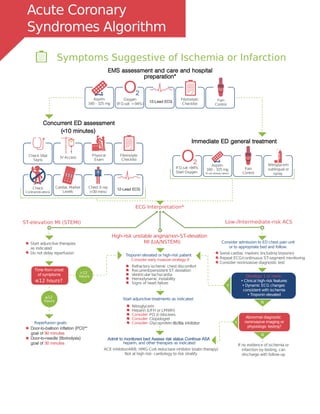
The document provides guidelines for treating cardiac arrest due to asystole or pulseless electrical activity (PEA). It outlines the pulseless arrest algorithm which involves checking the rhythm, performing CPR at 100 compressions per minute, establishing IV/IO access, administering epinephrine every 3-5 minutes, and treating potential reversible causes such as hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, tamponade, thrombosis, and toxins. For asystole, the priorities are high-quality CPR, identifying and correcting reversible causes, and considering termination of efforts if no electrical activity is present after initial treatment. For PEA, the best chance of return of spontaneous circulation is through quick treatment of reversible causes such
![Cardiac Arrest
Circular Algorithm
2 minutes
Drug Therapy
access
If VF/VT
Shock
Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response
Doses/Details for the Cardiac Arrest Algorithms
Drug Therapy
Return of Spontaneous
Circulation (ROSC)
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- Hydrogen ion (acidosis)
- Hypo-/Hyperkalemia
- Hypothermia
- Tension pneumothorax
- Tamponade, cardiac
- Toxins
- Thrombosis, pulmonary
- Thrombosis, coronary
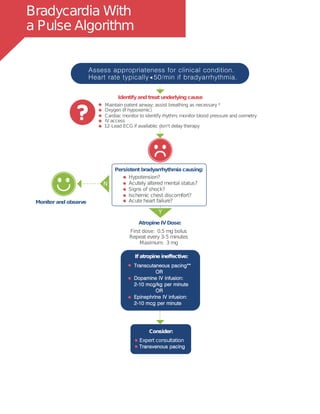
CPR Quality
Advanced Airway***
Supraglottic advanced airway or endotracheal intubation
Waveform capnography to confirm and monitor ET tube
placement
8-10 breaths per minute with continuous chest compressions
Epinephrine IV/IO Dose: 1 mg every 3-5 minutes
Vasopressin IV/IO Dose: 40 units can replace first or
second dose of epinephrine
Amiodarone IV/IO Dose**:First dose: 300 mg bolus.
second dose: 150 mg
Reversible Causes
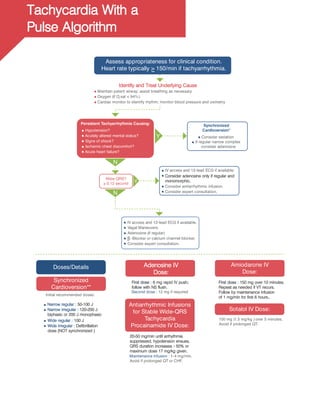
Shock Energy
Biphasic: Manufacturer recommendation (eg, initial dose of
120-200 J): if unknown, use maximum available.
Second and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and
higher doses may be considered
Monophasic: 360 J
CPRSTART
Push hard ( 2 inches [5cm]) and fast ( 100/min) and allow
complete chest recoil.
Minimize interruptions in compressions.*
Avoid excessive ventilation
Rotate compressor every 2 minutes
If no advanced airway, 30:2 compression-ventilation ratio
Quantitative waveform capnography
If PETCO2 10mm Hg, attempt to improve CPR quality
Intra-arterial pressure
If relaxation phase (diastolic) pressure
20 mm Hg, attempt to improve CPR quality.
Pulse and blood pressure
Abrupt sustained increase in PETCO2 (typically
40 mm Hg)
Spontaneous arterial pressure waves with intra-arterial
monitoring
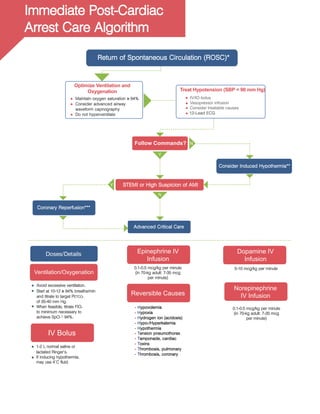
Post-Cardiac
Arrest Care
Circulation (ROSC)
Return of Spontaneous
Check
Rhythm
Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorGive Oxygen
Epinephrine every 3-5 minutes
Amiodarone for refractory VF / VT
Consider Advanced Airway
Quantitative waveform capnography
Treat Reversible Causes
(c) ACLS Training Center 877-560-2940 support@acls.net(c)
Complete your ACLS recertification online with the highest quality courses at http://www.acls.net and use promo code PDF2014 during checkout for 15% off.
IV/IO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acls-150715144459-lva1-app6891/85/ACLS-algorithms-1-320.jpg)














![ALS Pharmacology Summary
Drugs indicated for use in Advanced Life Support cases[1]
Adenosine
(Adenocard)
15-30°C (59-86°F)
Do not refrigerate
Amiodarone
(Cordarone)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Protect from light
Atropine Sulfate
(Hospira Inc.)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Dopamine
(Dopamine HCl)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing.
Epinephrine
(EpiPen)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Protect from light. Do not refrigerate.
Lidocaine
(Xylocaine-MPF)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Protect from light.
Magnesium Sulfate
(Ansyr)[3]
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Vasopressin
(Desmopressin Acetate)
20-25°C (68-77°F)
Drug Storage[3]
Saline
(0.9% NaCl)[1]
25°C (77°F)
Administer 4°C (39°F) for
therapeutic hypothermia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acls-150715144459-lva1-app6891/85/ACLS-algorithms-21-320.jpg)