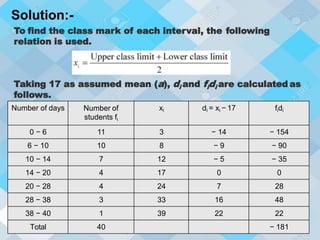
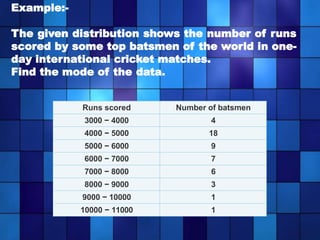
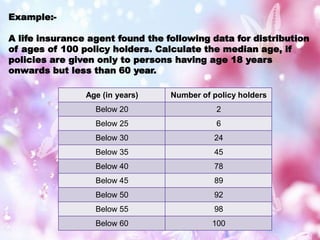
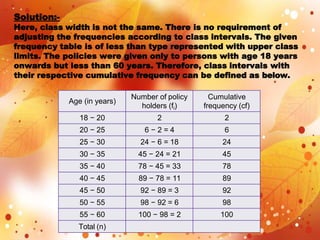
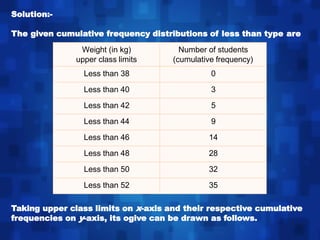
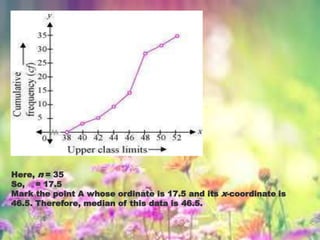
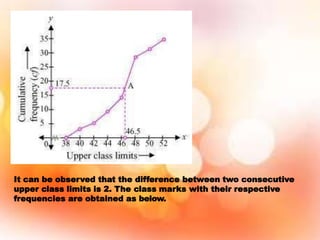
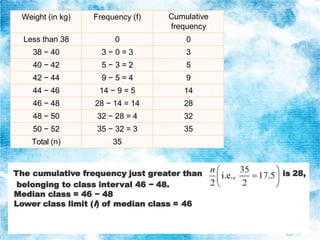
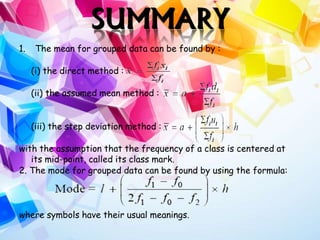
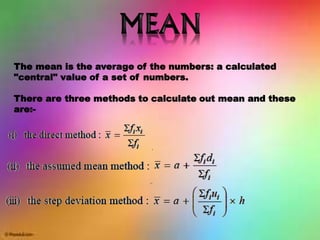Statistics is the study of data collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation. It involves planning data collection through surveys and experiments. The mean, median, and mode are common measures used to describe central tendencies in data. For grouped data, the mean can be calculated using direct, assumed mean, or step deviation methods assuming class frequencies are centered at class marks. Formulas are used to find the mode and median, which can also be found graphically using ogives to plot cumulative frequencies against class limits.