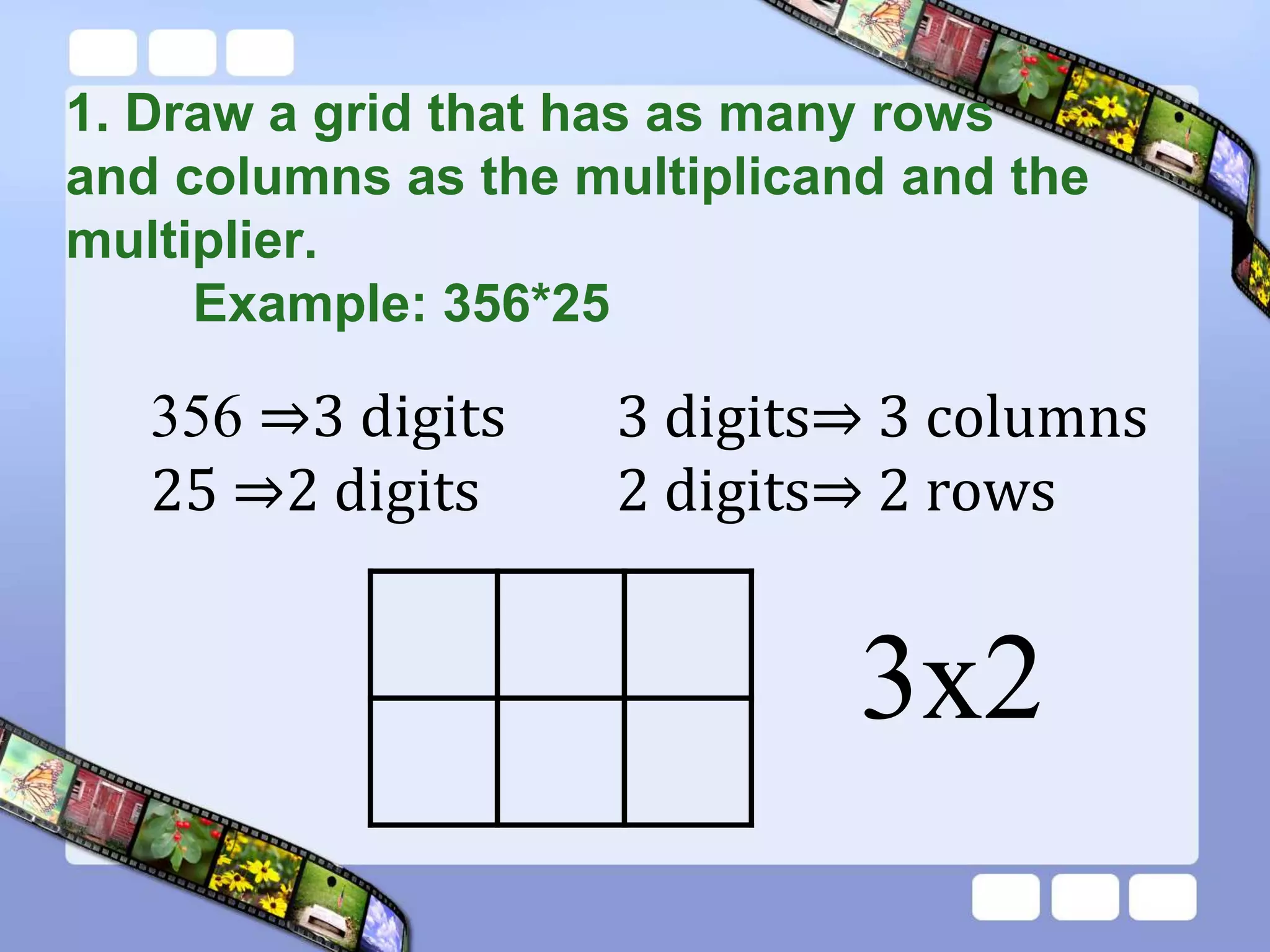
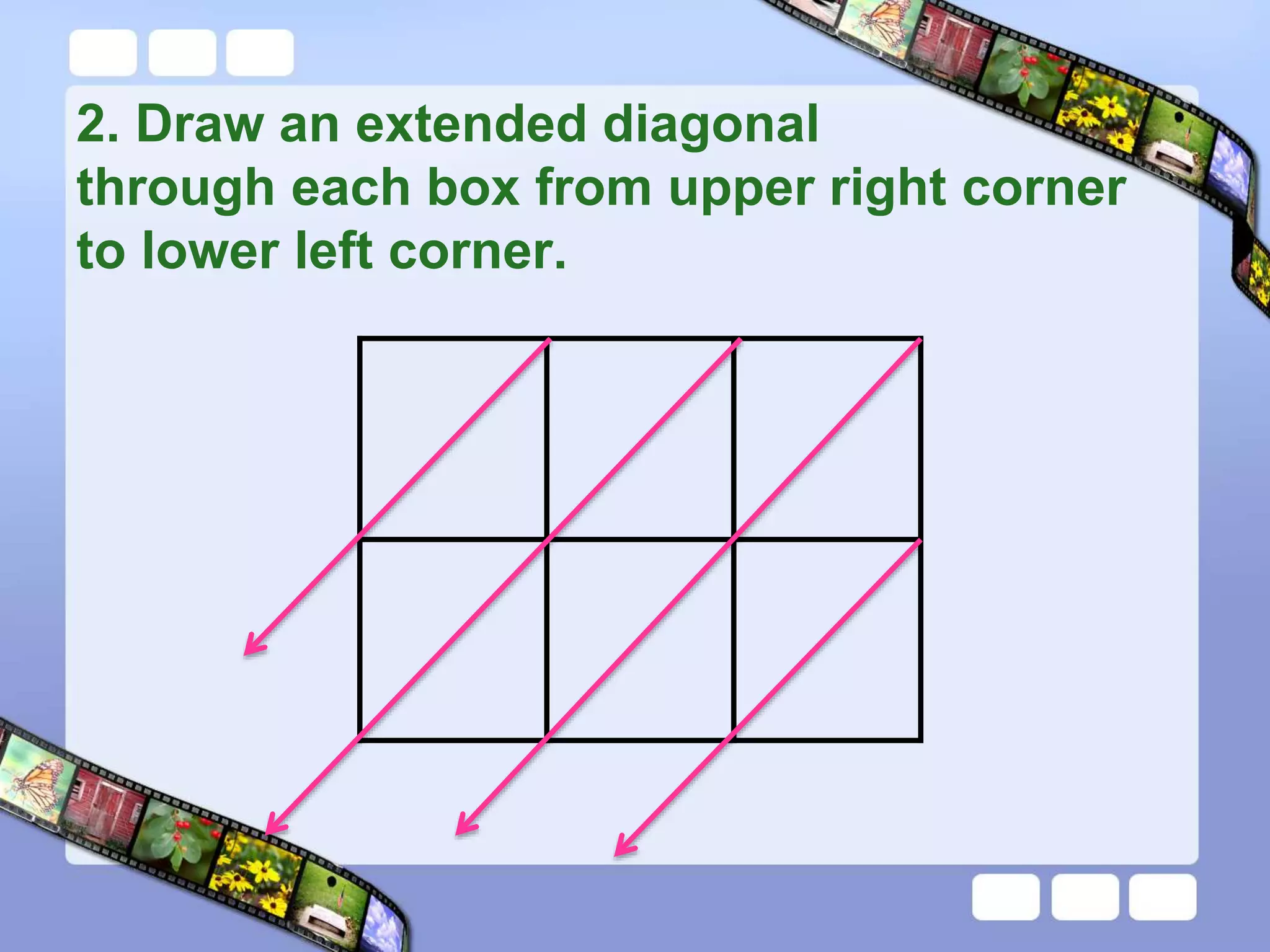
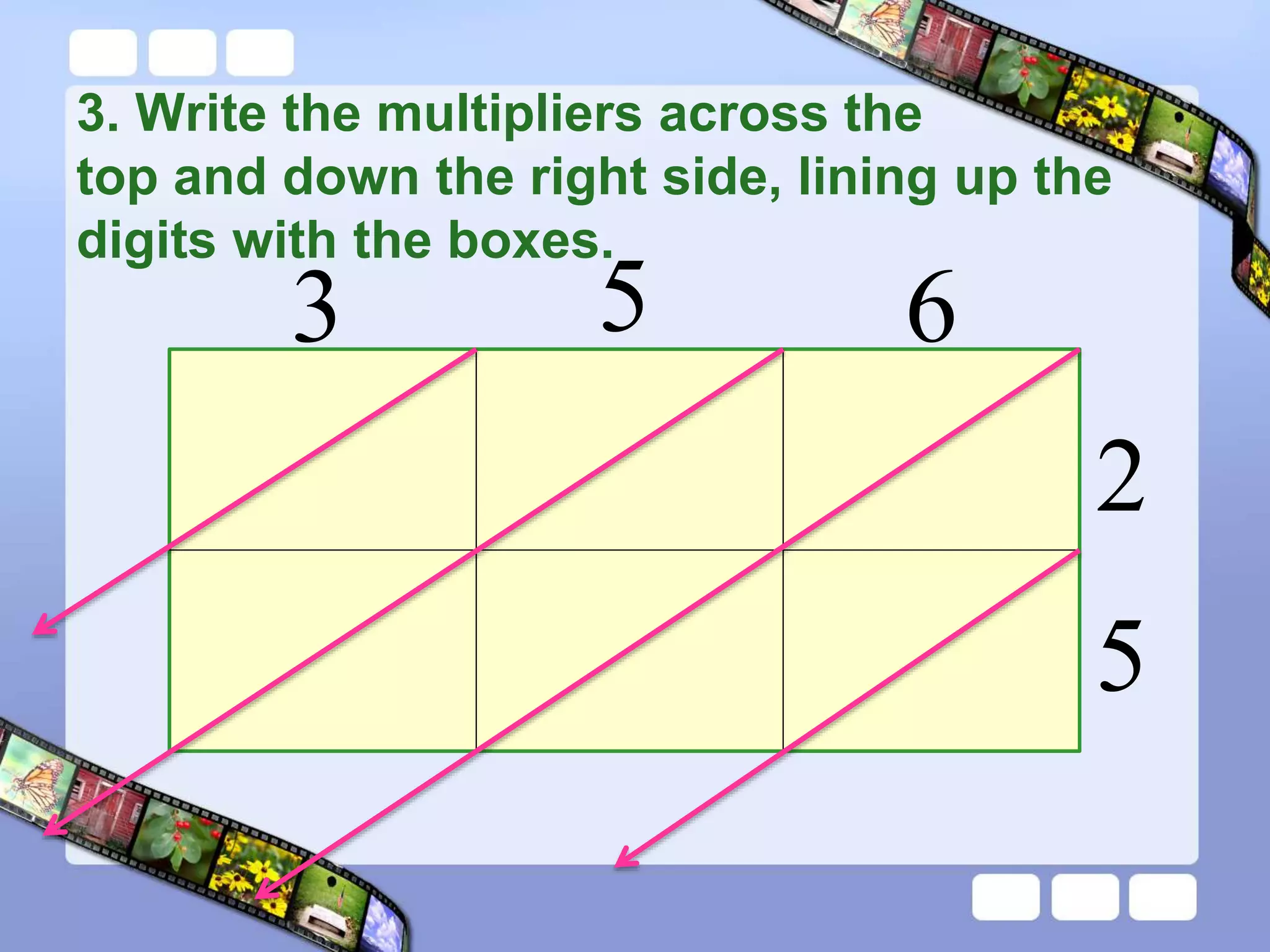
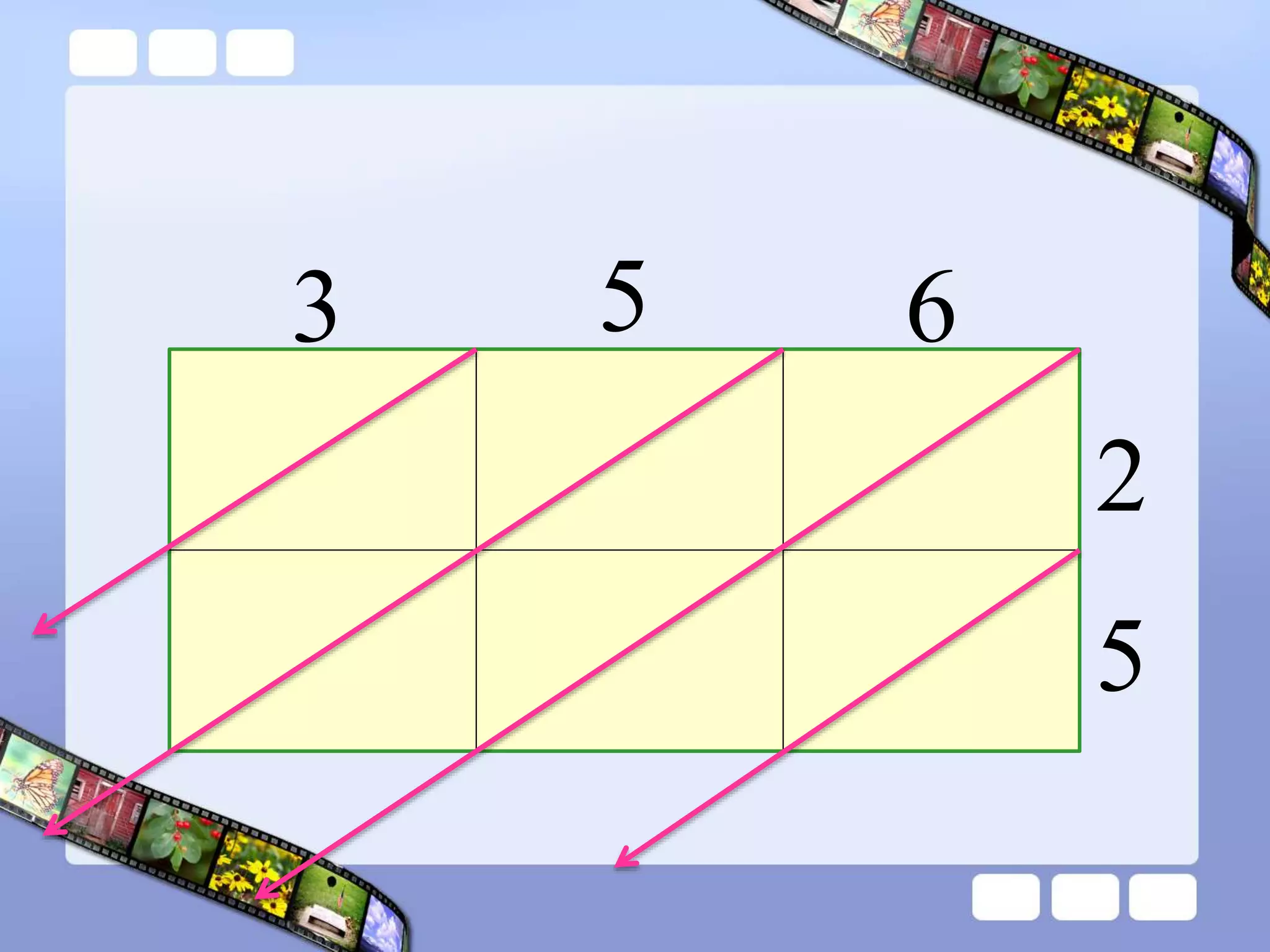
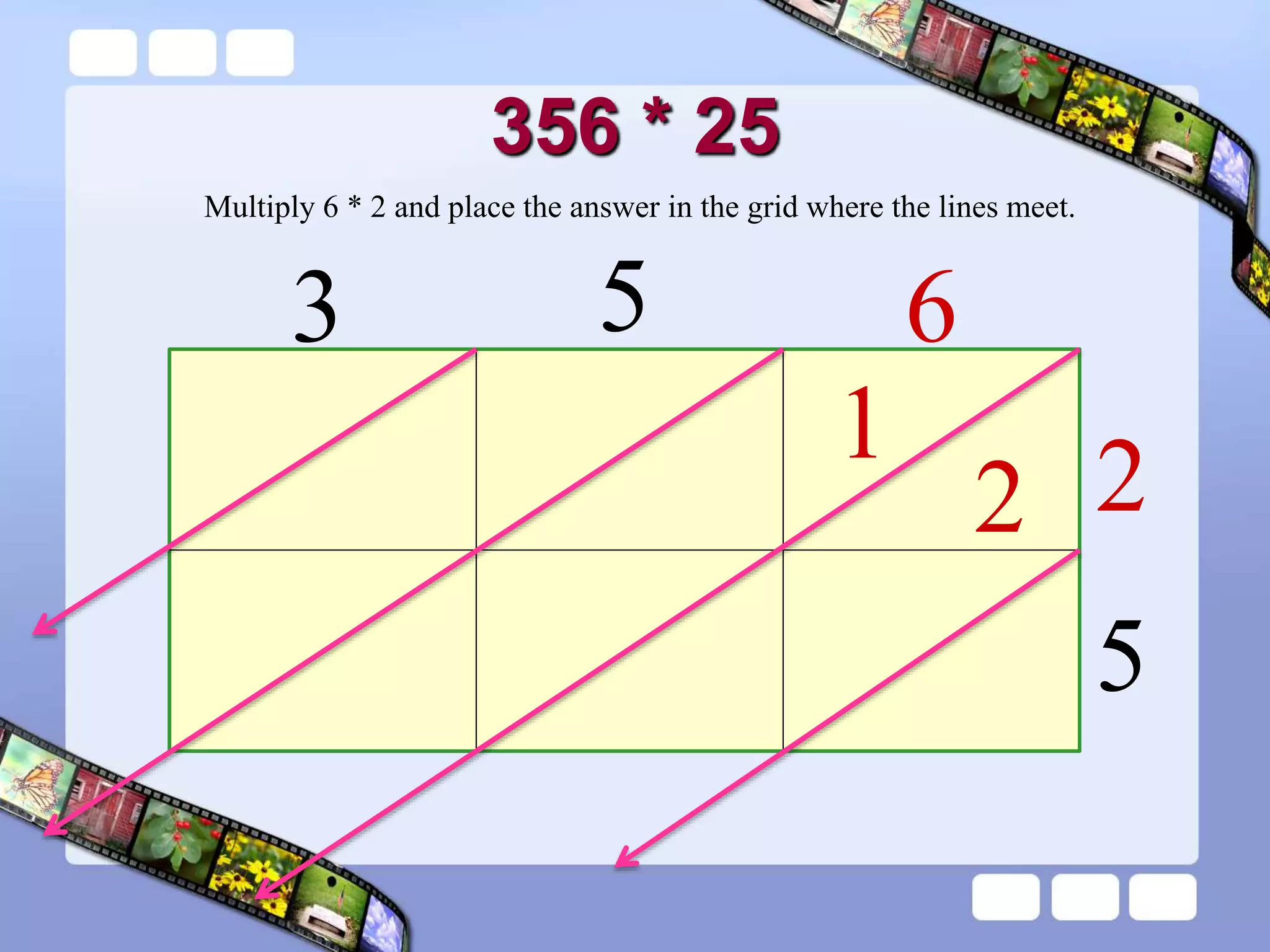
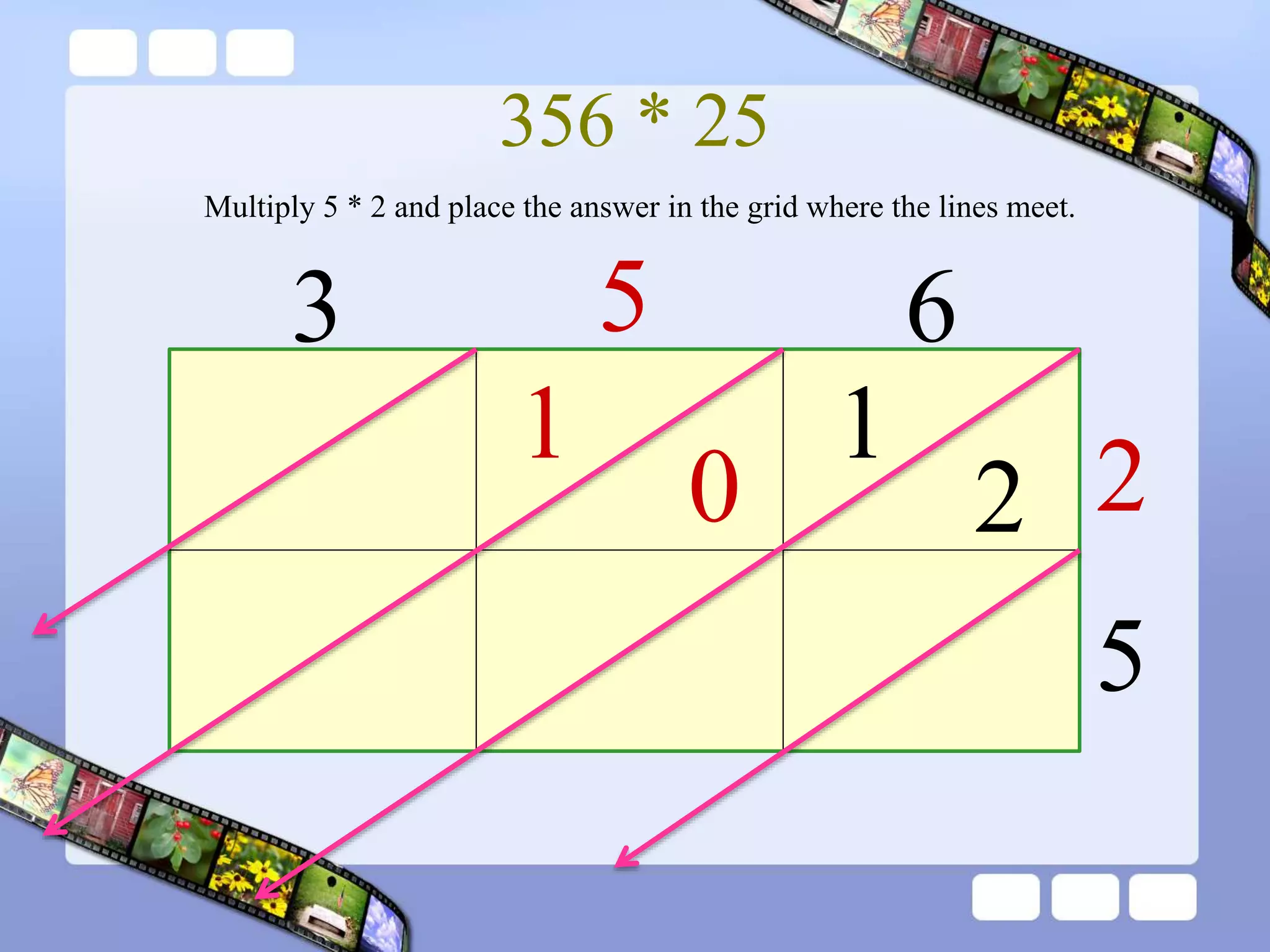
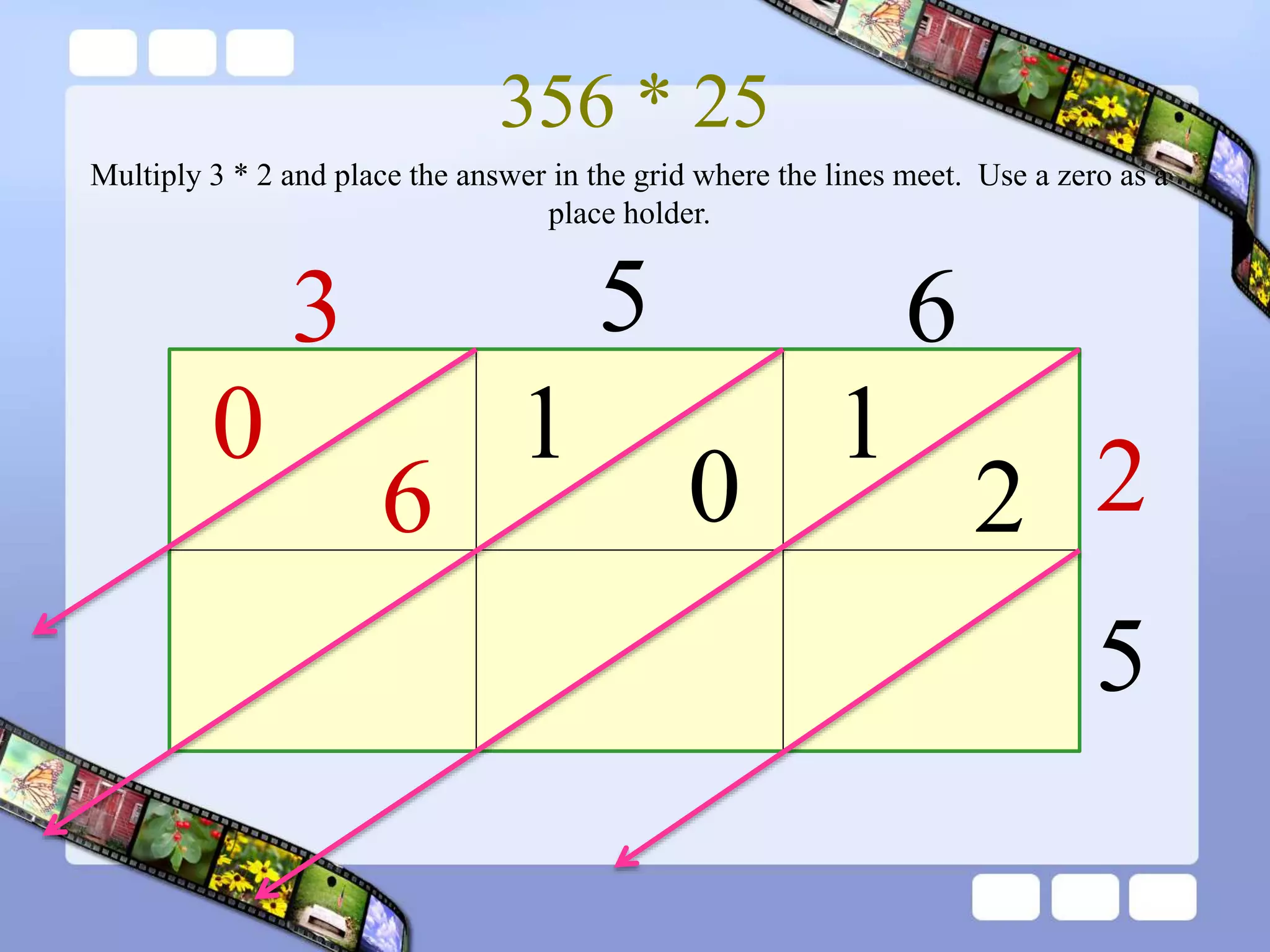
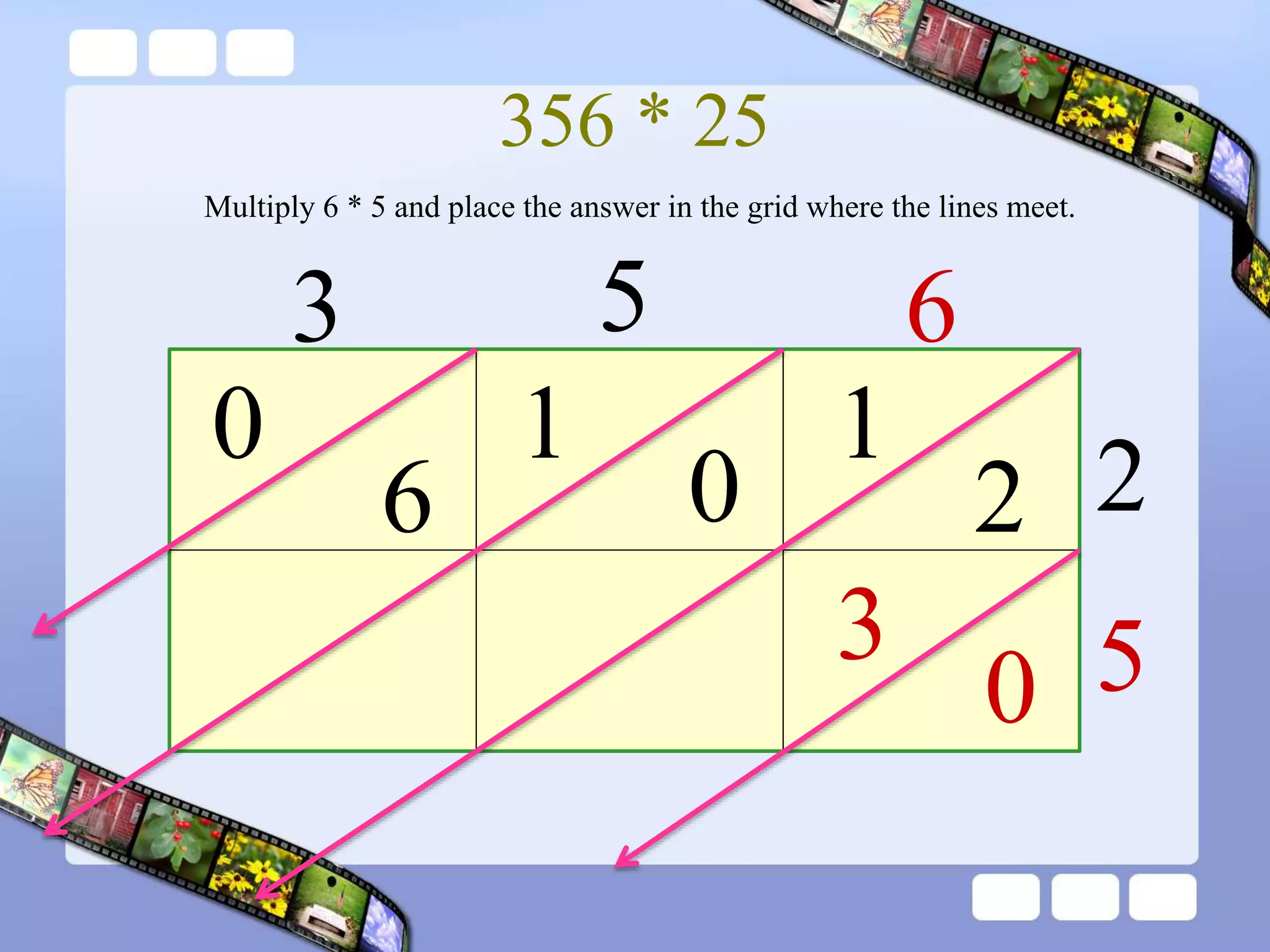
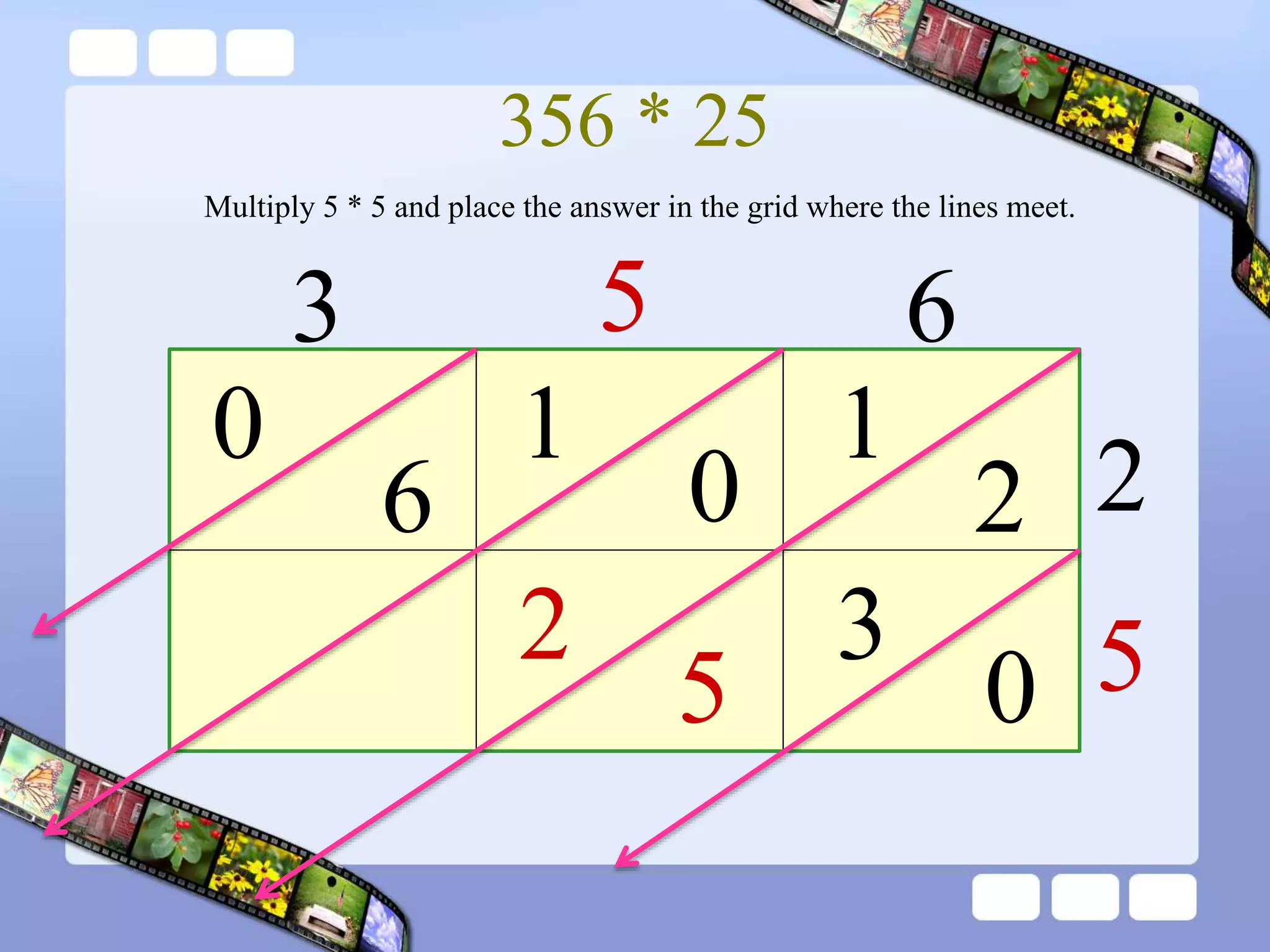
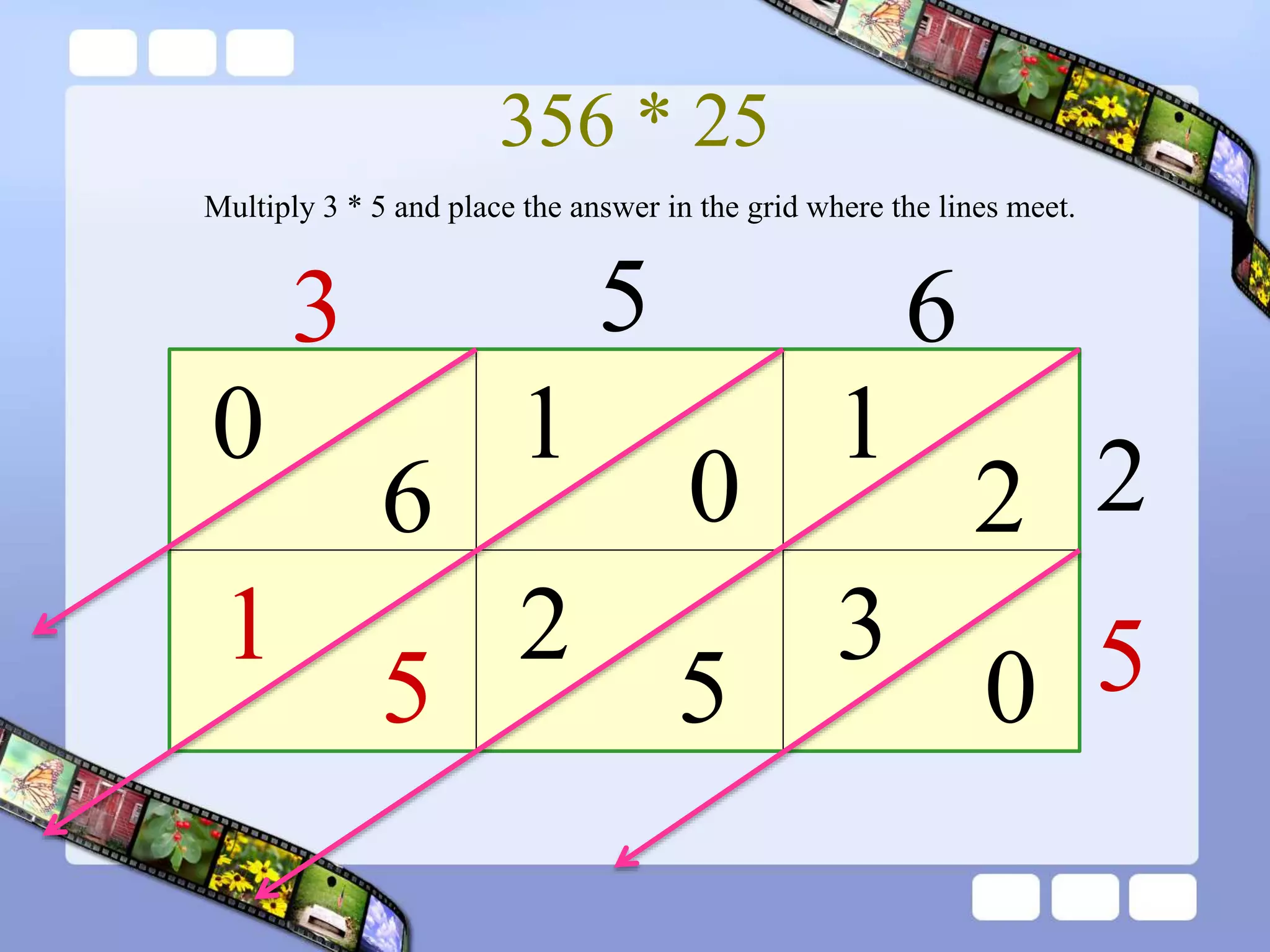
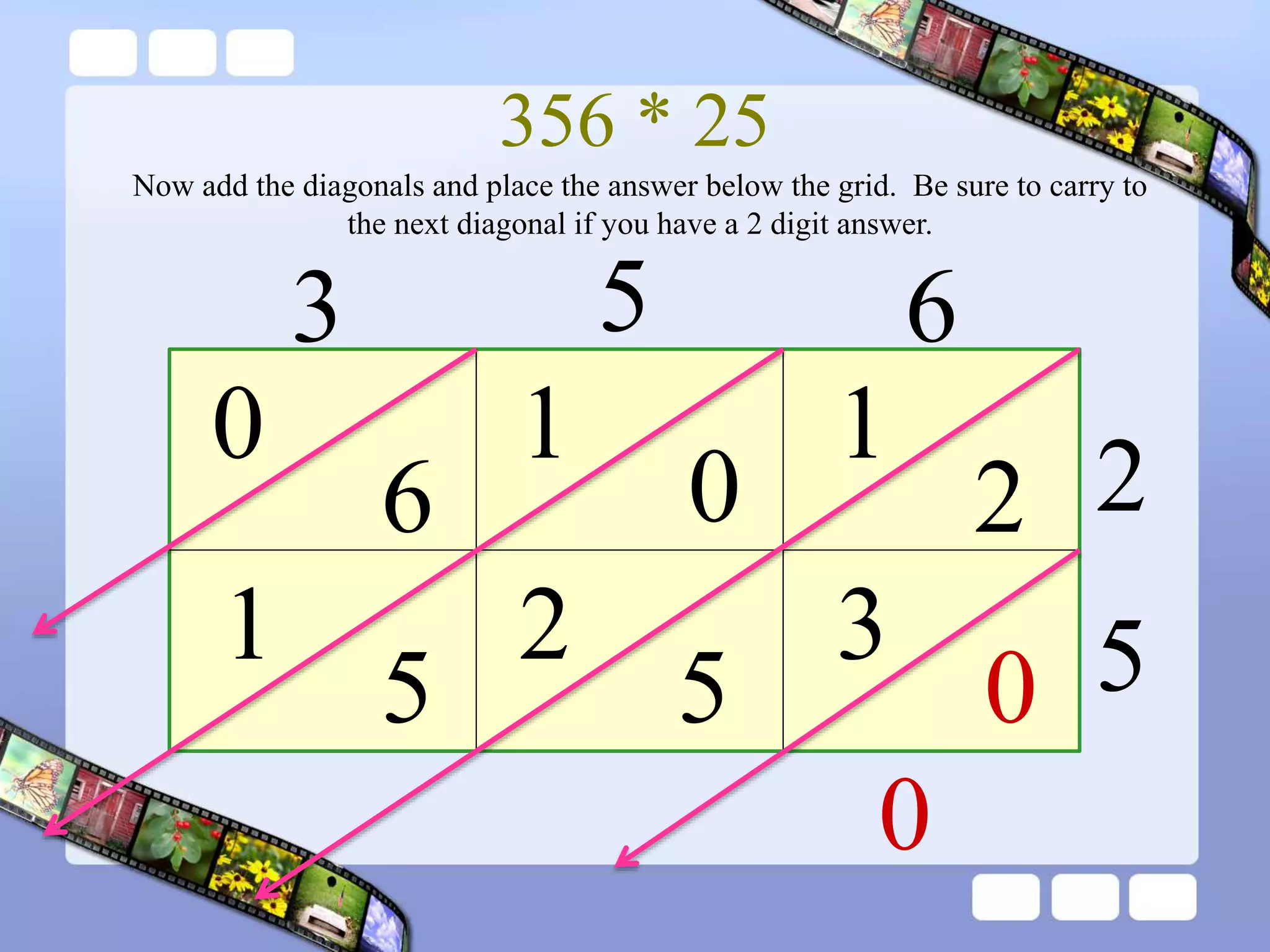
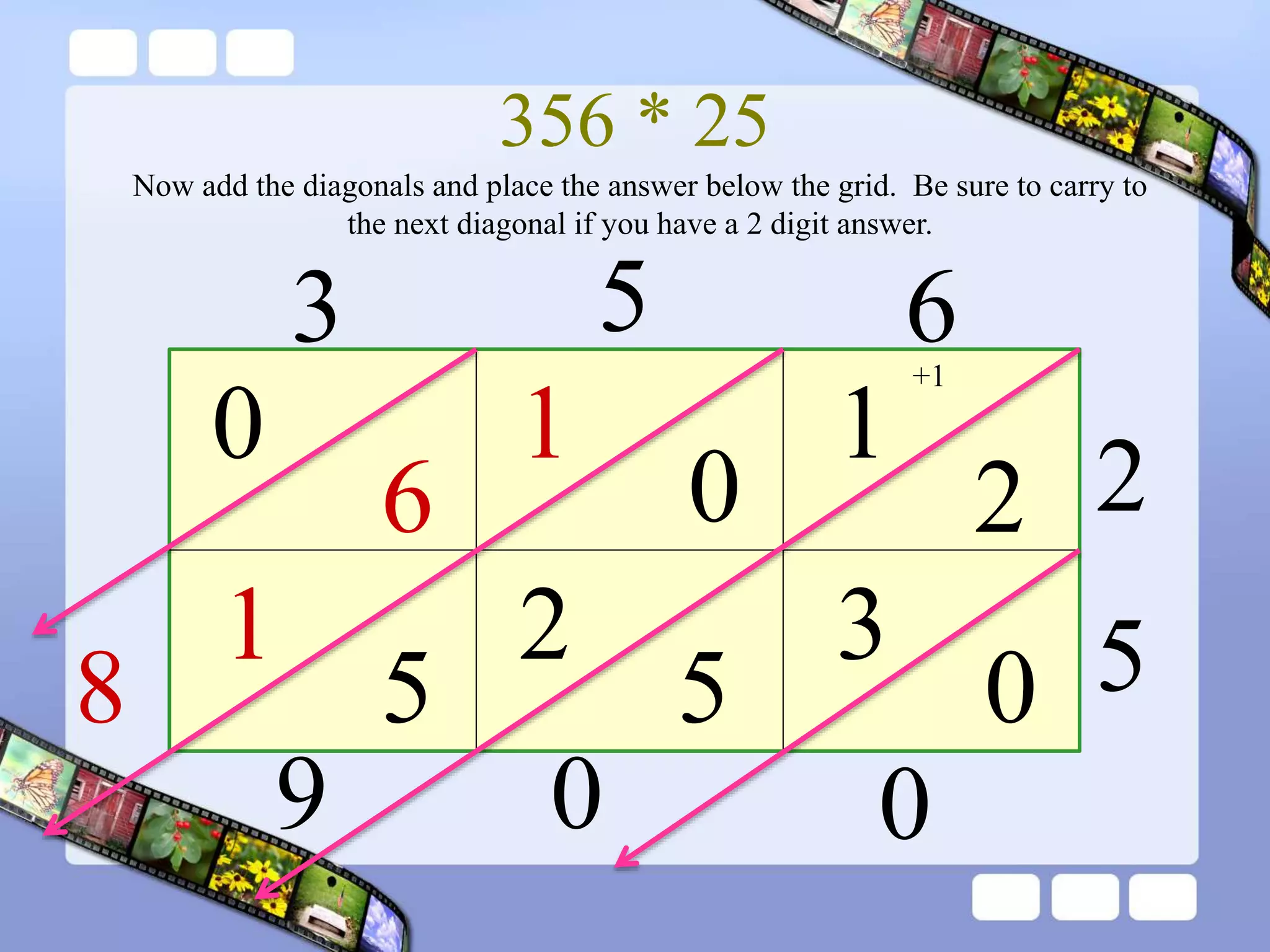
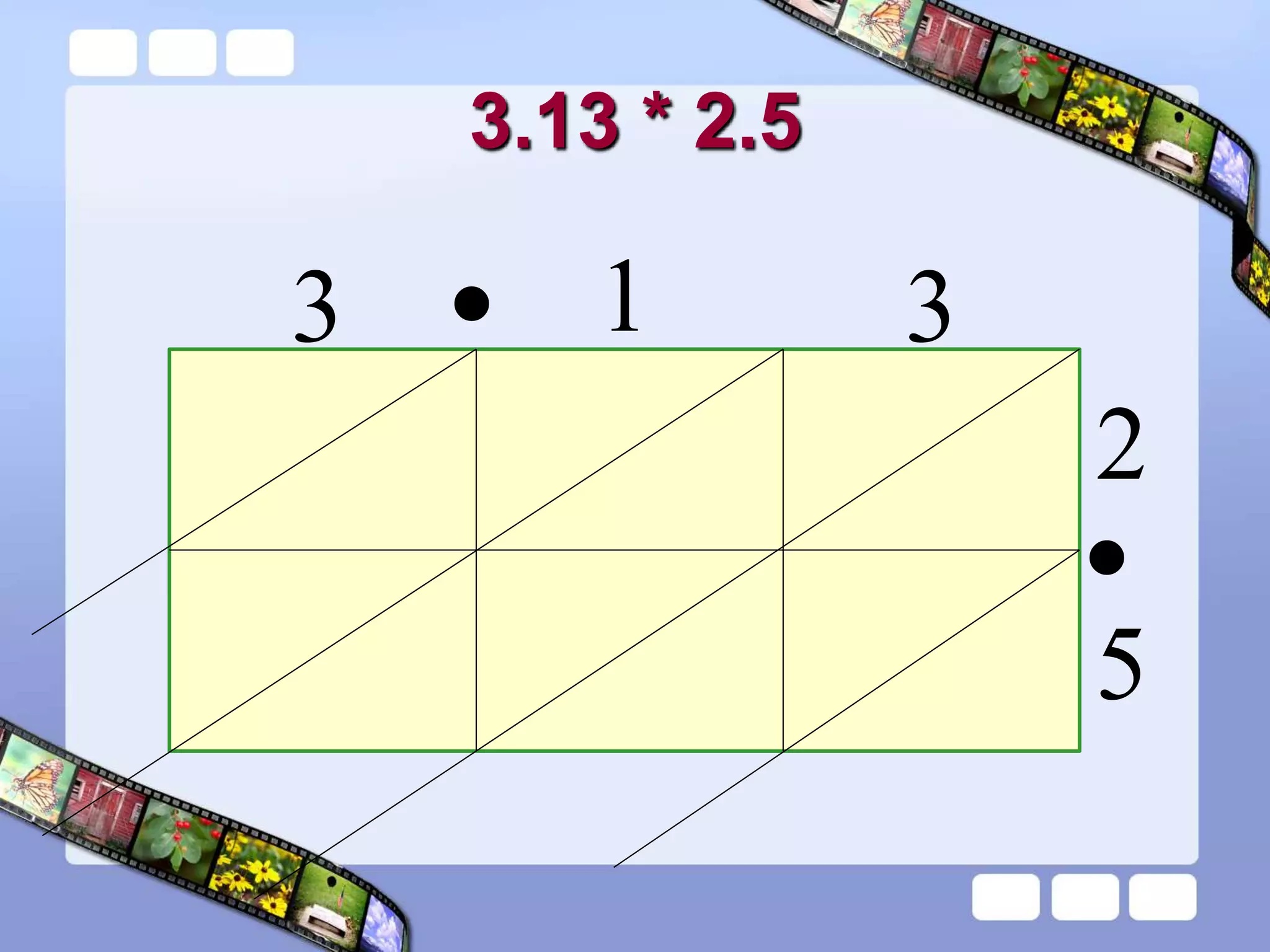
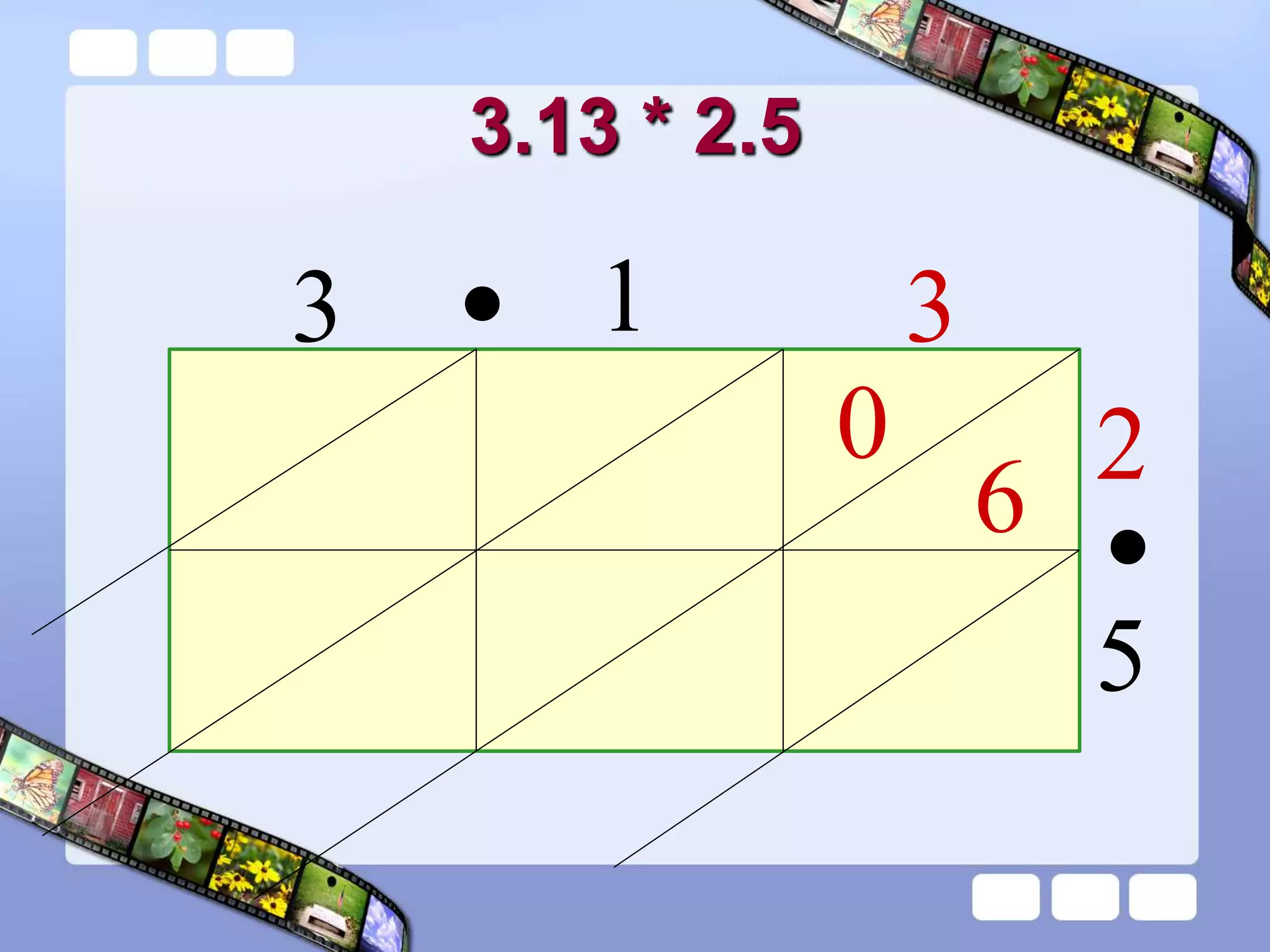
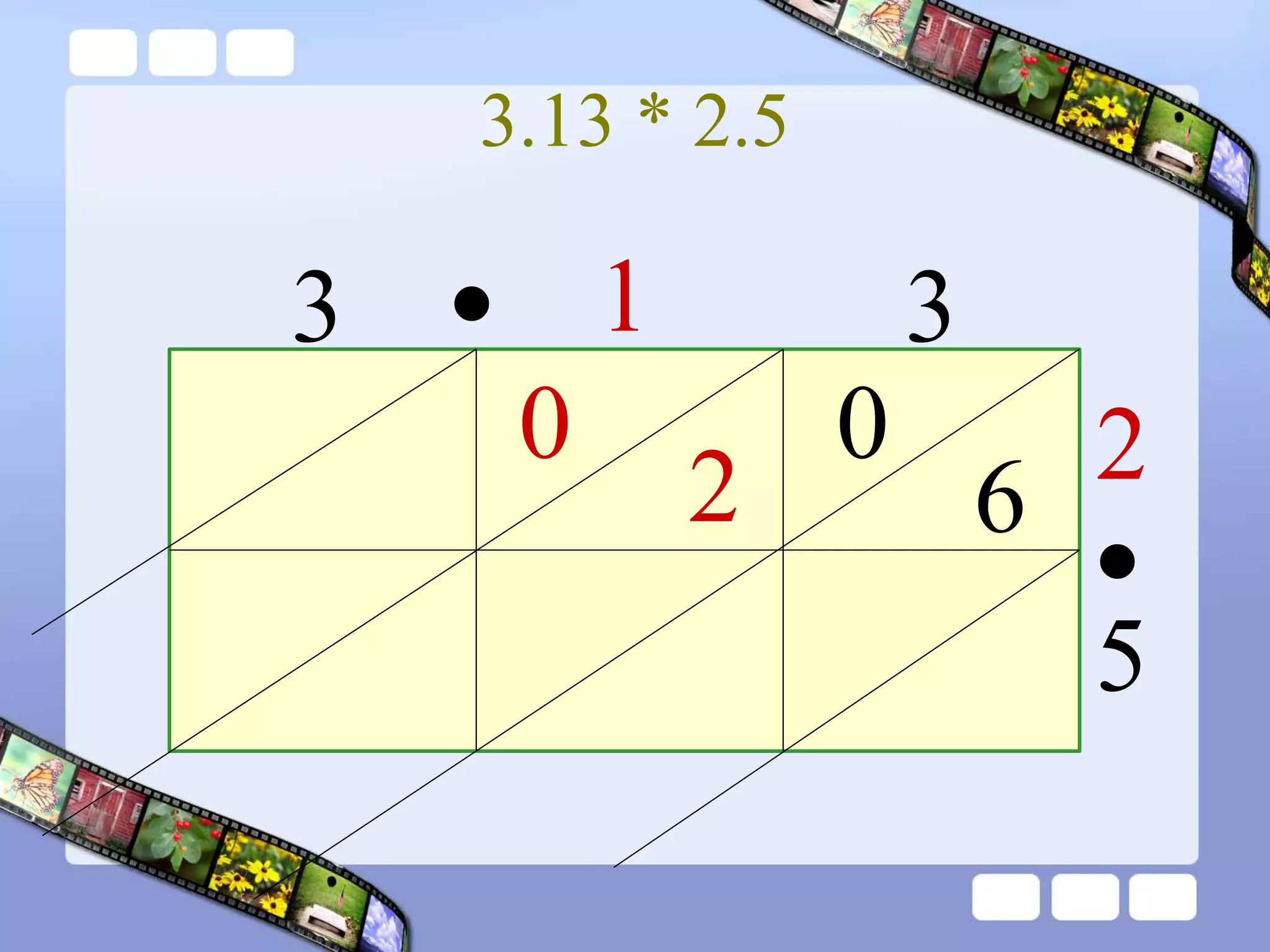
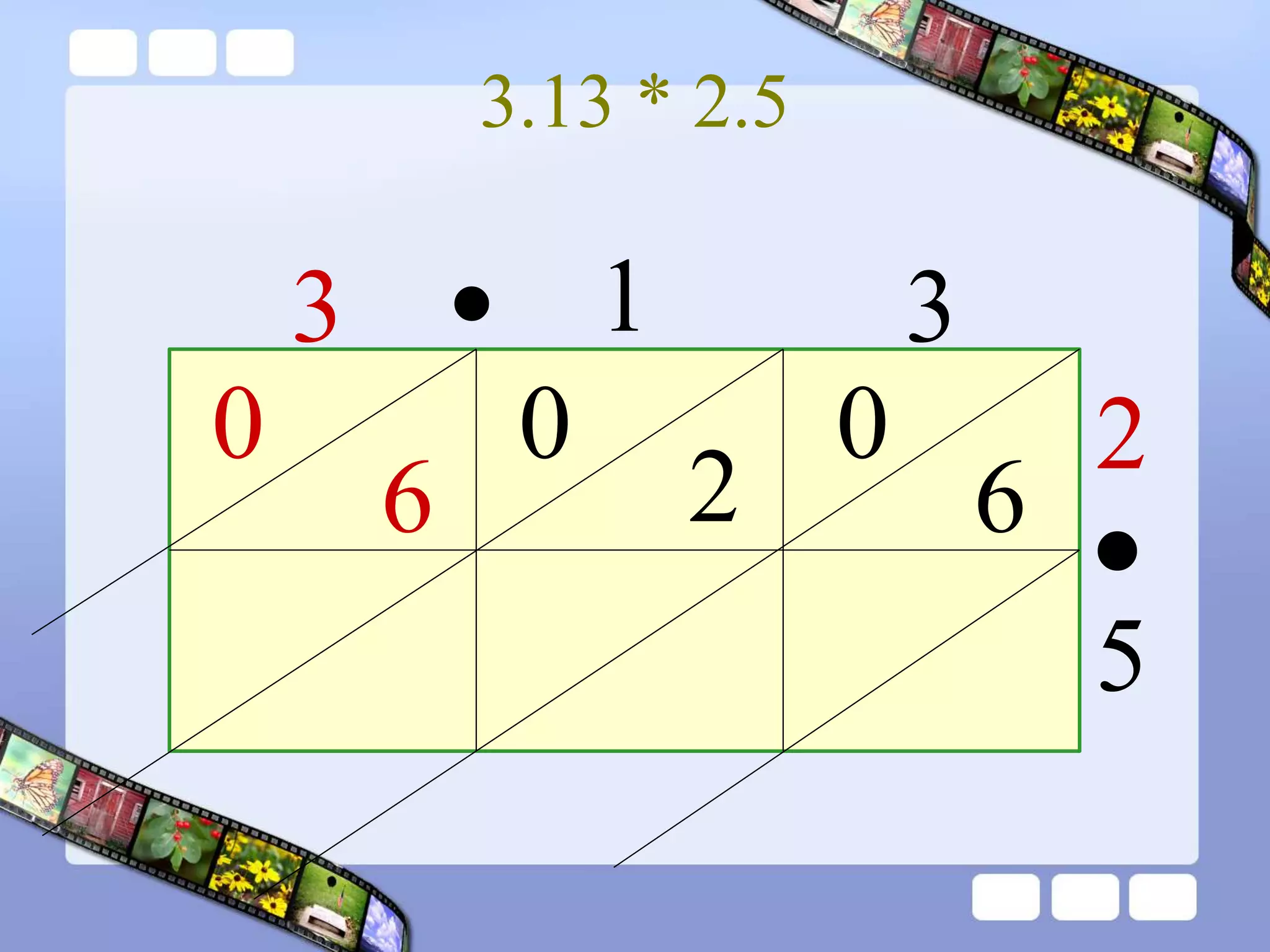
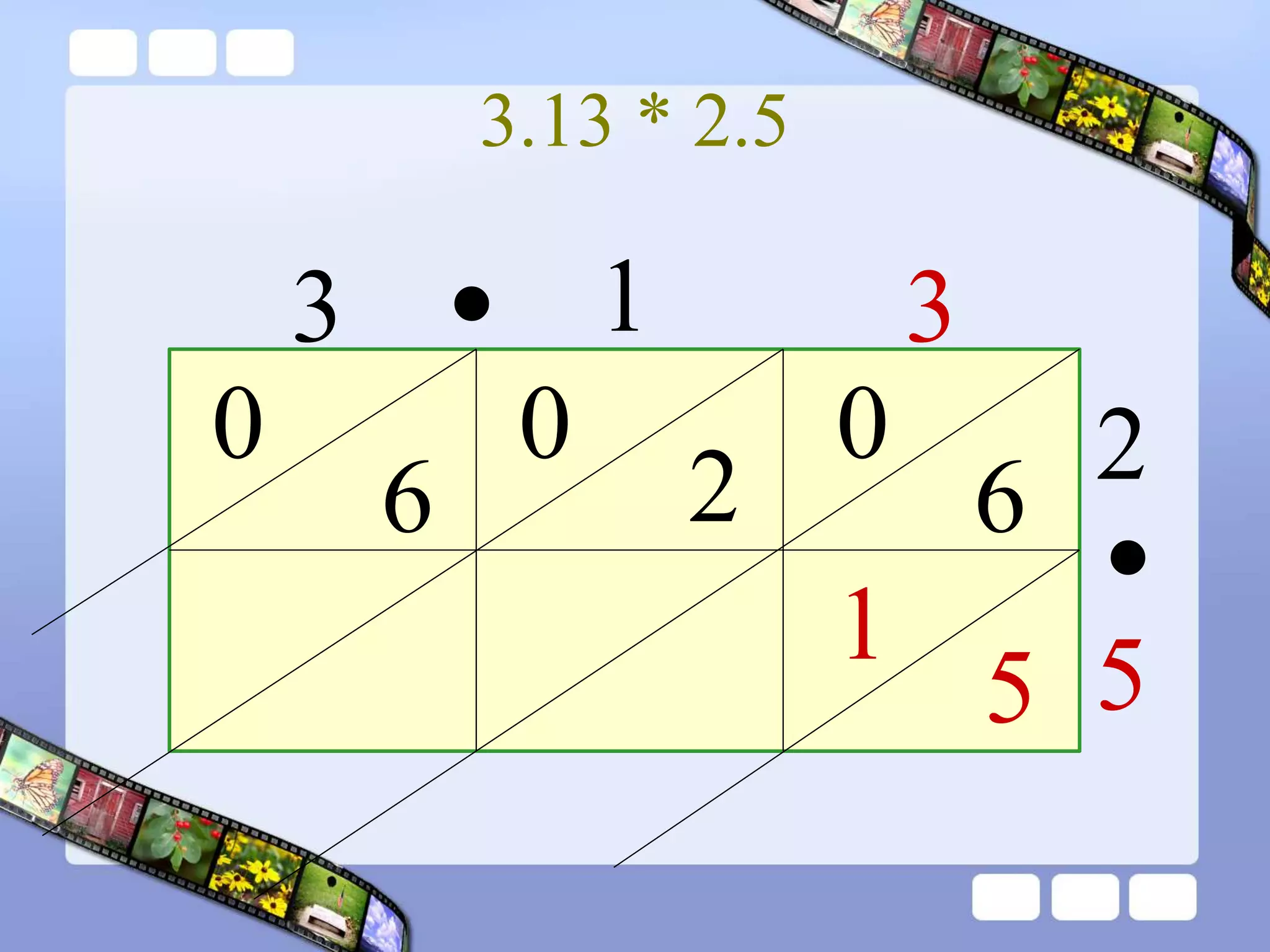
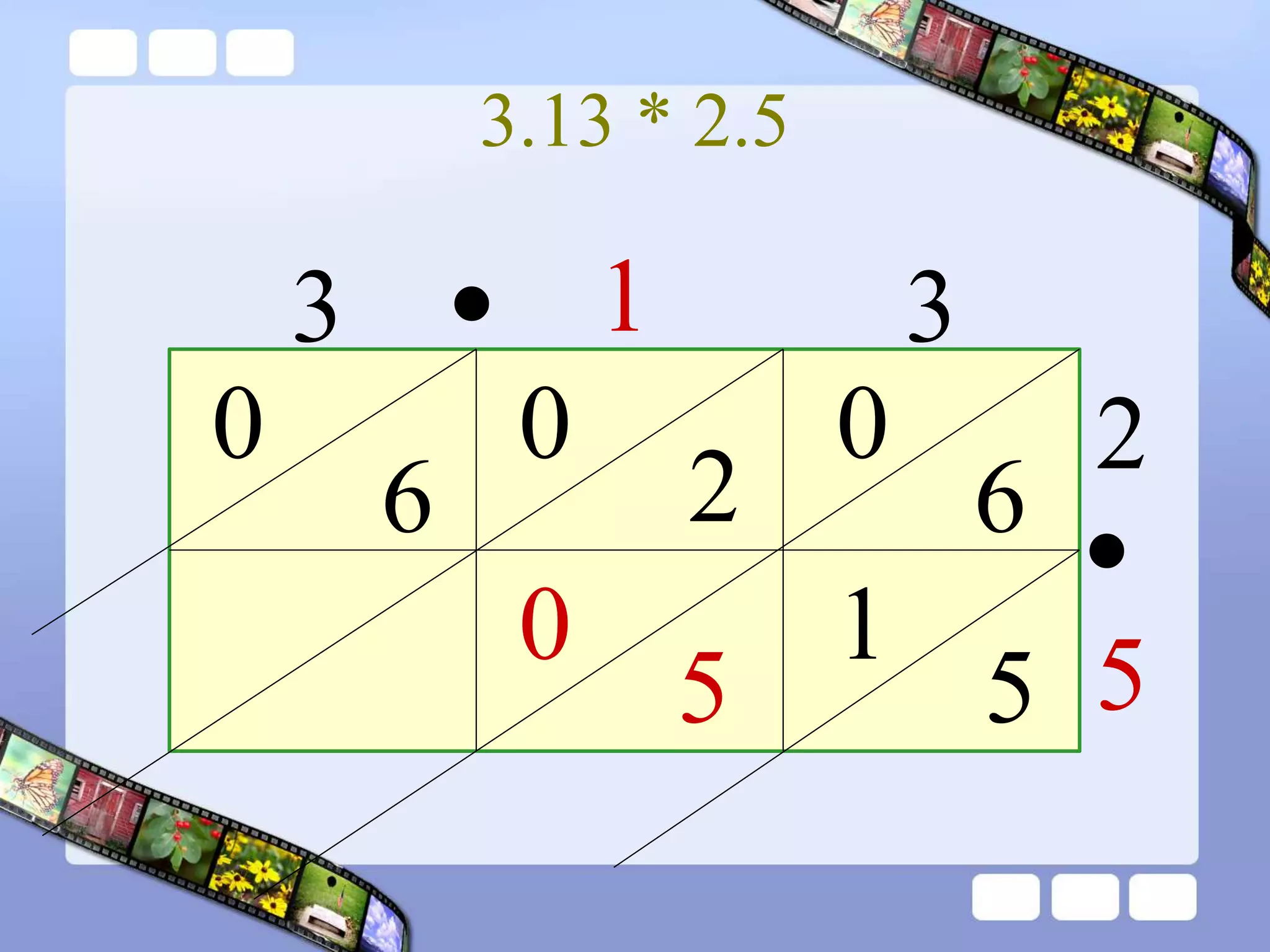
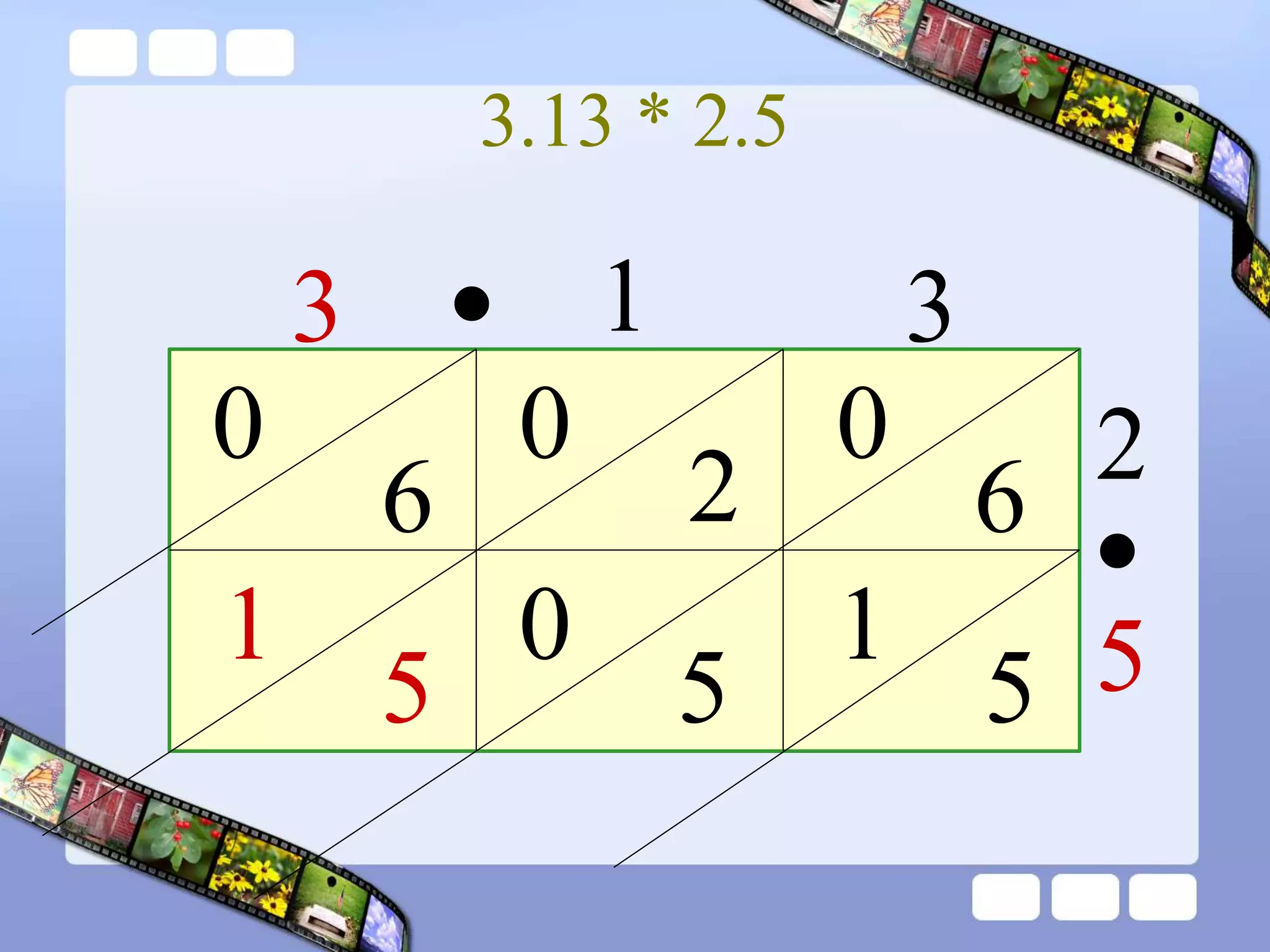
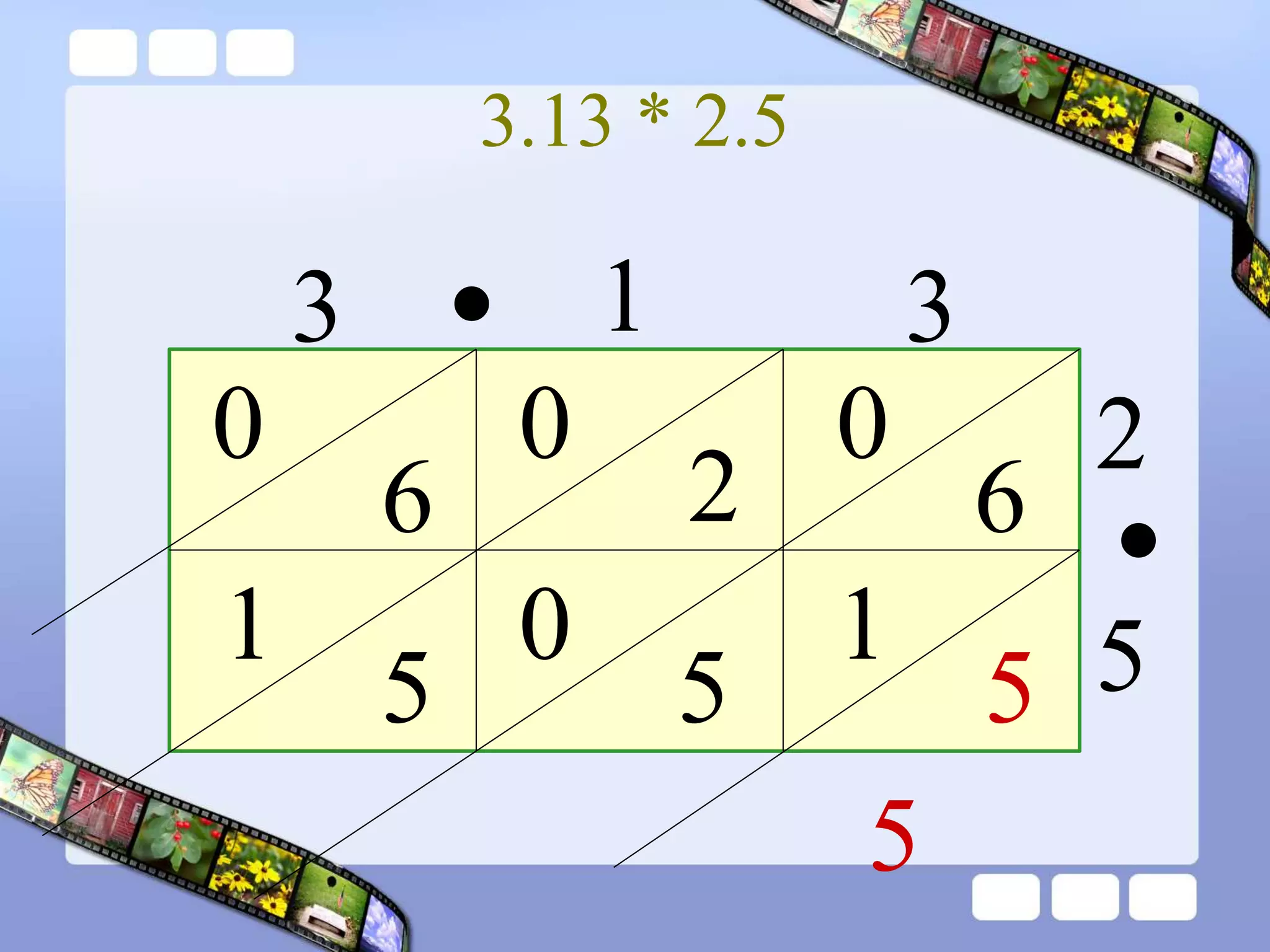
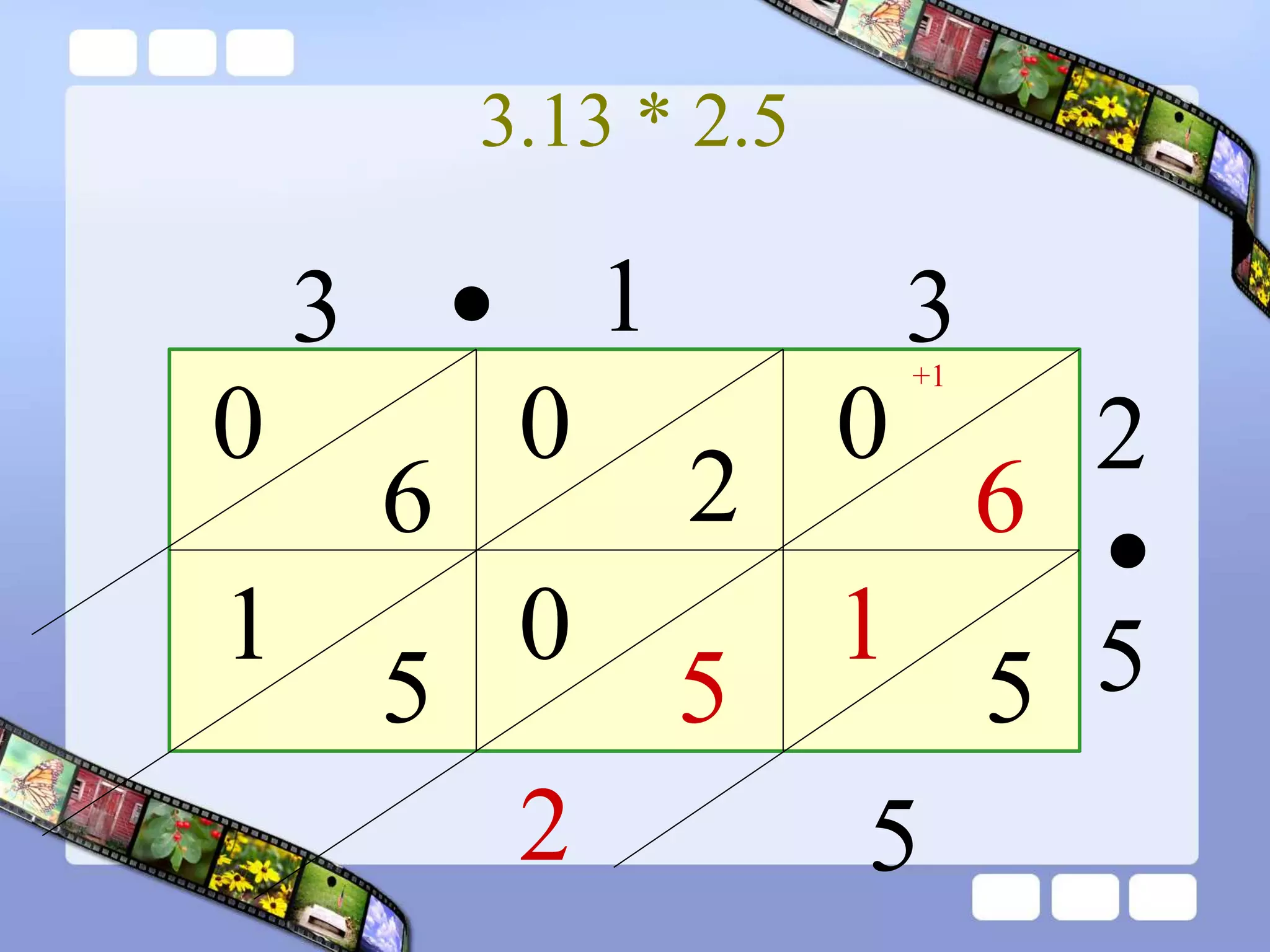
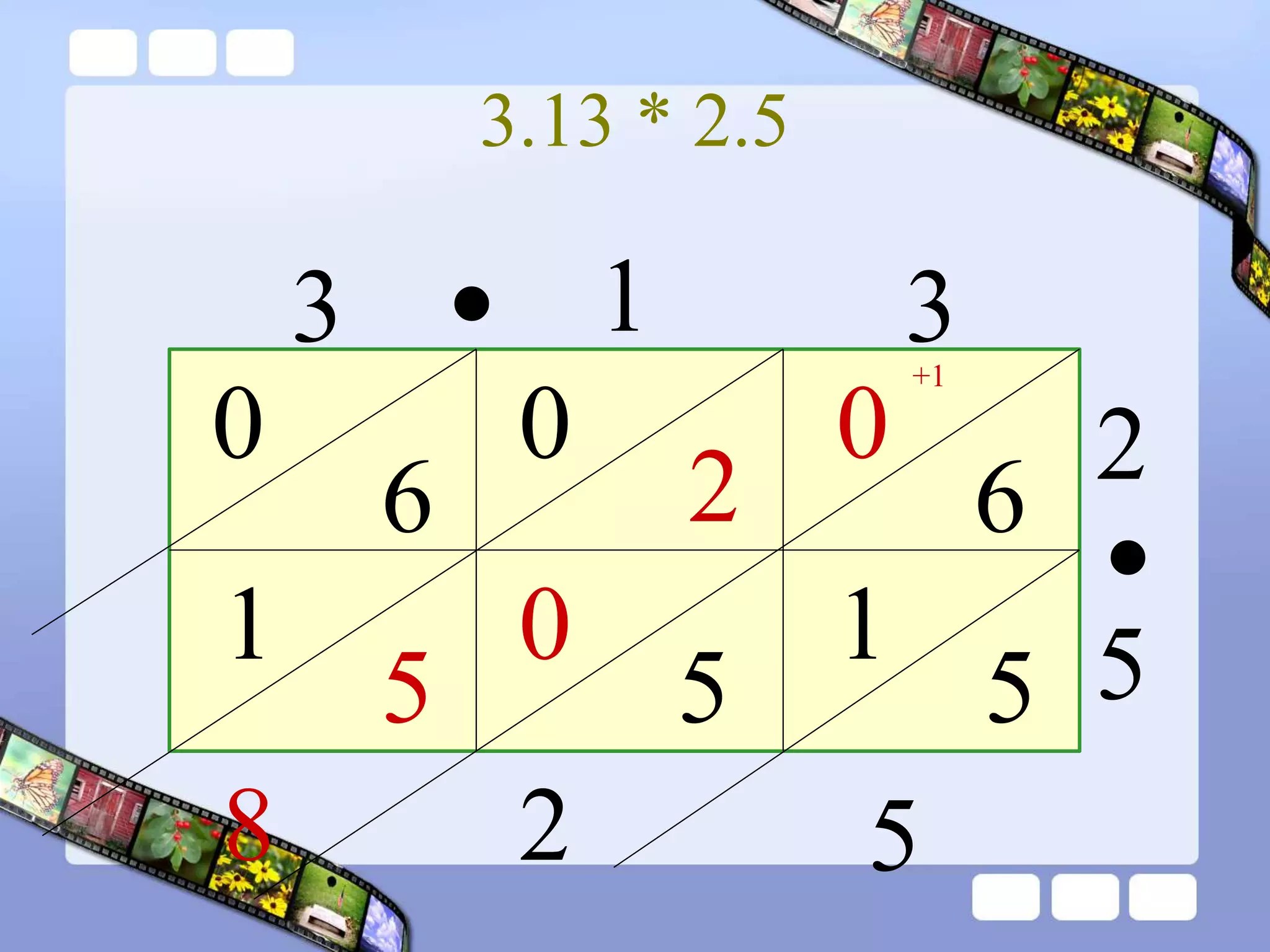
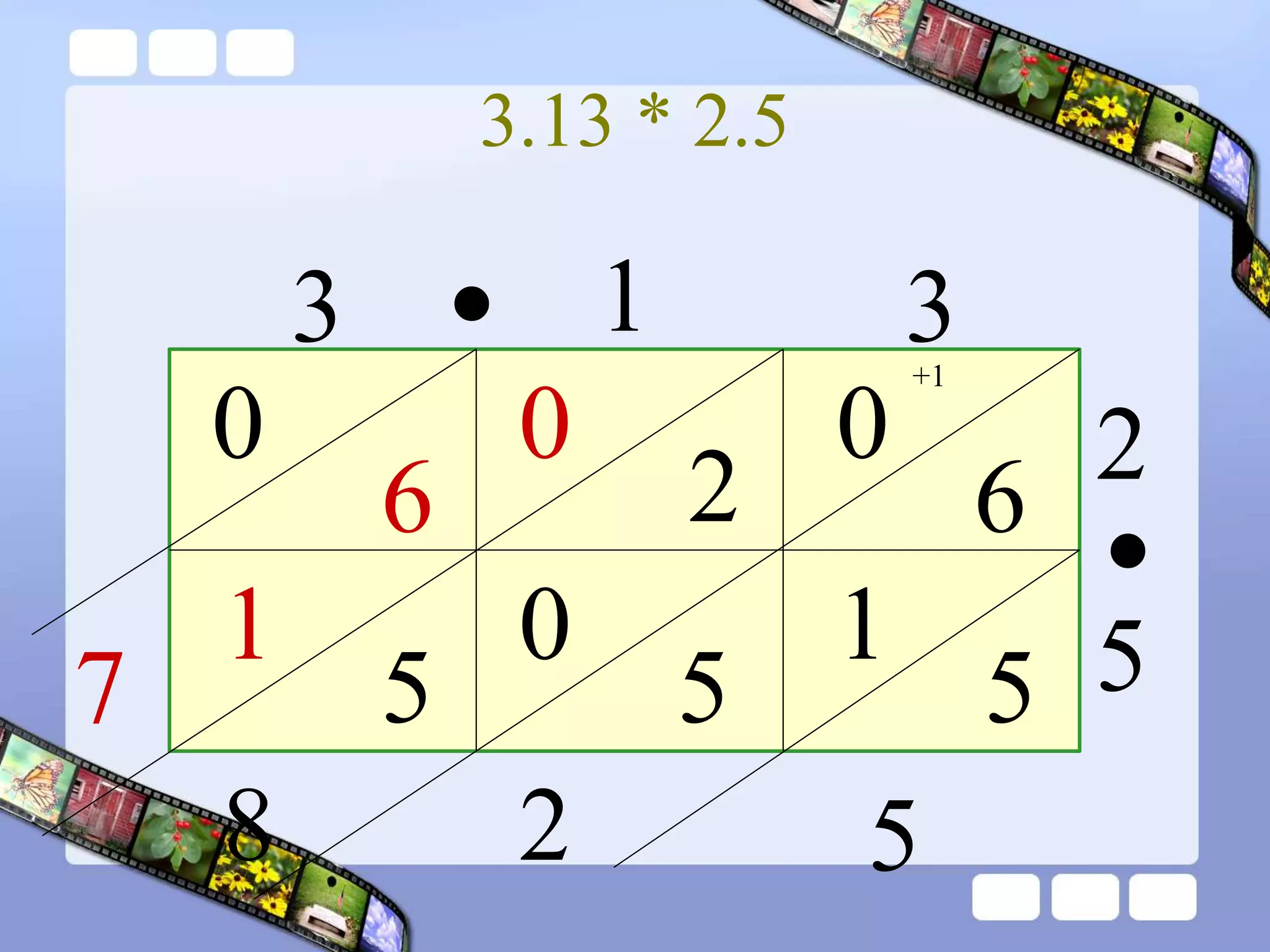
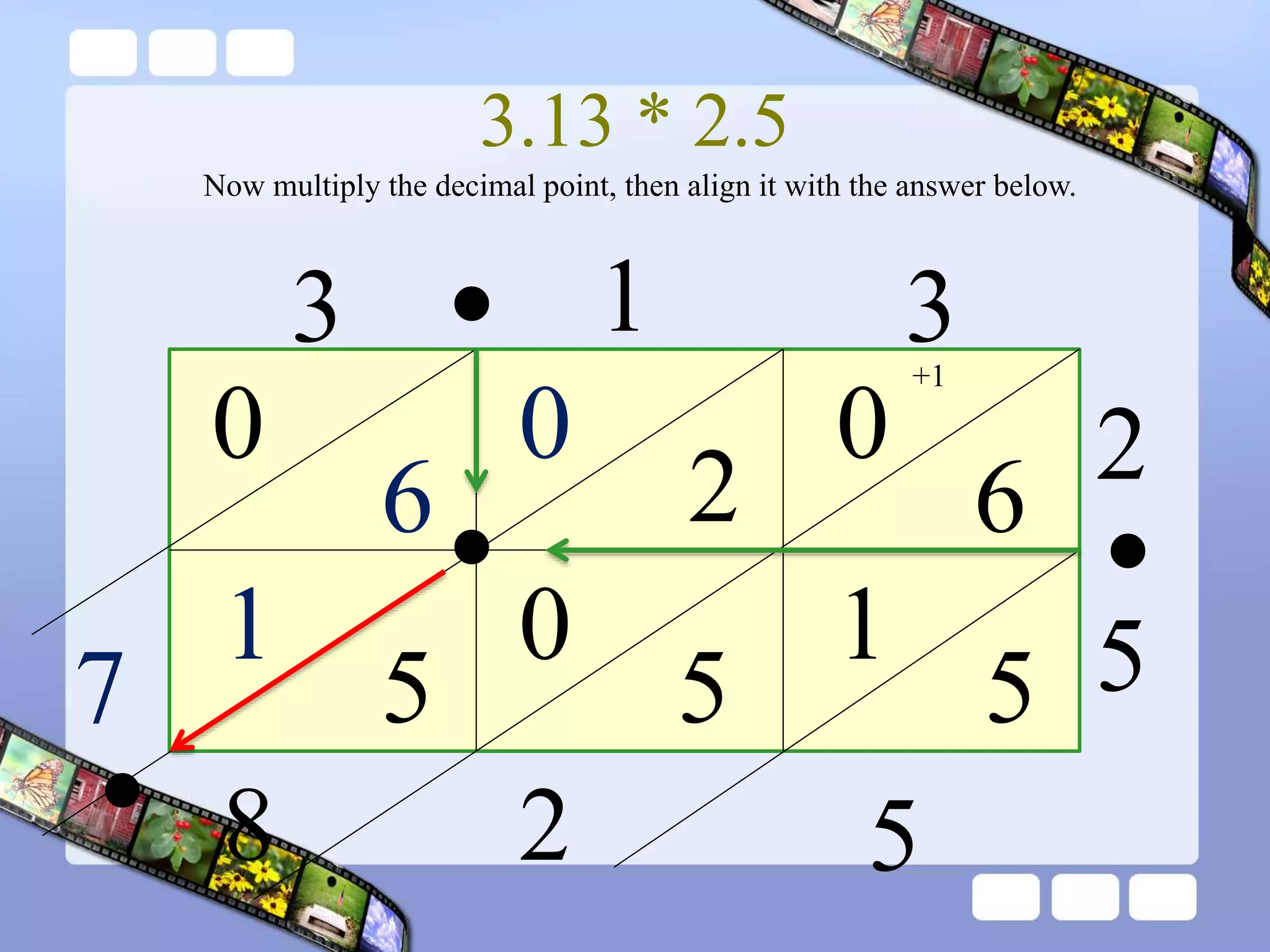
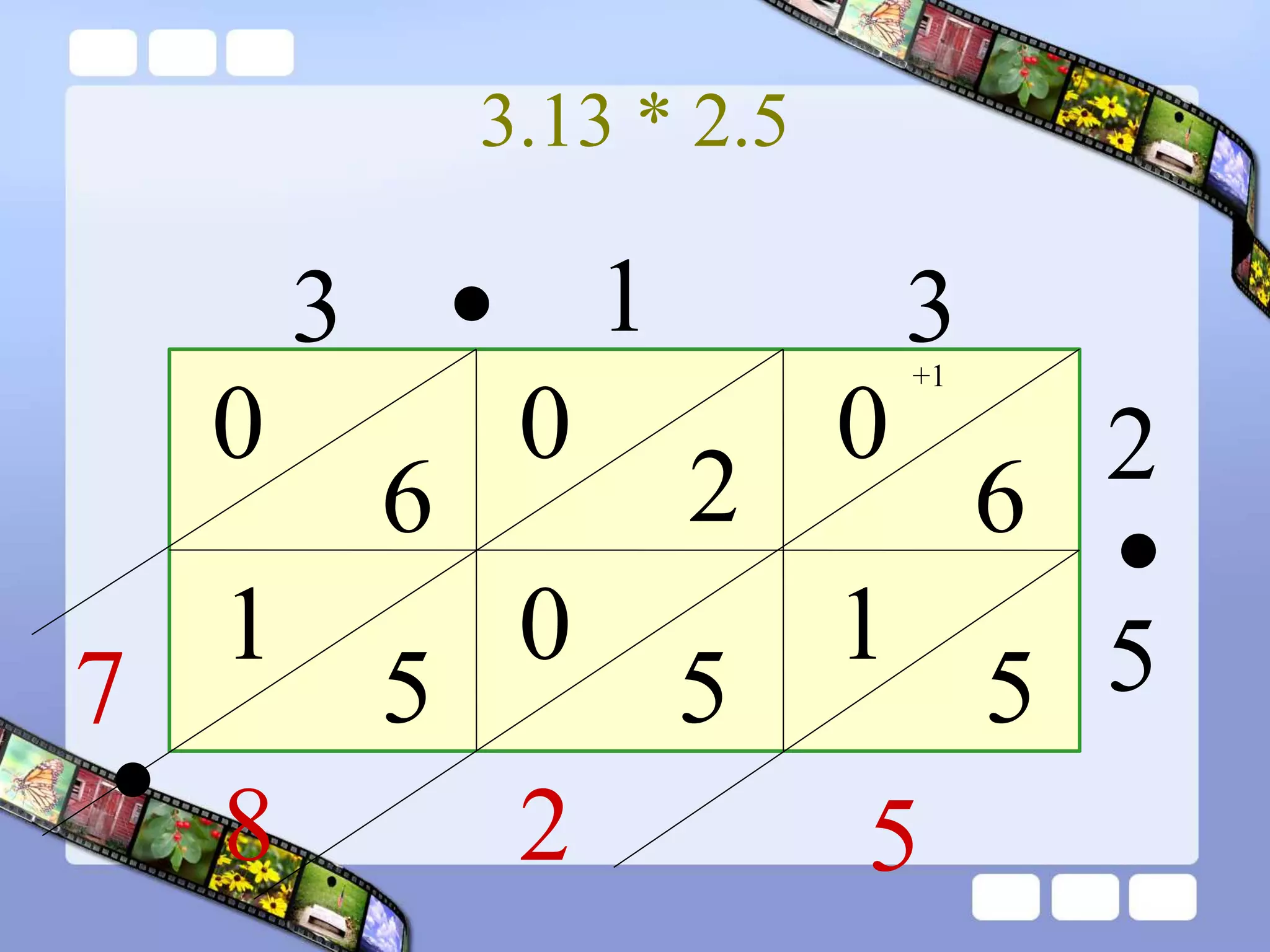
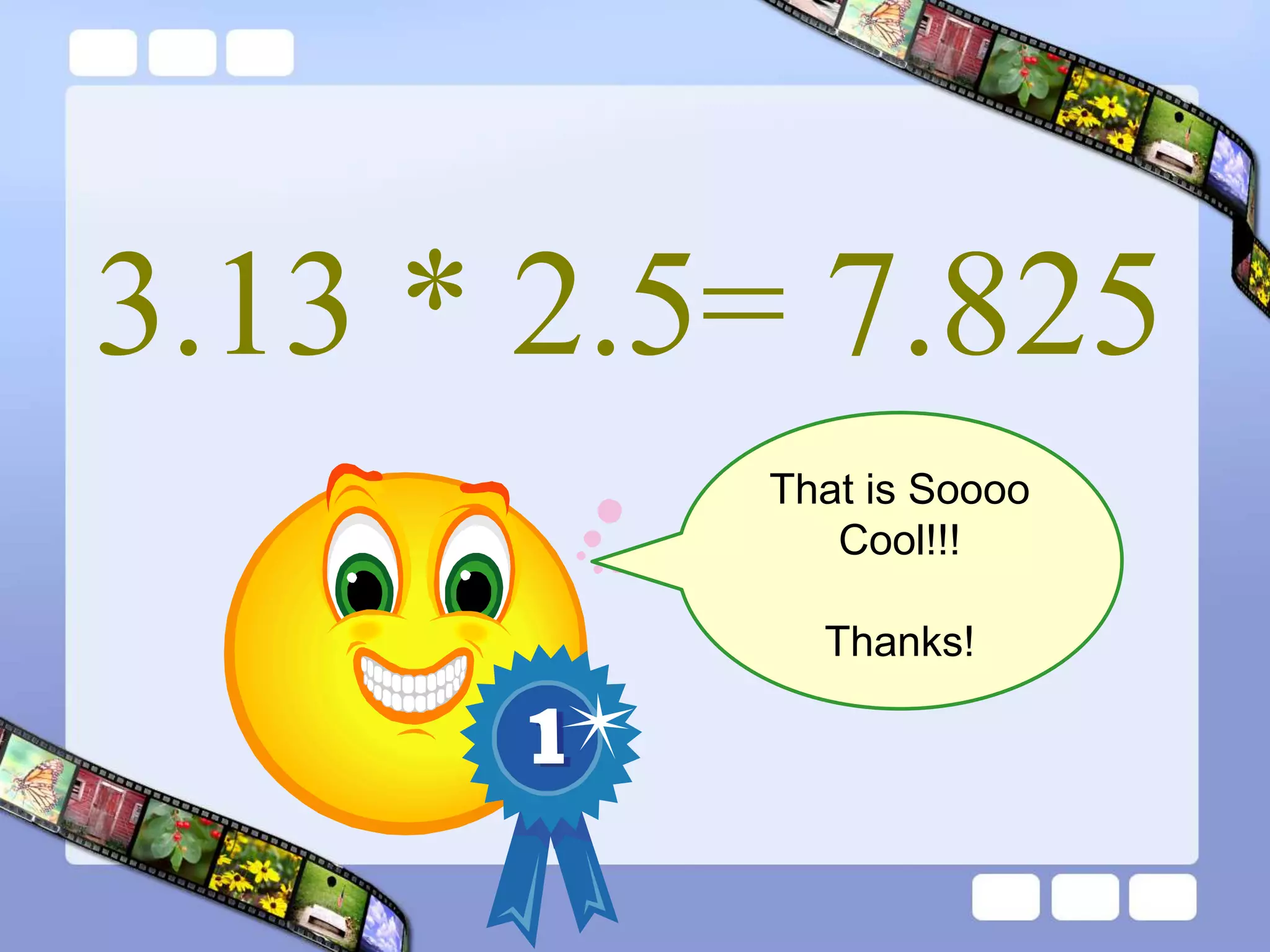
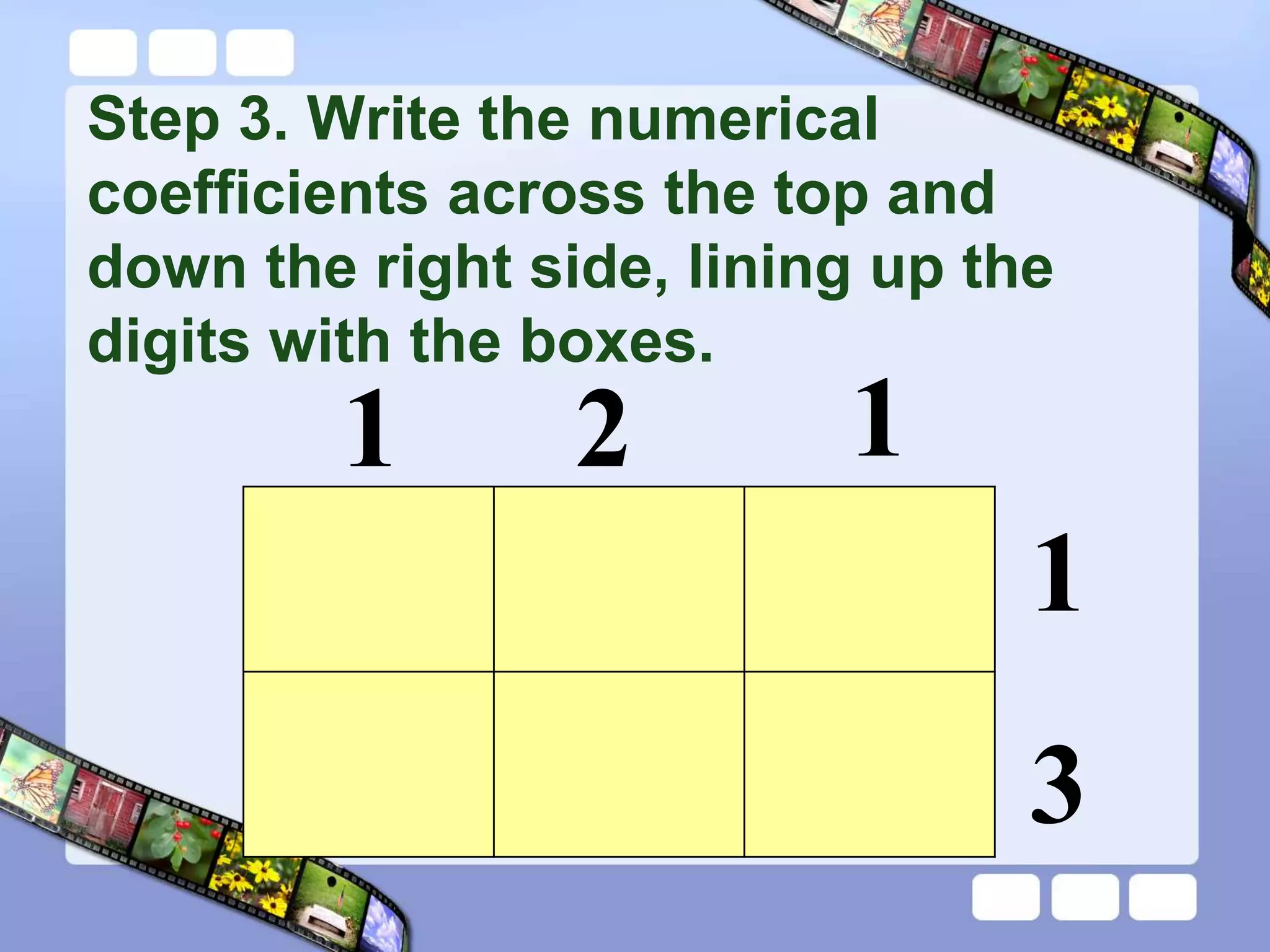
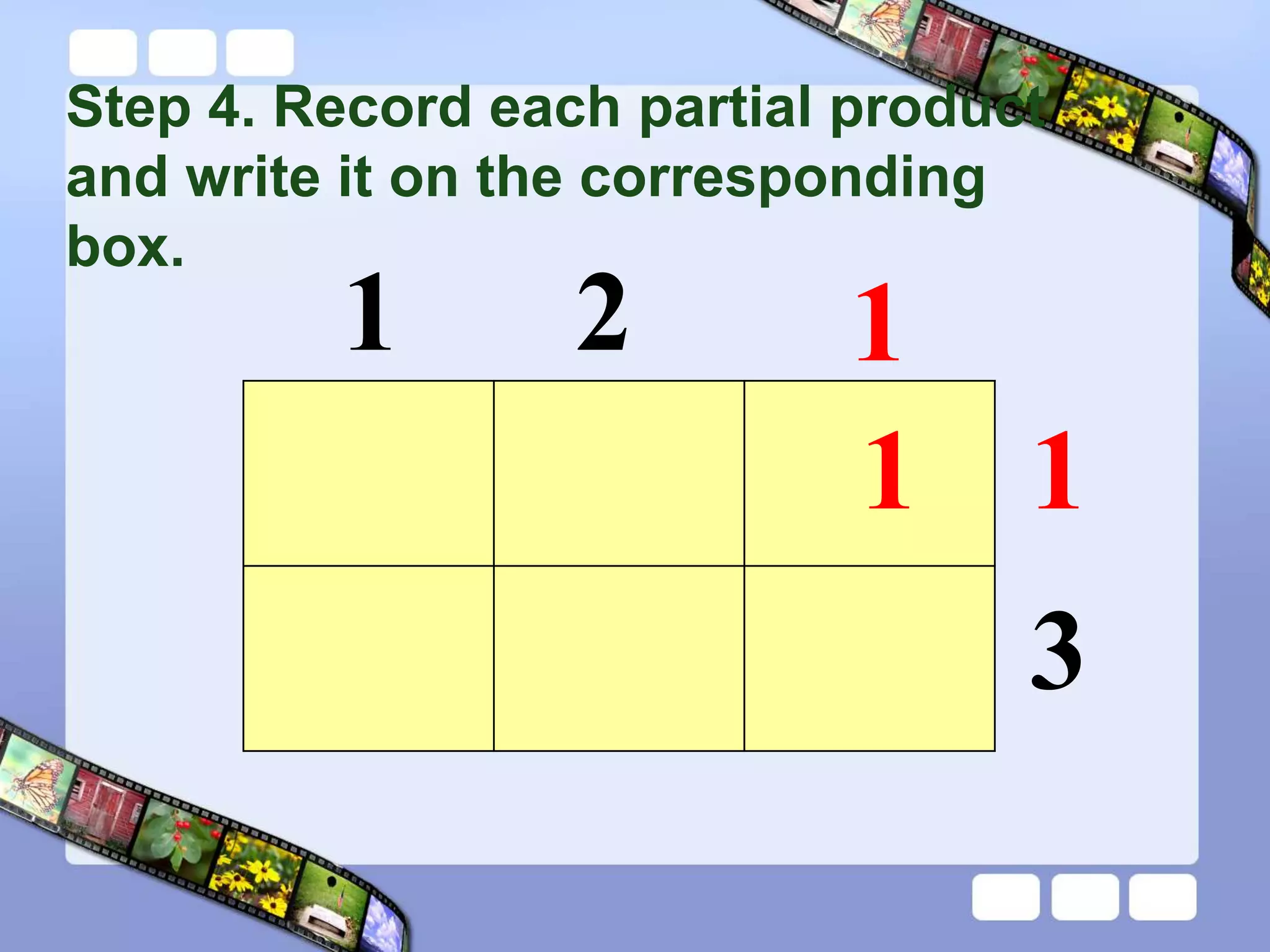
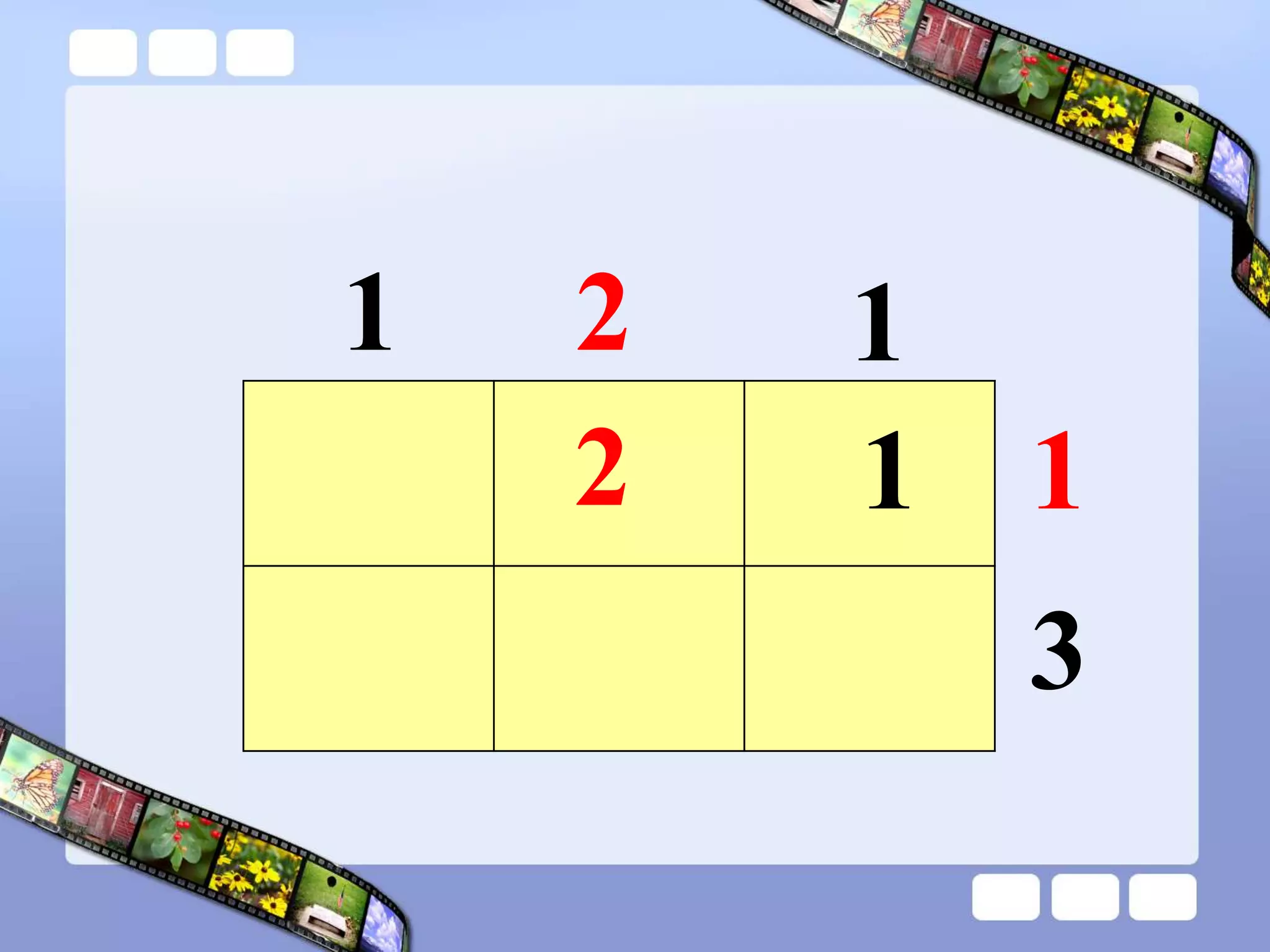
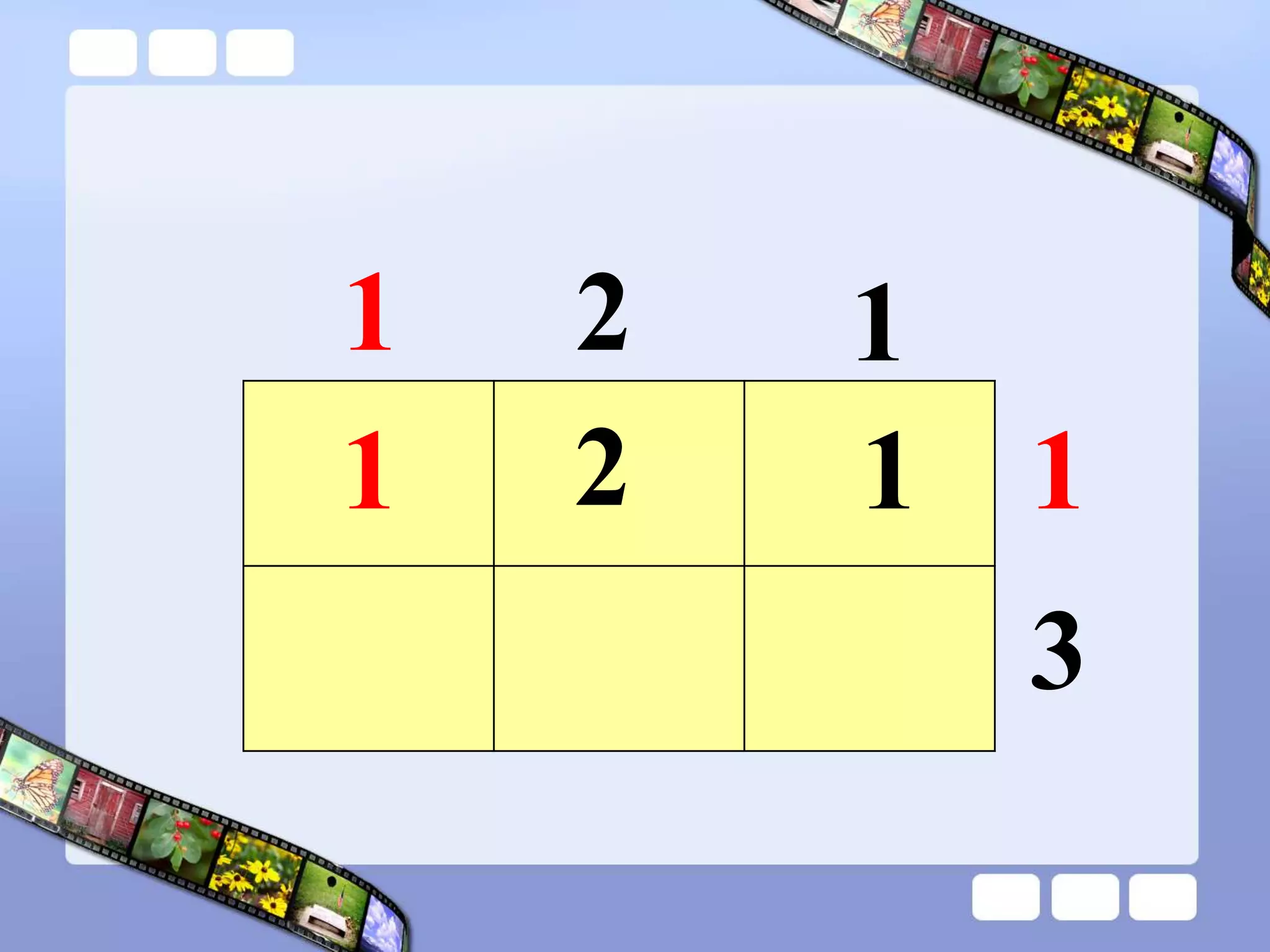
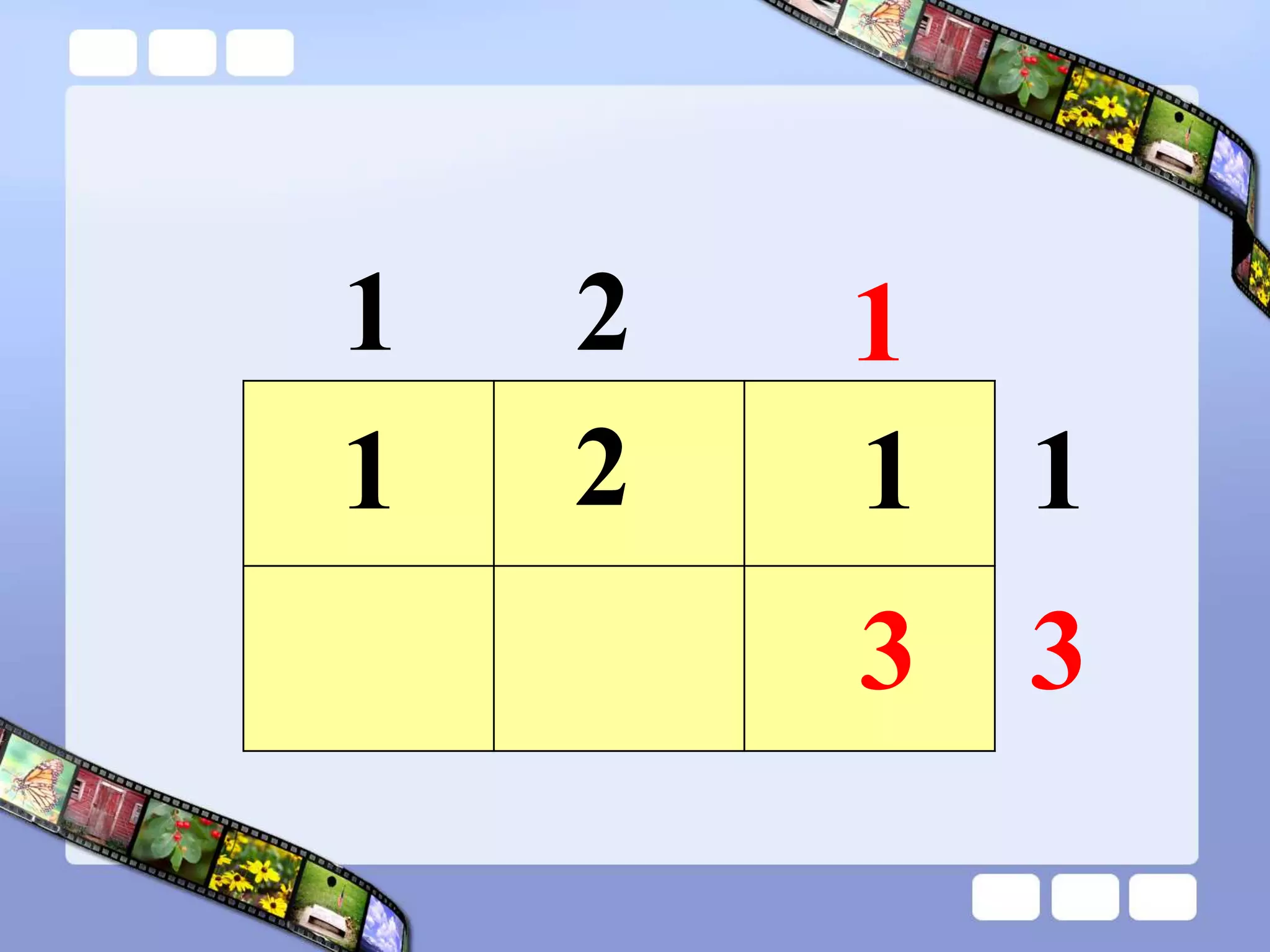
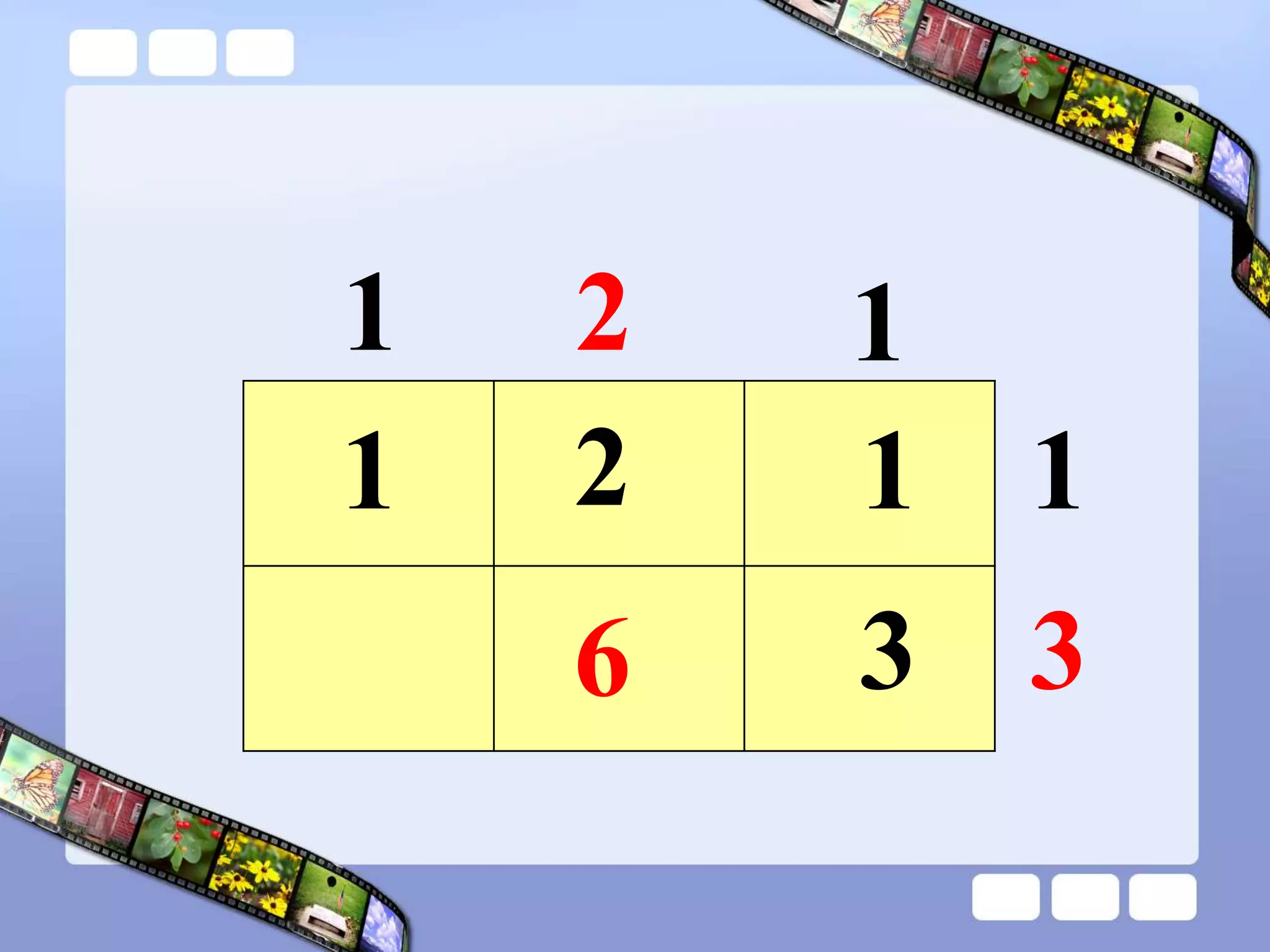
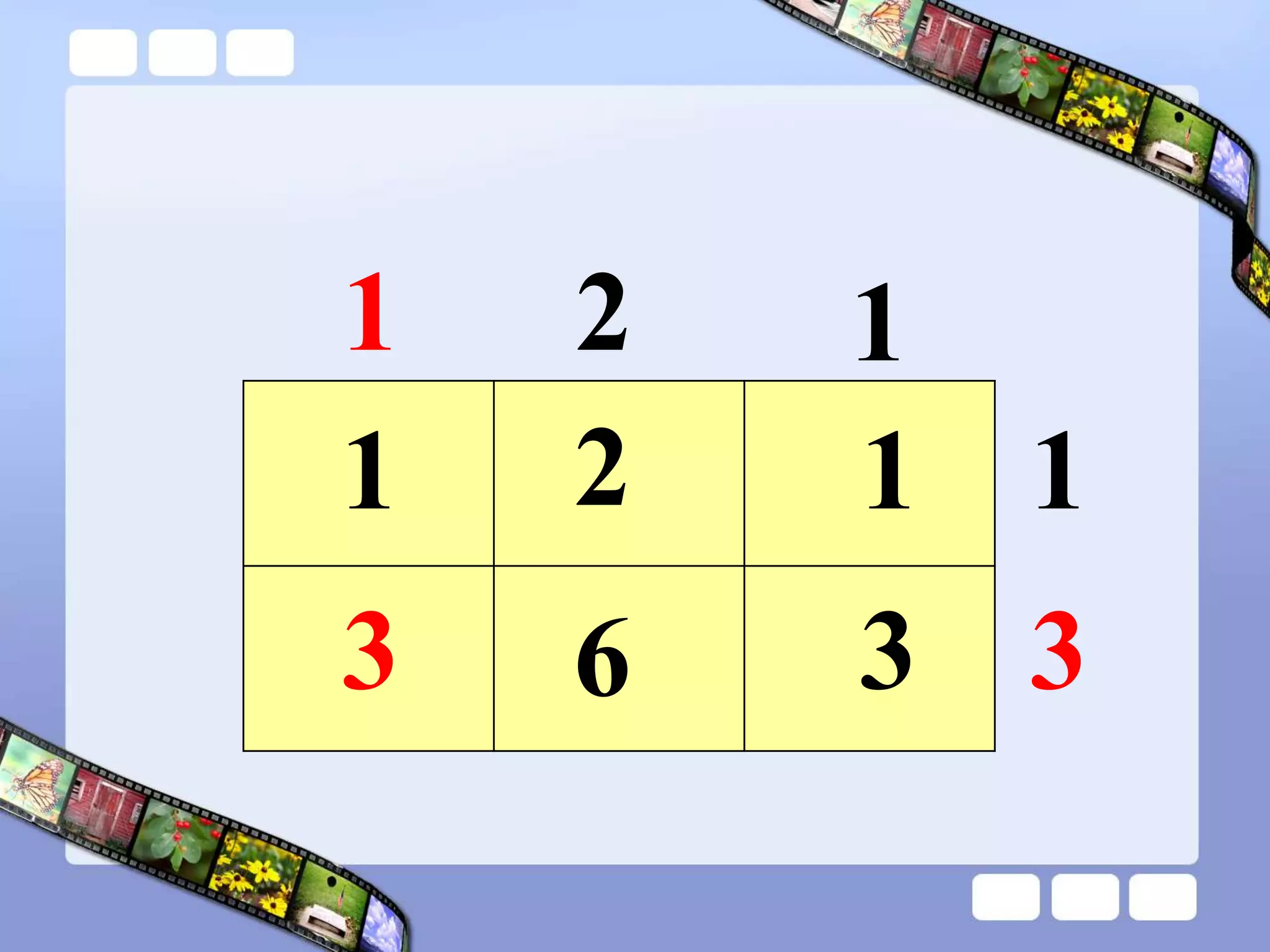
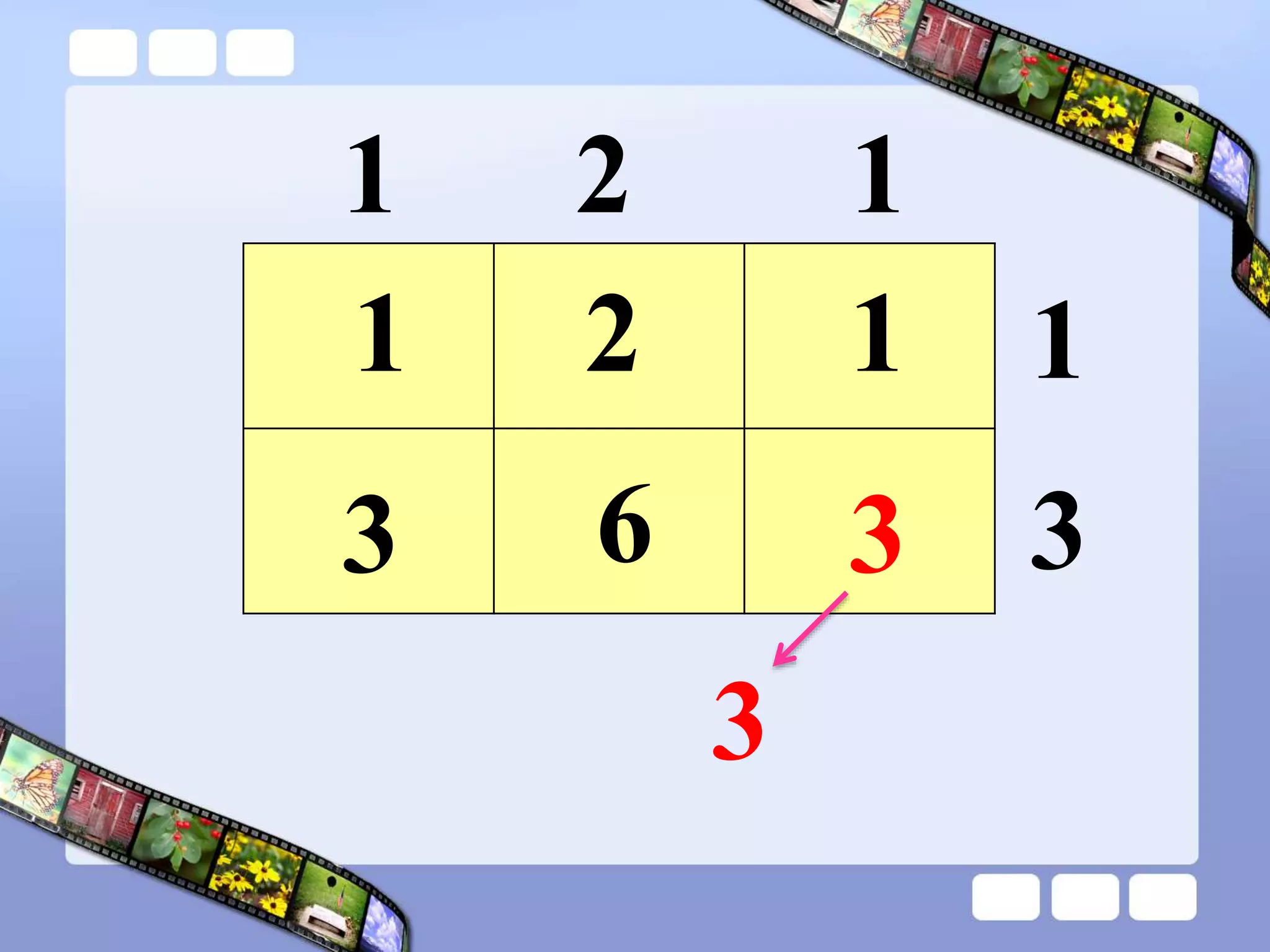
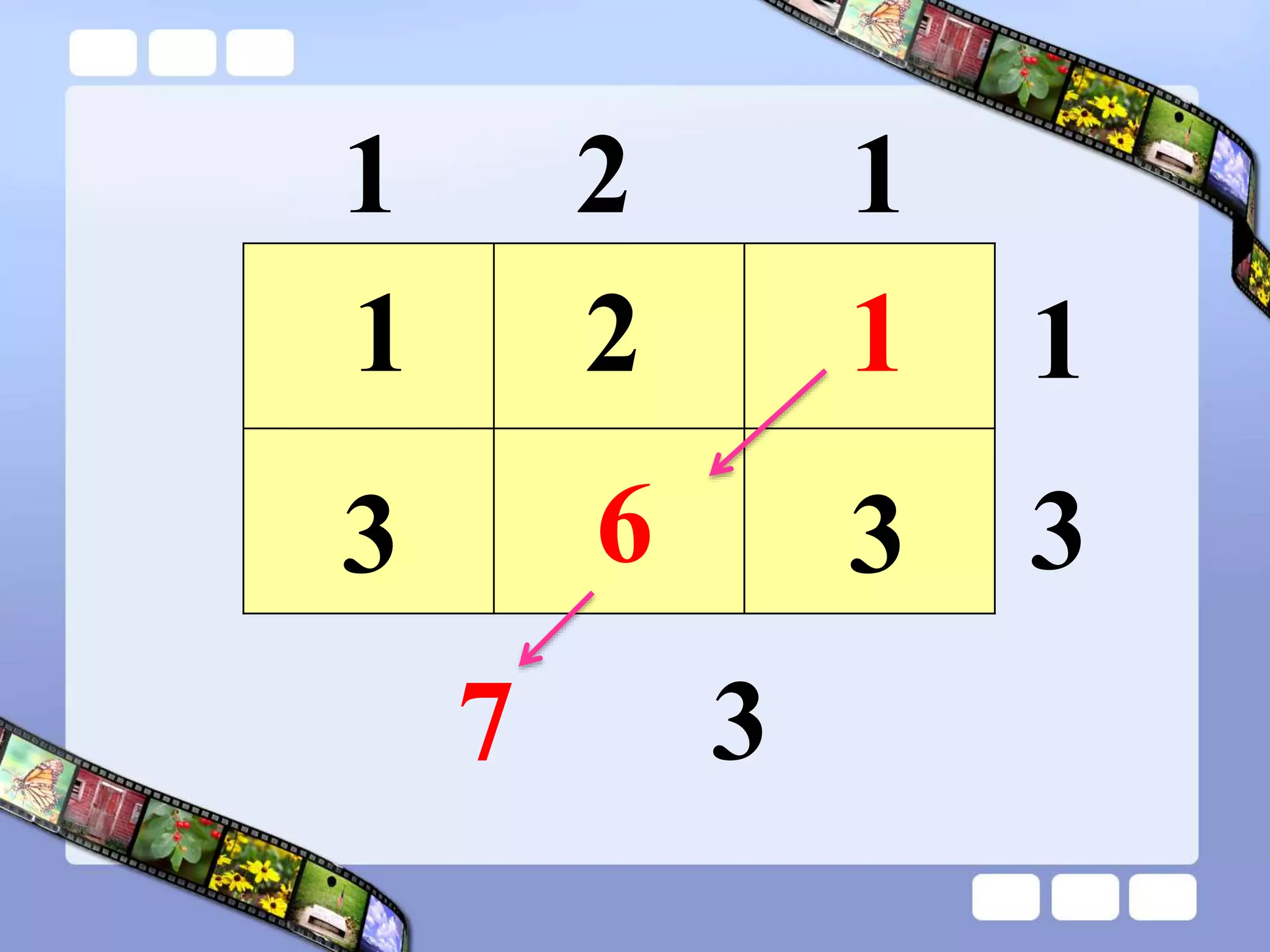
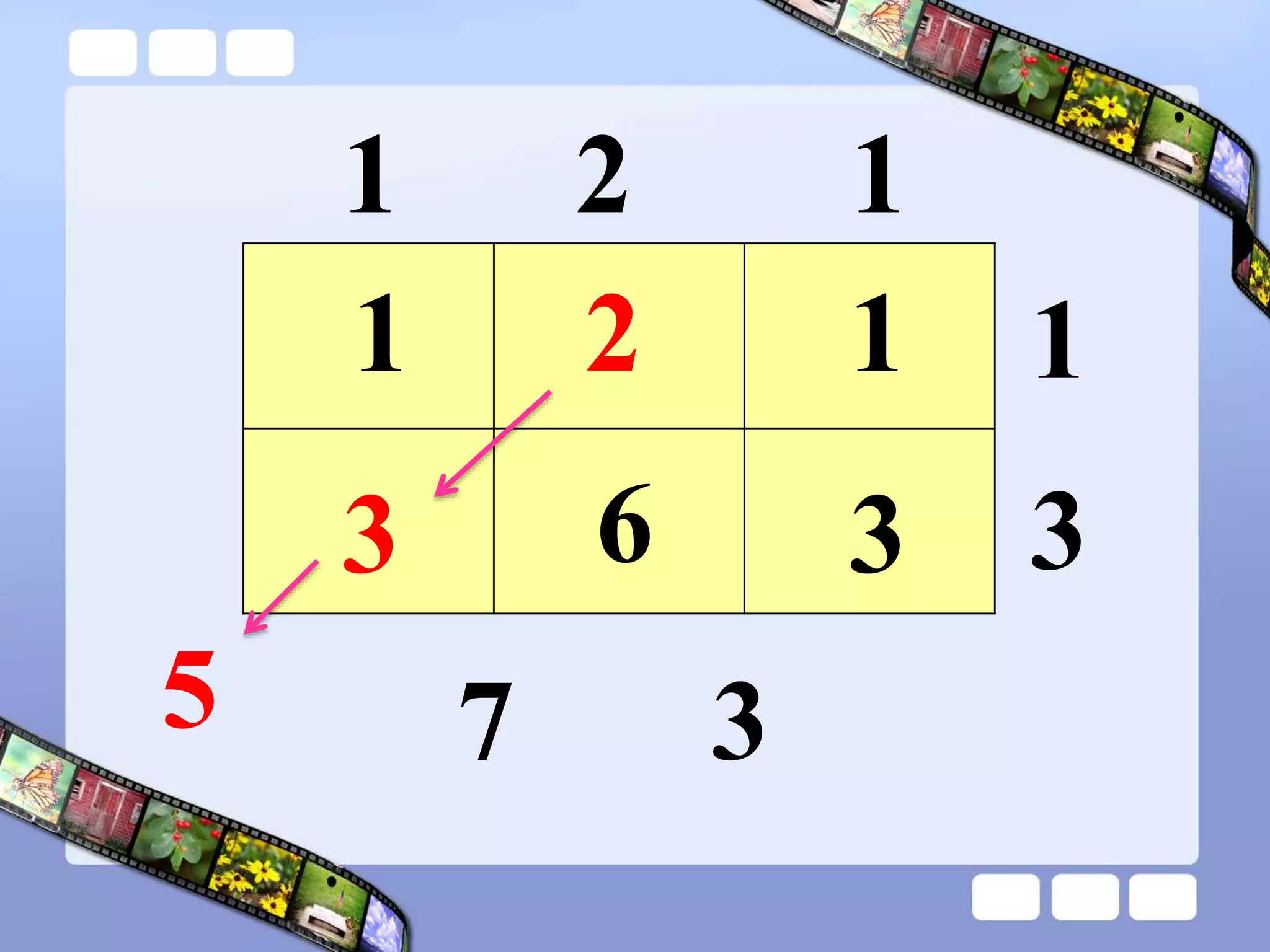
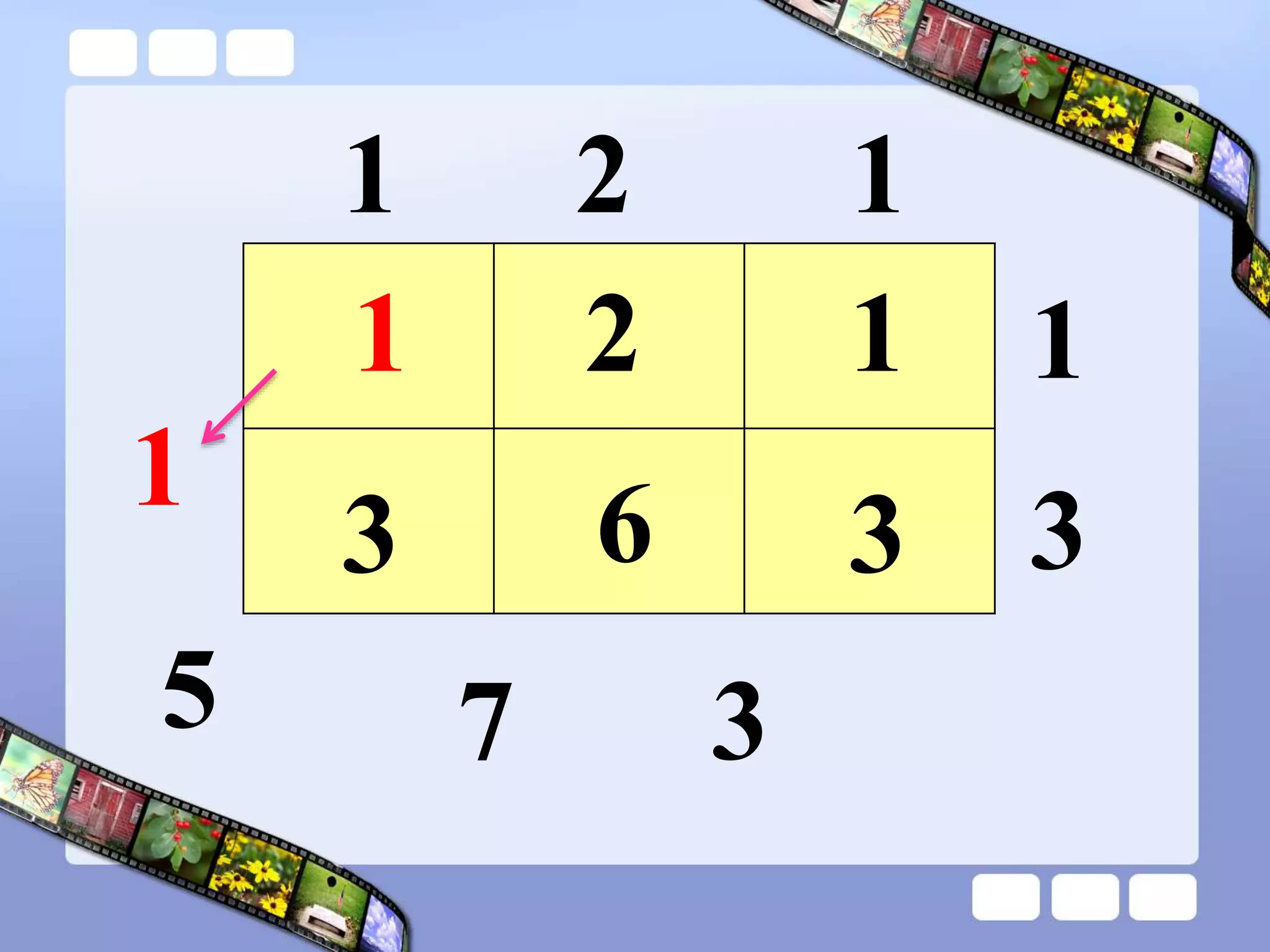
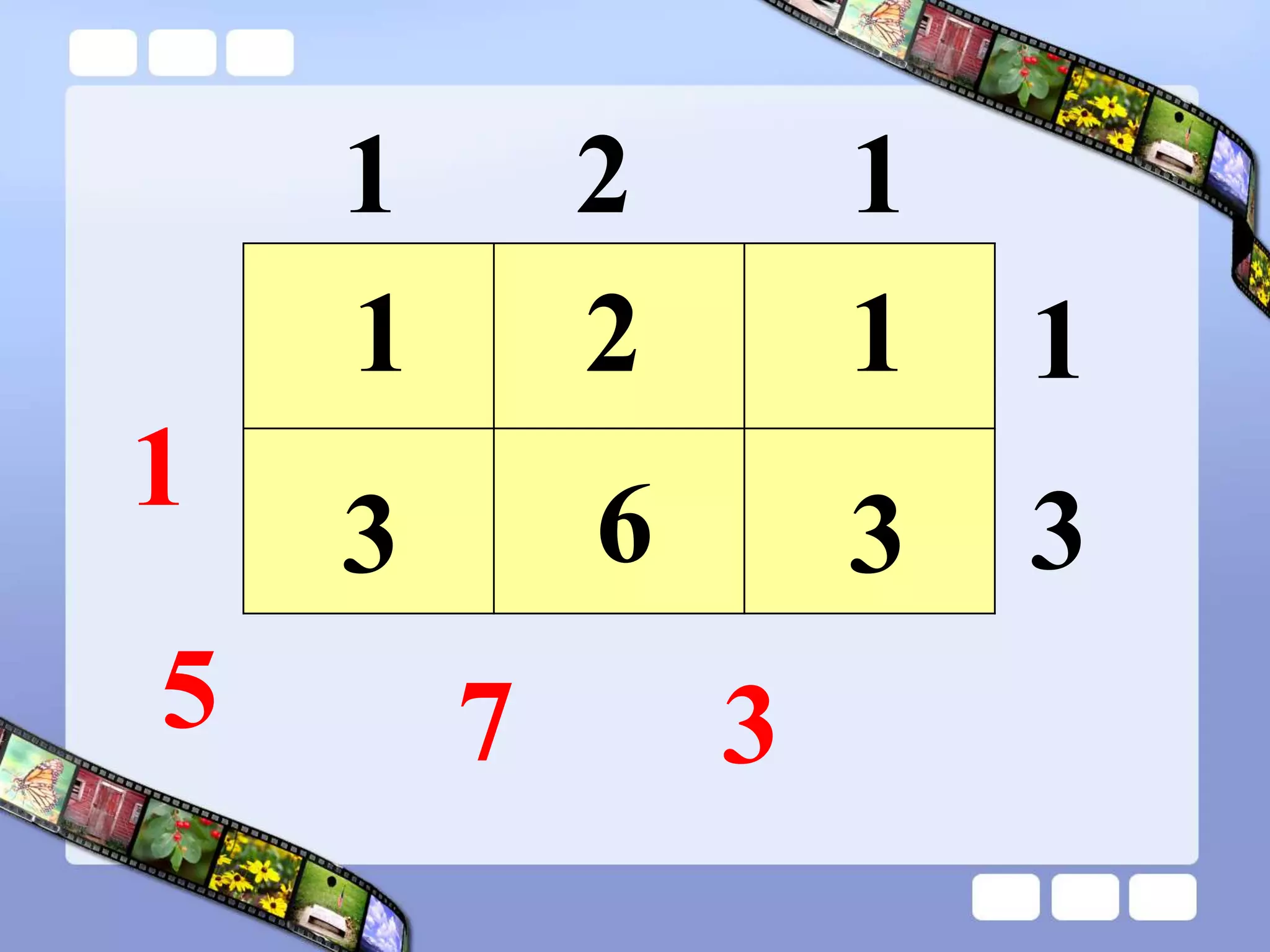
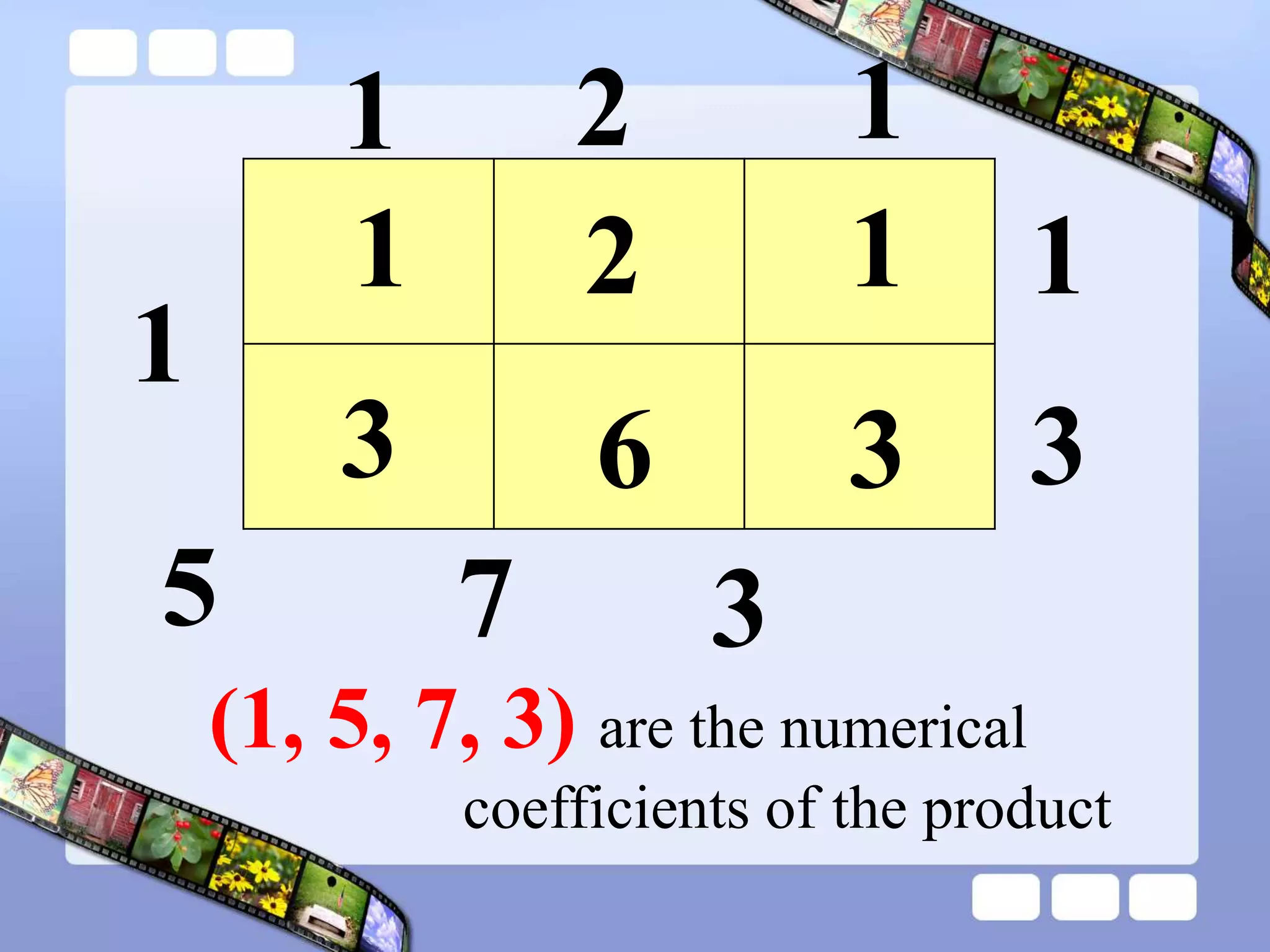
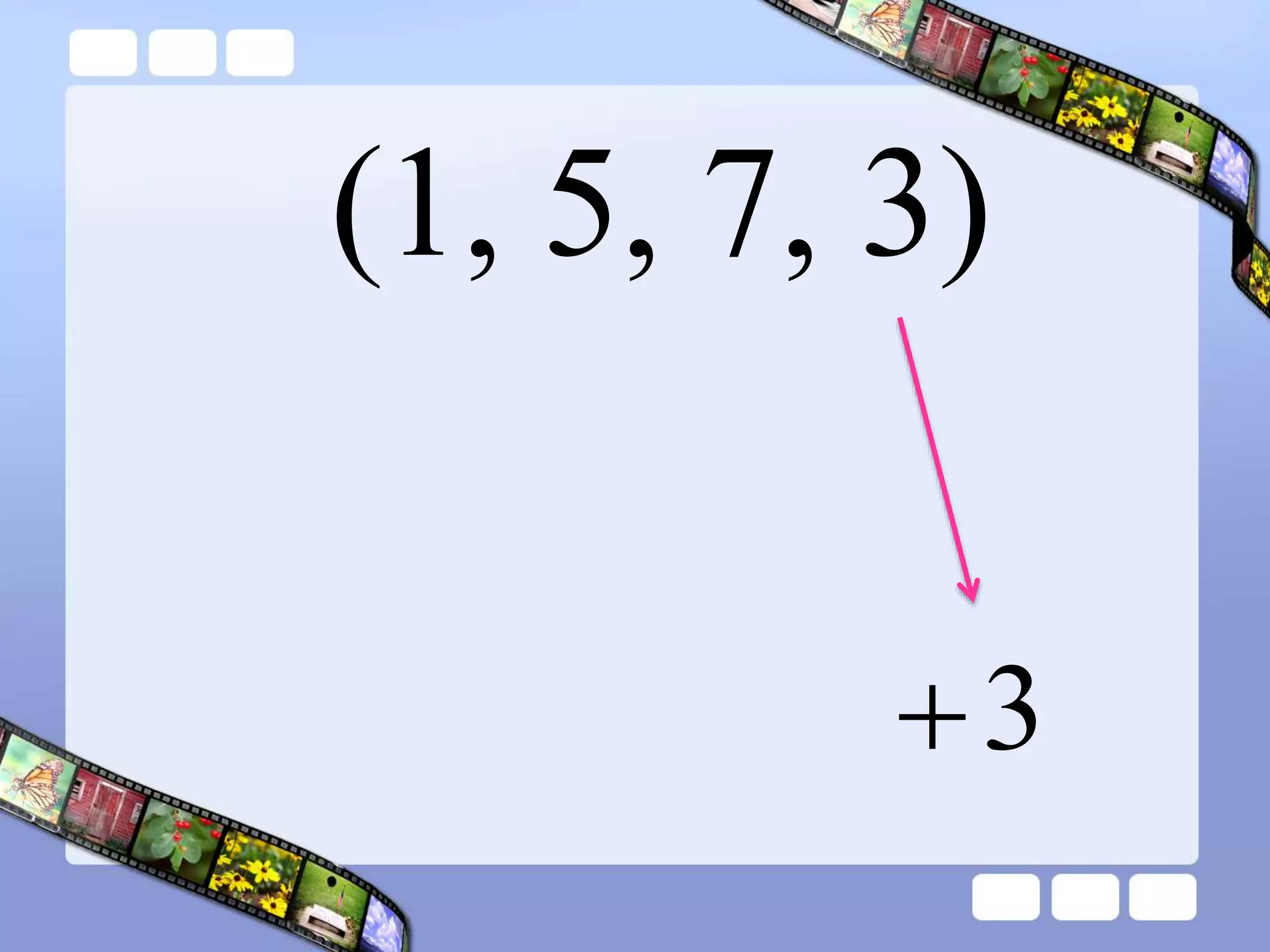
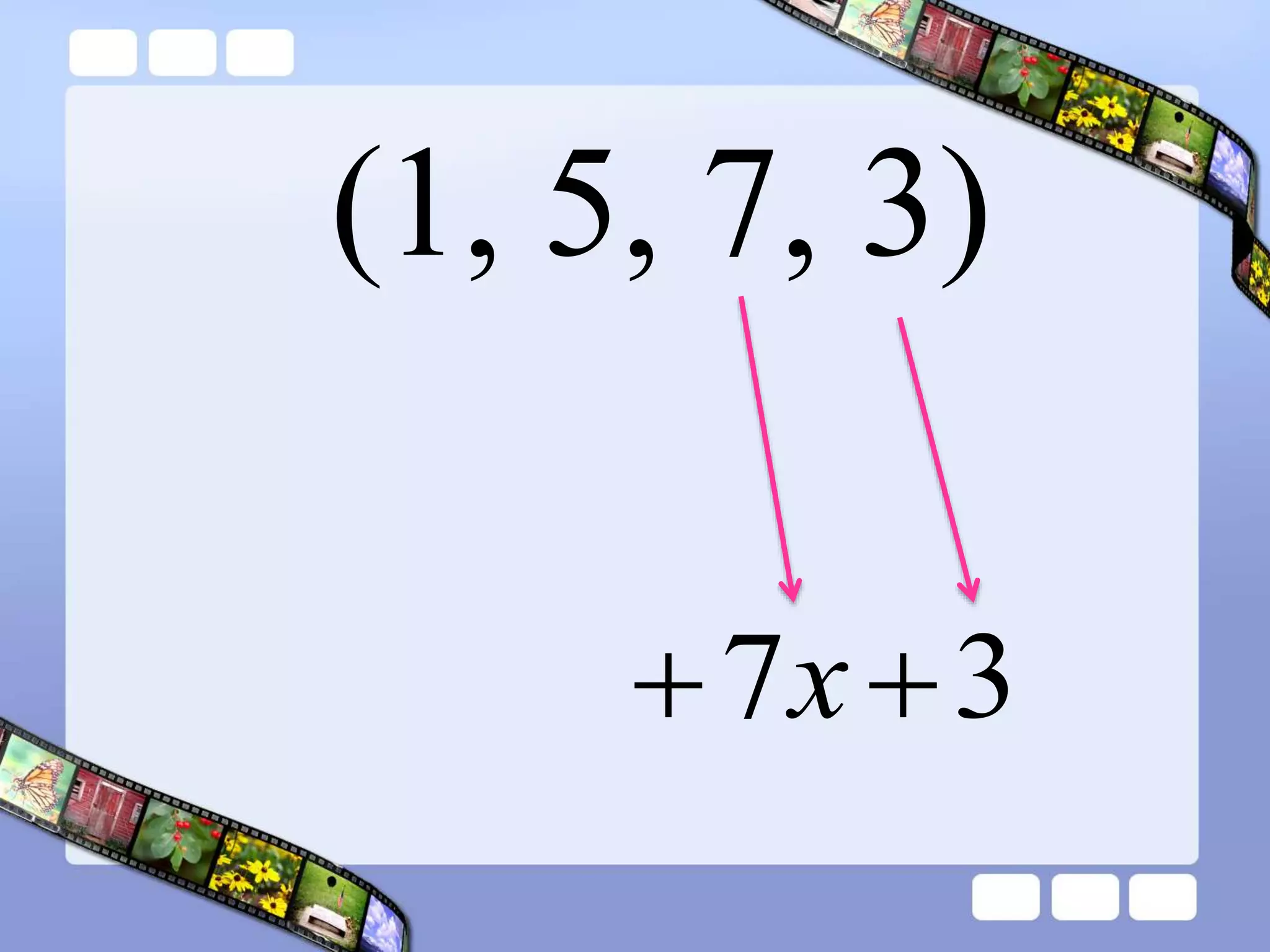
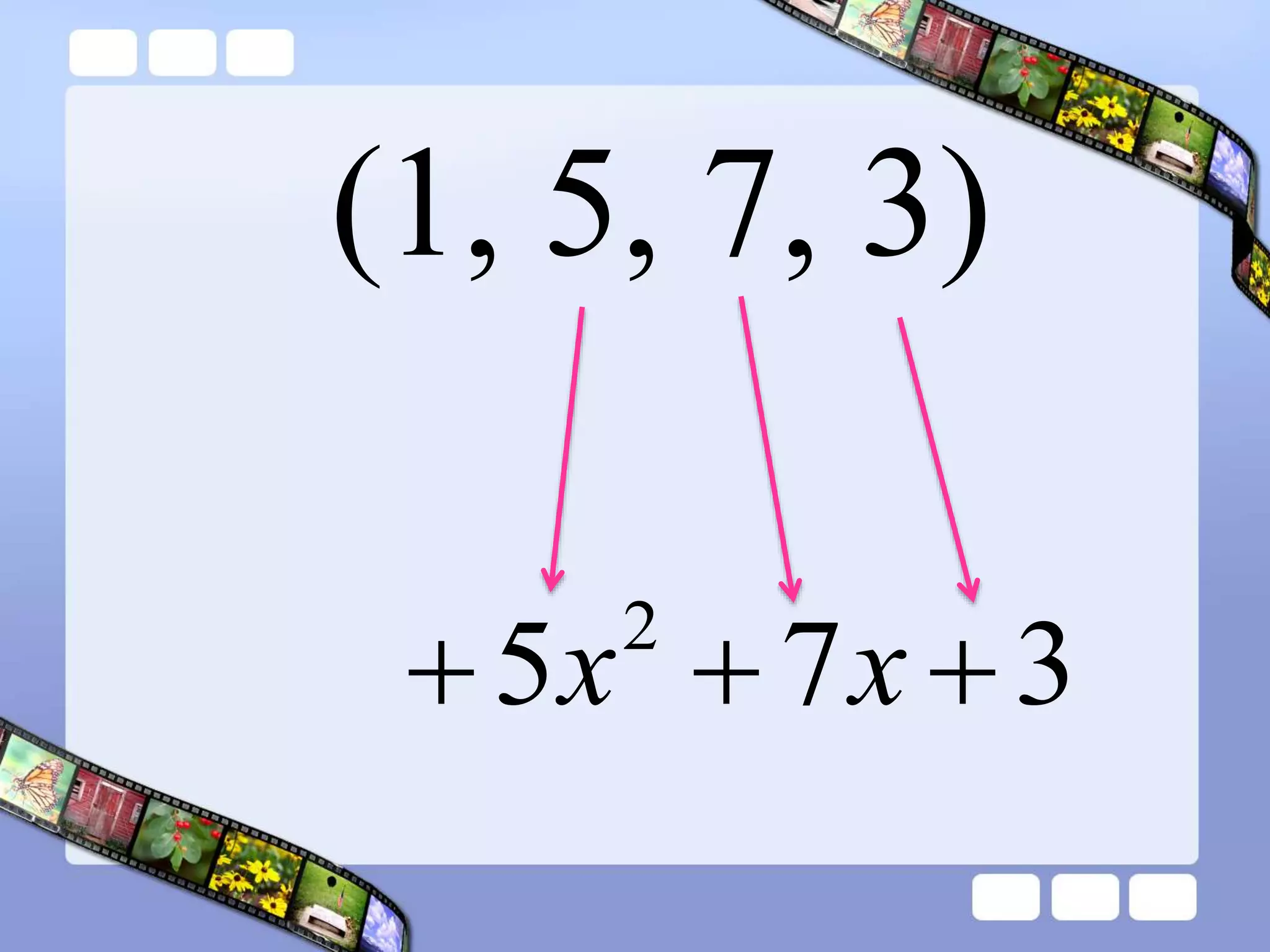
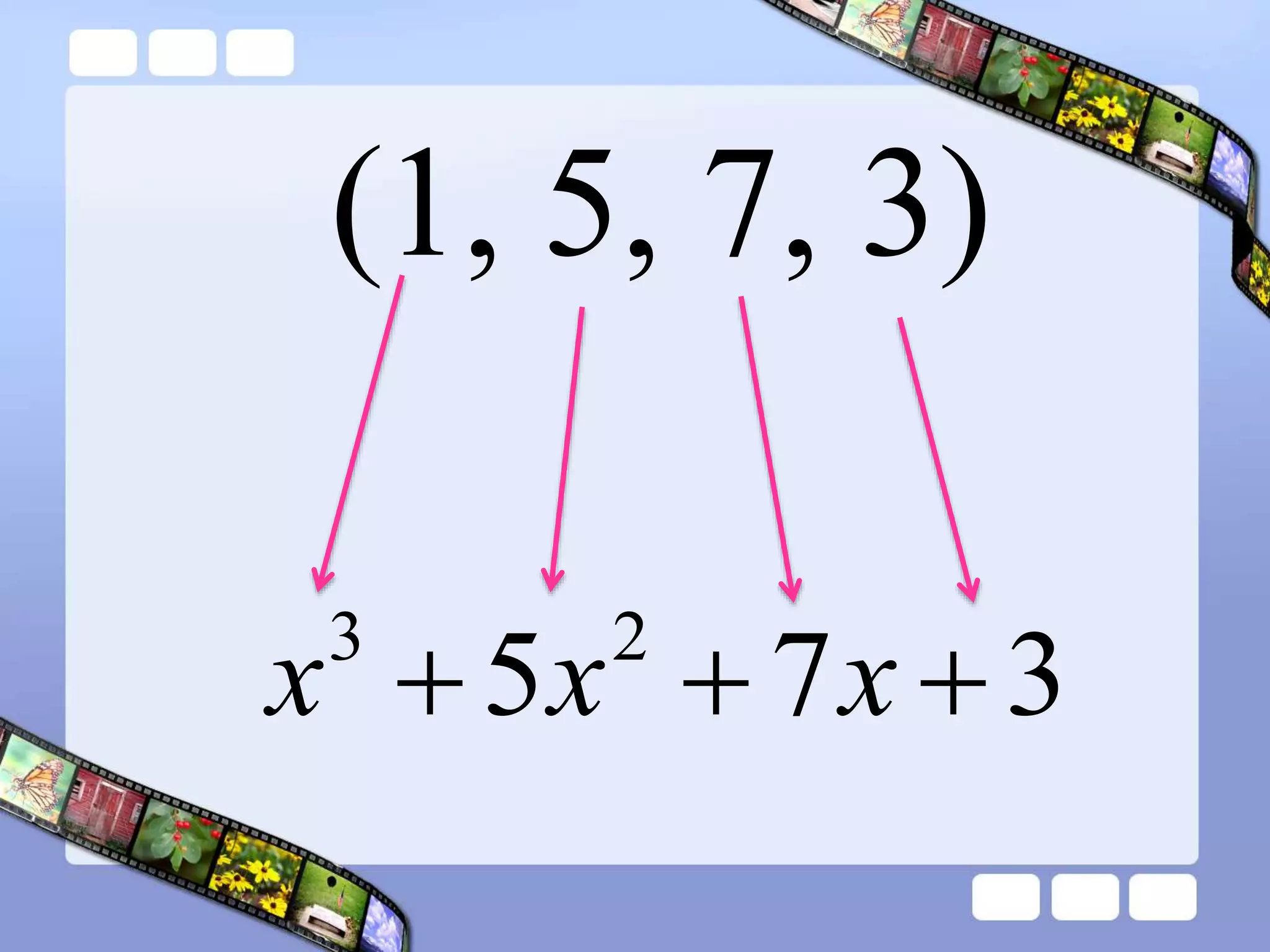
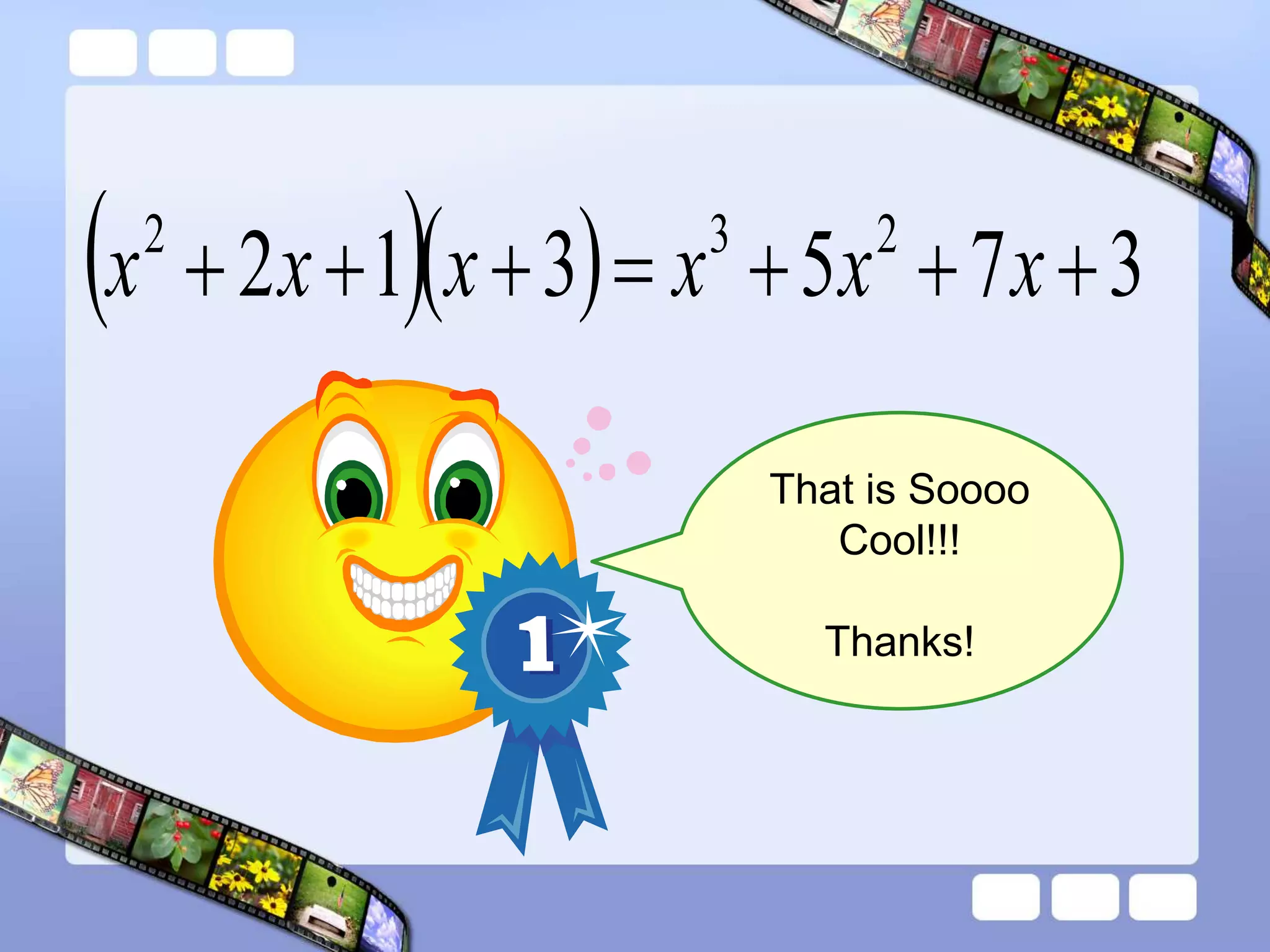
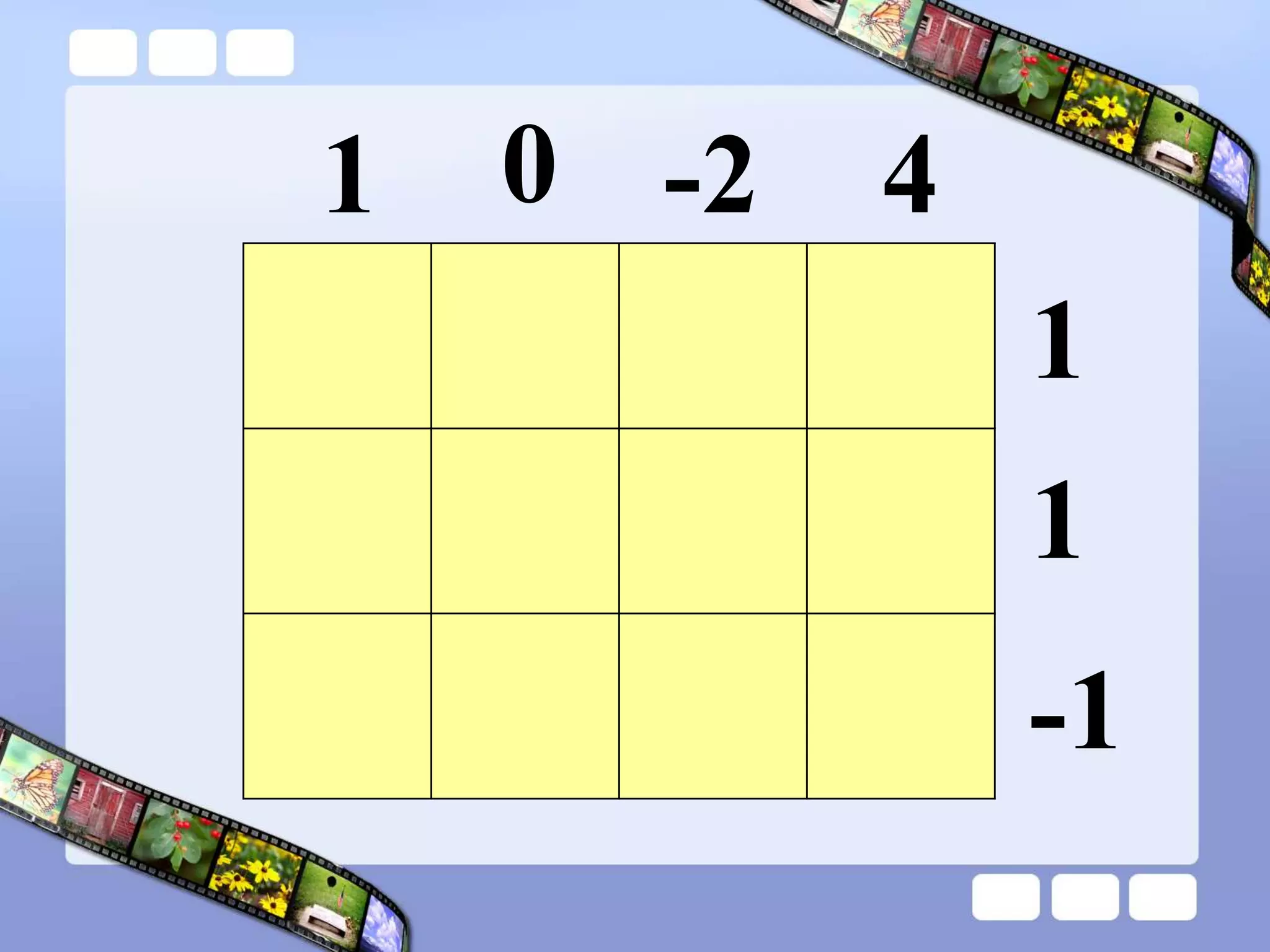
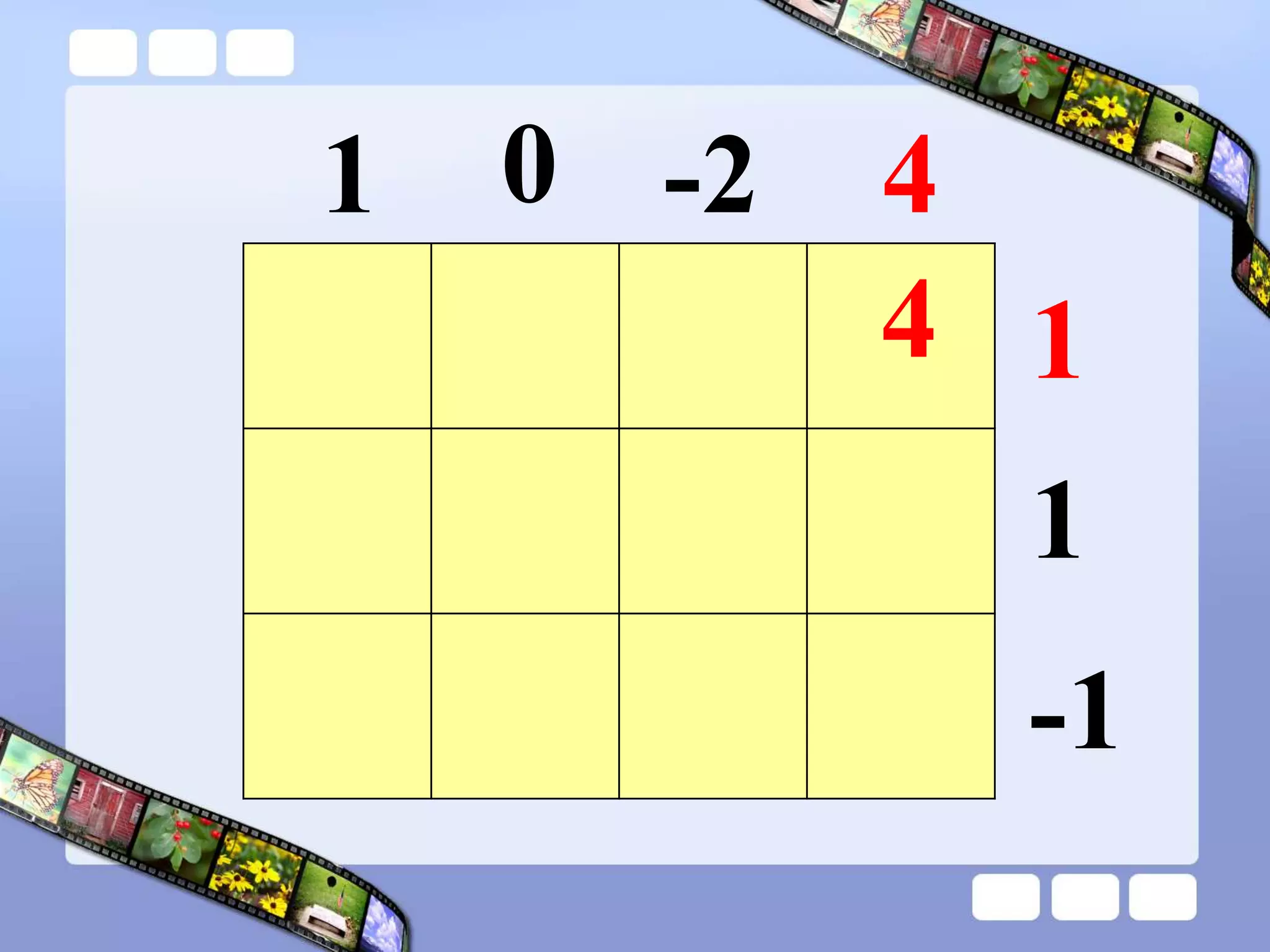
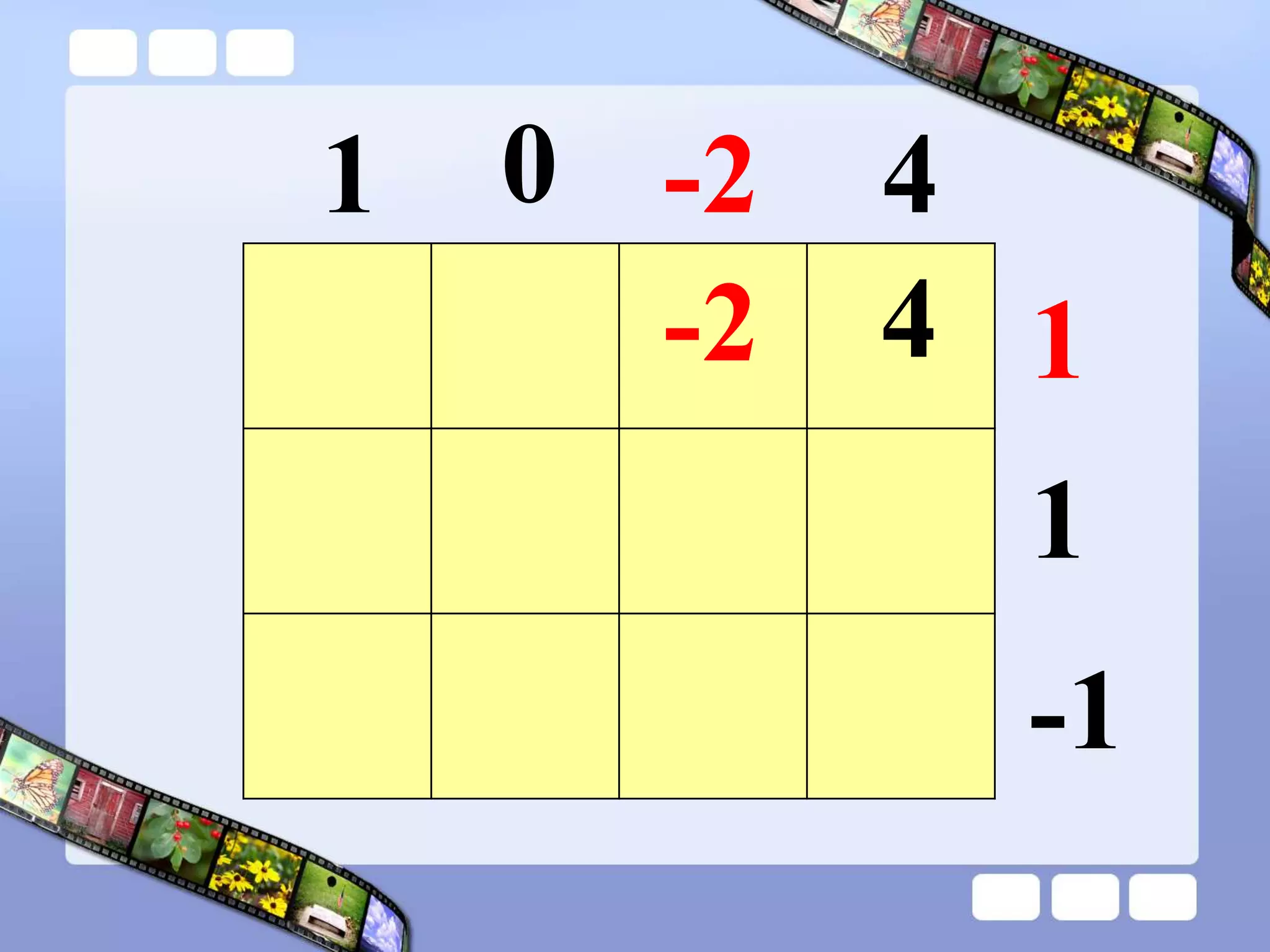
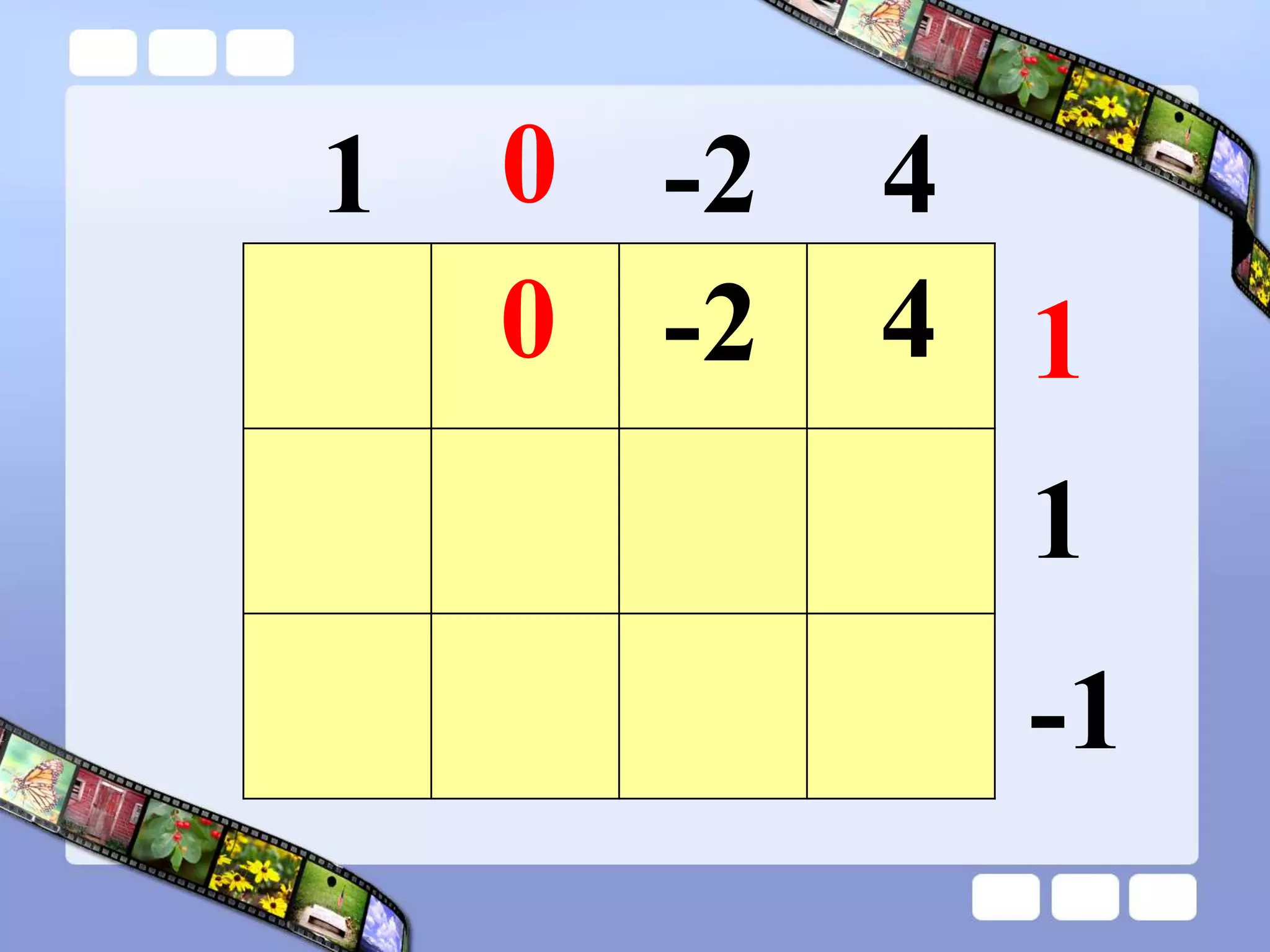
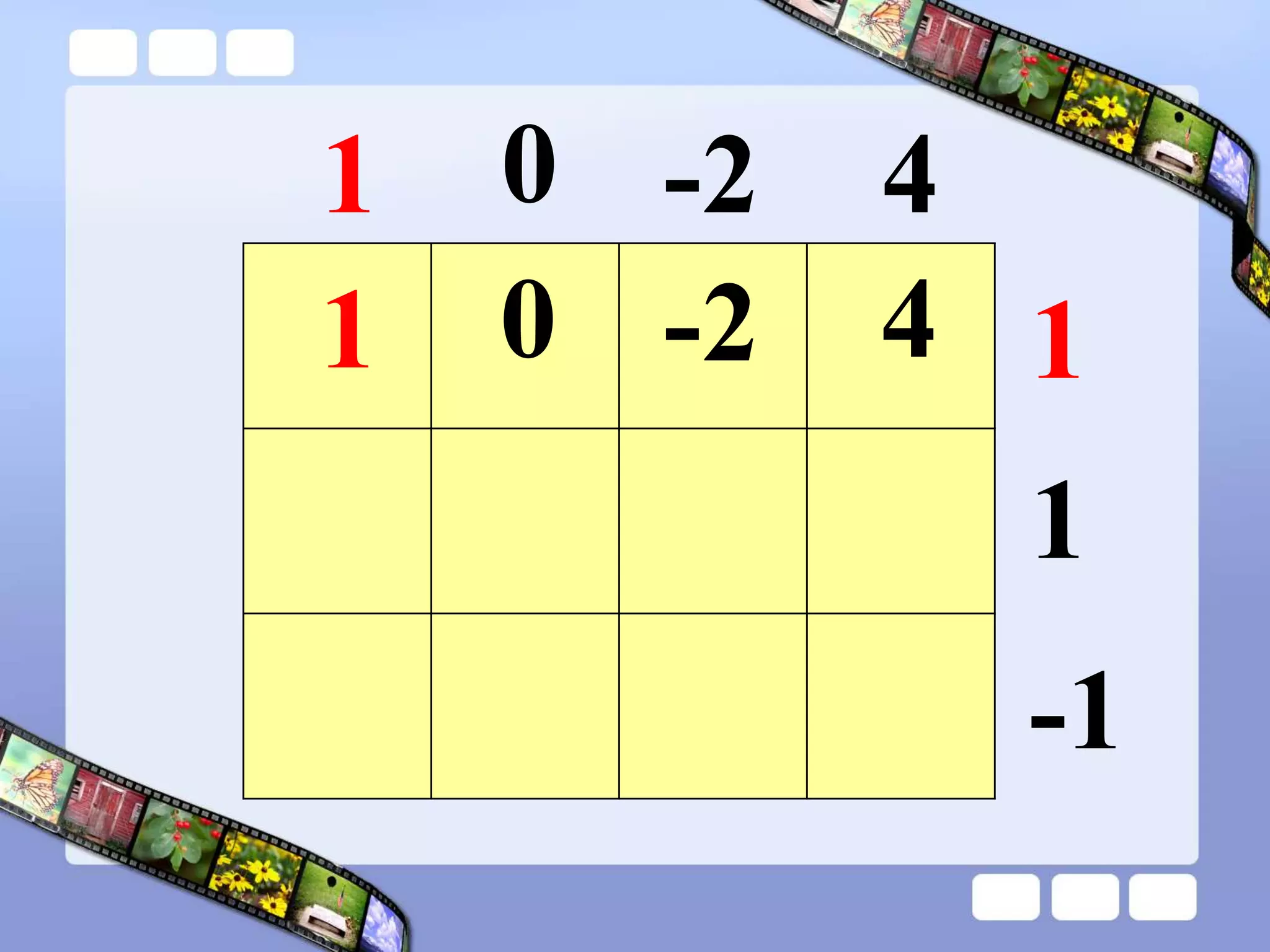
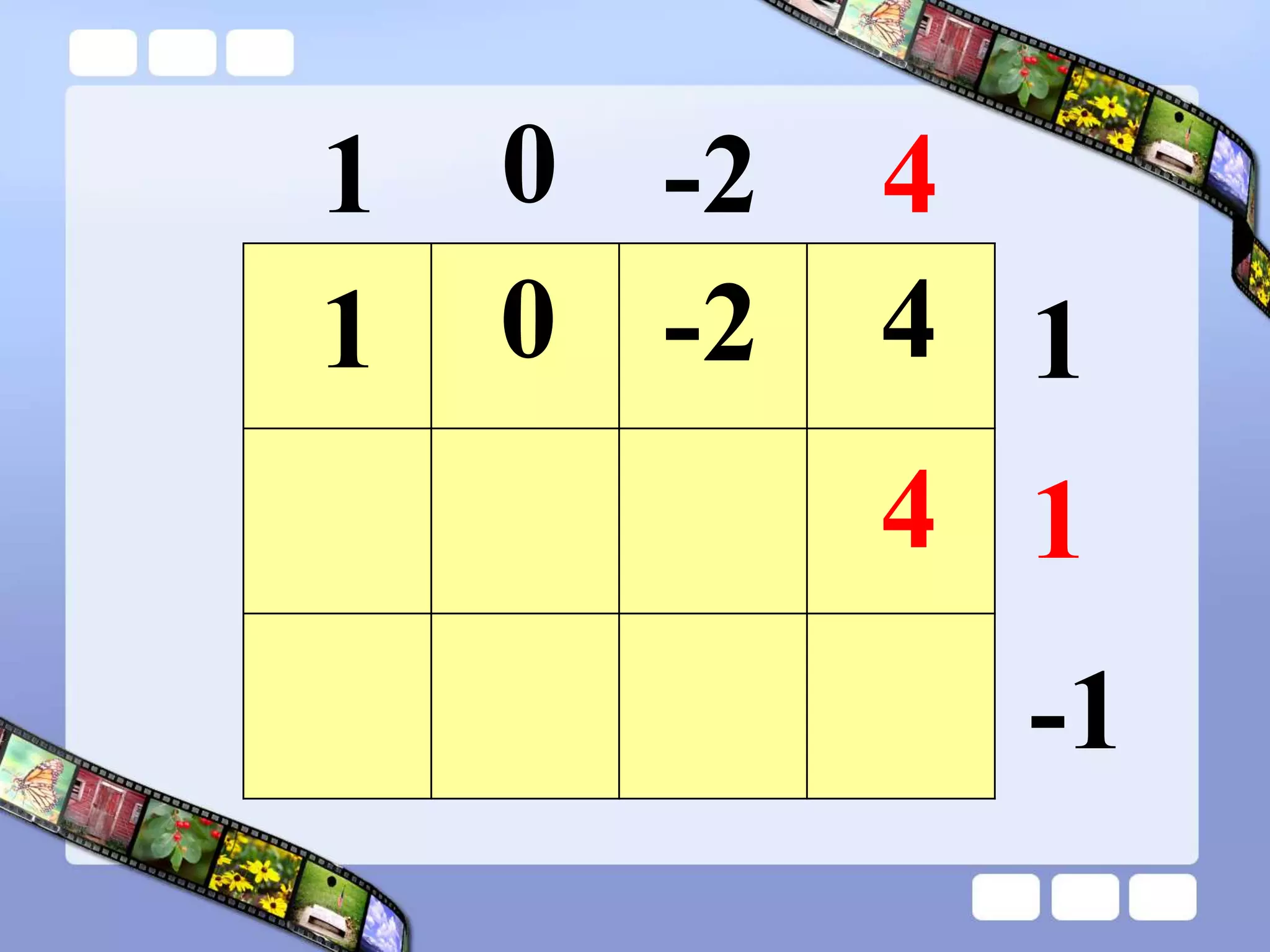
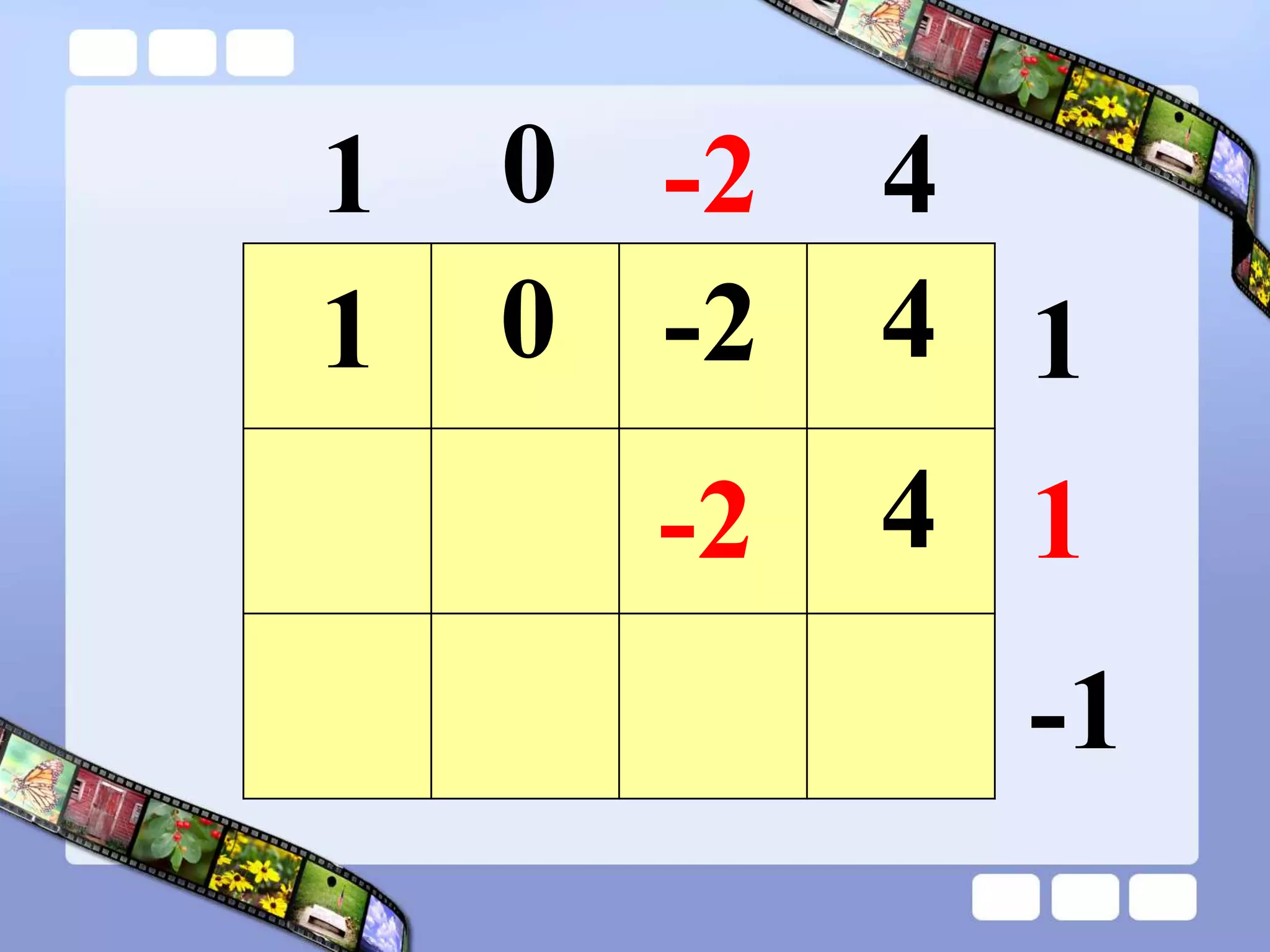
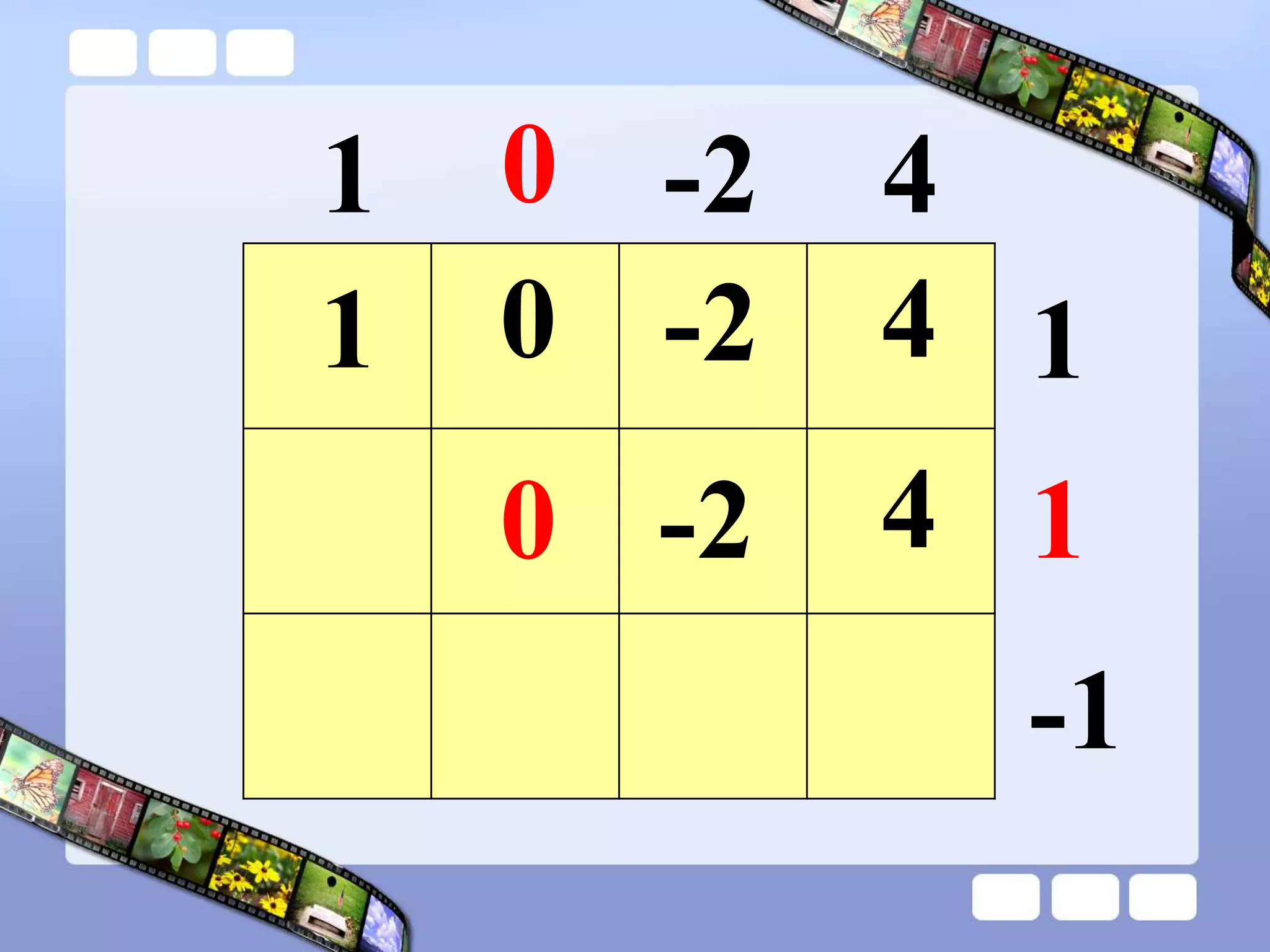
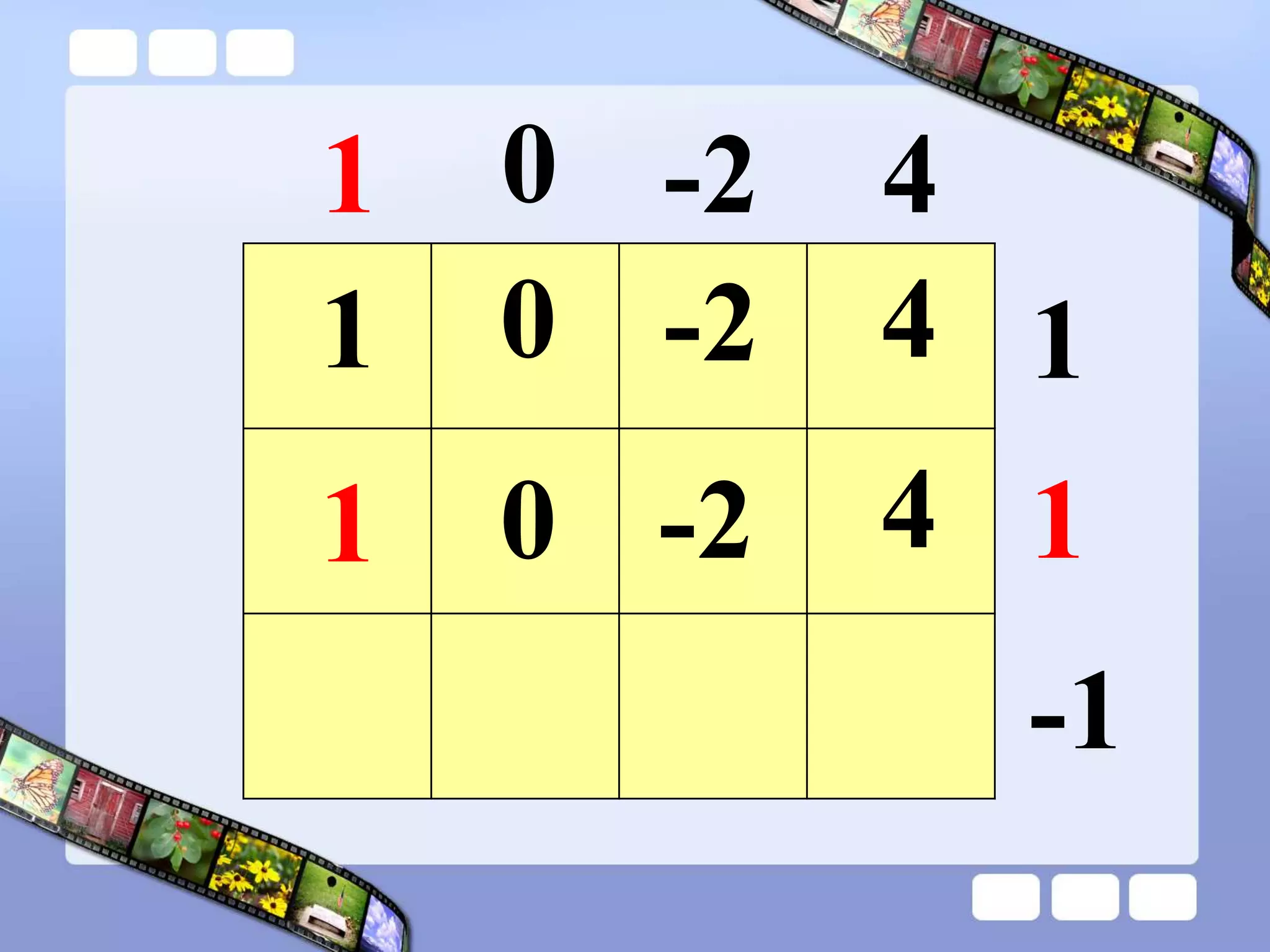
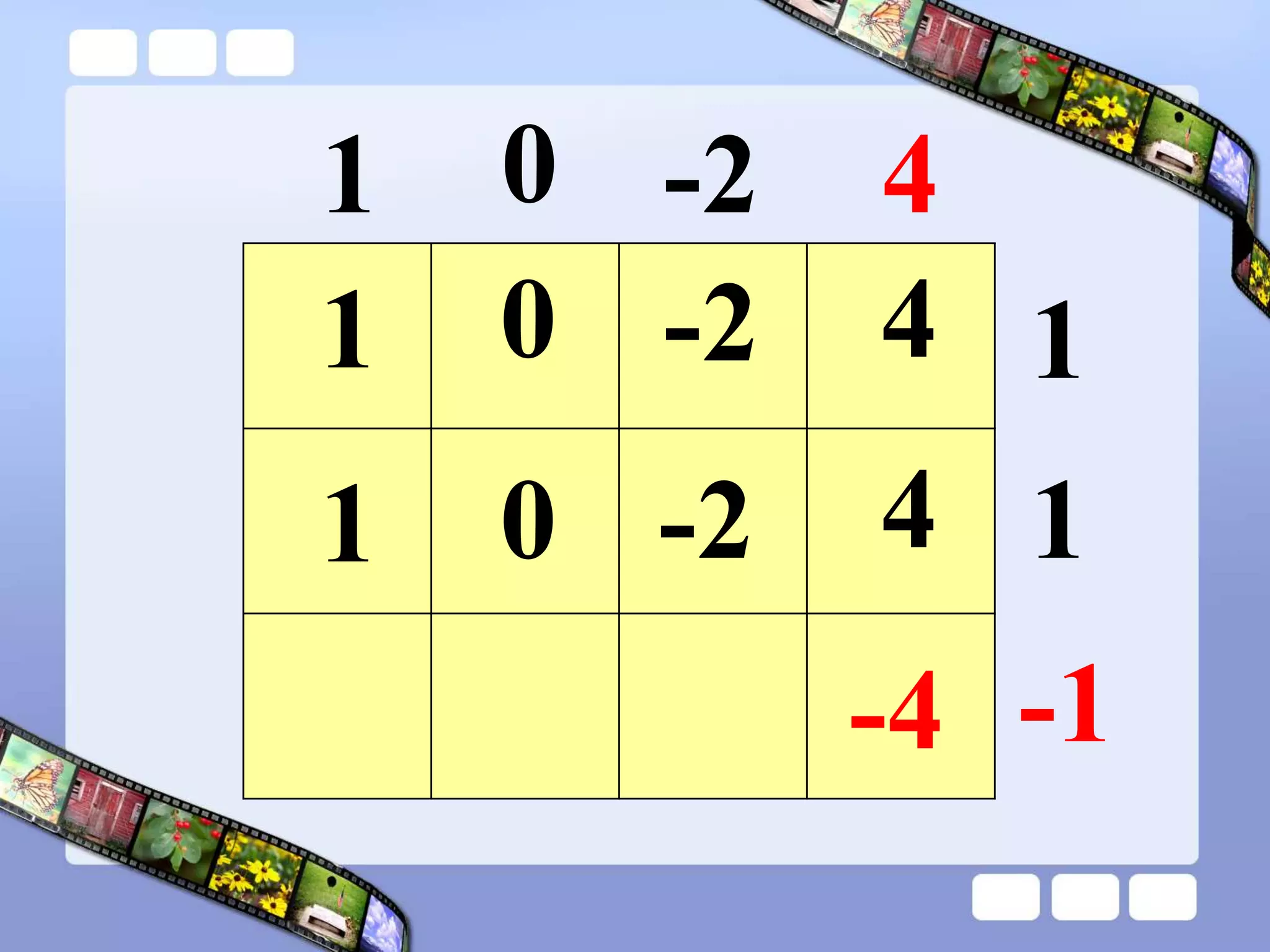
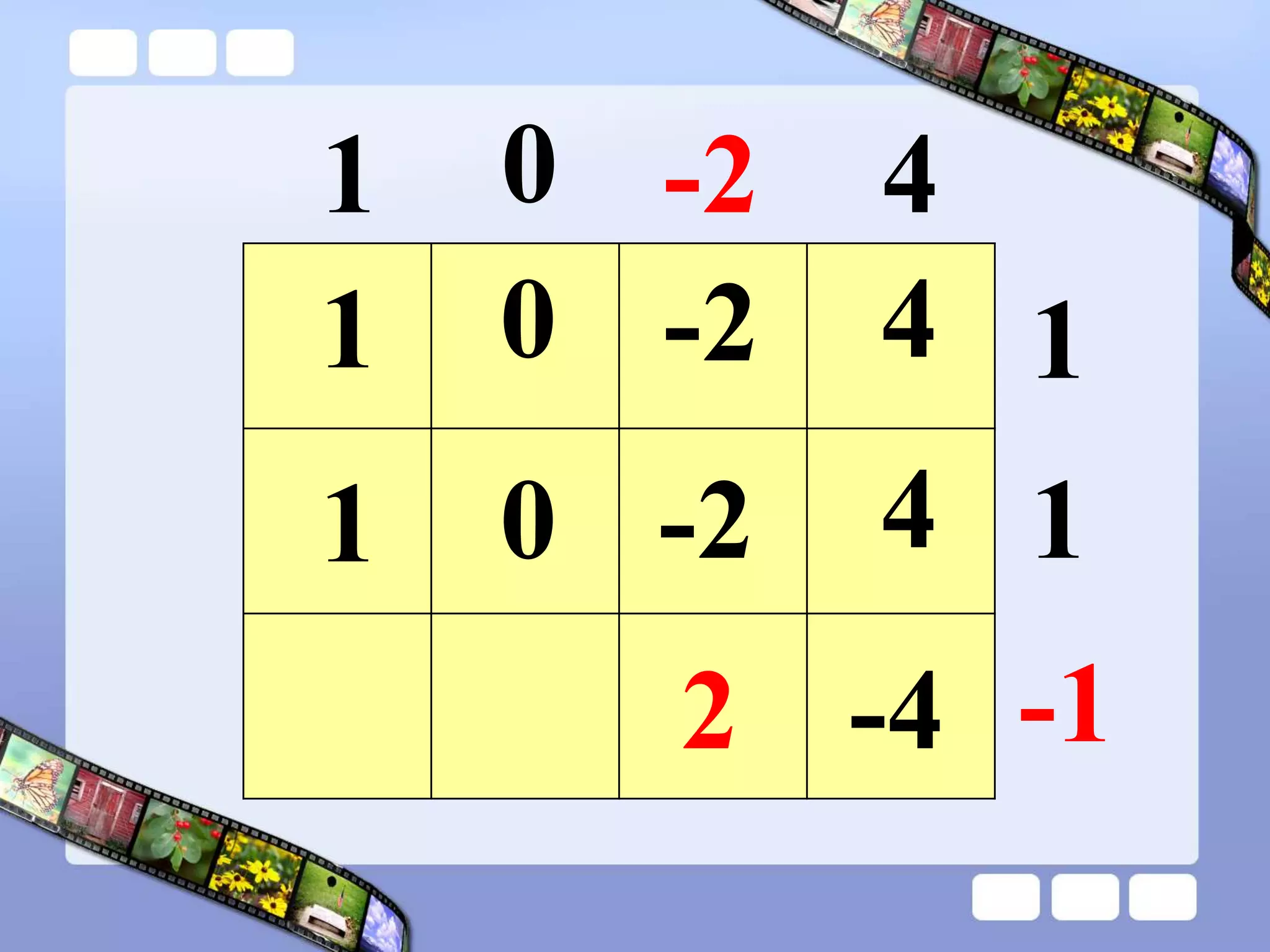
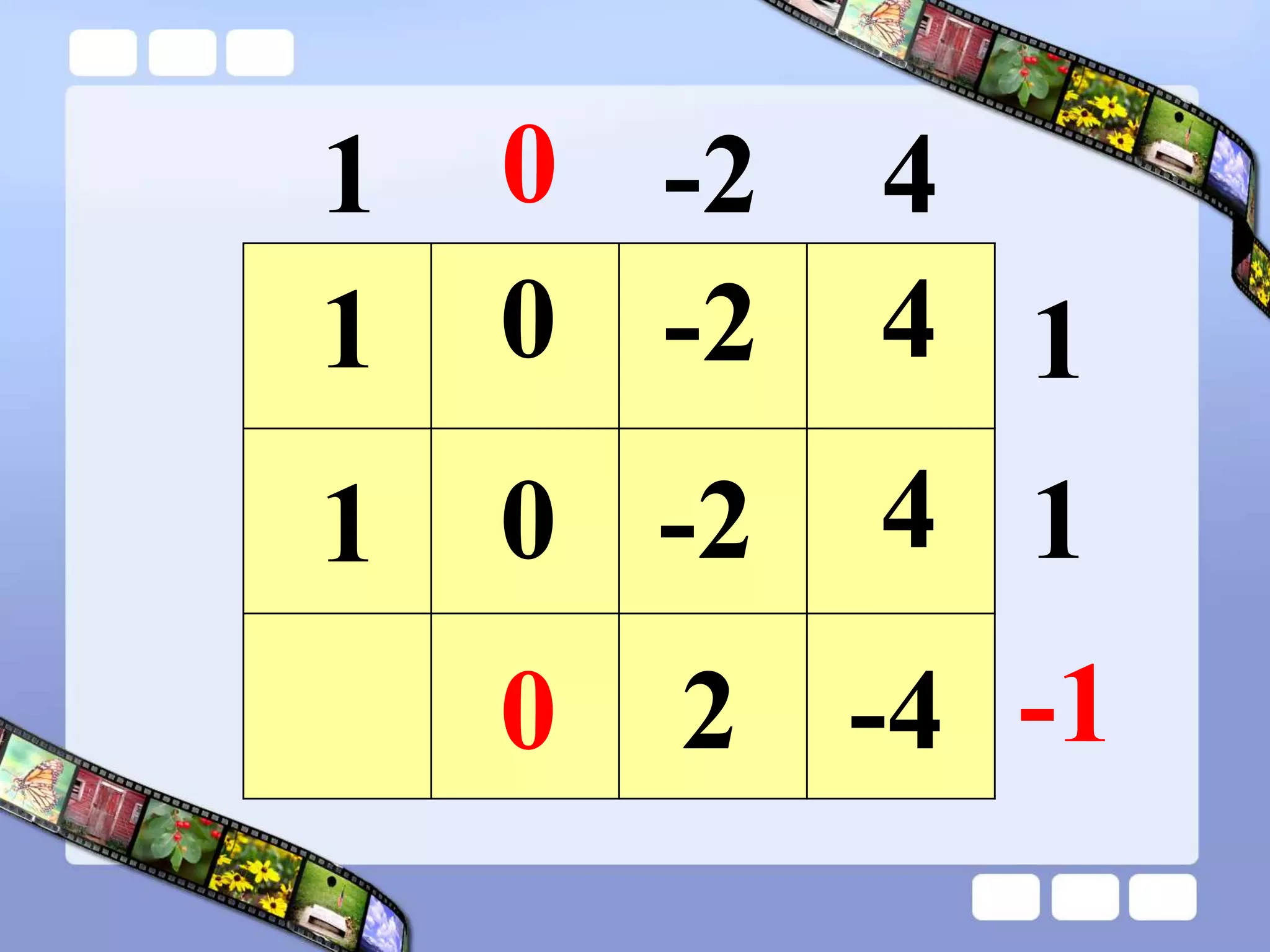
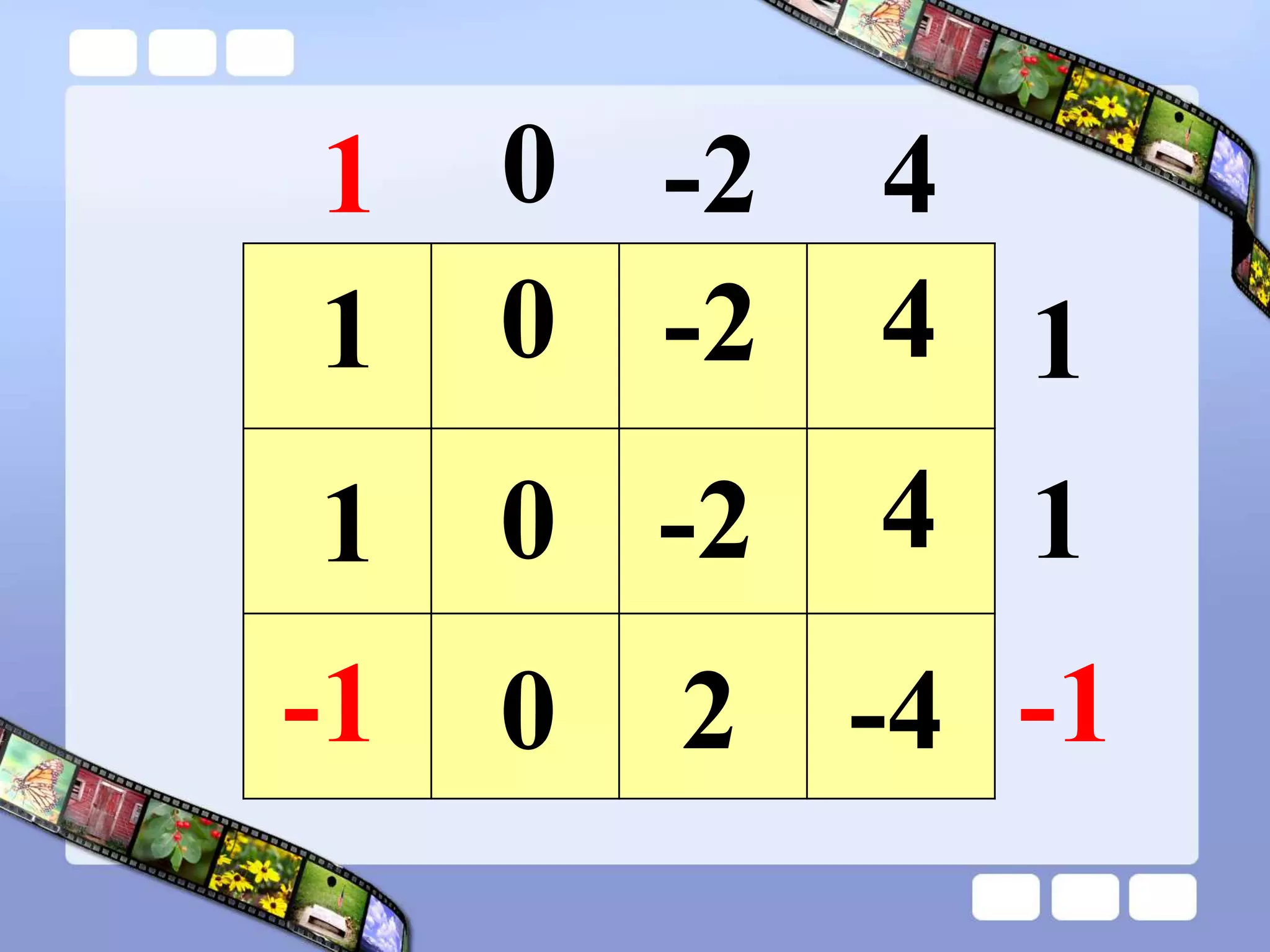
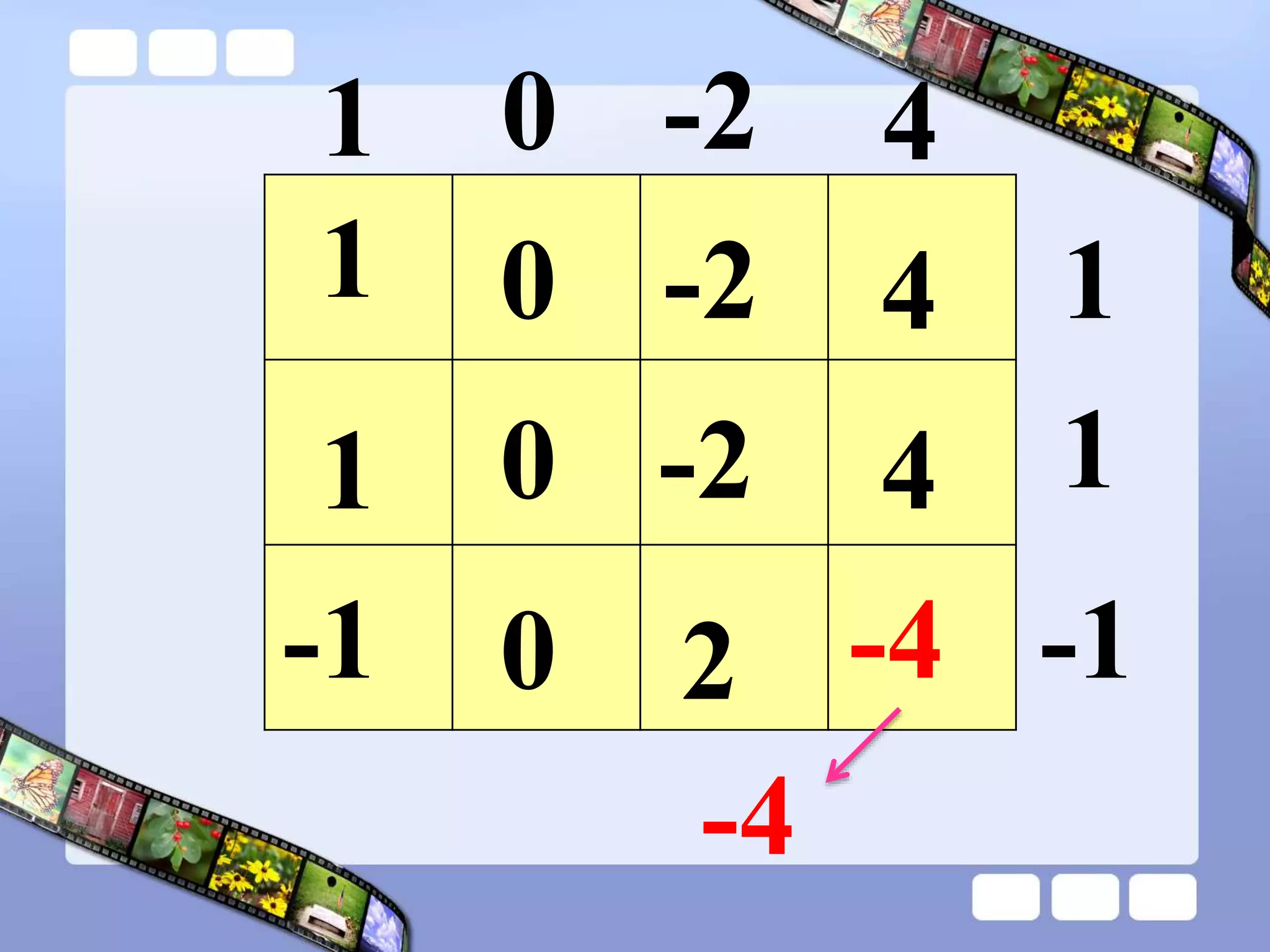
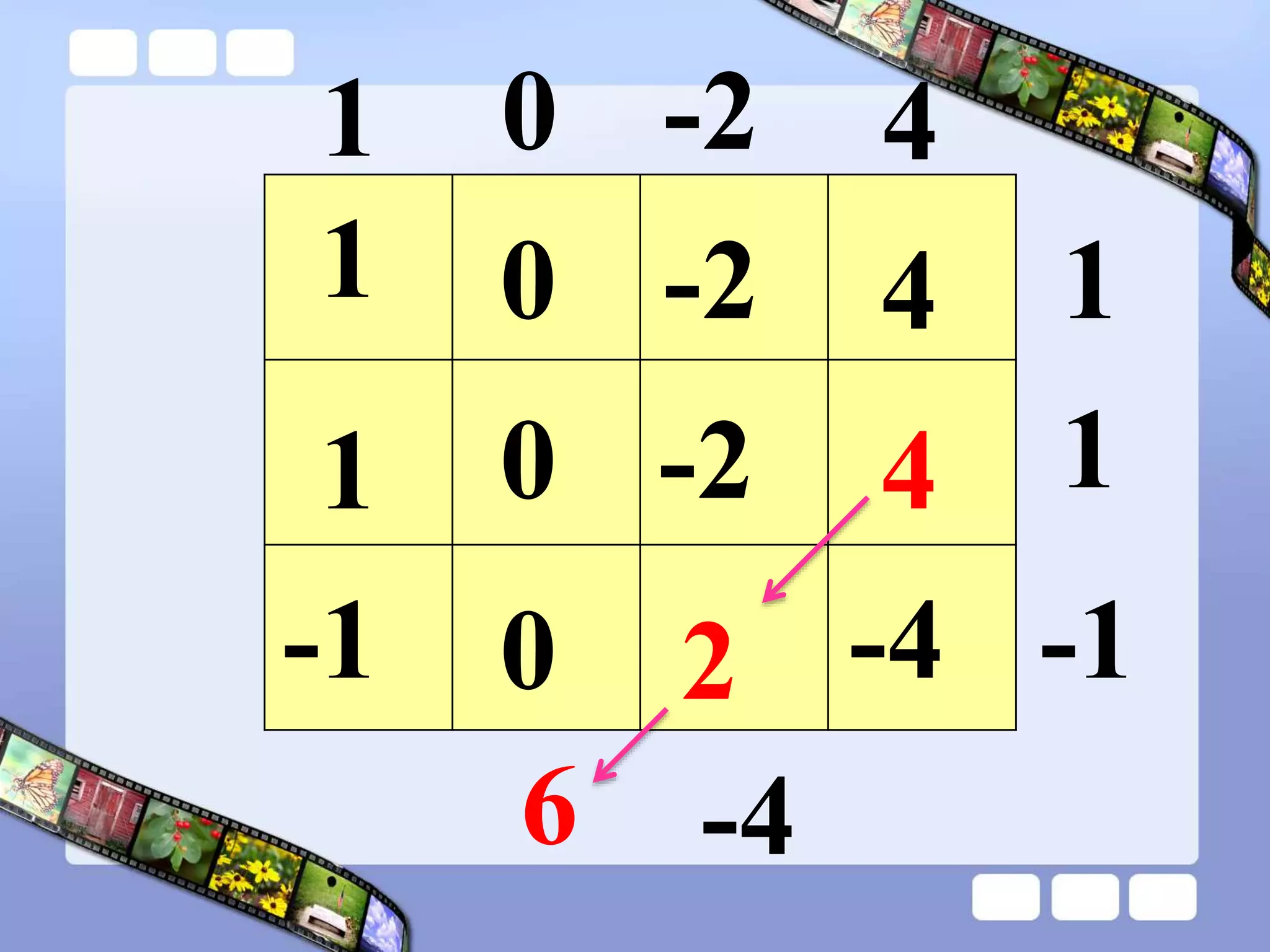
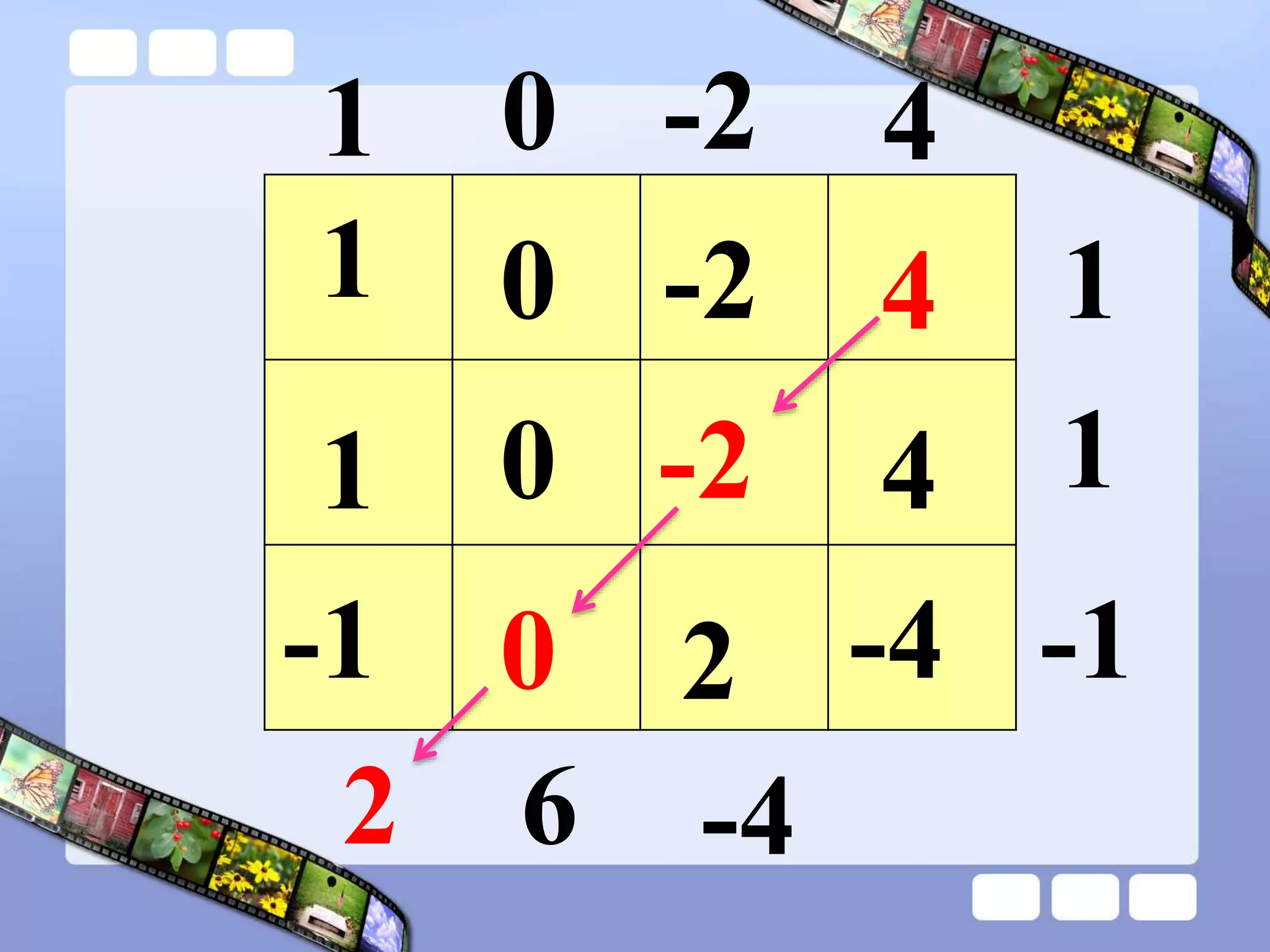
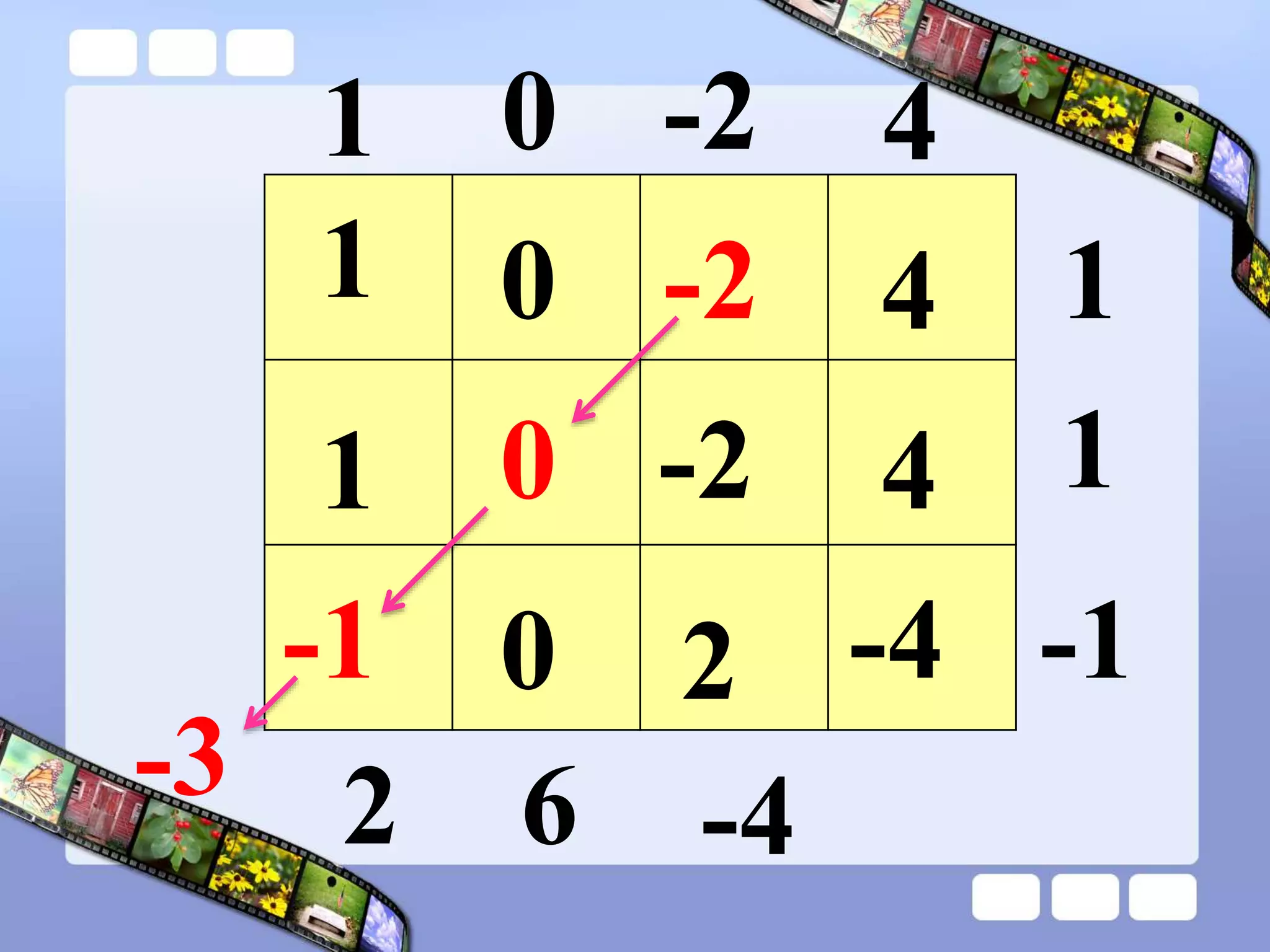
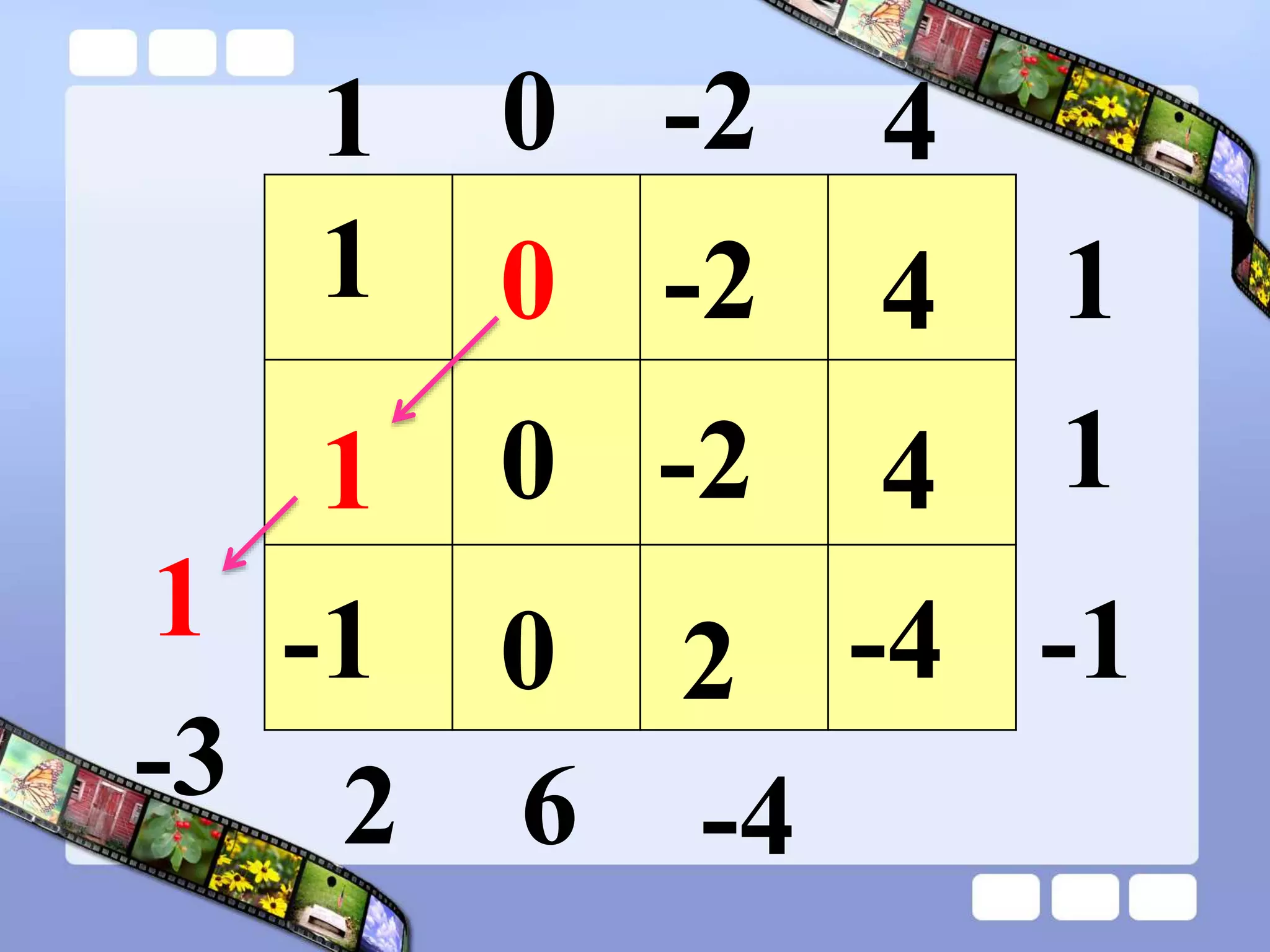
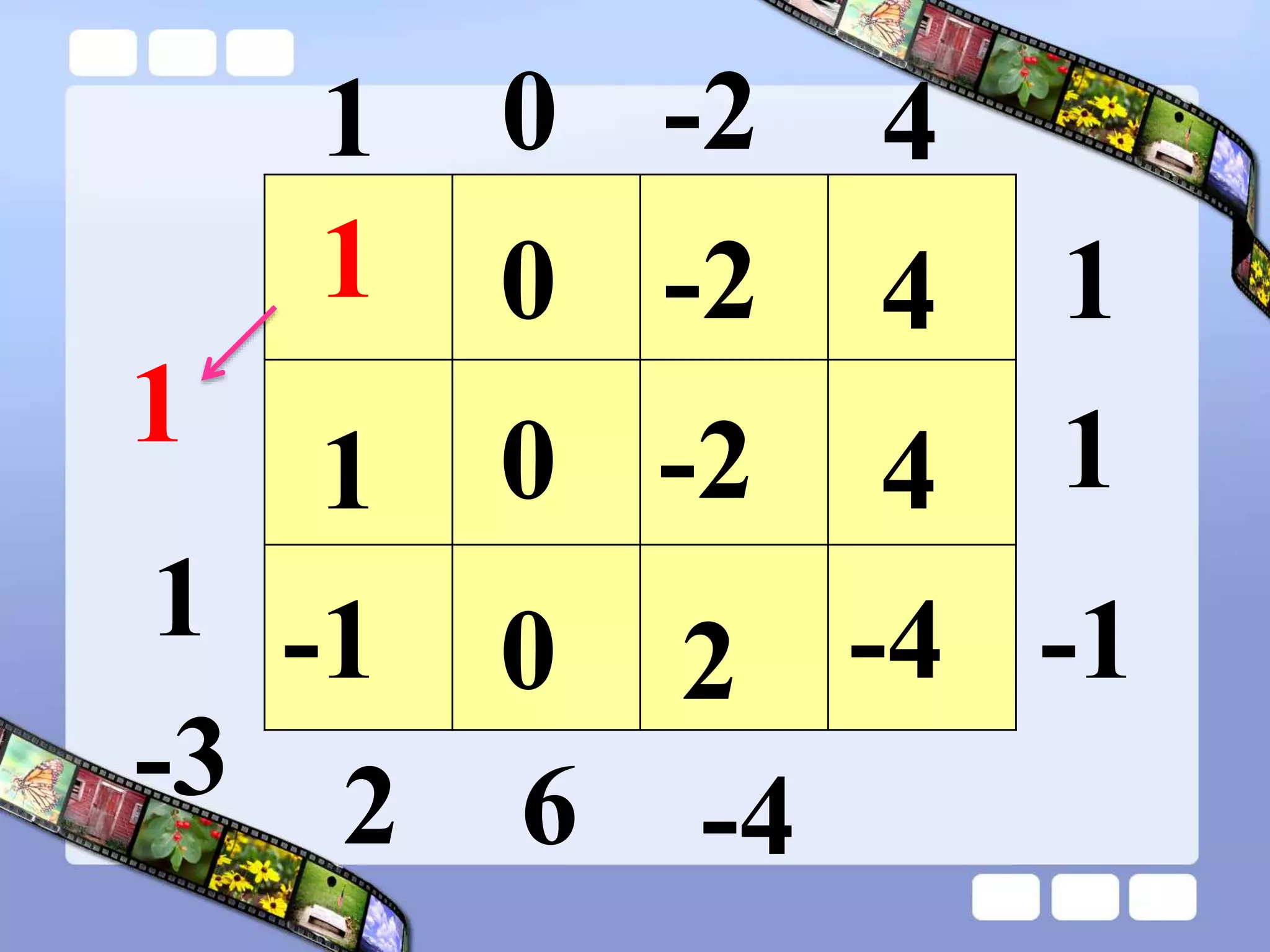
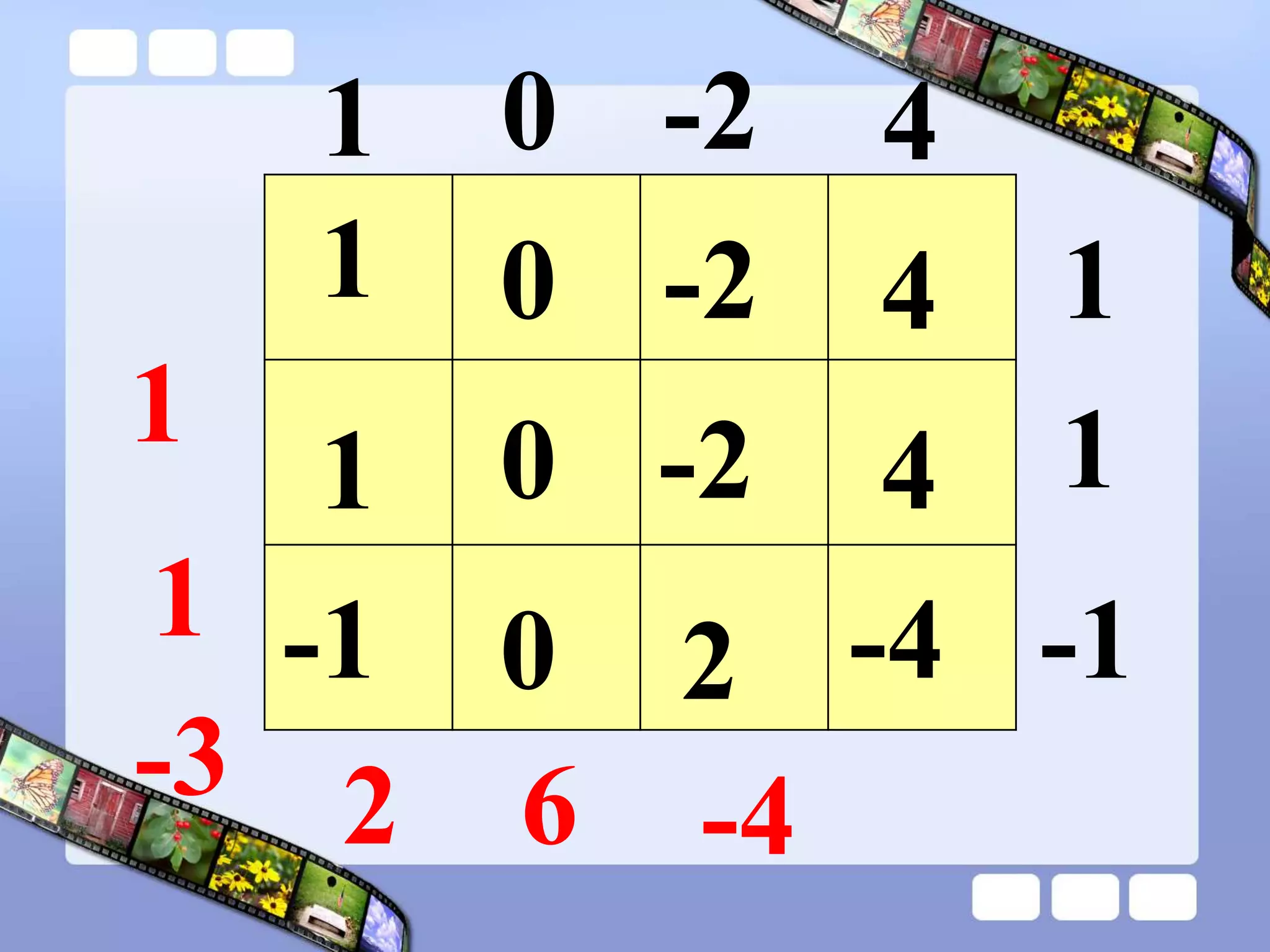
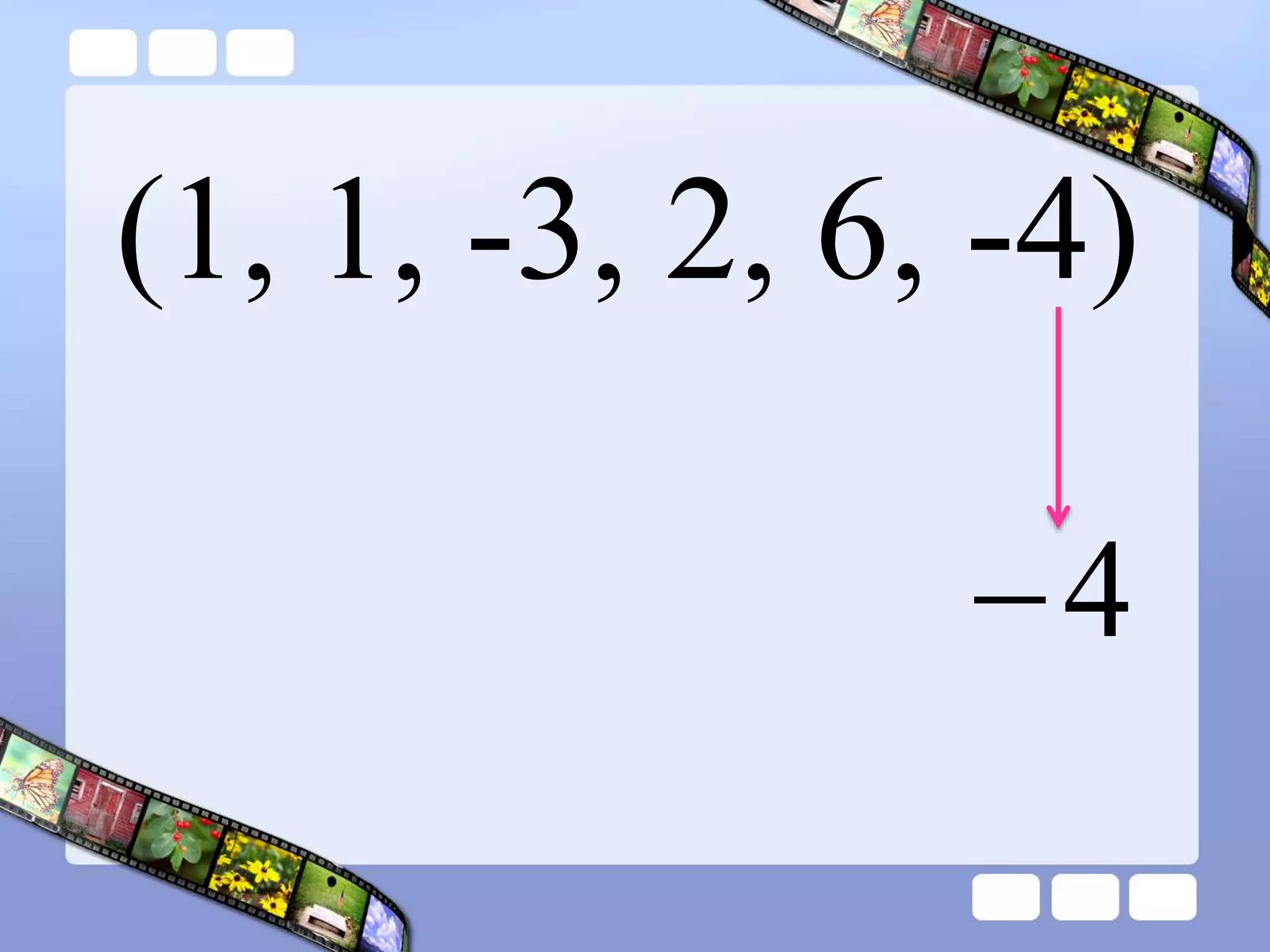
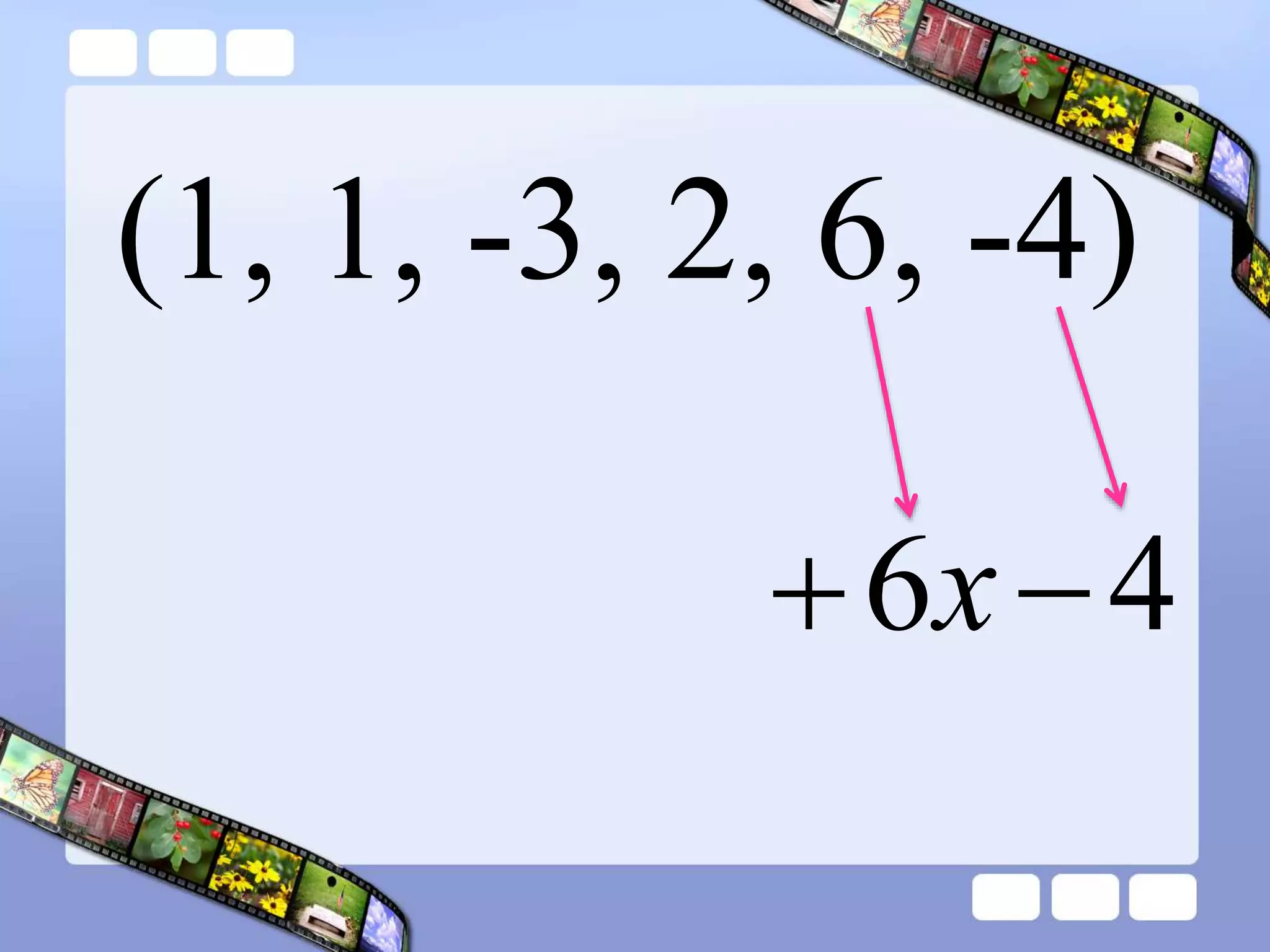
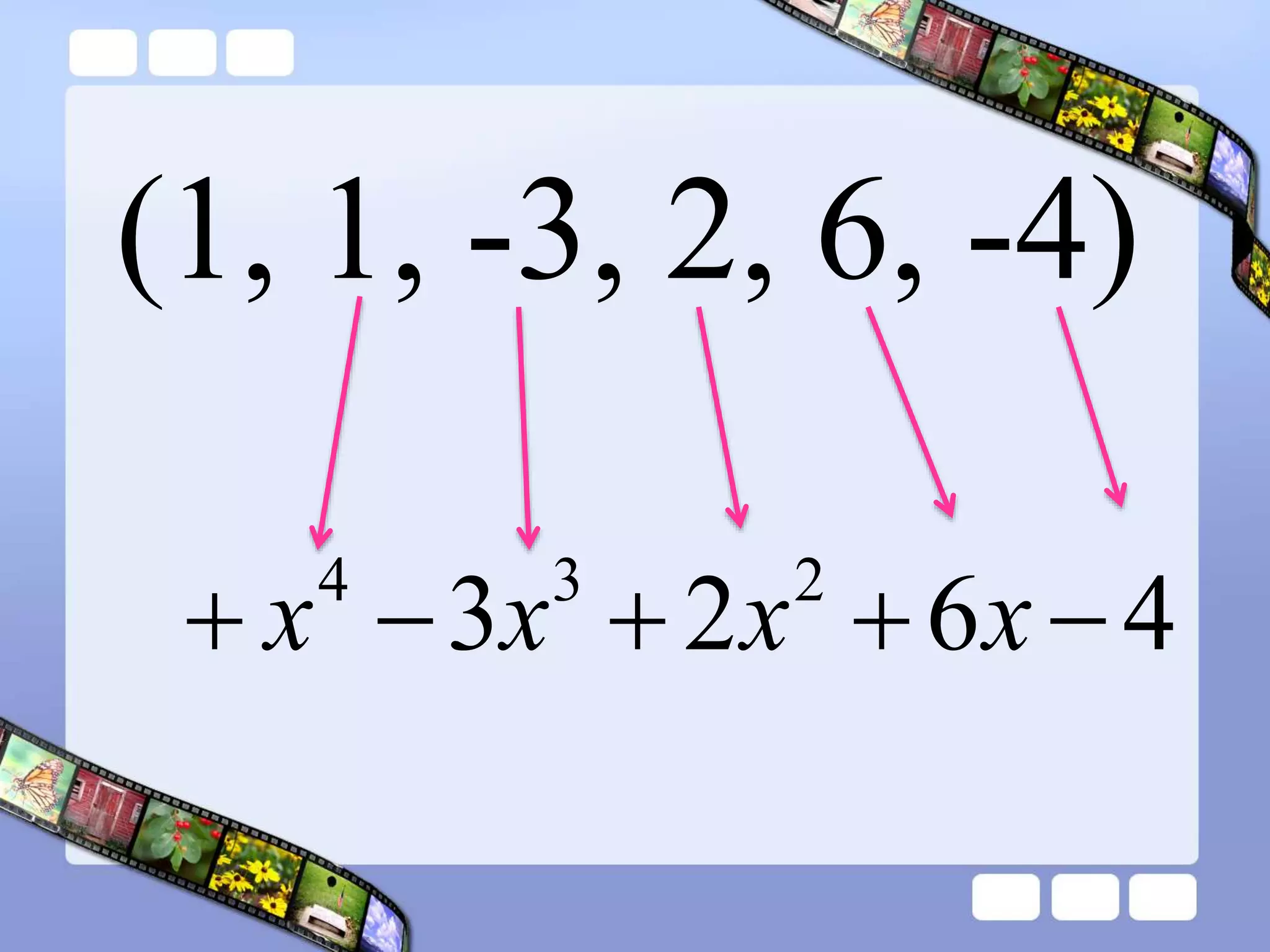
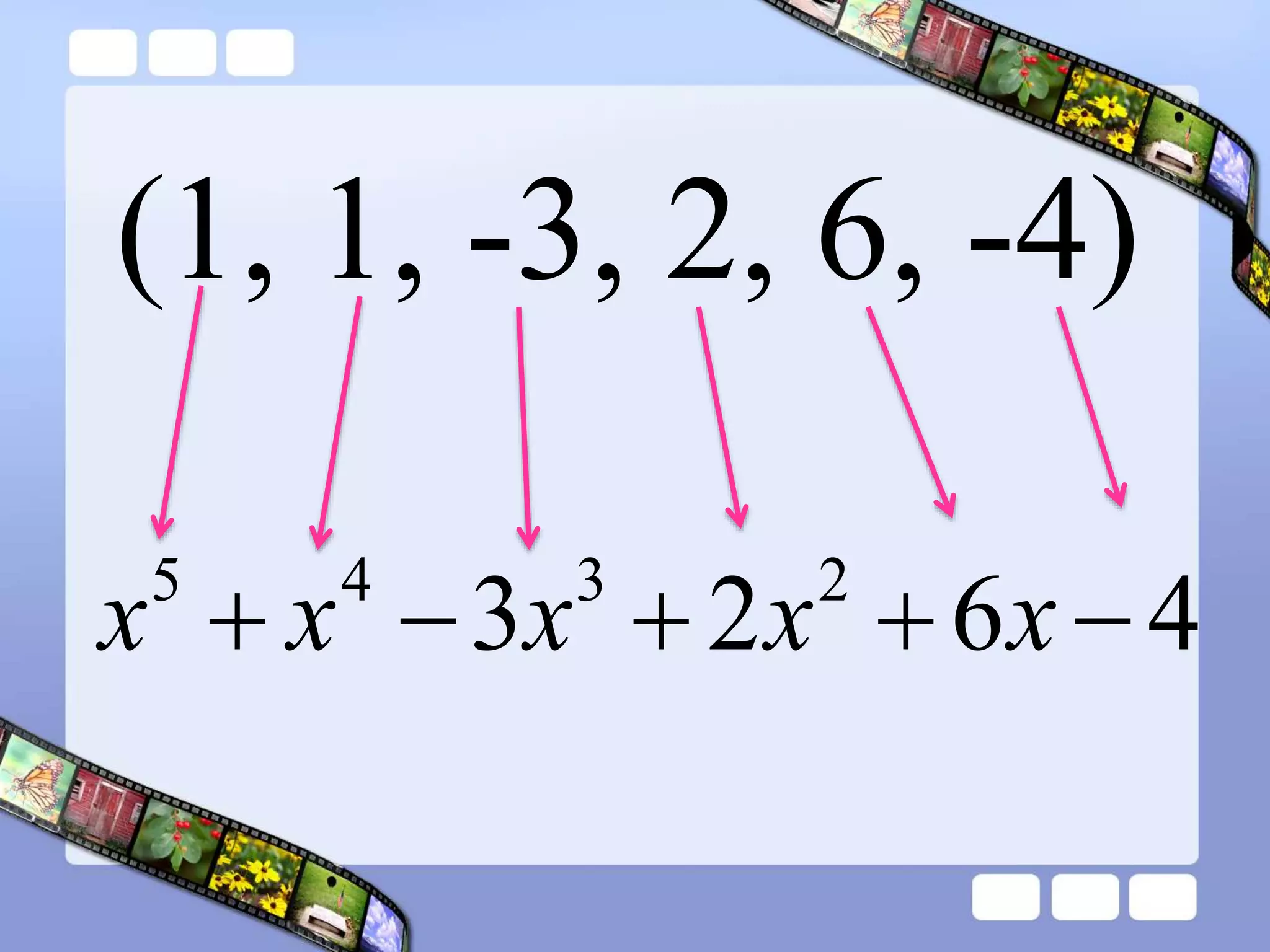
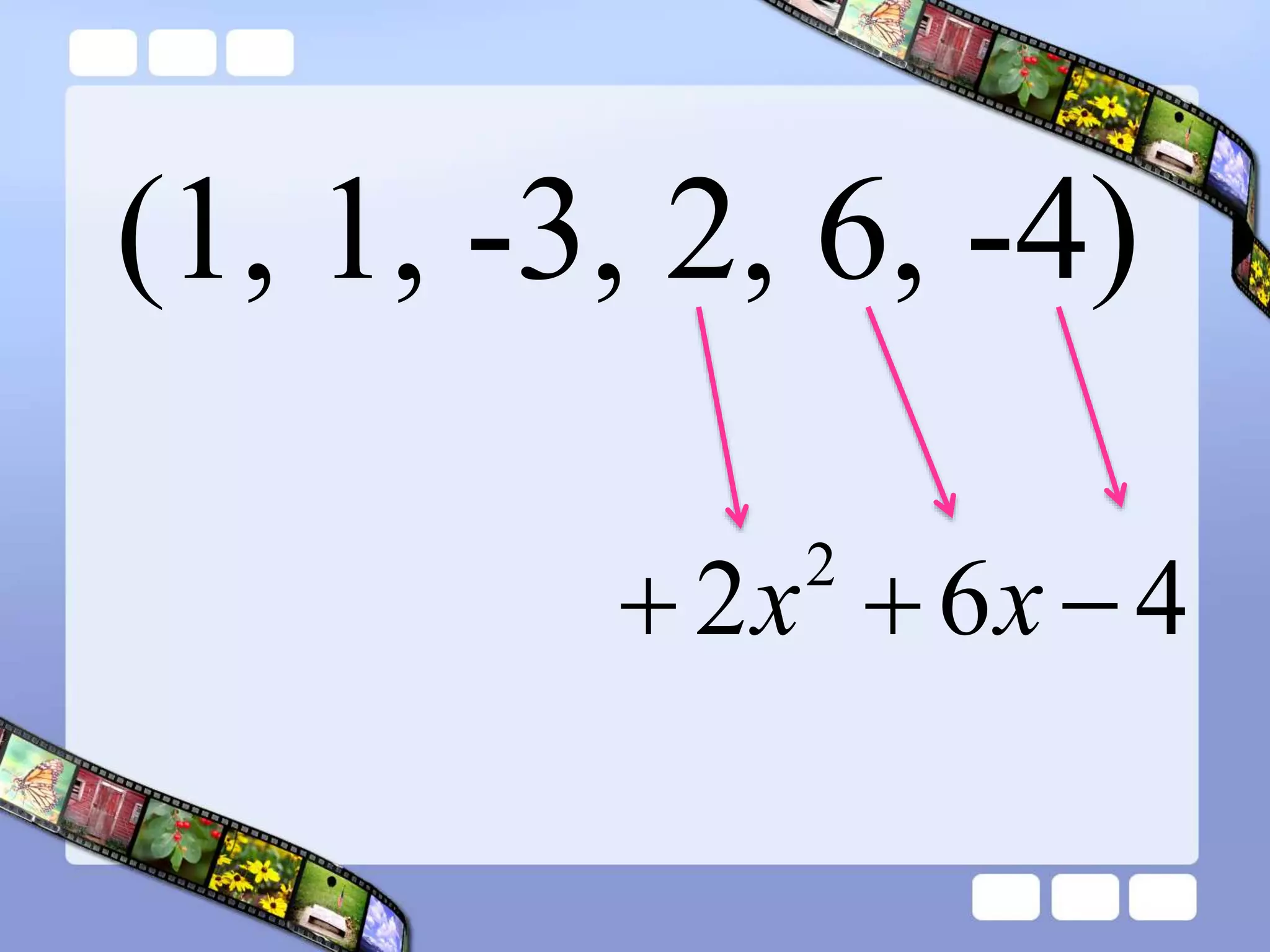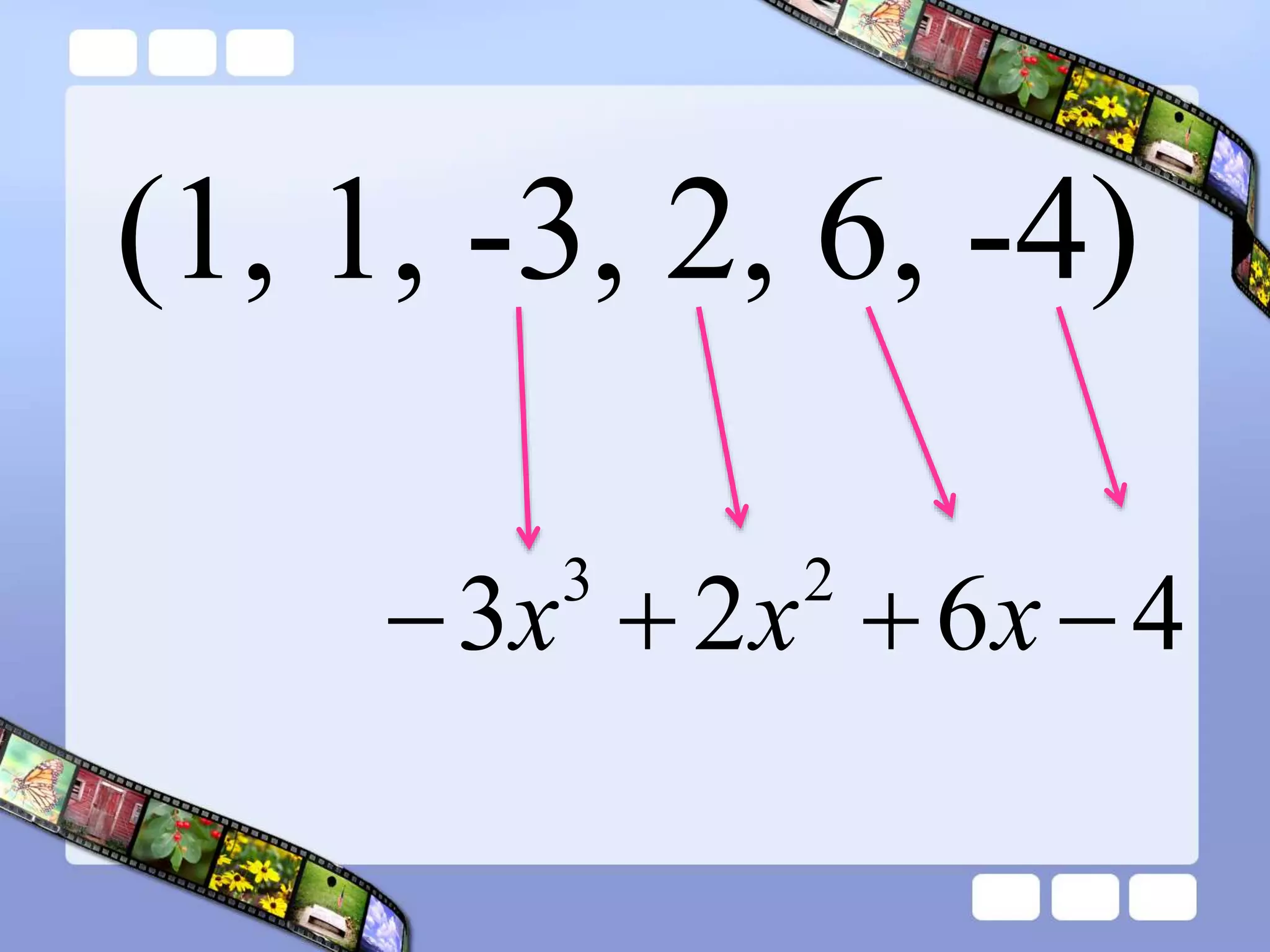The document presents the steps of lattice multiplication to multiply whole numbers, decimals, and polynomials. It begins by explaining that lattice multiplication breaks down the traditional long multiplication method into smaller steps by using a grid. For whole number multiplication, the steps are to draw a grid with rows and columns equal to the number of digits in the factors, write the factors in the grid, multiply pairs of digits and record partial products in the grid, and sum the products along the diagonals. The same process is used for decimal multiplication. For polynomial multiplication, the coefficients of the factors determine the grid size, each term is multiplied out, and the results are combined into a polynomial. Examples are provided to demonstrate the lattice multiplication process.