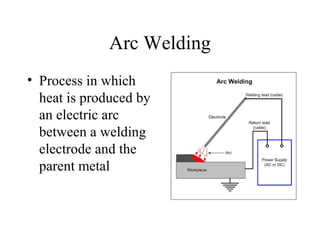
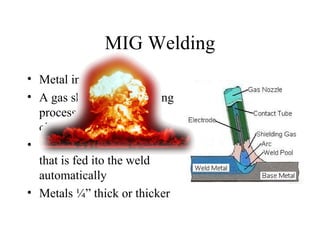
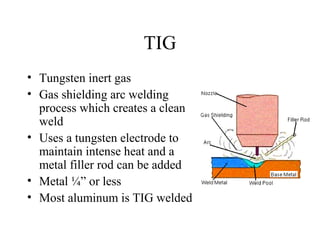
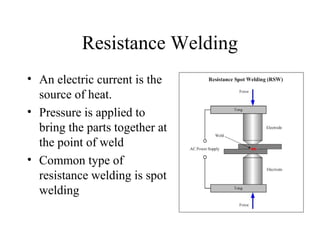
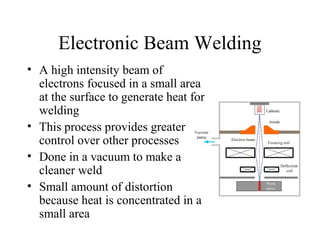
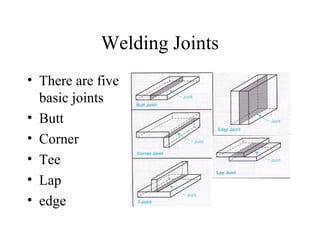
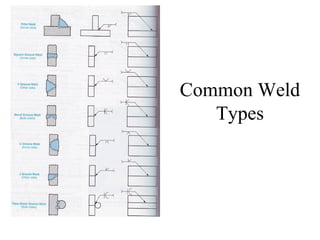
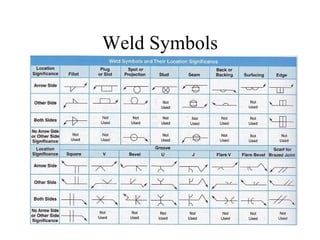
Welding is a process that joins metals through heating and melting. There are several types of welding processes including brazing, oxyfuel gas welding, arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, resistance welding, and electronic beam welding. Each process varies in how heat is generated and applied. Common welding joints include butt, corner, tee, lap, and edge joints. Weld symbols are used to indicate welding specifications and requirements on technical drawings.