Embed presentation
Downloaded 852 times




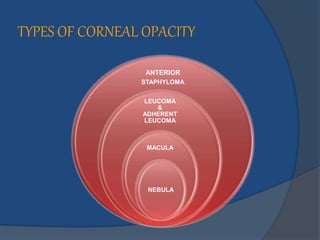
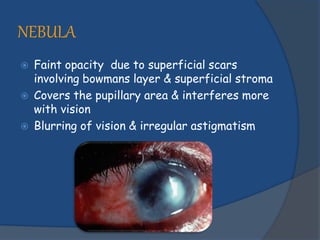
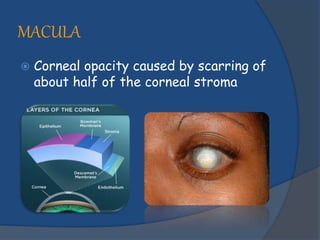
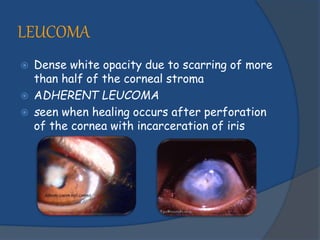
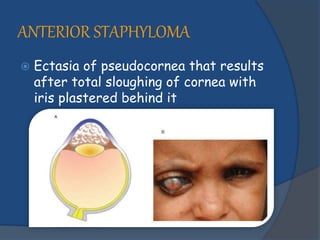


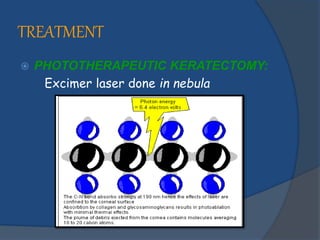
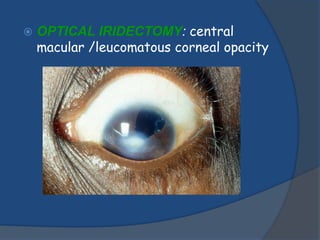
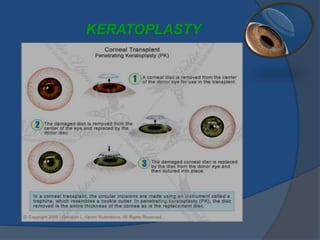

Corneal opacity is a loss of normal transparency of the cornea due to scarring. It can be caused by healed corneal wounds, ulcers, or congenital defects. Risk factors include vitamin A deficiency, measles, eye injuries, infections, contact lens overwear, and cold sores. Symptoms are reduced or lost vision, pain, redness, photophobia, and cloudy appearances in parts of the eye. Types of opacity include nebula, macula, leukoma, and anterior staphyloma. Treatment options are phototherapeutic keratectomy using excimer laser for nebula, optical iridectomy for central opacities, and keratoplasty.














