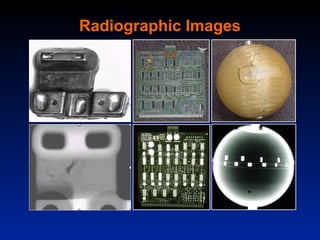
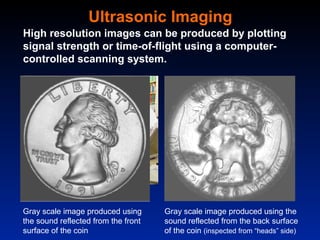
This document provides an introduction to nondestructive testing (NDT) methods. It discusses the most common NDT methods including visual inspection, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and radiography. It then provides examples of how these methods are used across various industries to inspect products and structures during manufacturing and in-service without causing damage. Applications discussed include inspecting aircraft, bridges, pipelines, power plants, storage tanks, and more.