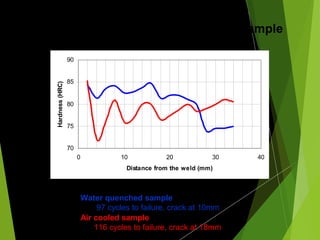
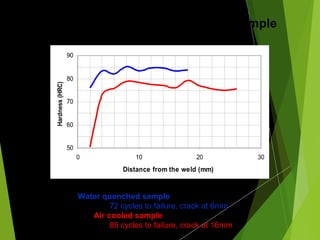
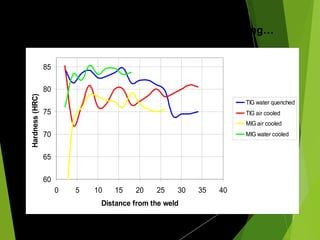
The document analyzes the heat affected zone (HAZ) resulting from three types of welding (TIG, MIG, gas welding) and two cooling methods (air cooling and water quenching) on low carbon steel. It finds that TIG welding results in the strongest welds with good hardness and ductility, while MIG welding provides slightly harder yet less ductile welds; gas welding produces weak welds with insufficient strength. Additionally, water quenching generally increases hardness but may introduce cracks closer to the weld compared to air cooling.