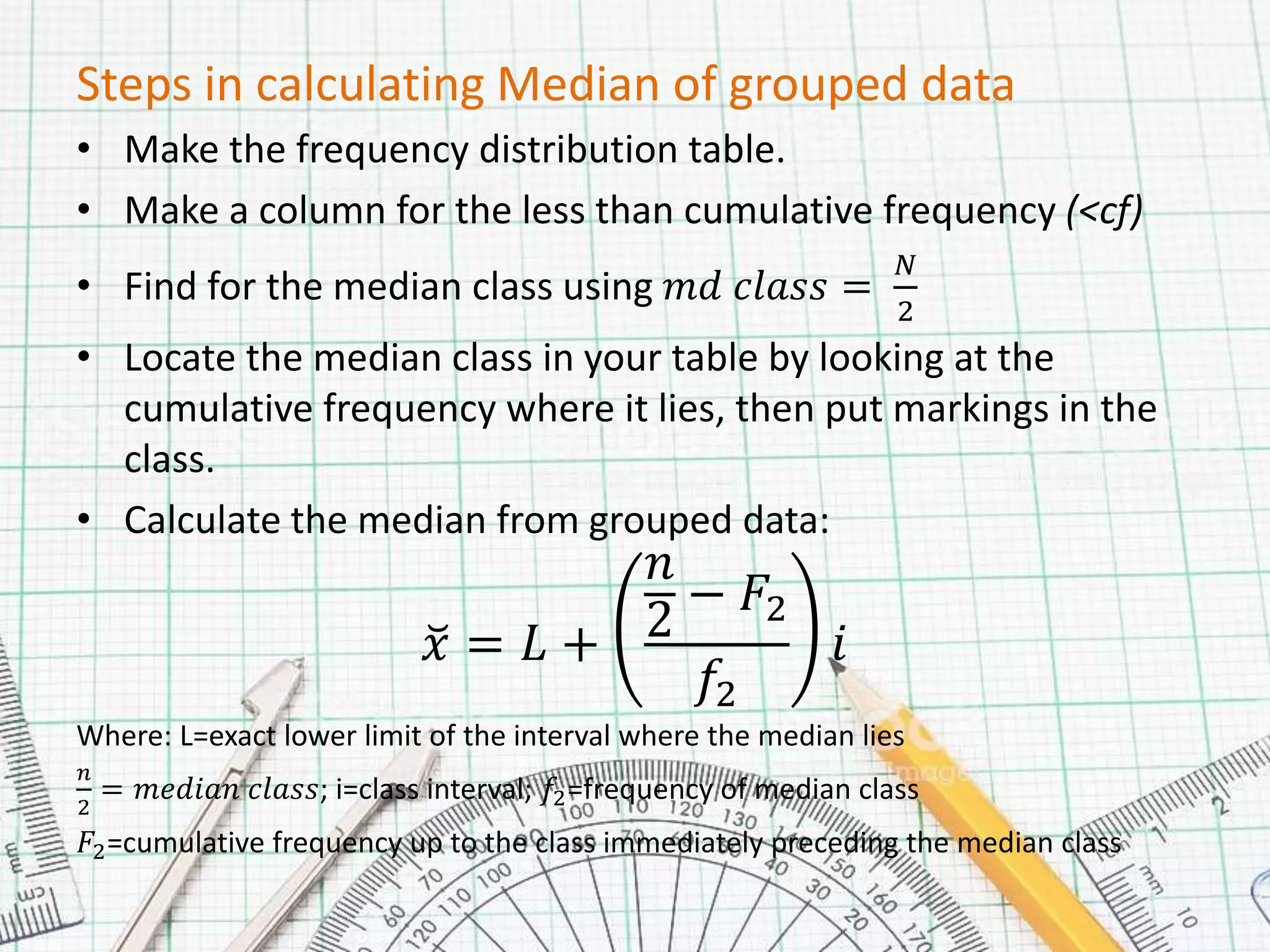
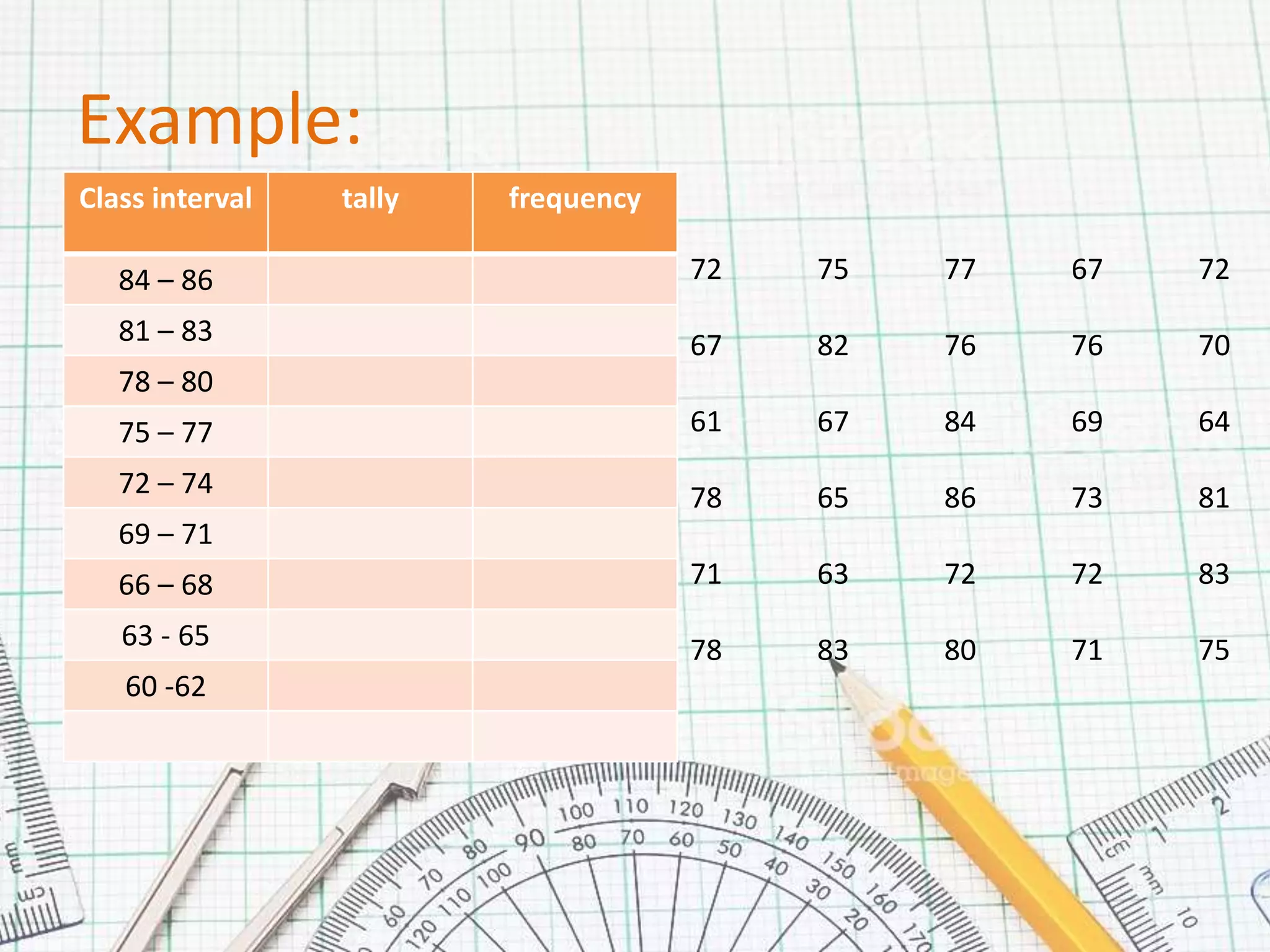
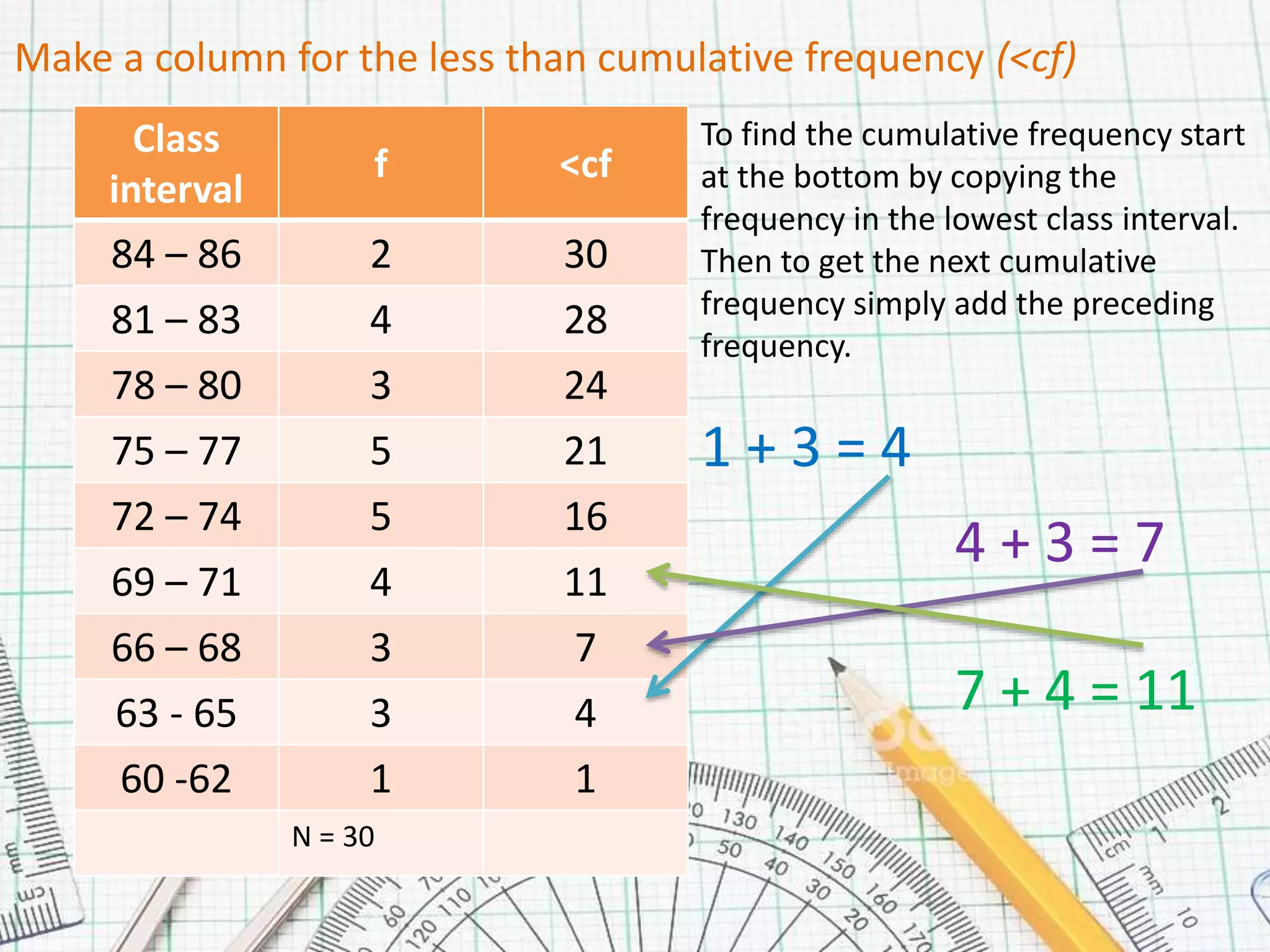
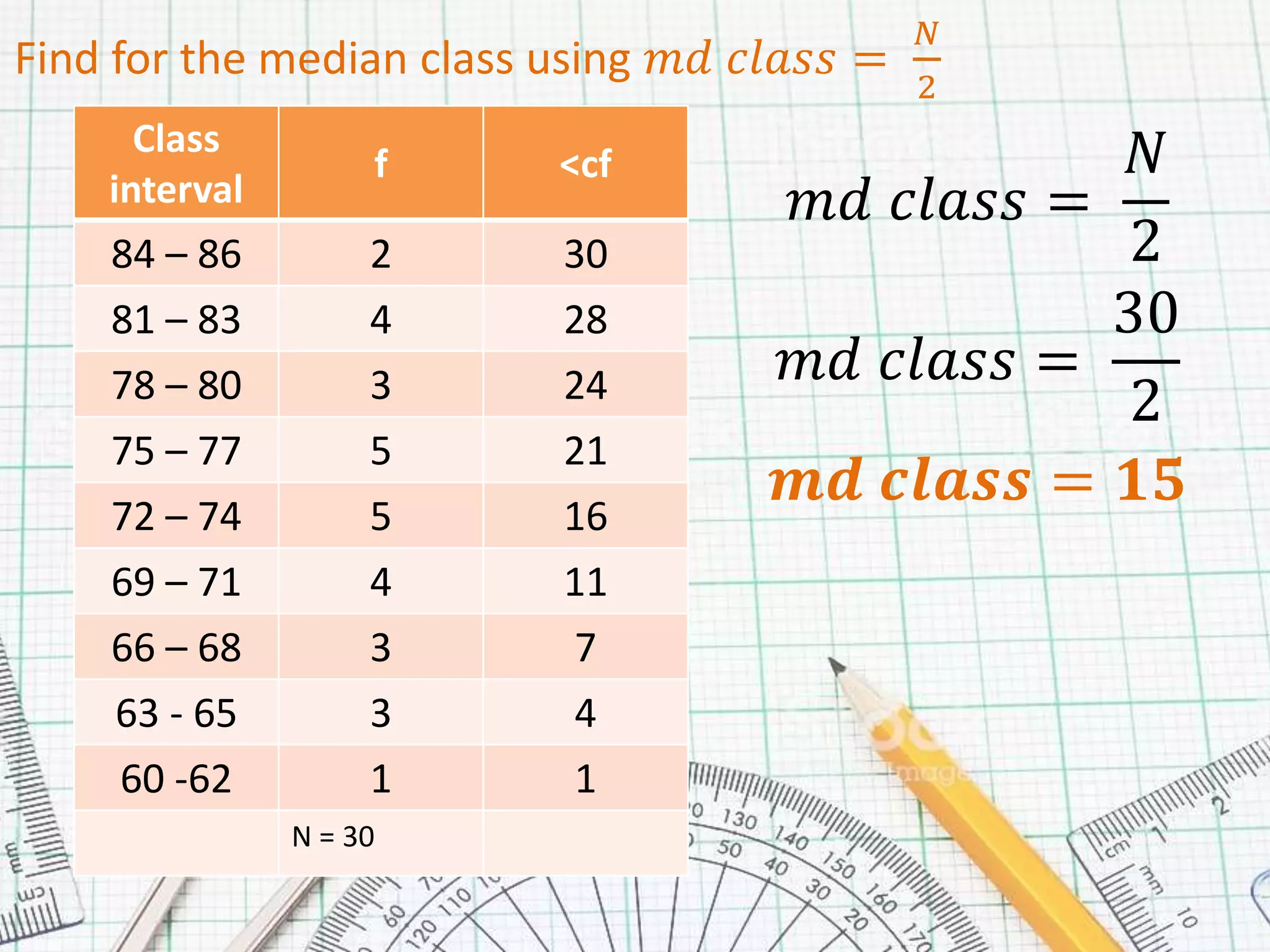
This document provides steps for calculating the median of grouped data:
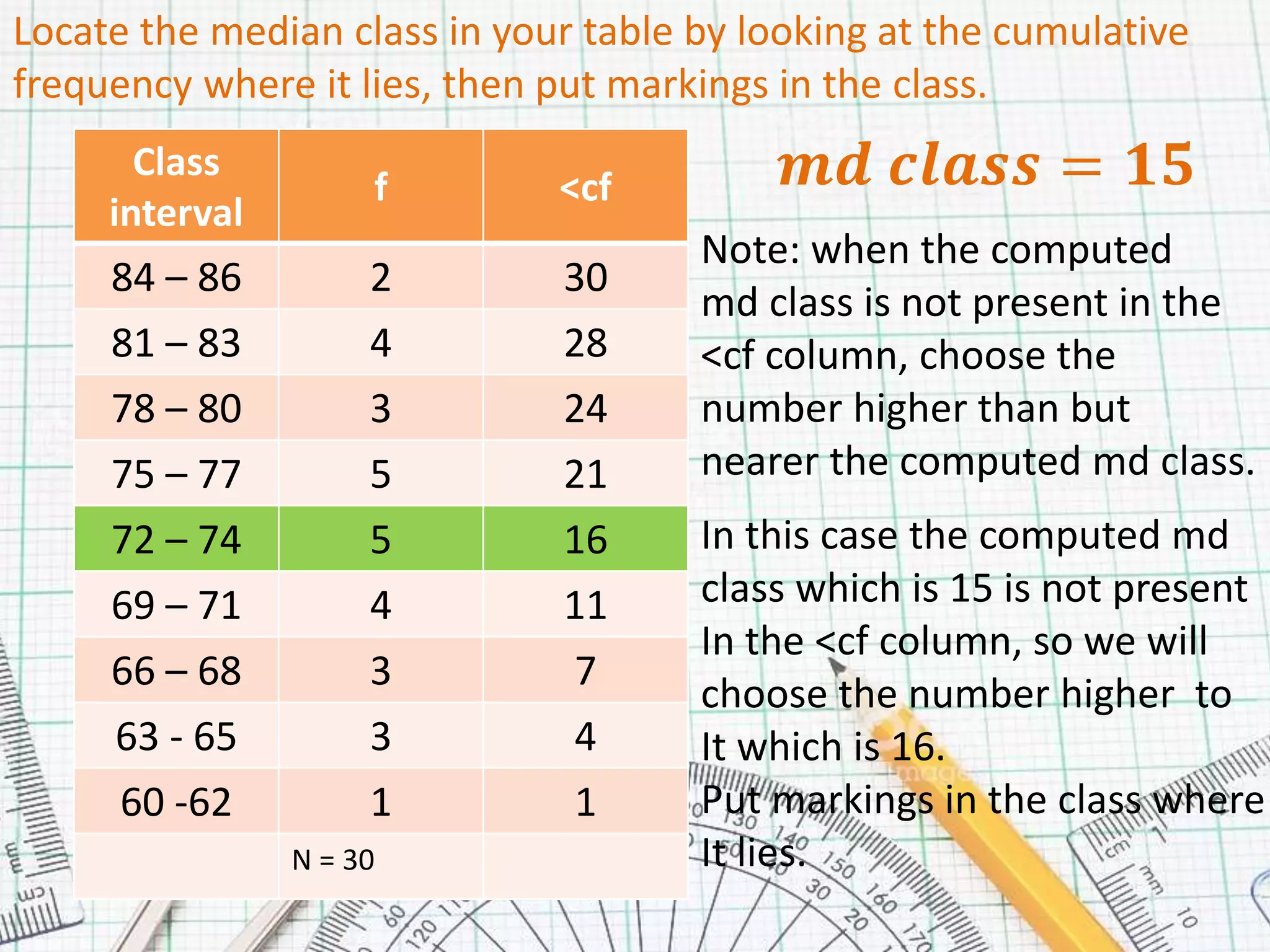
1. Create a frequency distribution table with class intervals, frequencies, and cumulative frequencies.
2. Find the median class by calculating N/2, where N is the total number of data points.
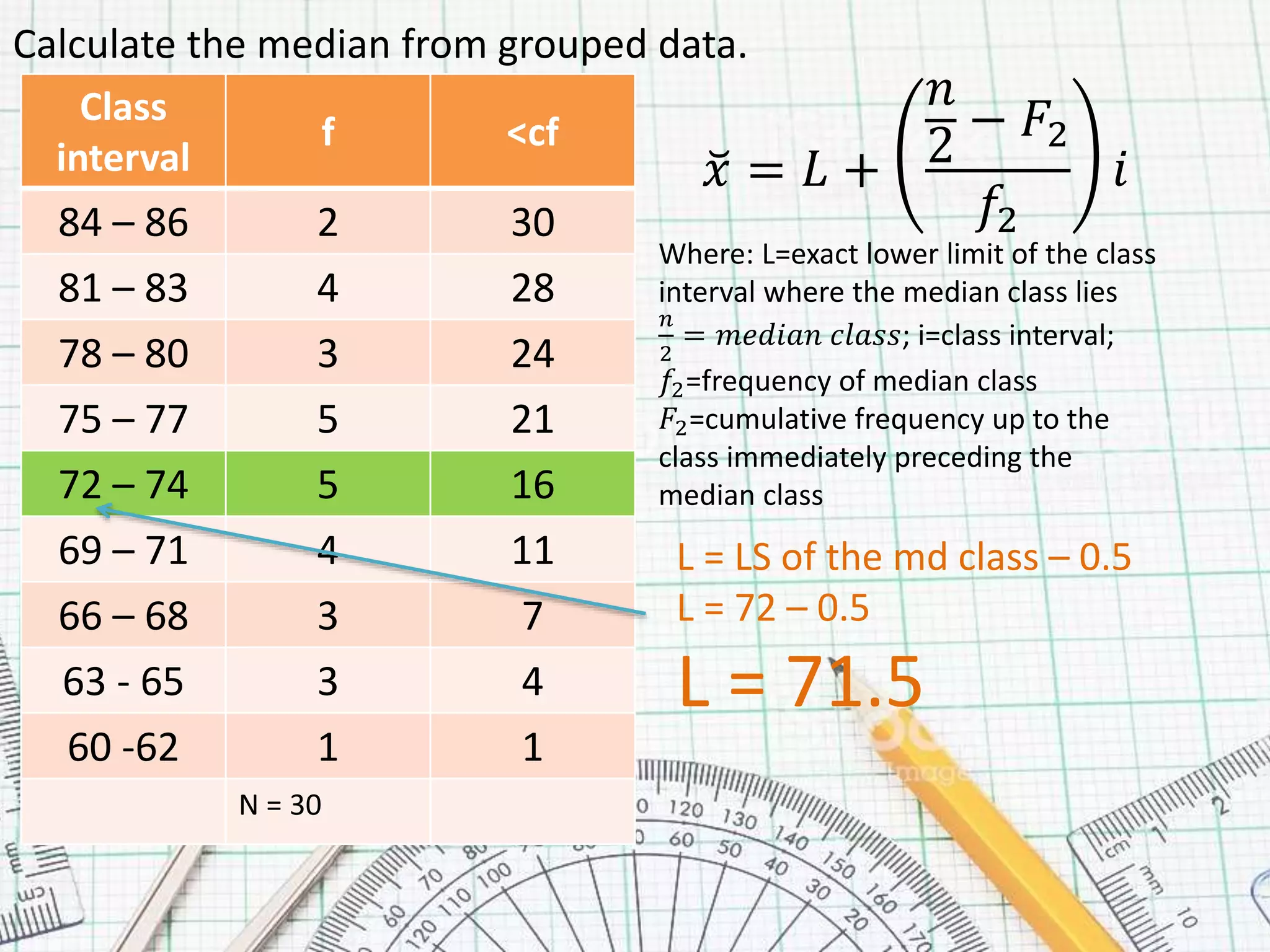
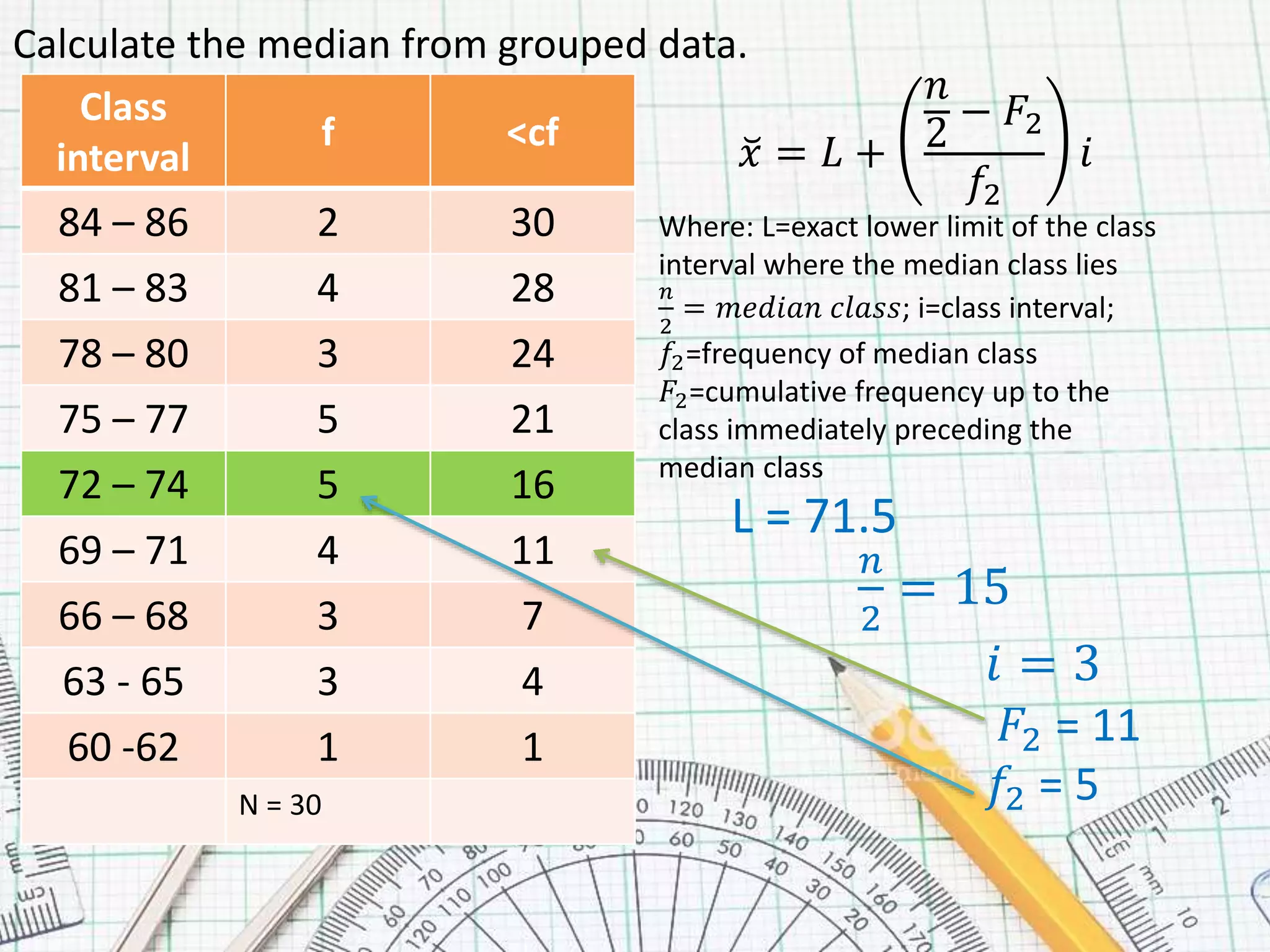
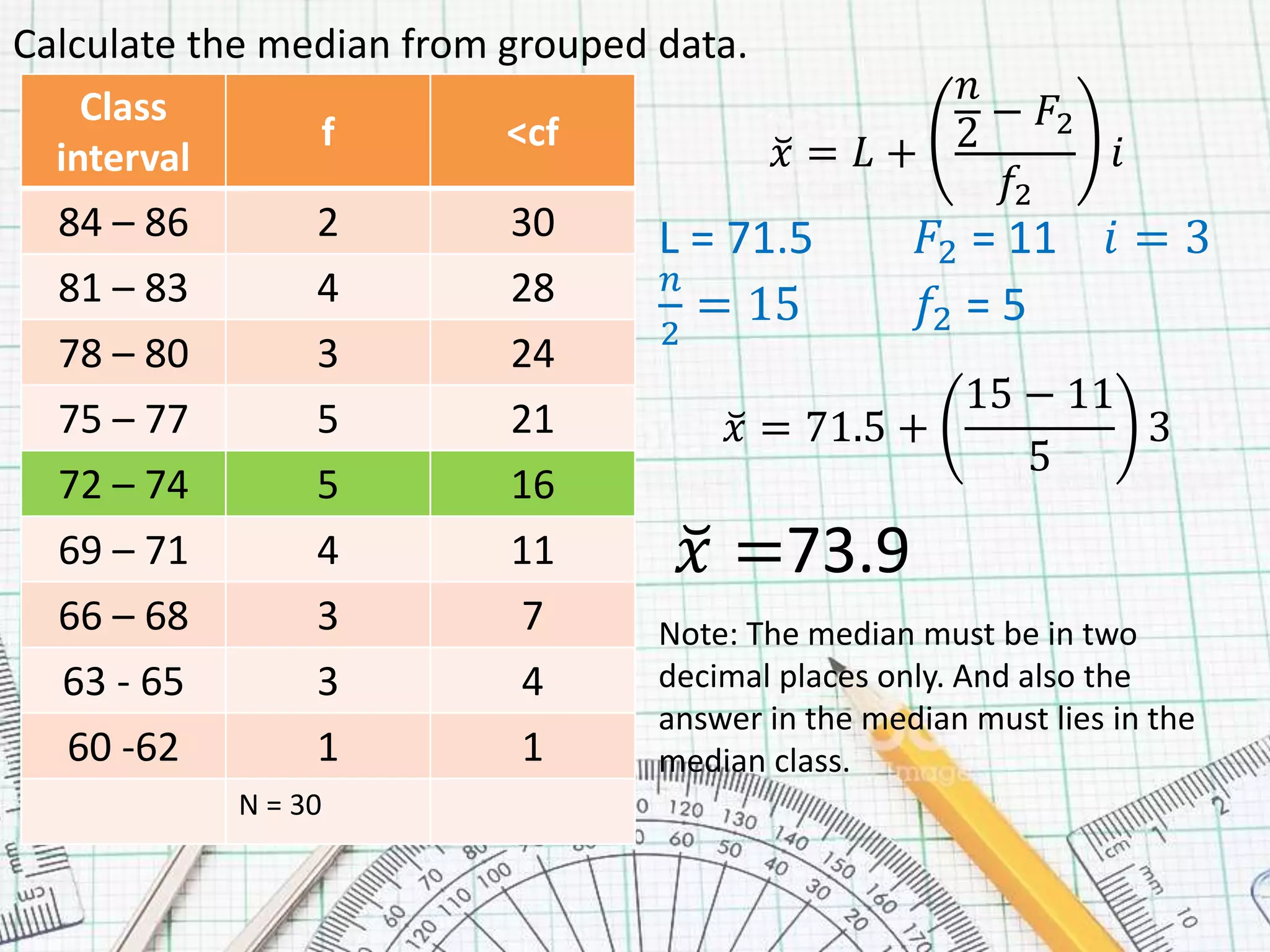
3. The median is calculated using the formula: x = L + (n2 - F2)/f2 * i, where L is the lower limit of the median class, n2 is the median class, F2 is the cumulative frequency before the median class, f2 is the frequency of the median class, and i is the class interval.