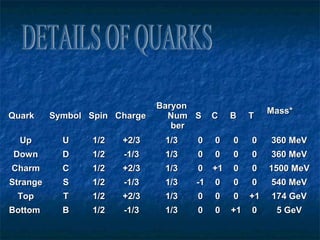
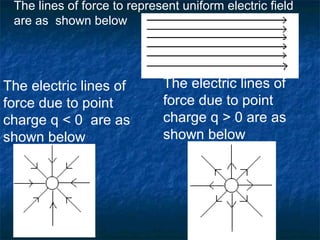
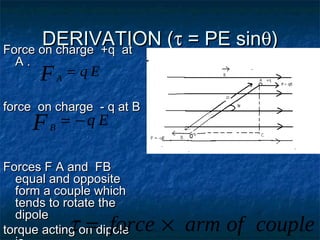
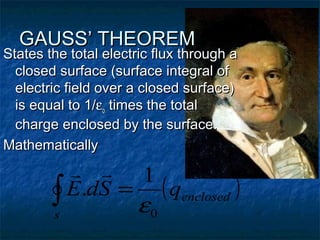
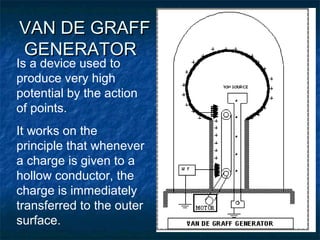
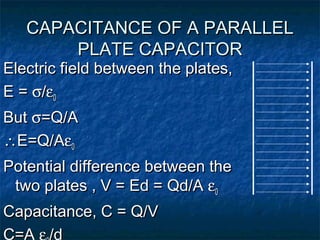
This document discusses electrostatics and defines key concepts in the field. It begins by defining electrostatics as the branch of physics dealing with charges at rest and their properties. It then provides a brief history, noting that static electricity was first observed by Thales of Miletus in 600 BC and that William Gilbert published the first systematic study of electrostatics in 1600. The document goes on to define concepts like electric charge, fields, dipoles, and flux, and laws such as conservation of charge and Gauss's law.