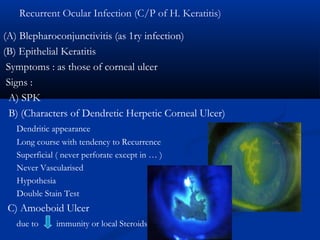
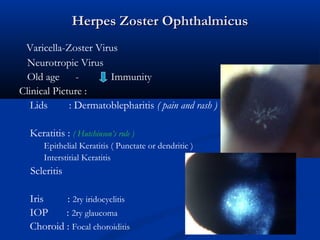
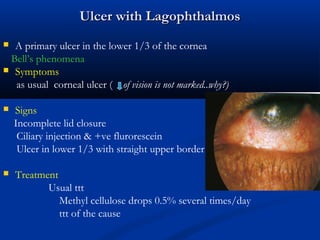
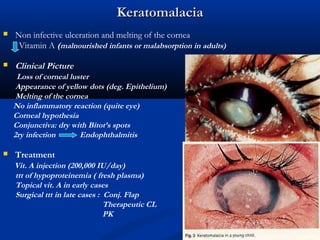
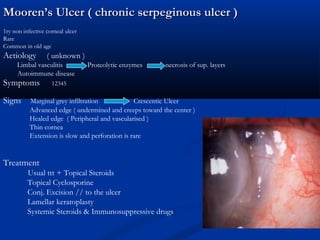
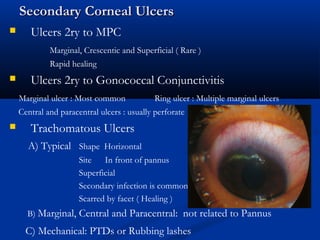
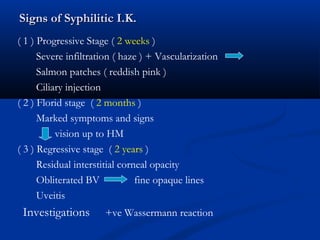
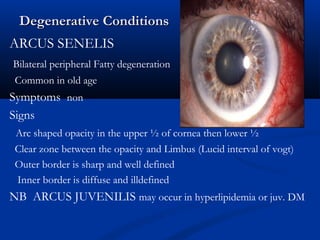
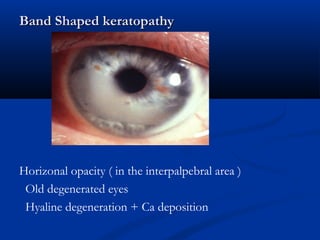
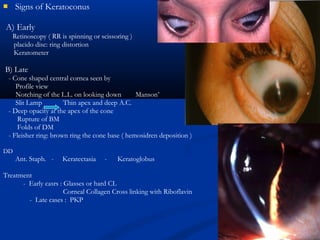
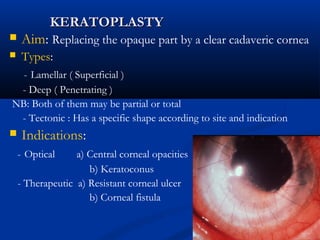
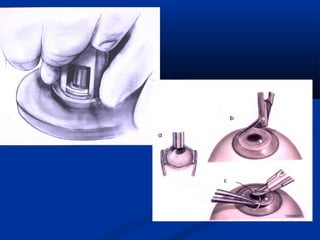
The document discusses the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the cornea. It provides details on the layers of the cornea and describes corneal ulcers. Key points include:
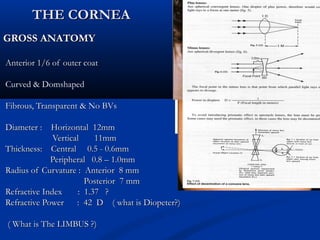
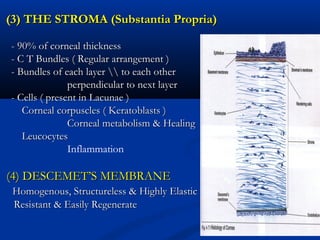
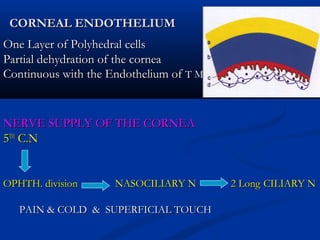
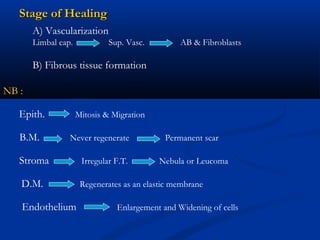
1) The cornea has 5 layers - epithelium, Bowman's layer, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The stroma makes up 90% of the corneal thickness.
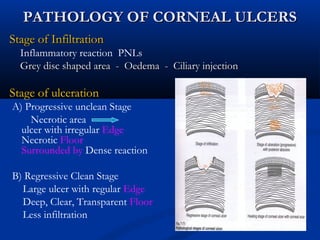
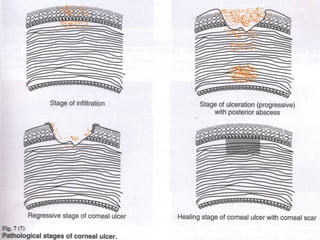
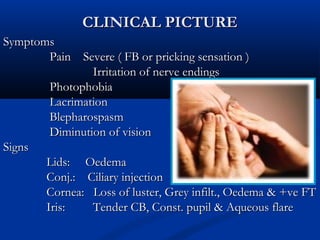
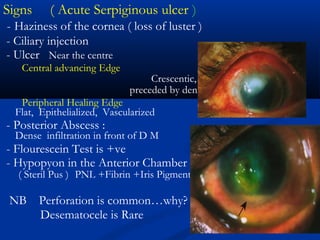
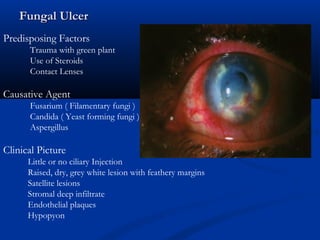
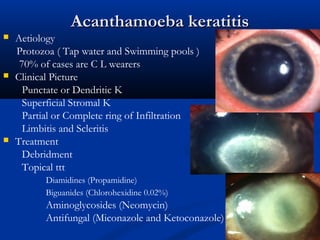
2) Corneal ulcers are localized areas of necrosis in the superficial stroma caused by trauma, infection, or other insults. Common causes of infection include bacteria like Staphylococcus and Pneumococcus.
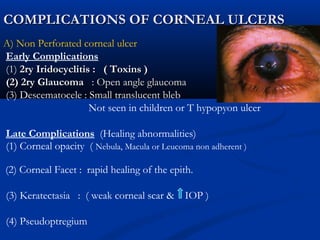
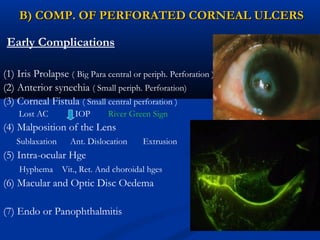
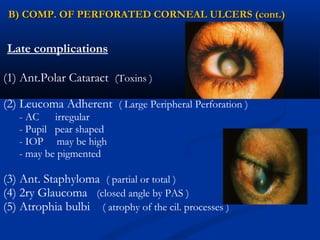
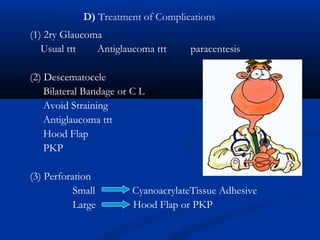
3) Complications of corneal ulcers can include iritis, glaucoma, corneal opacity