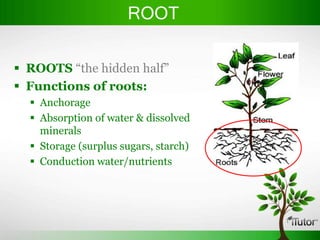
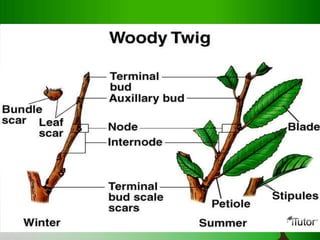
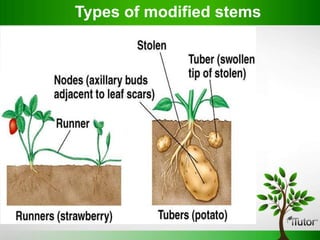
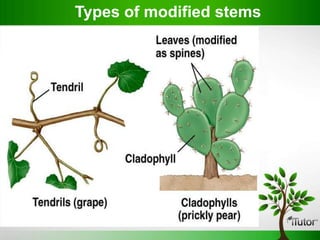
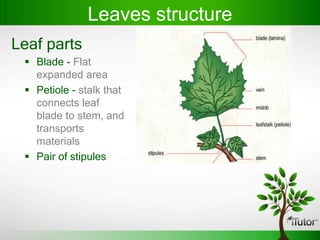
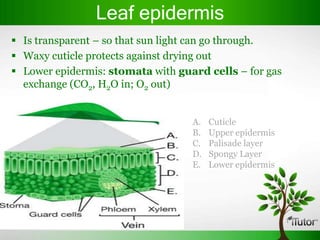
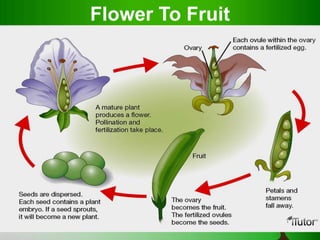
Plant organs include roots, stems, and leaves which are composed of tissues and serve specific functions. Roots function to anchor plants, absorb water and minerals, store food, and conduct fluids. Stems provide support, transport water and nutrients, and can store food. Leaves capture sunlight for photosynthesis. Flowers evolve from stems and leaves and produce fruits containing seeds.