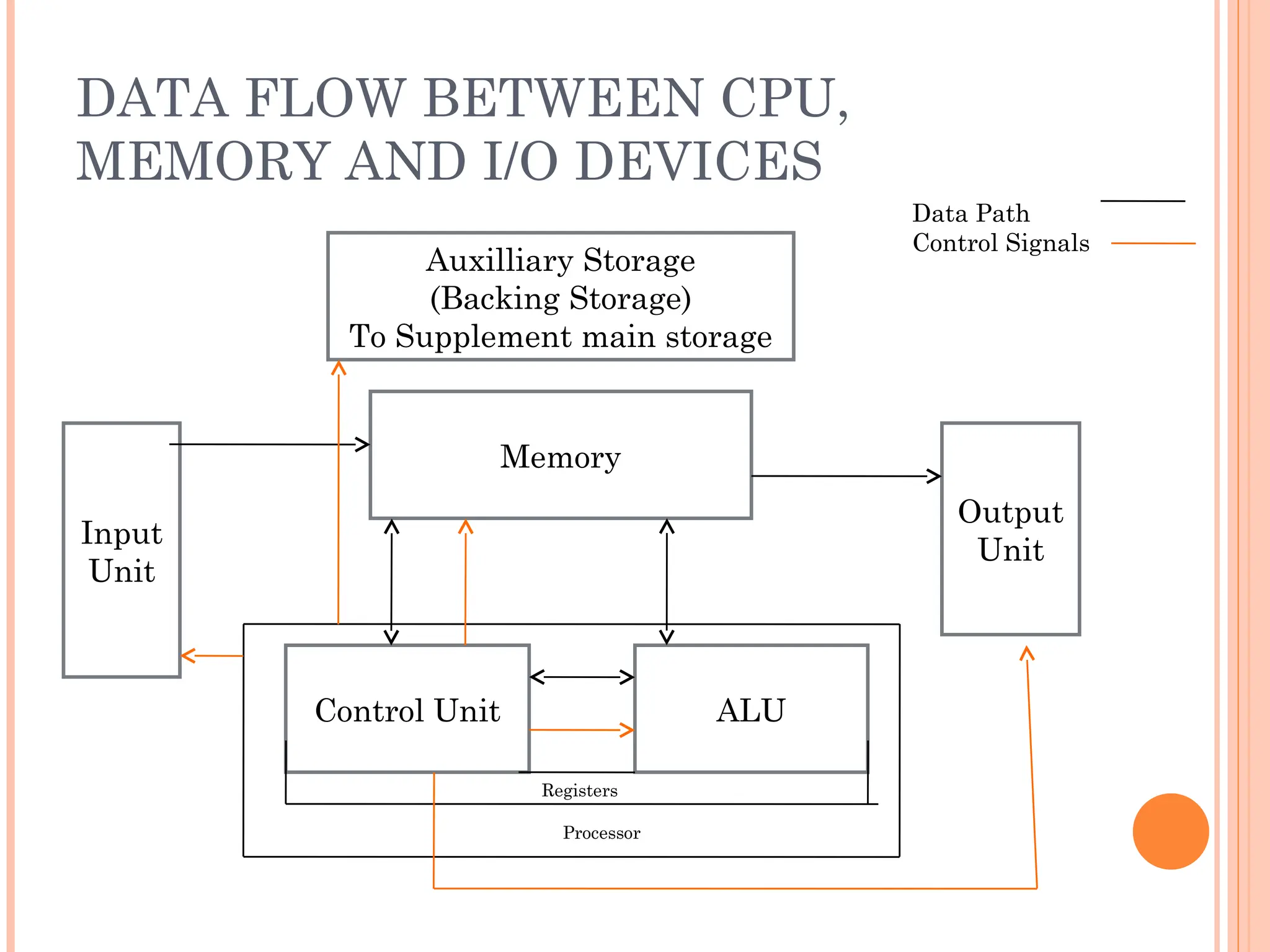
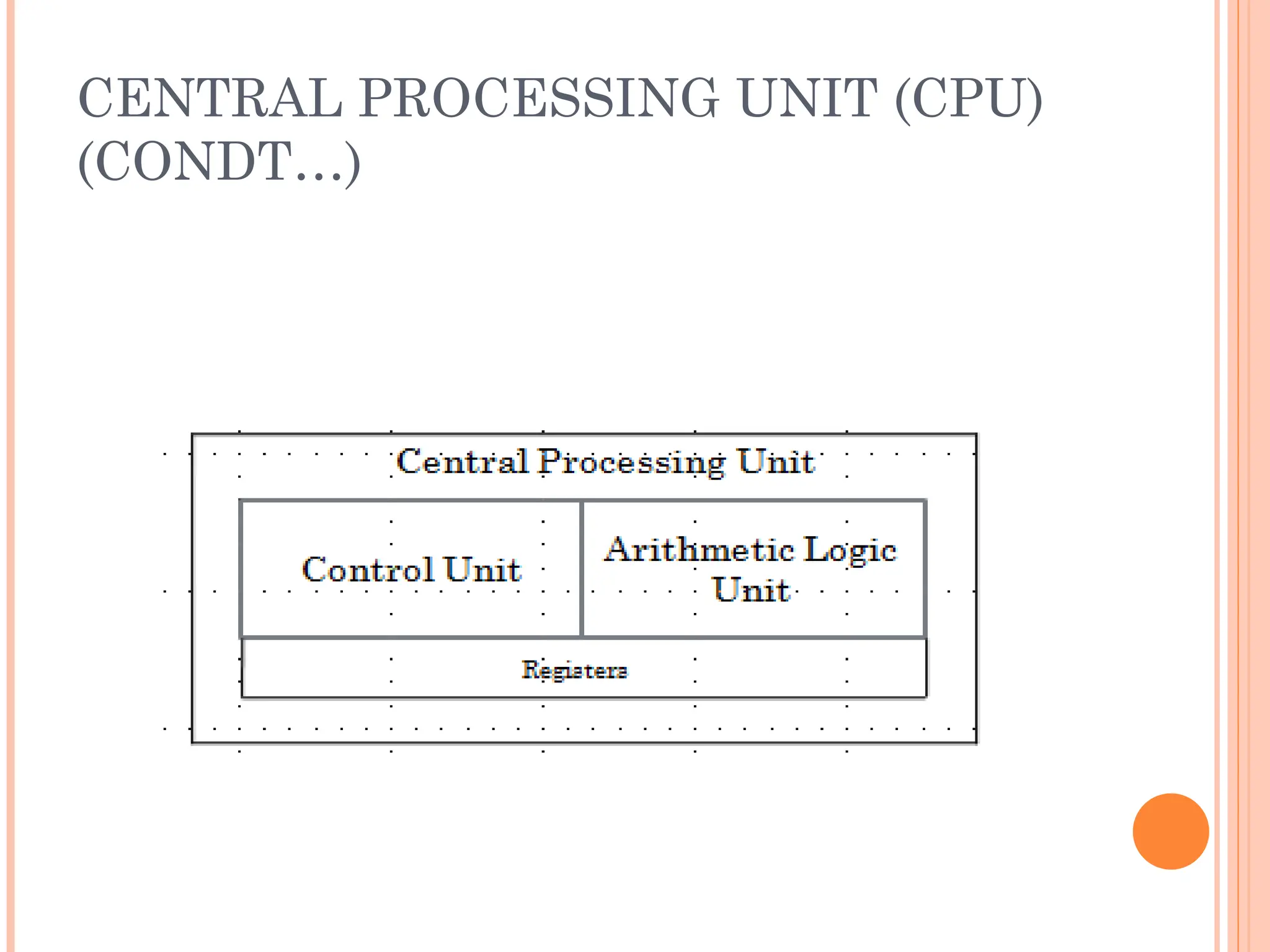
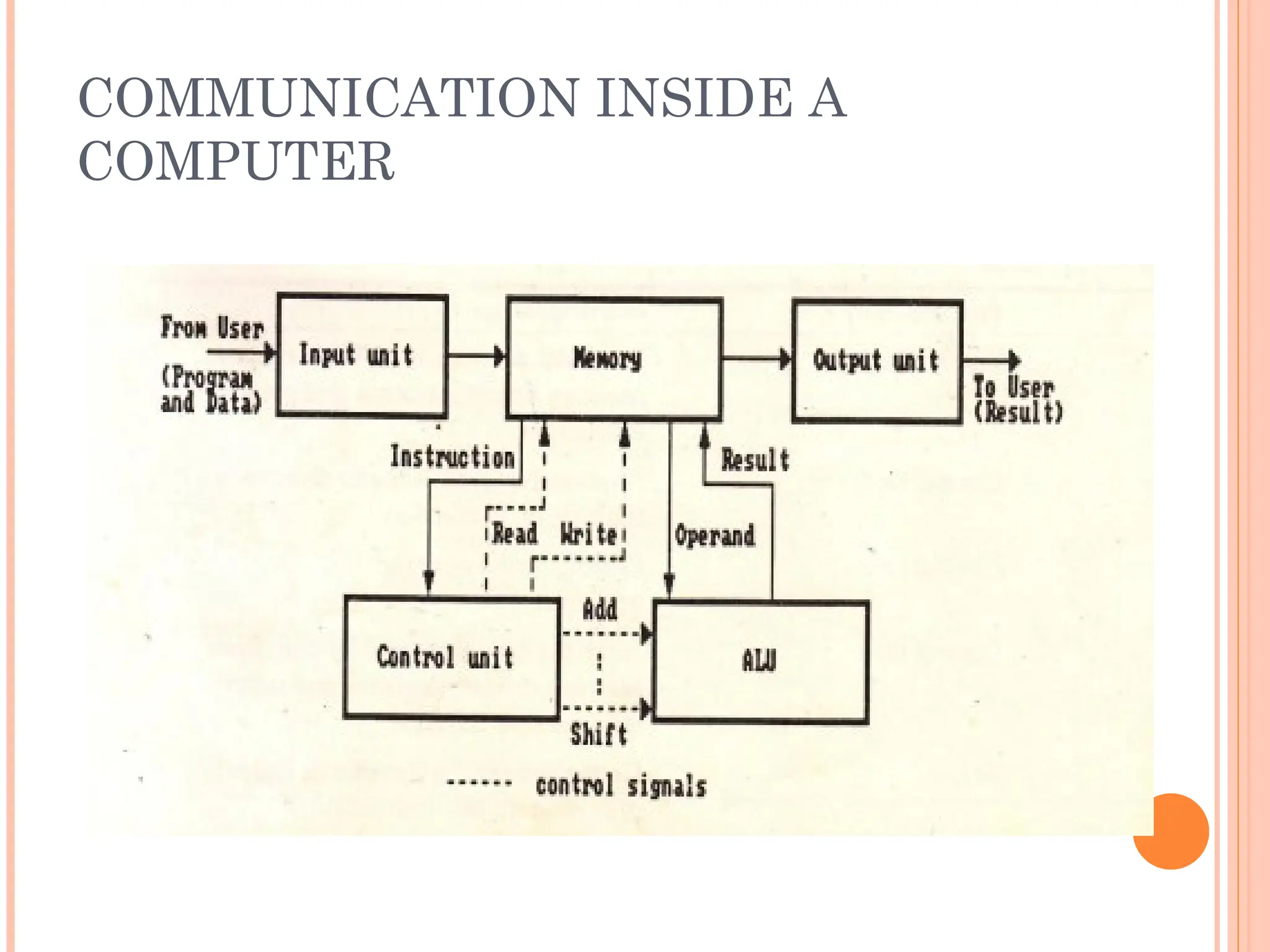
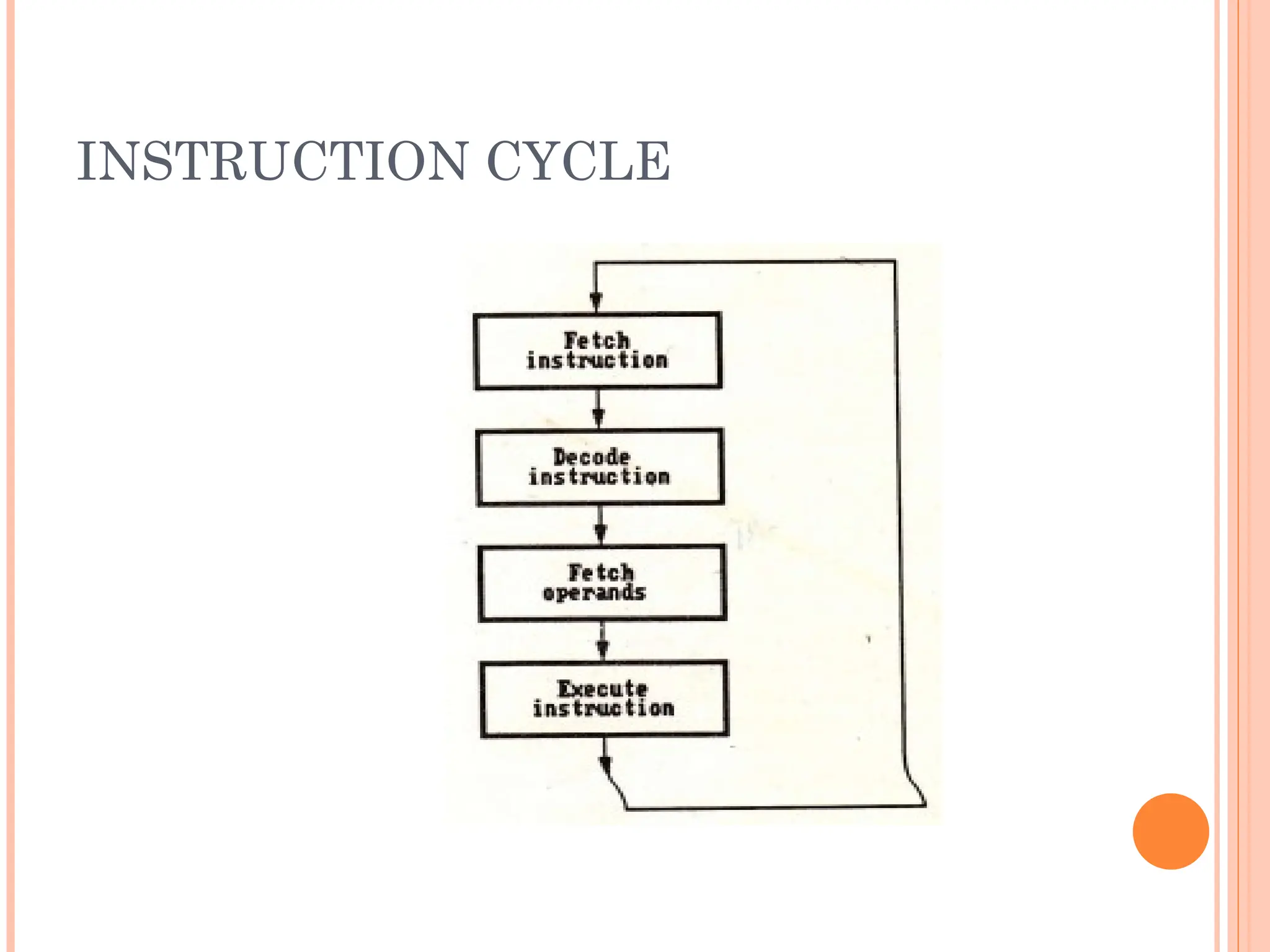
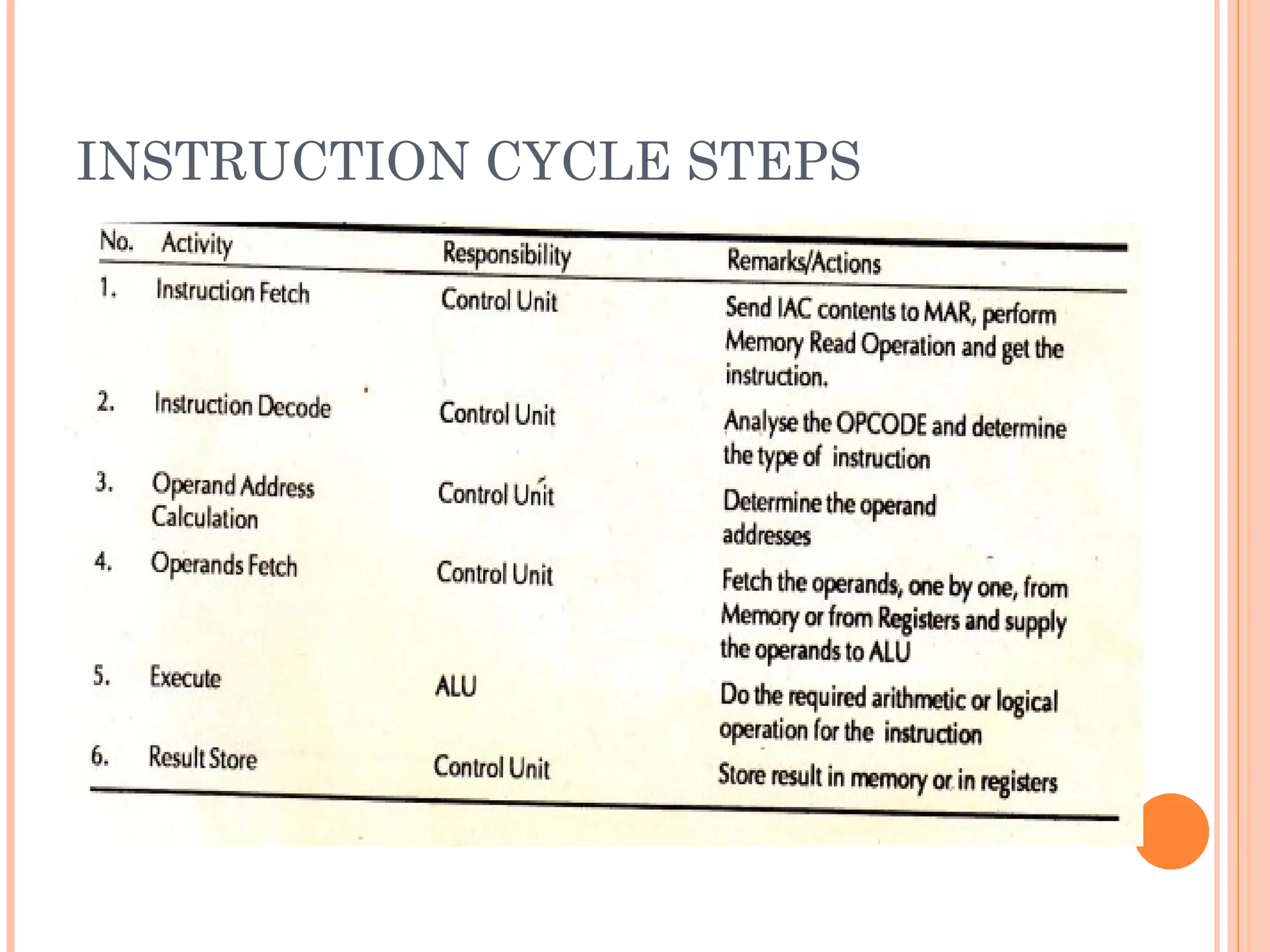
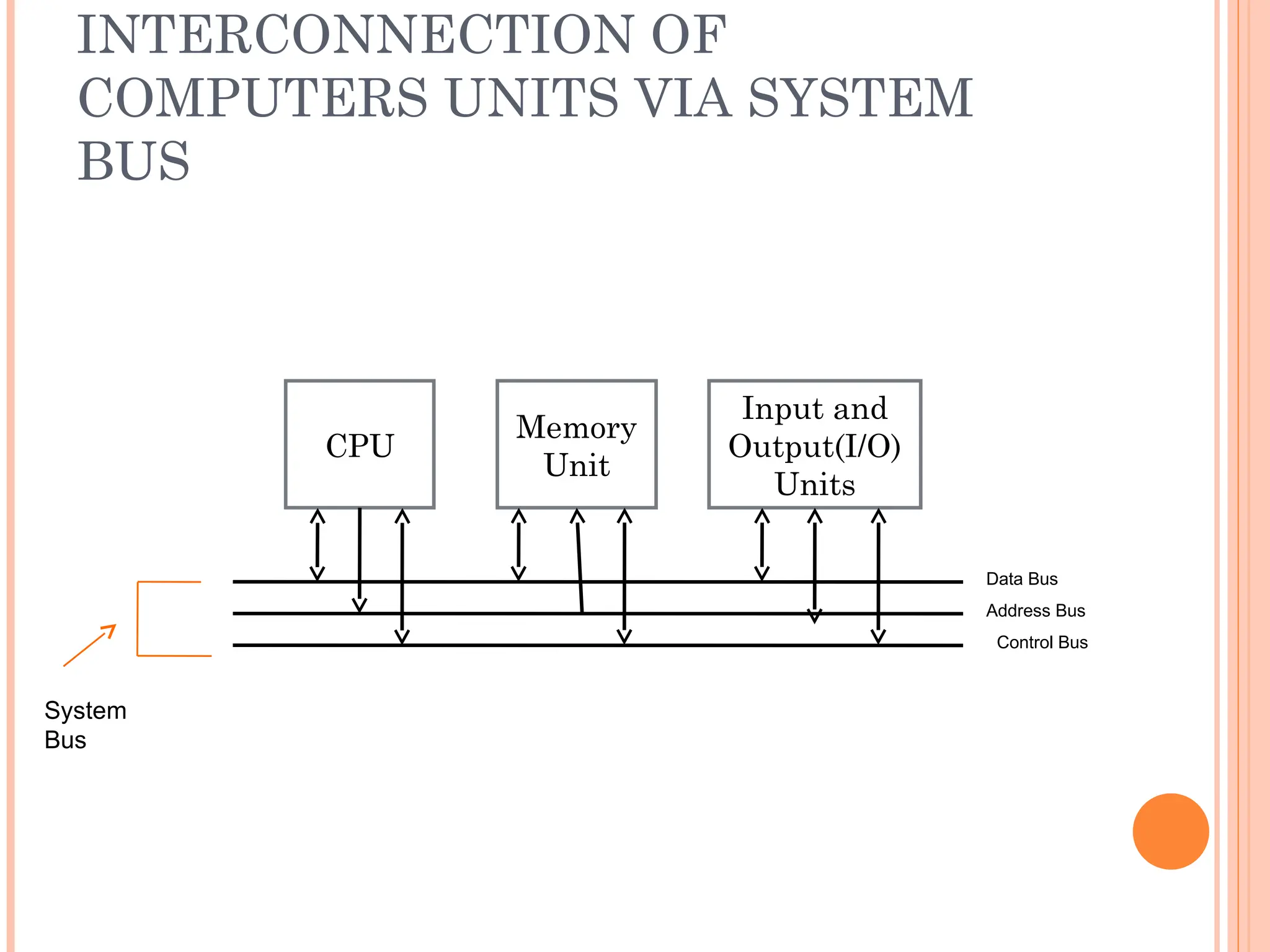
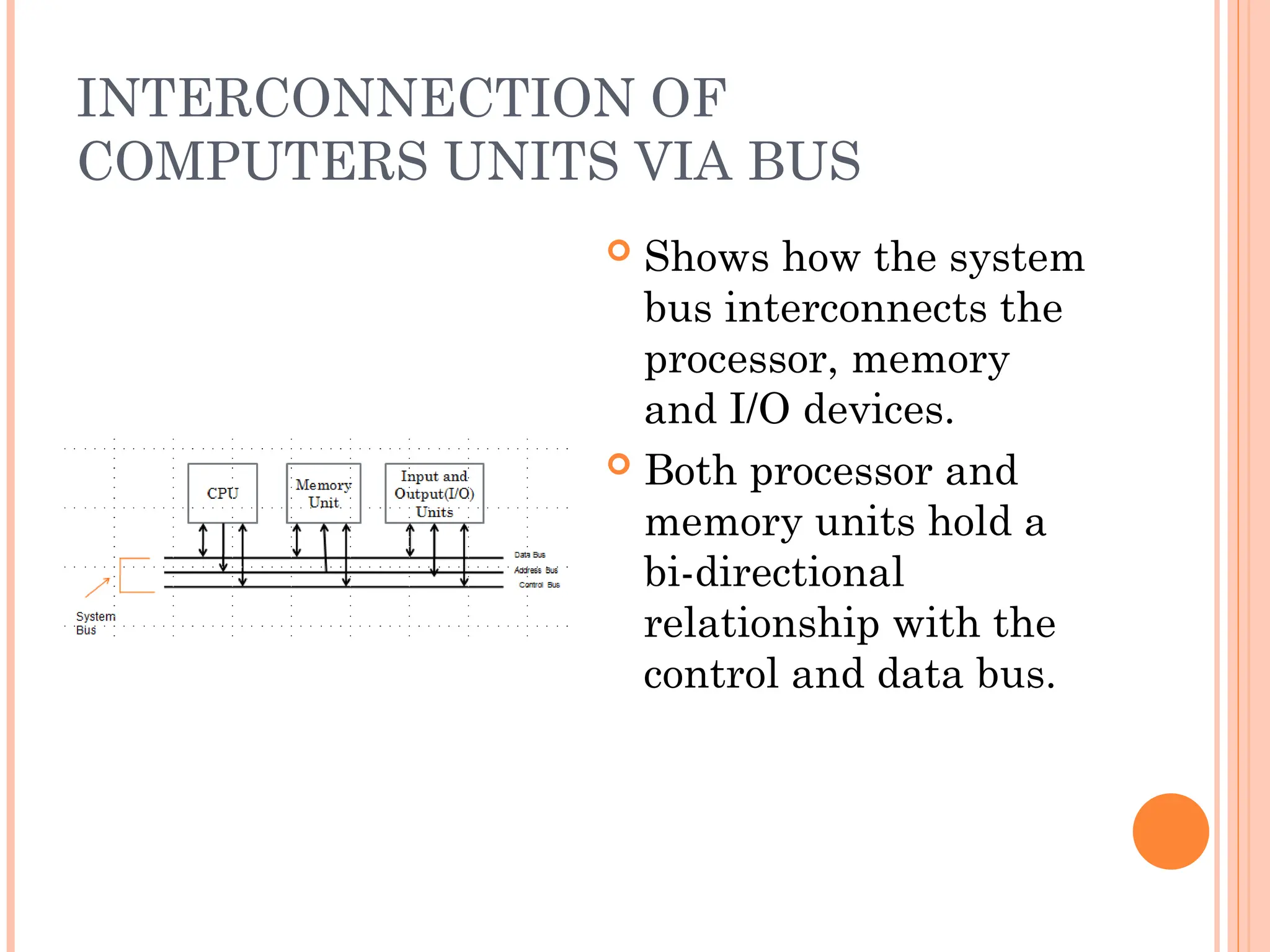
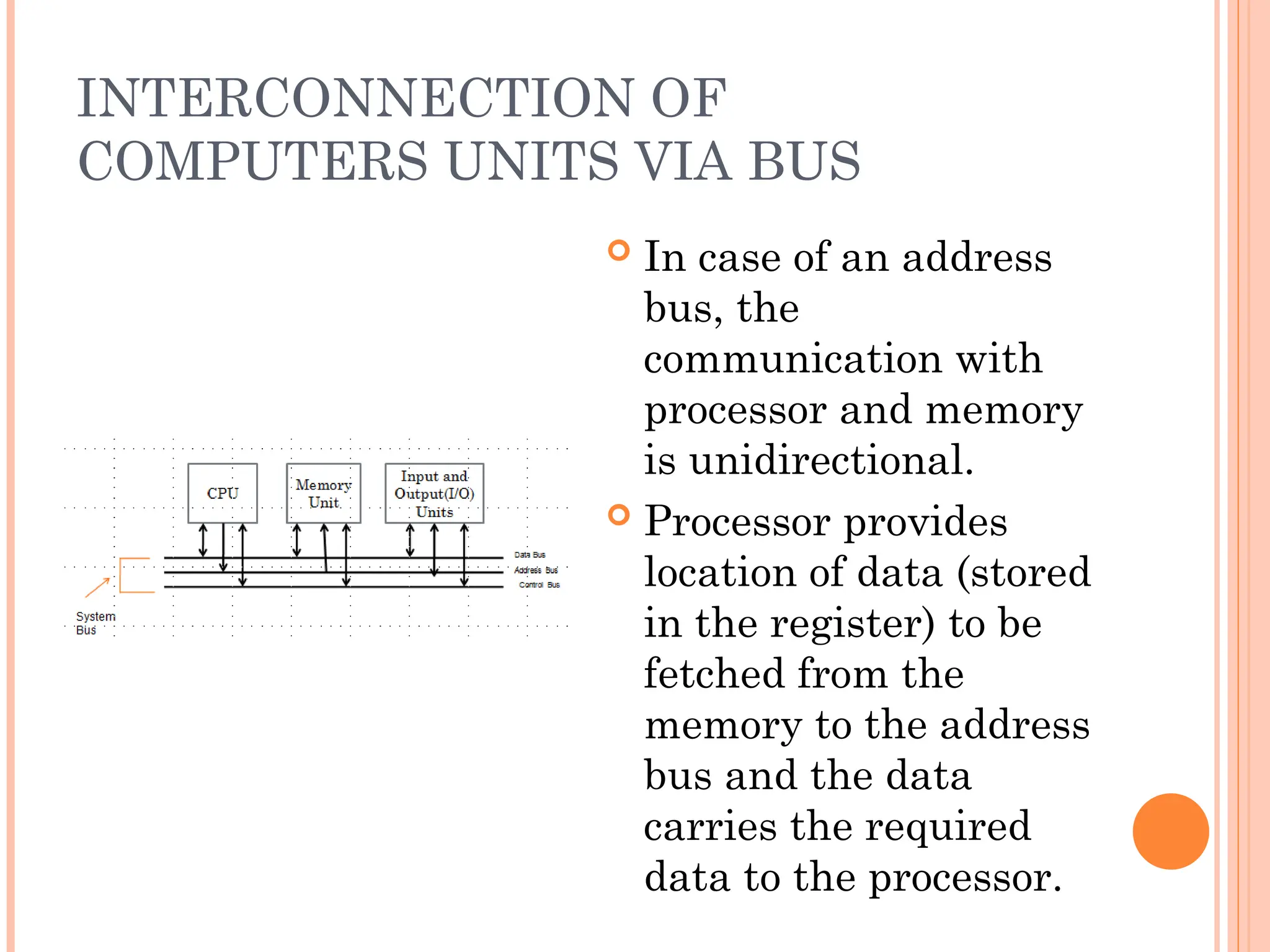
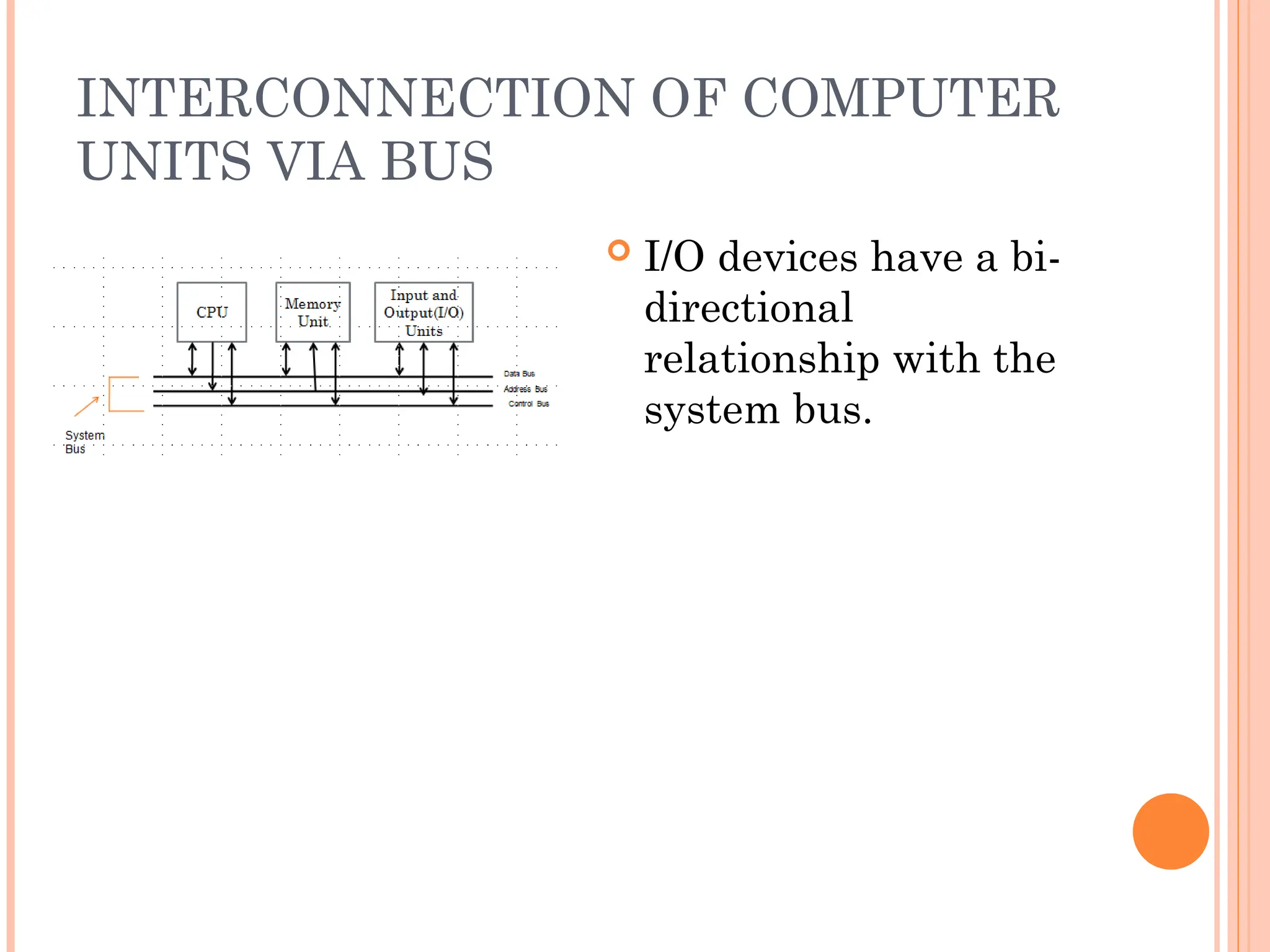
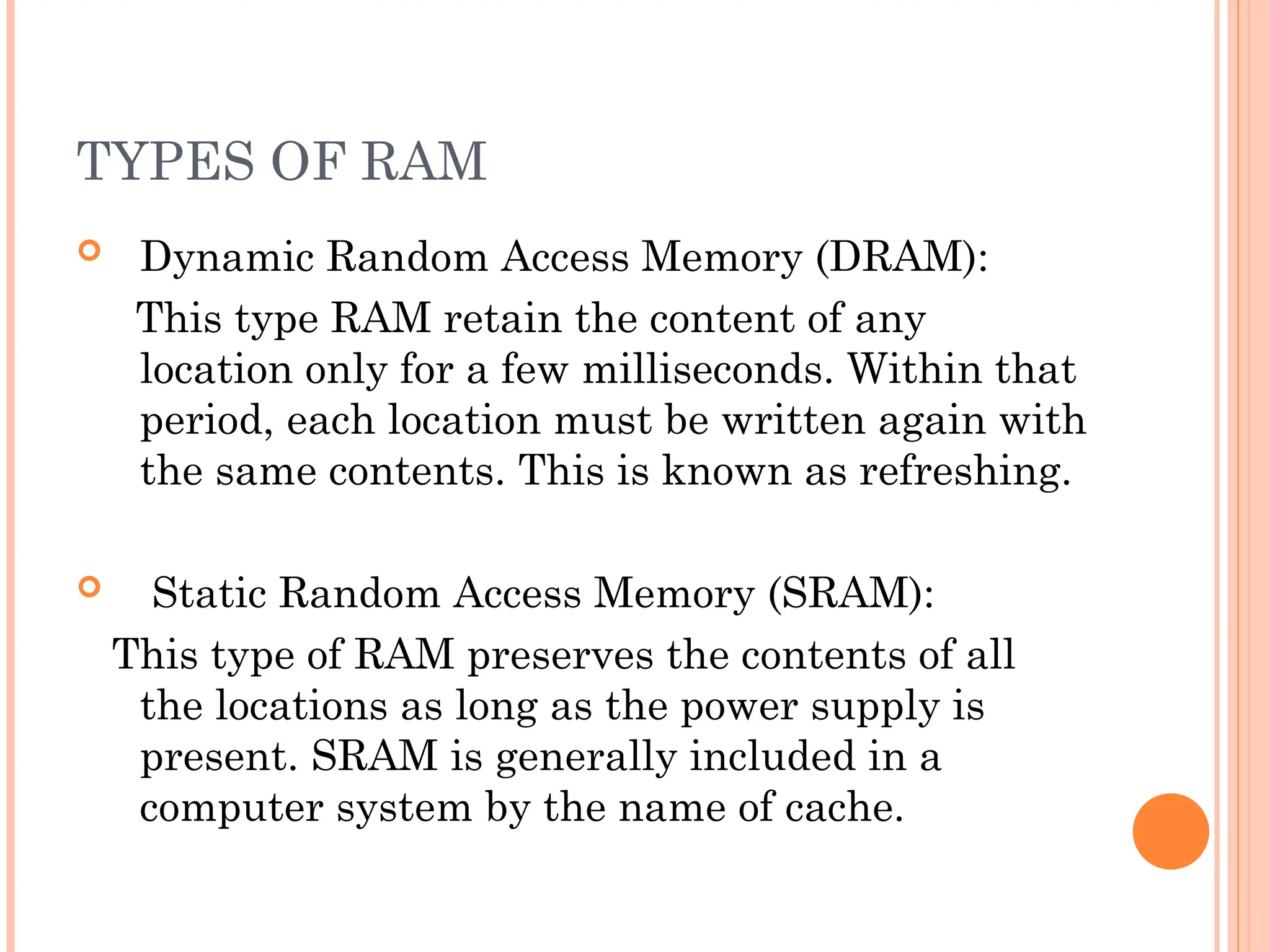
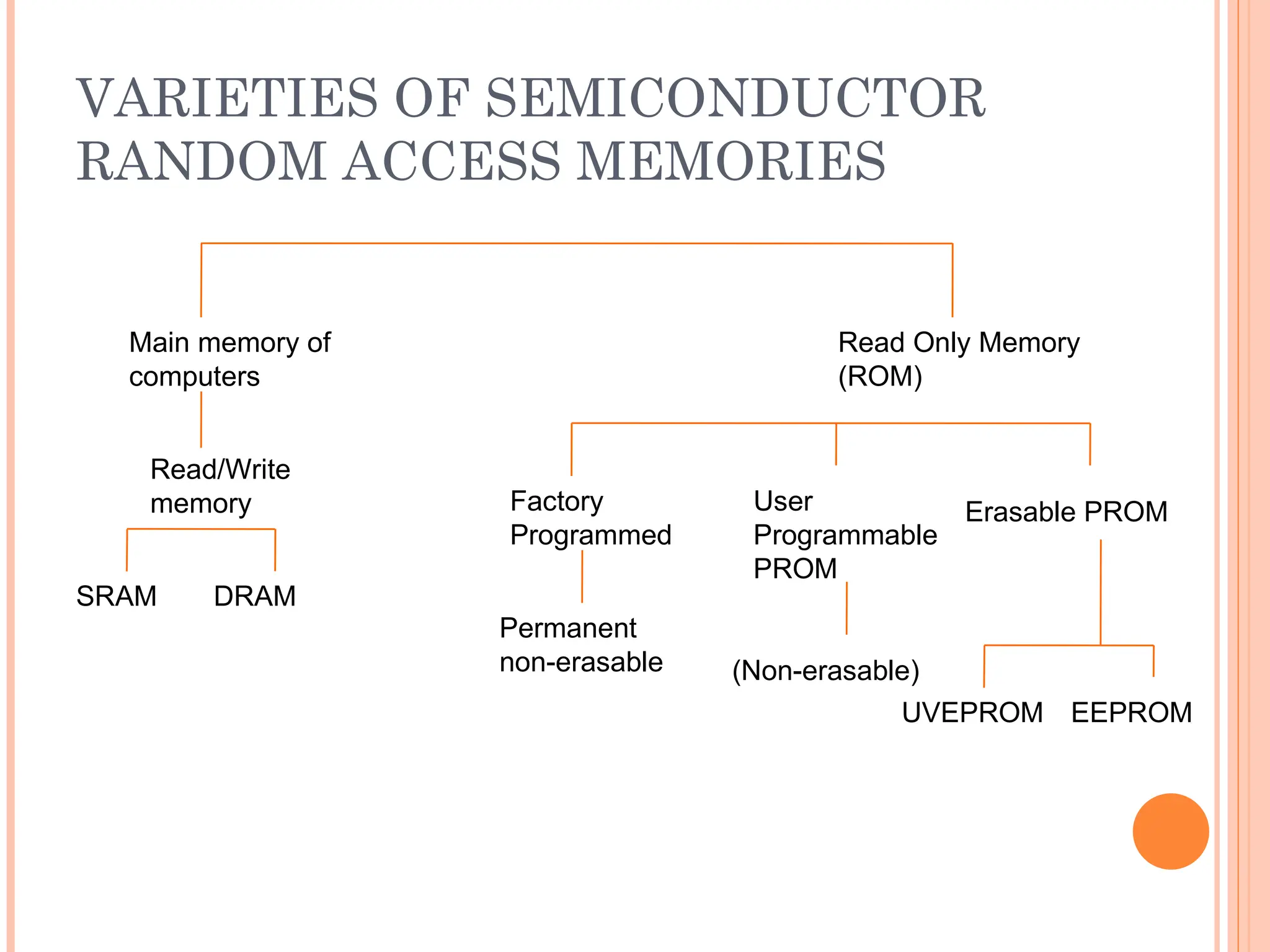
Computer organization and architecture involves selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create functional and efficient computers, centered around the central processing unit (CPU), which consists of the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers. The system bus, used for communication between the CPU, memory, and input/output units, plays a critical role in data transfer, while the instruction cycle defines the steps of fetching, decoding, executing, and storing instructions. Memory types such as RAM and ROM influence data storage and retrieval speed, impacting overall computer performance.