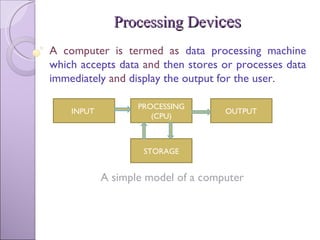
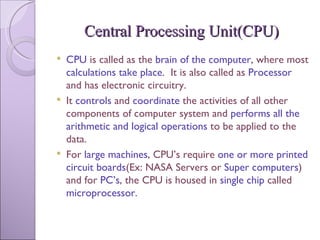
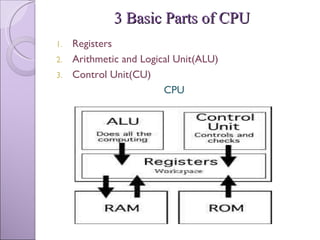
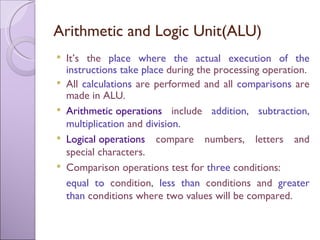
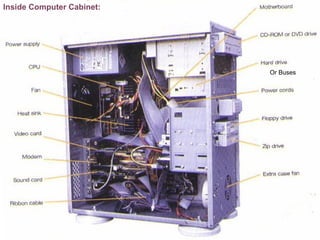
The document discusses processing devices and central processing units (CPUs). It describes a CPU as having three main parts: registers that hold information for processing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs calculations and comparisons, and a control unit that directs the system. The document outlines the evolution of CPUs from early chips like the Intel 4004 to modern multi-core processors. Buses connect the CPU and memory to transfer data and instructions for processing.