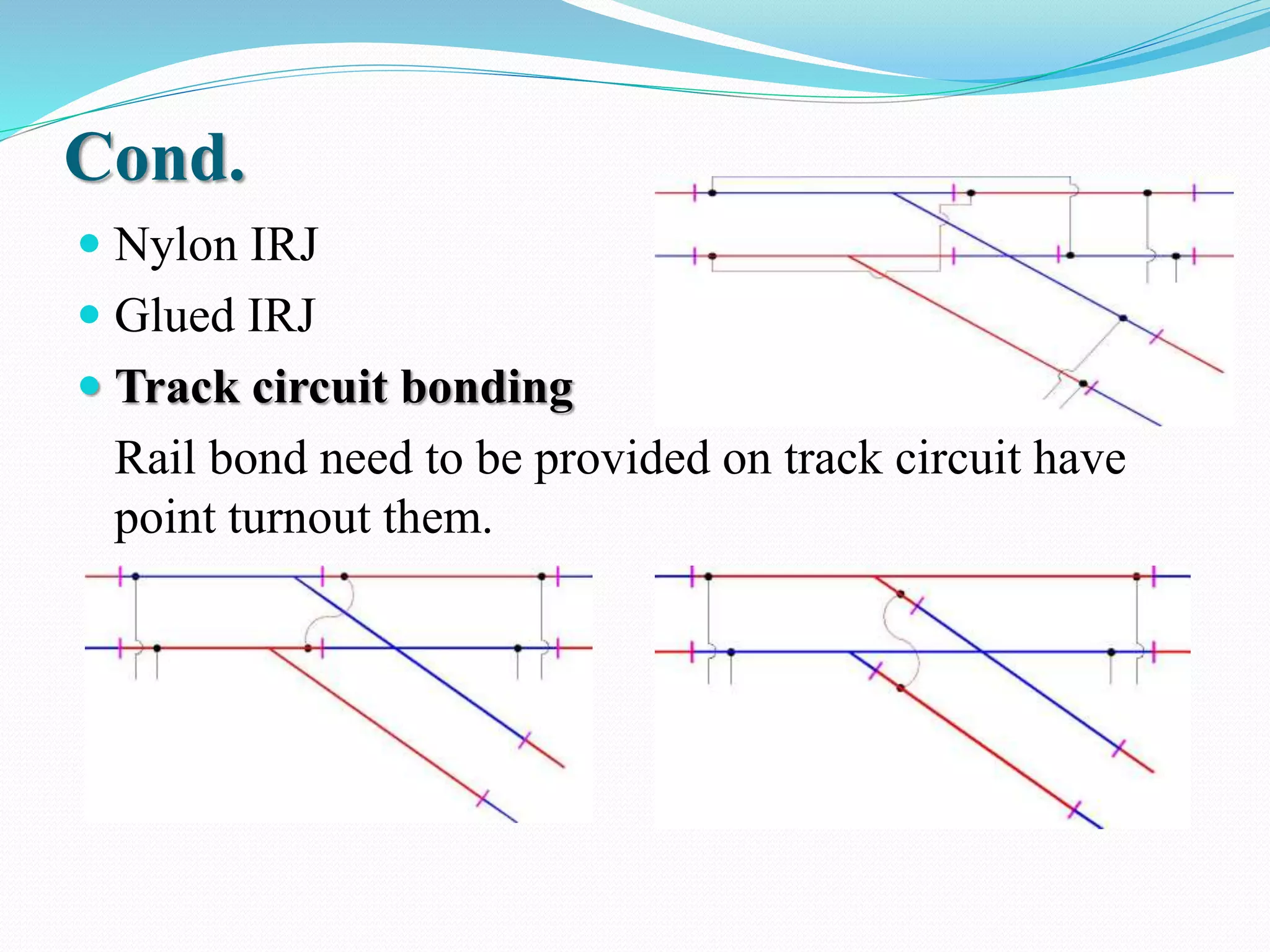
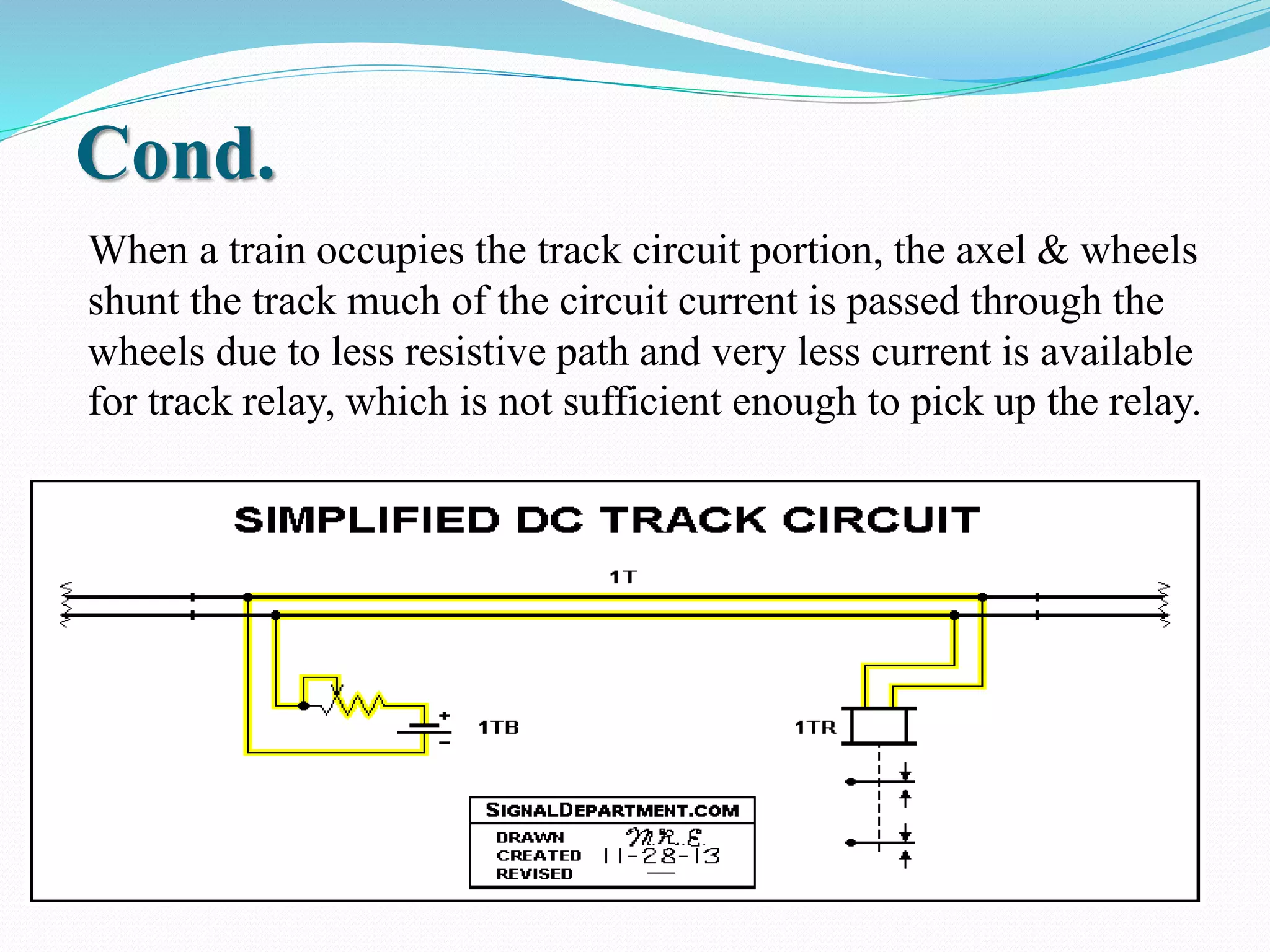
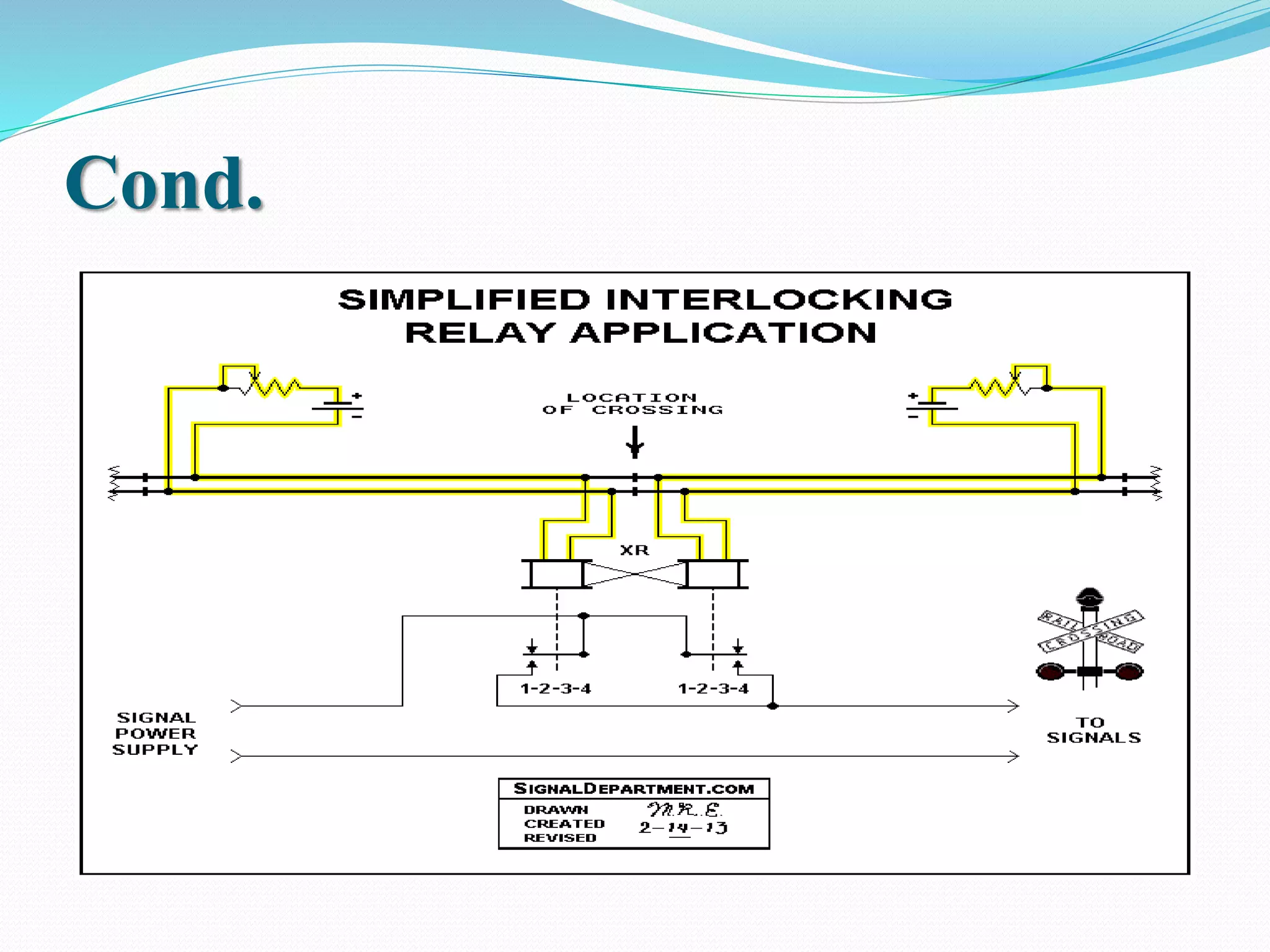
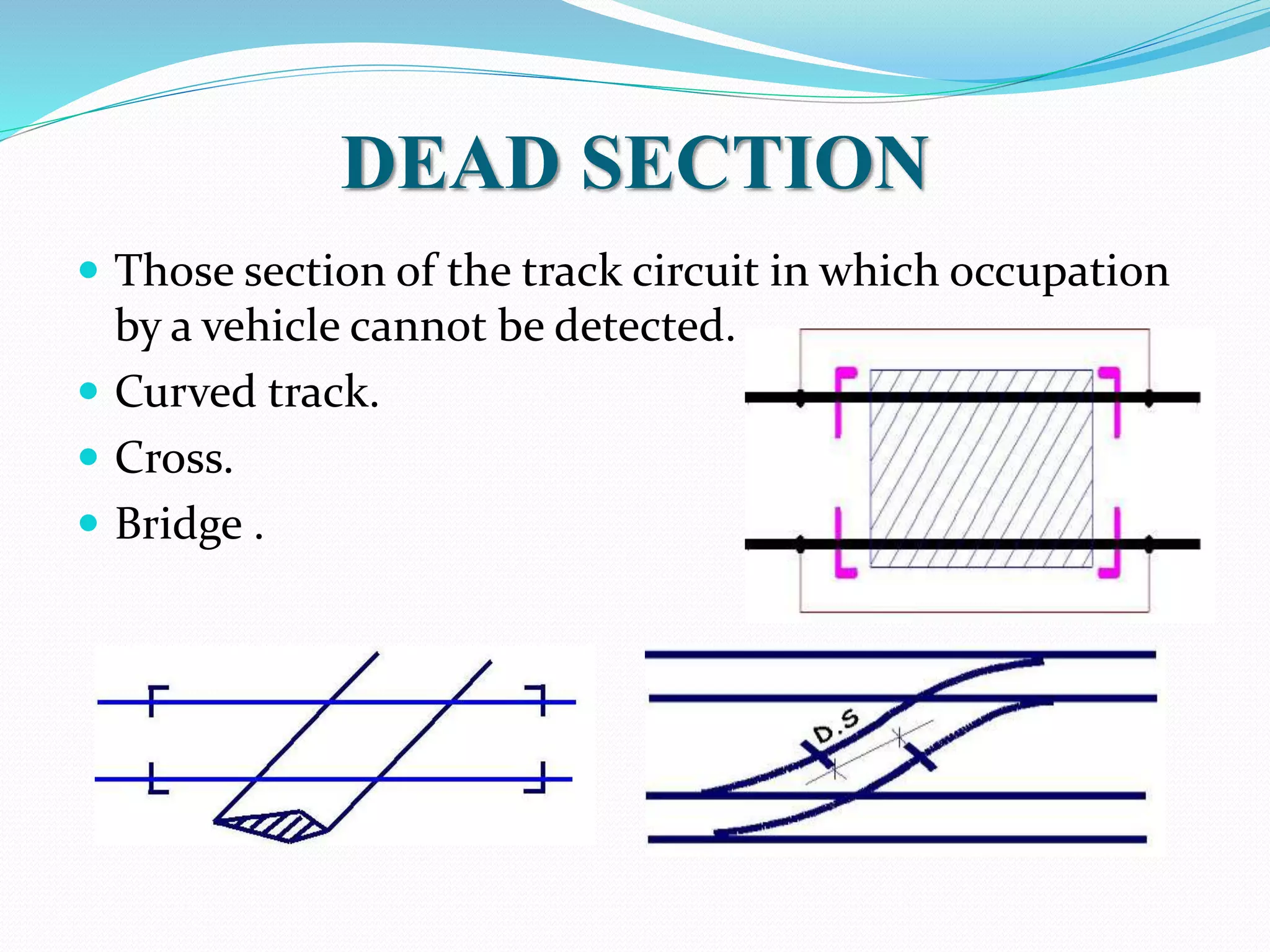
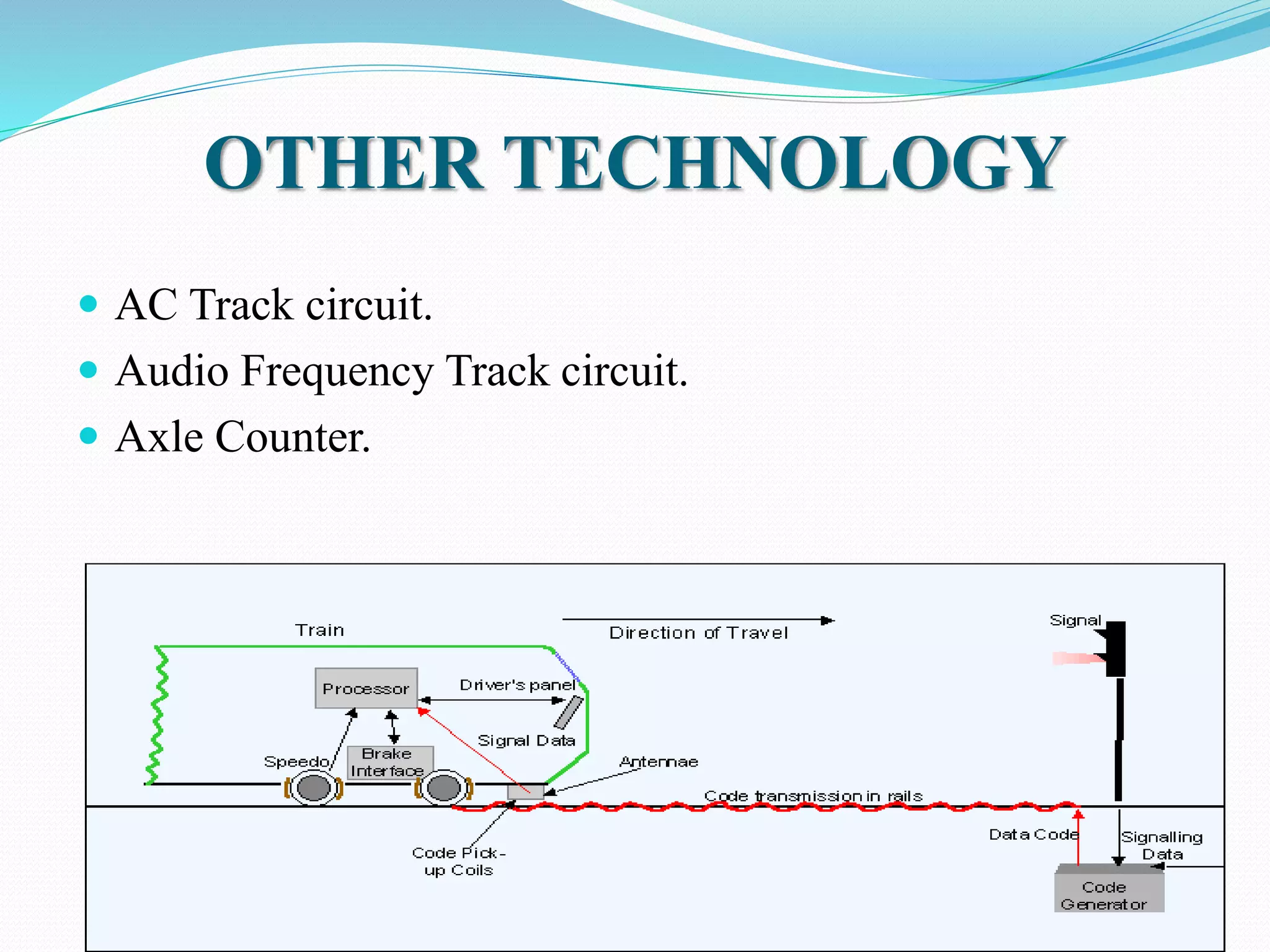
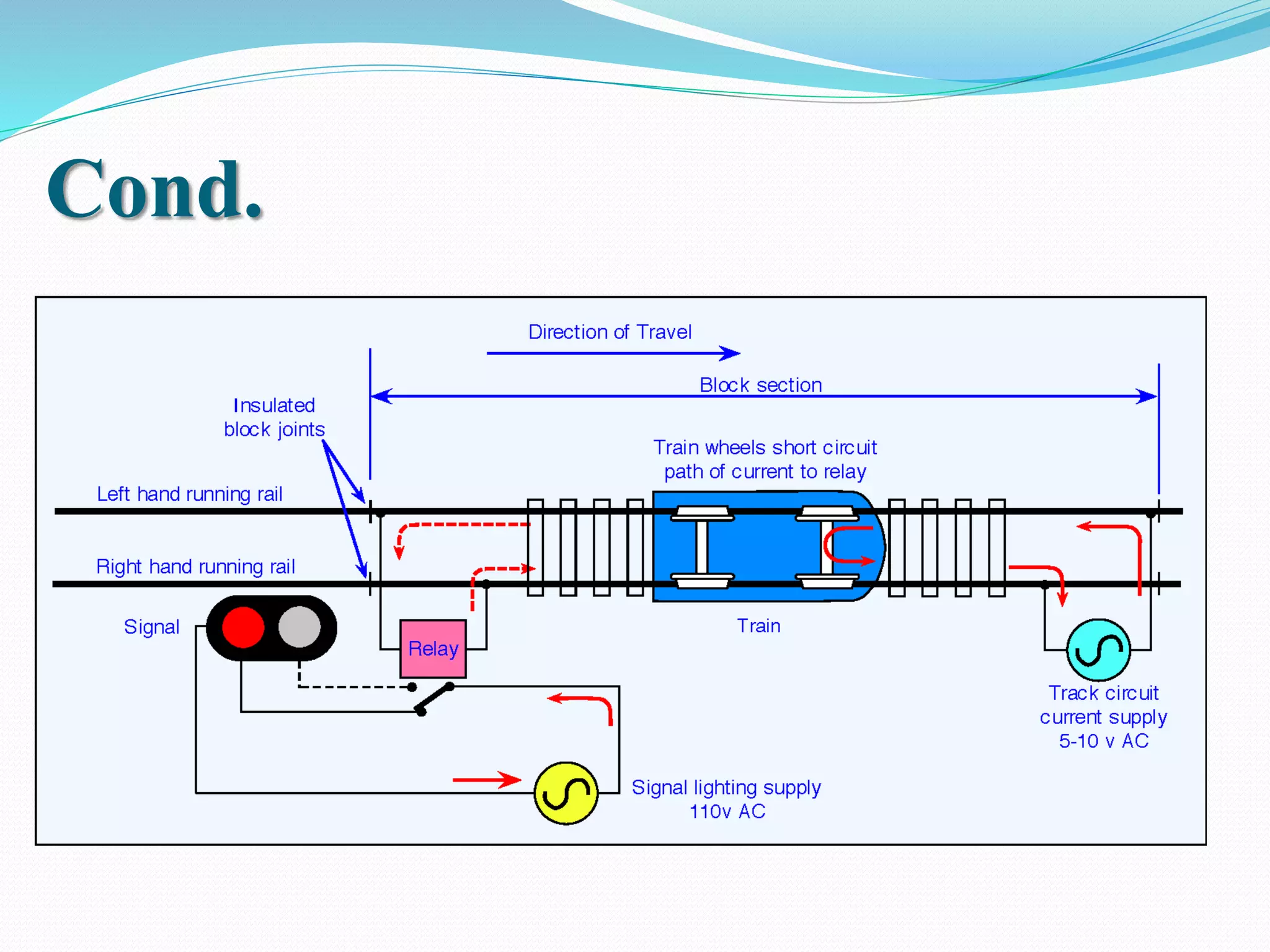
This document outlines the components, working, and applications of track circuits used in rail signaling. Track circuits use batteries, track relays, and adjustable resistances to detect train occupancy through changes in electrical current flow. Insulated rail joints are also used to isolate adjacent track circuits. When unoccupied, current flows through the track relay keeping it energized, but when a train is present its wheels shunt most of the current, causing the relay to deactivate. Track circuits allow signals to display red only when a track segment ahead is occupied by a train.