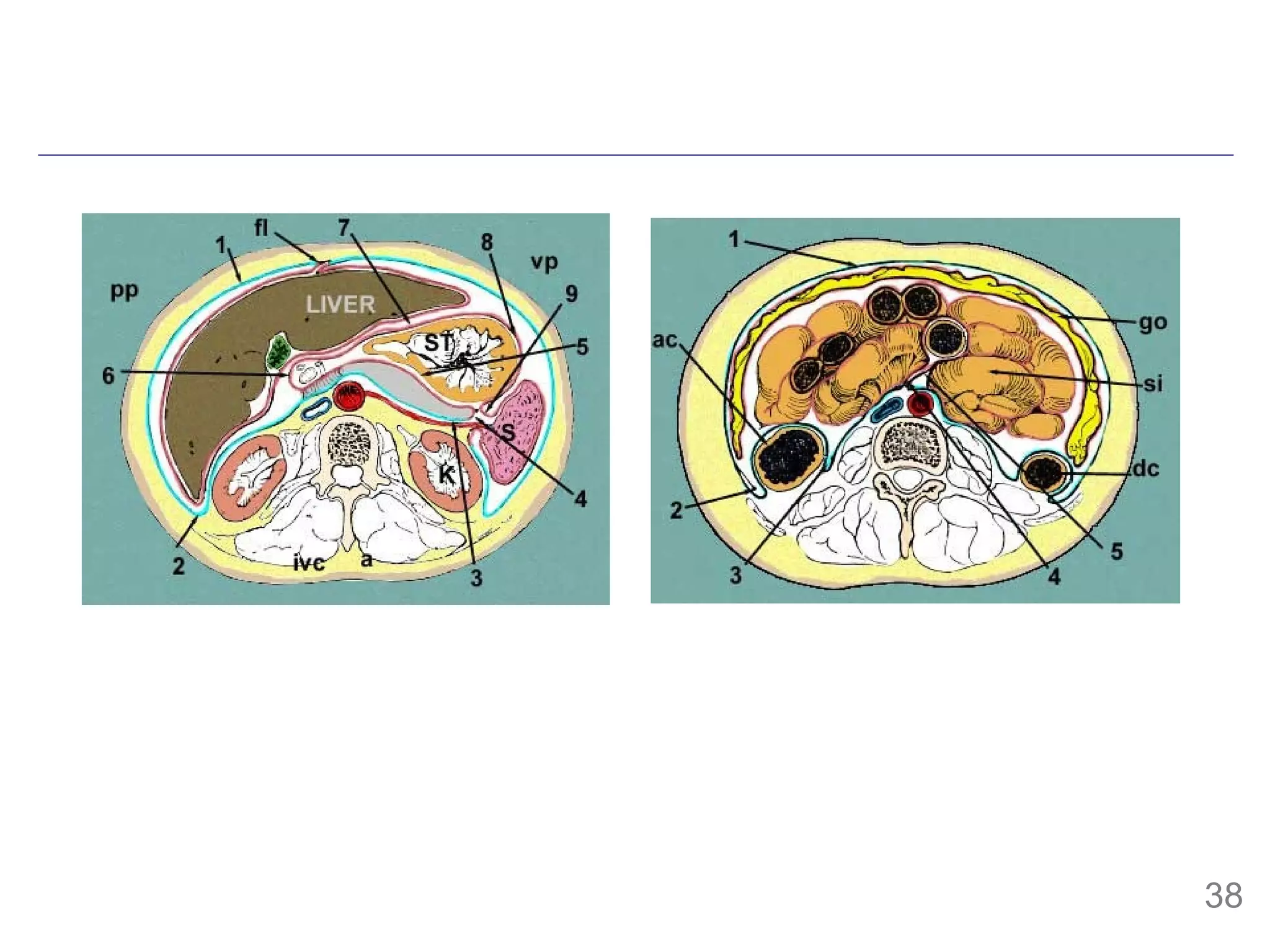
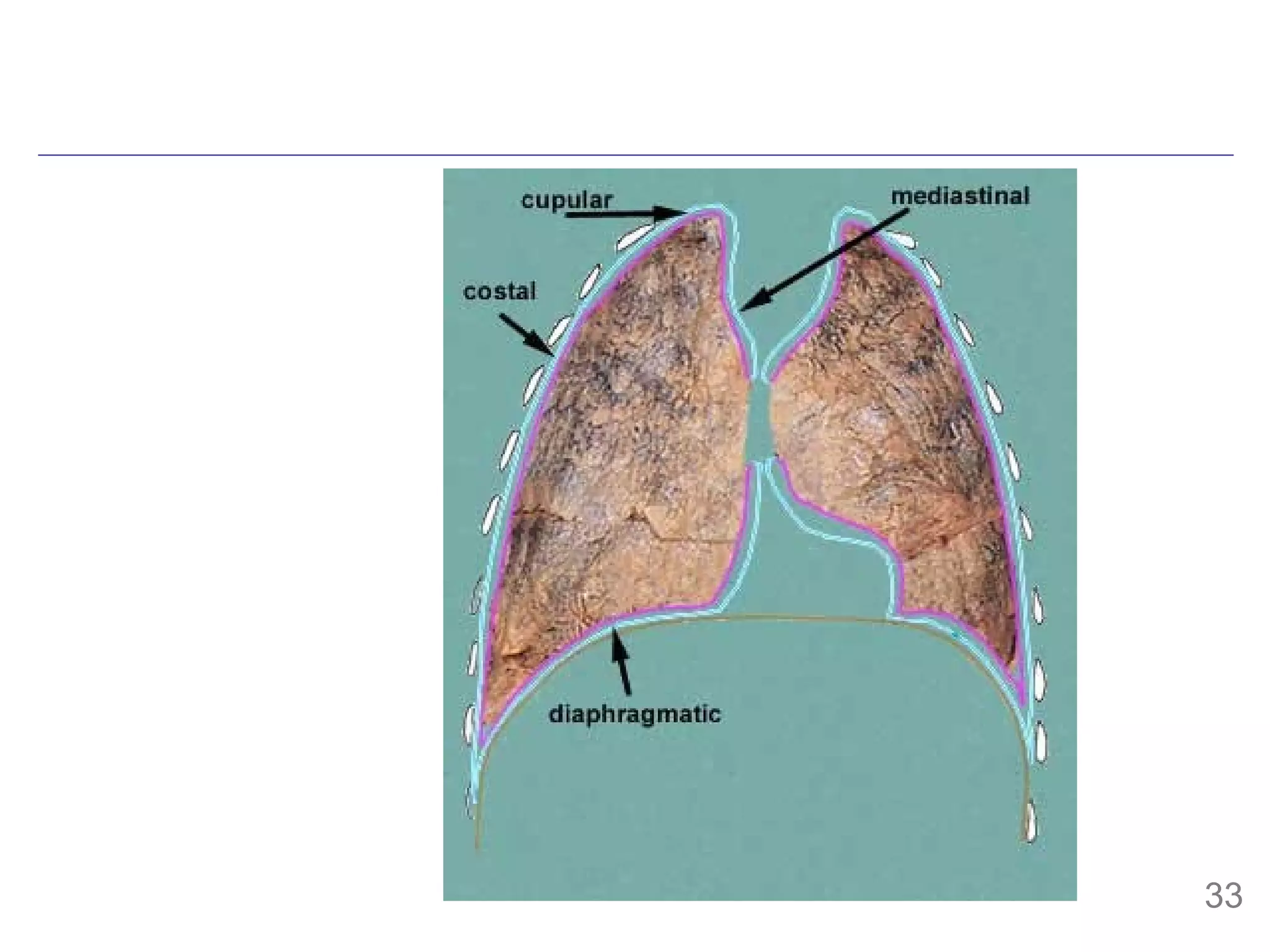
The document provides information about mesoderm development in human embryos, including:
- The mesoderm arises from epiblast cells that migrate through the primitive streak during gastrulation.
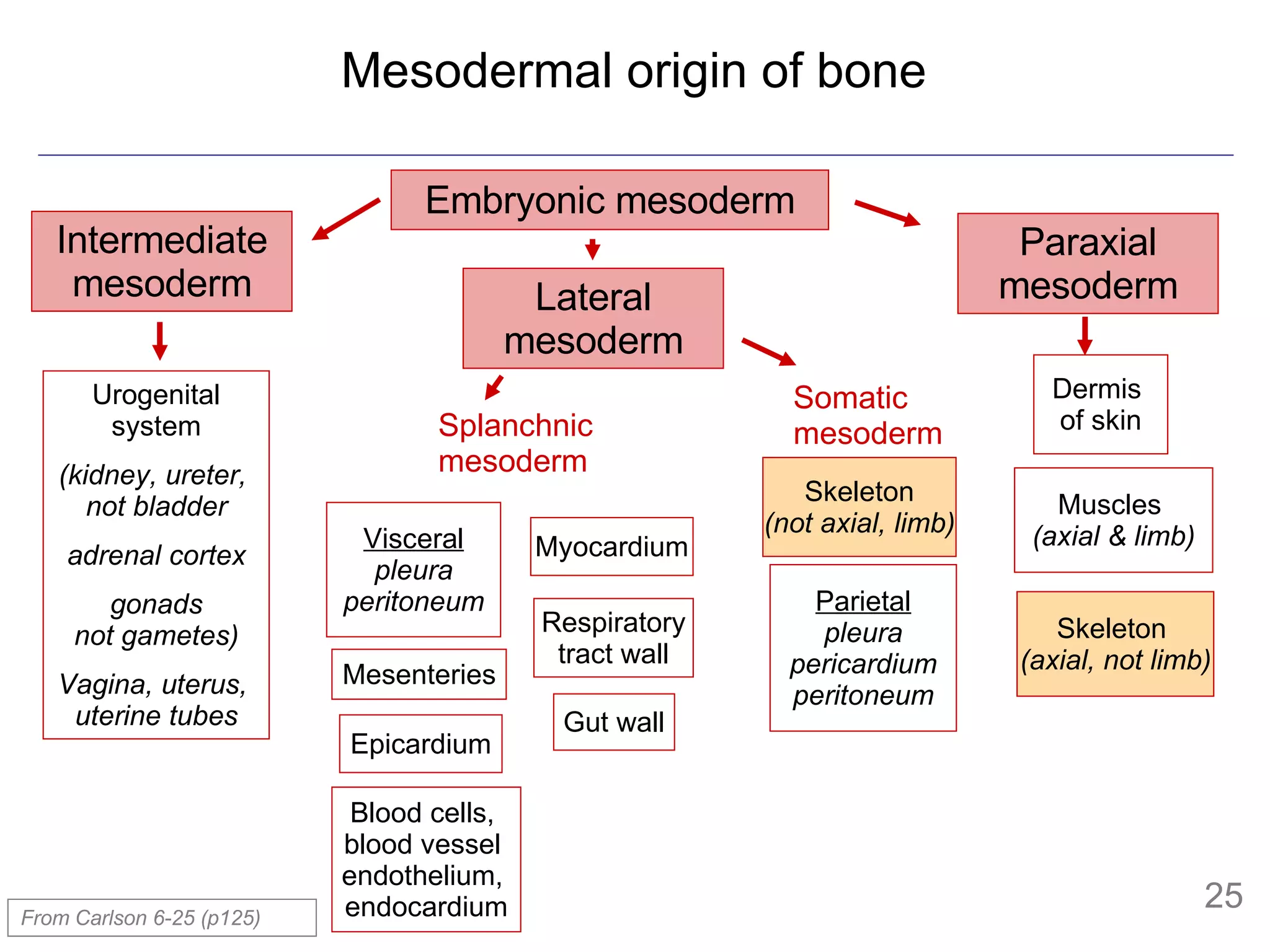
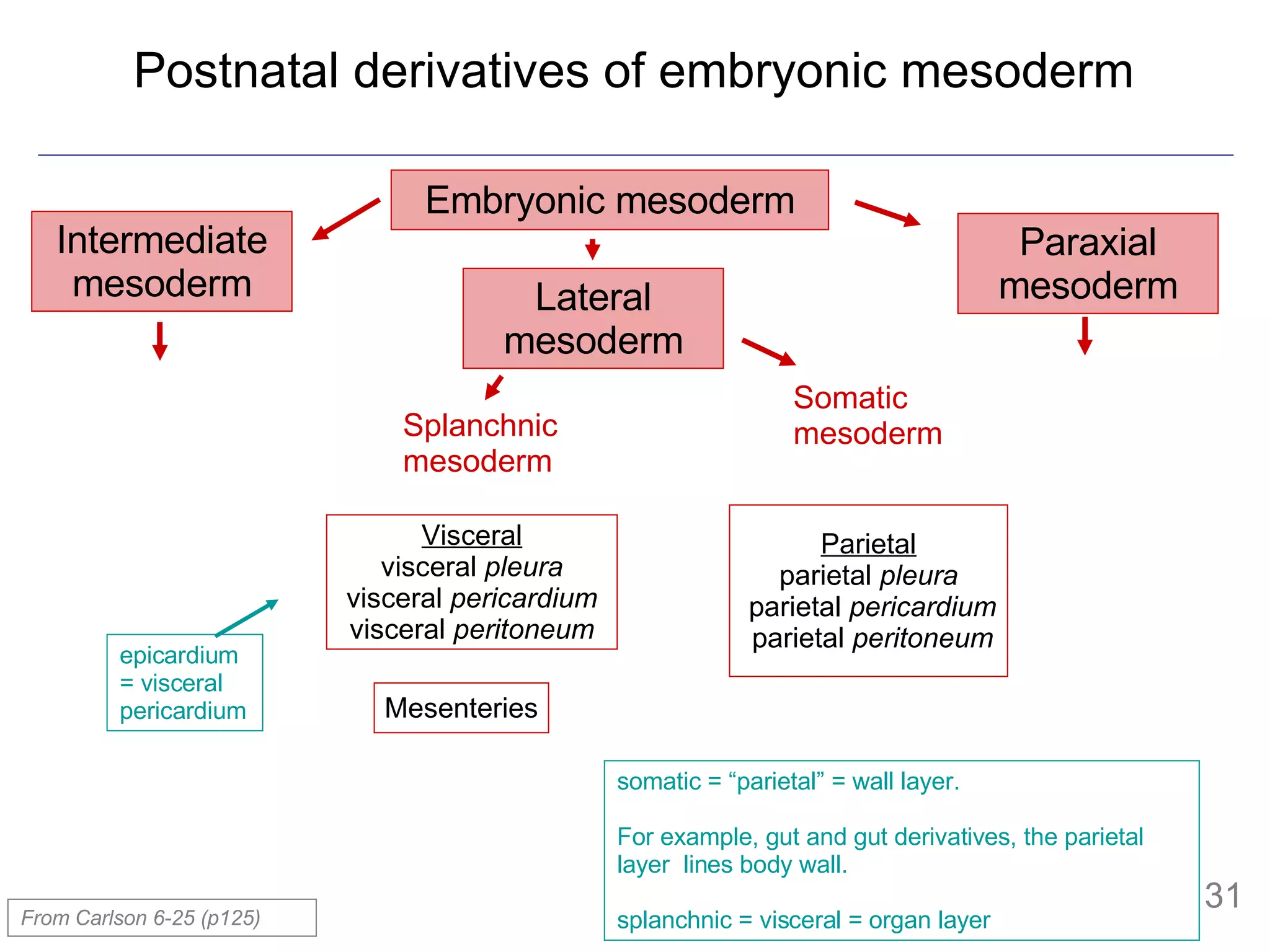
- The mesoderm is initially divided into paraxial, intermediate and lateral mesoderm. Lateral mesoderm further splits into splanchnic and somatic mesoderm.
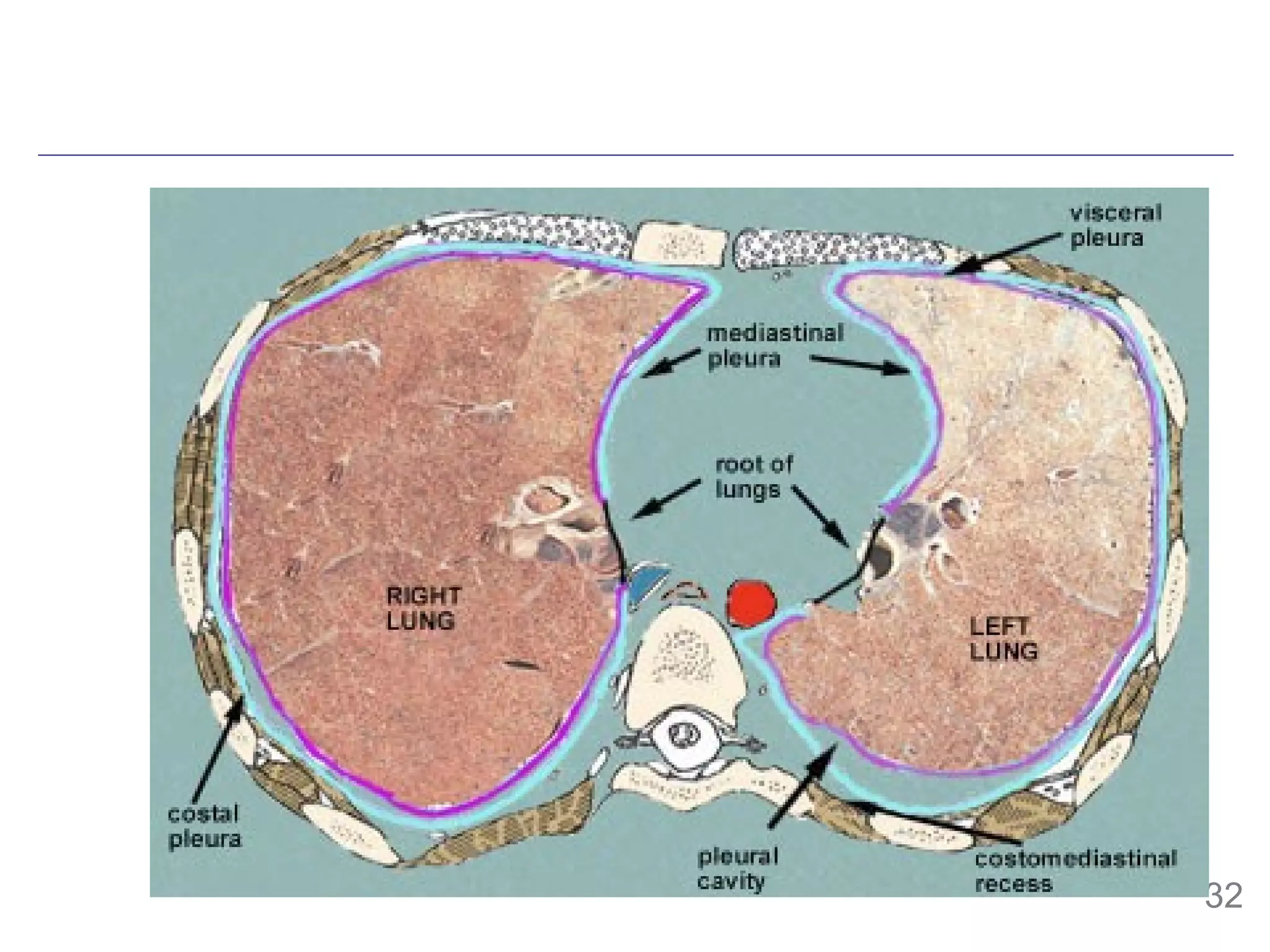
- The mesoderm gives rise to various tissues and organs, including muscle, bone, kidney and other parts of the urogenital system. It also forms the walls of body cavities.









![Though early on you were a quite flat disk, now are a doughnut http://www.abdn.ac.uk/langling/resources/usflimgs.html [And what is in the middle?]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0808252fallsmesoderm-i-b-1219801026579860-9/75/Mesoderm-I-11-2048.jpg)

















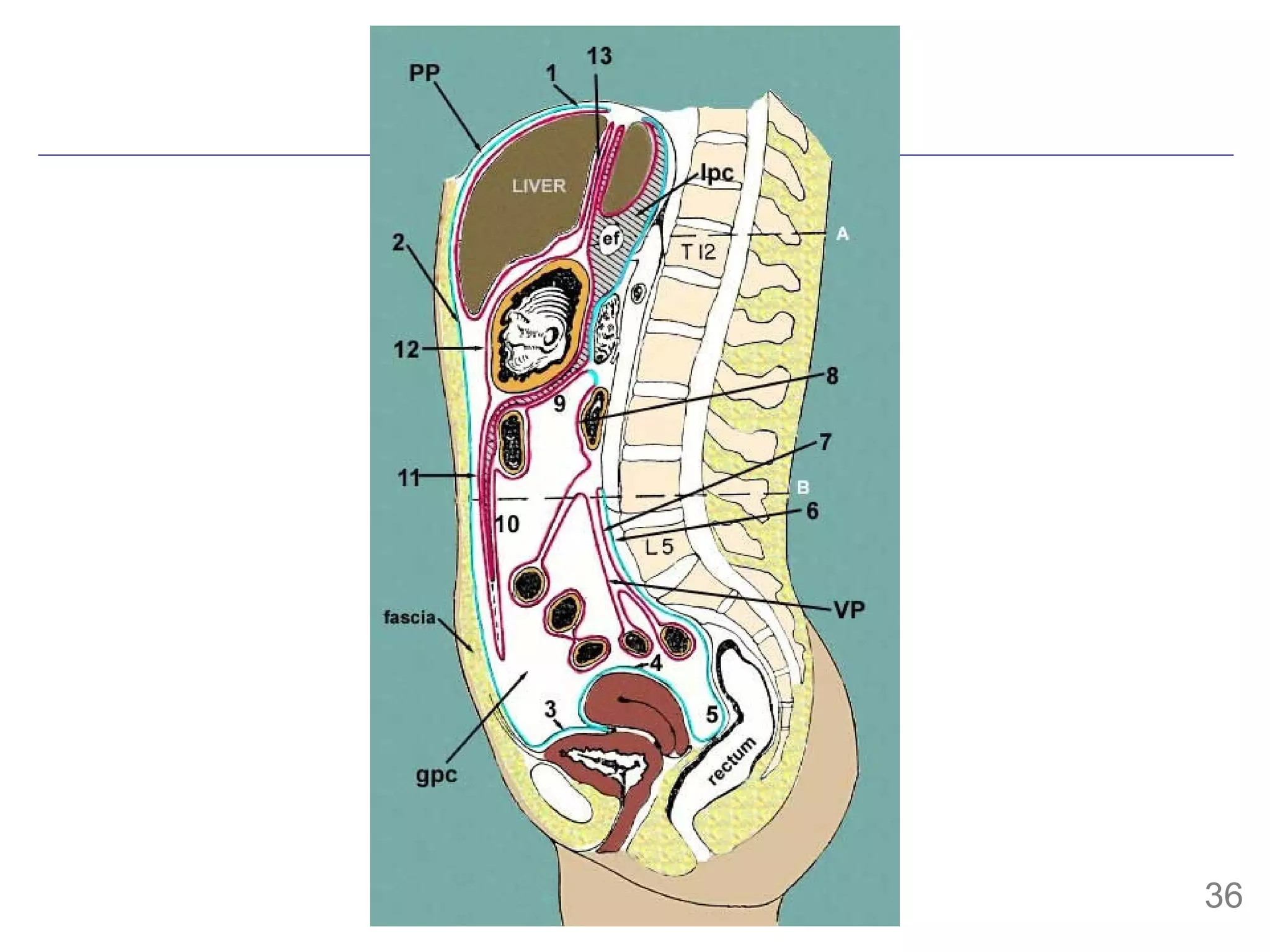
![mesentery mesentery (mes en-ter- ) [TA] A double layer of peritoneum attached to the abdominal wall and enclosing in its fold a portion or all of one of the abdominal viscera, conveying to it its vessels and nerves. The fan-shaped fold of peritoneum suspending the greater part of the small intestines (jejunum and ileum) and attaching it to the posterior abdominal wall at the root of the mesentery (radix mesenterii). Syn: mesenterium dorsale commune , mesostenium Syn: mesenterium TA [Mod. L. mesenterium, fr. G. mesenterion, fr. G. mesos, middle, + enteron, intestine] Stedman’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0808252fallsmesoderm-i-b-1219801026579860-9/75/Mesoderm-I-37-2048.jpg)