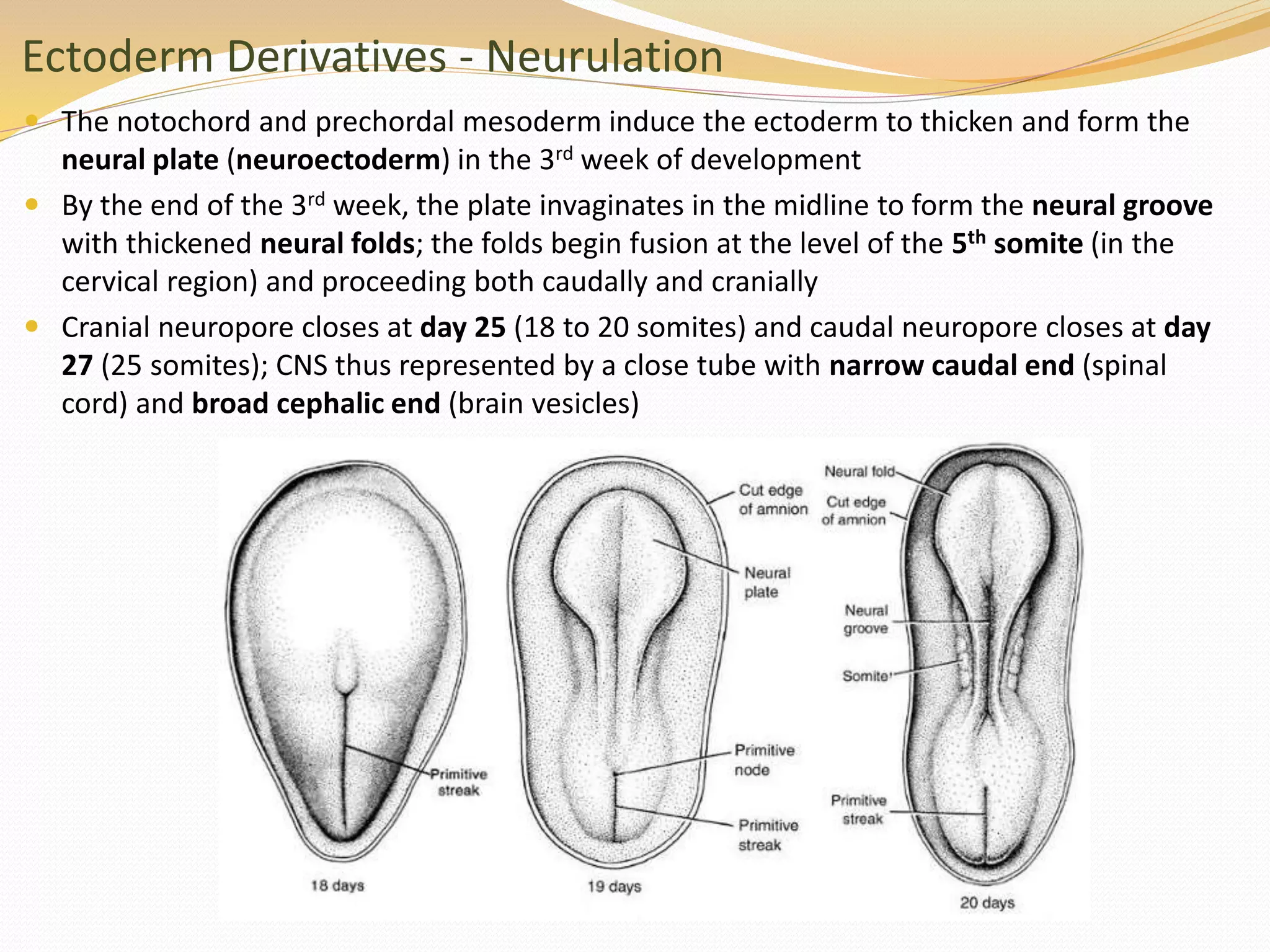
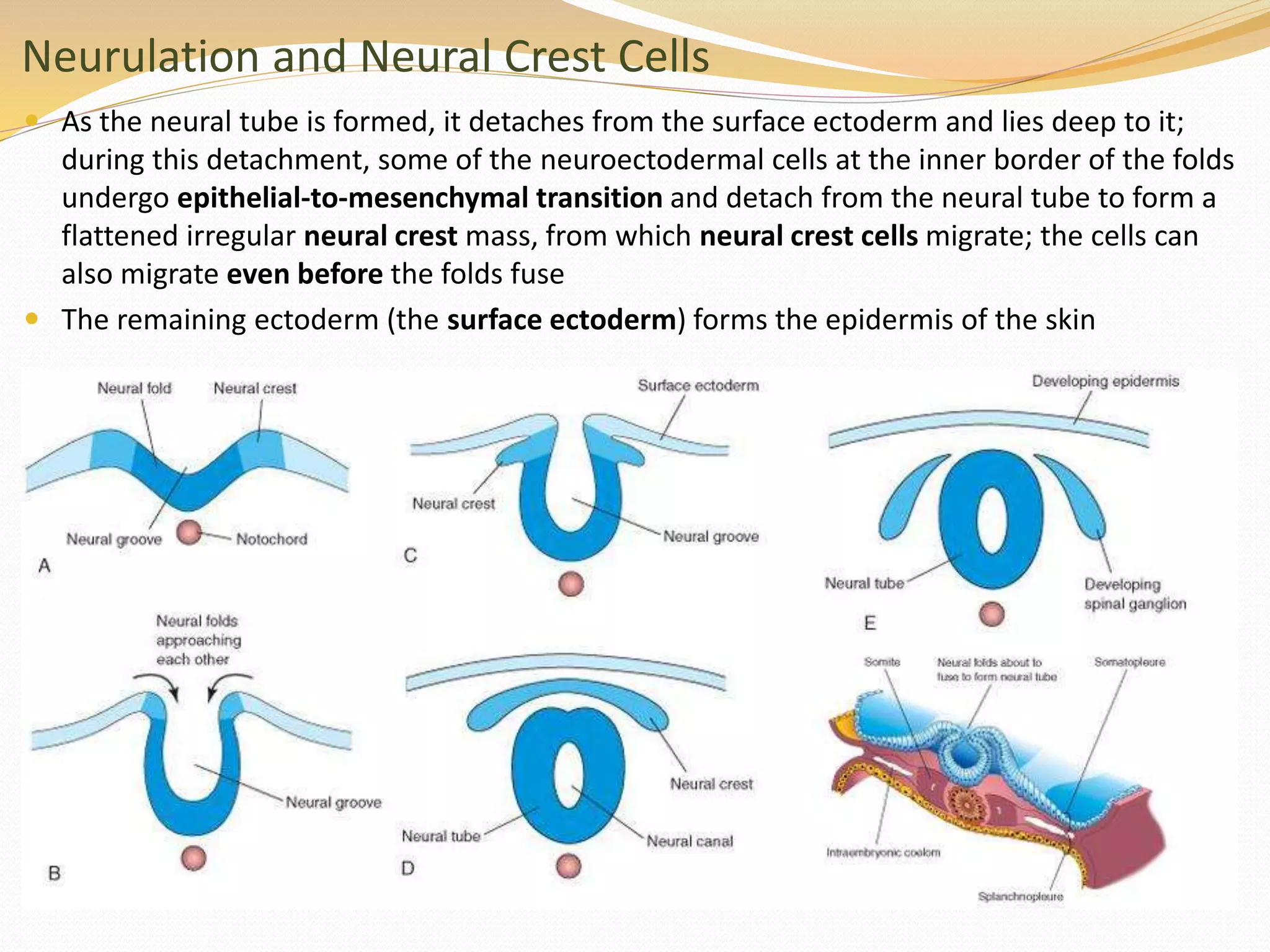
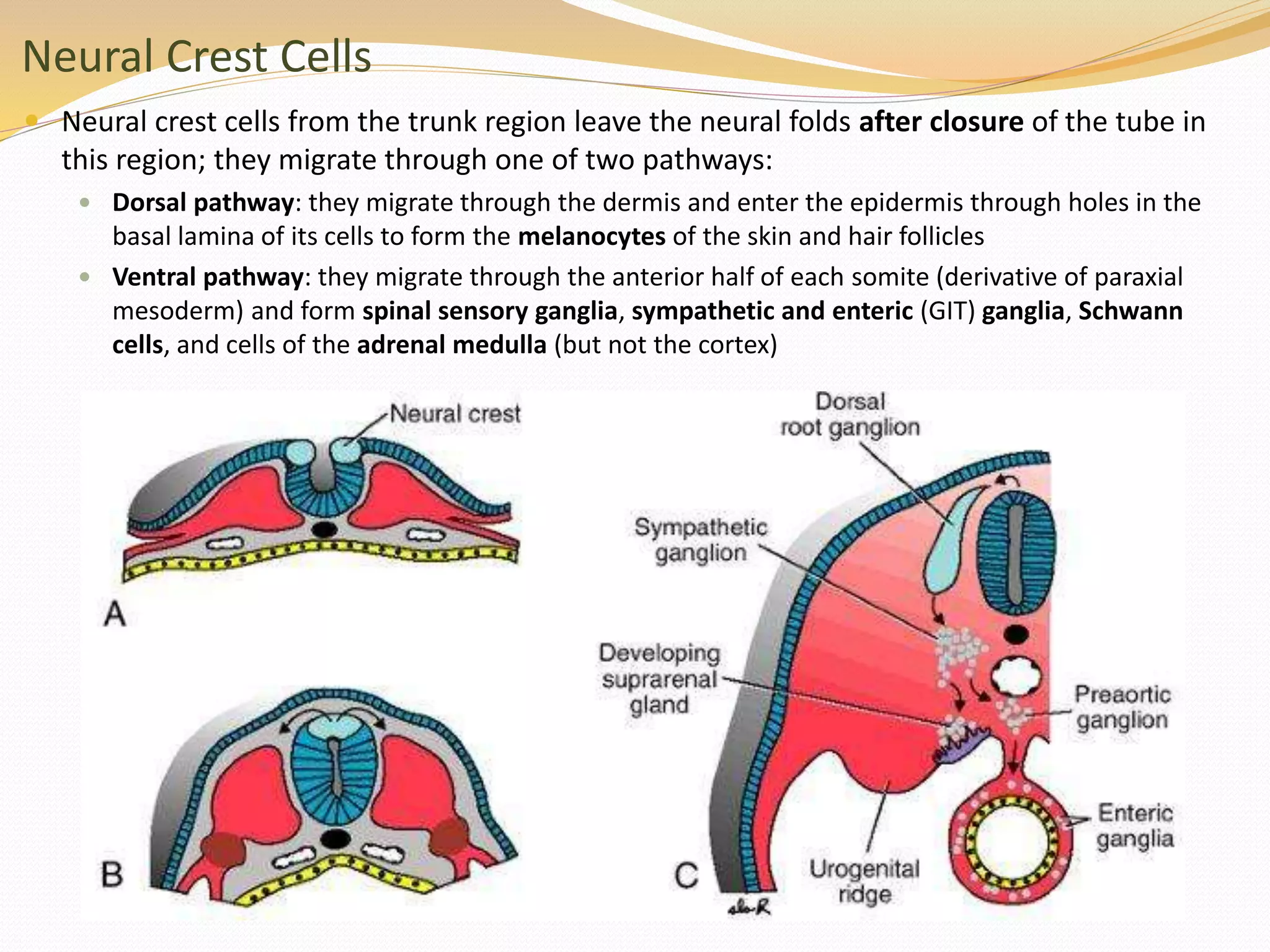
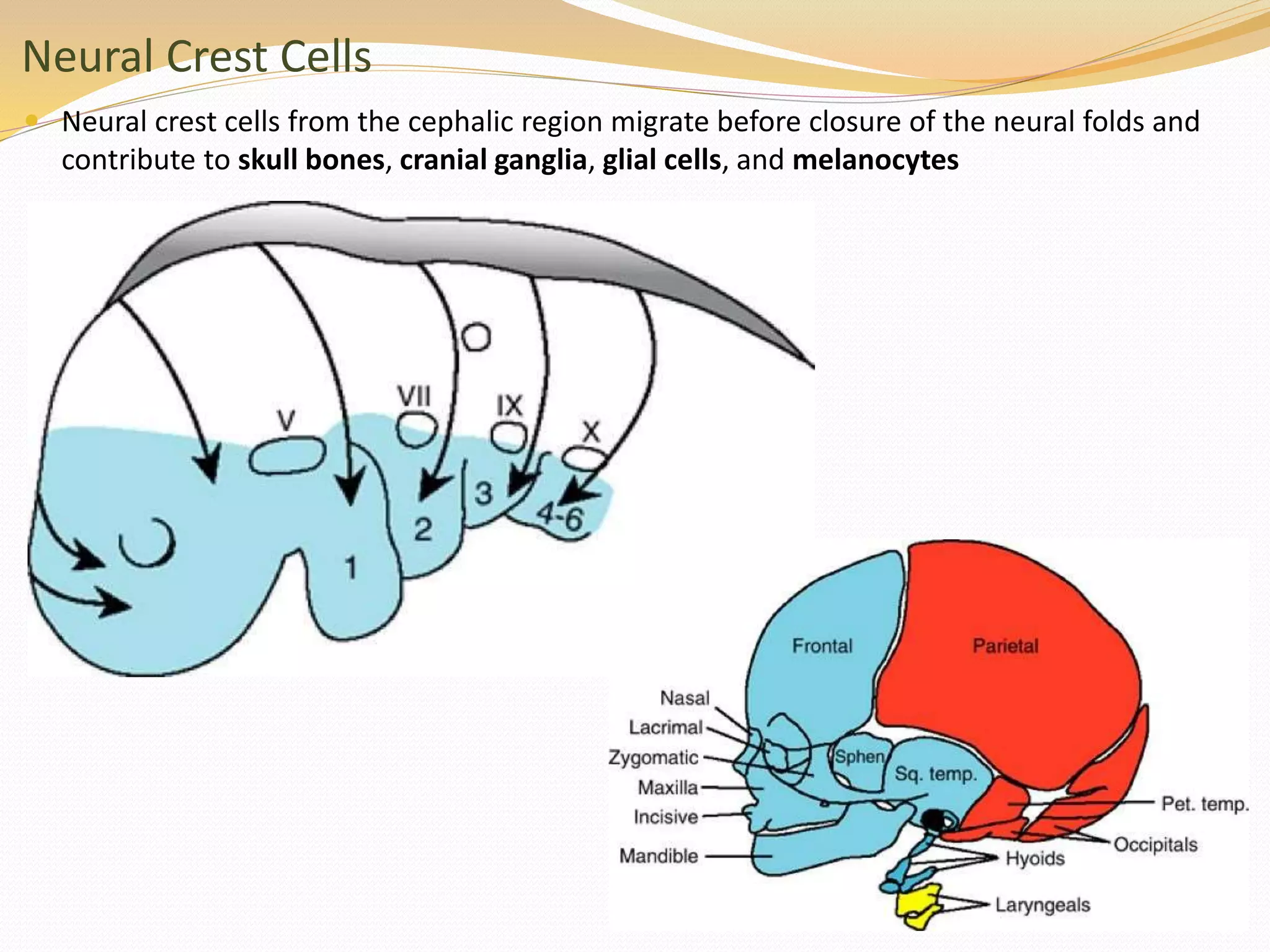
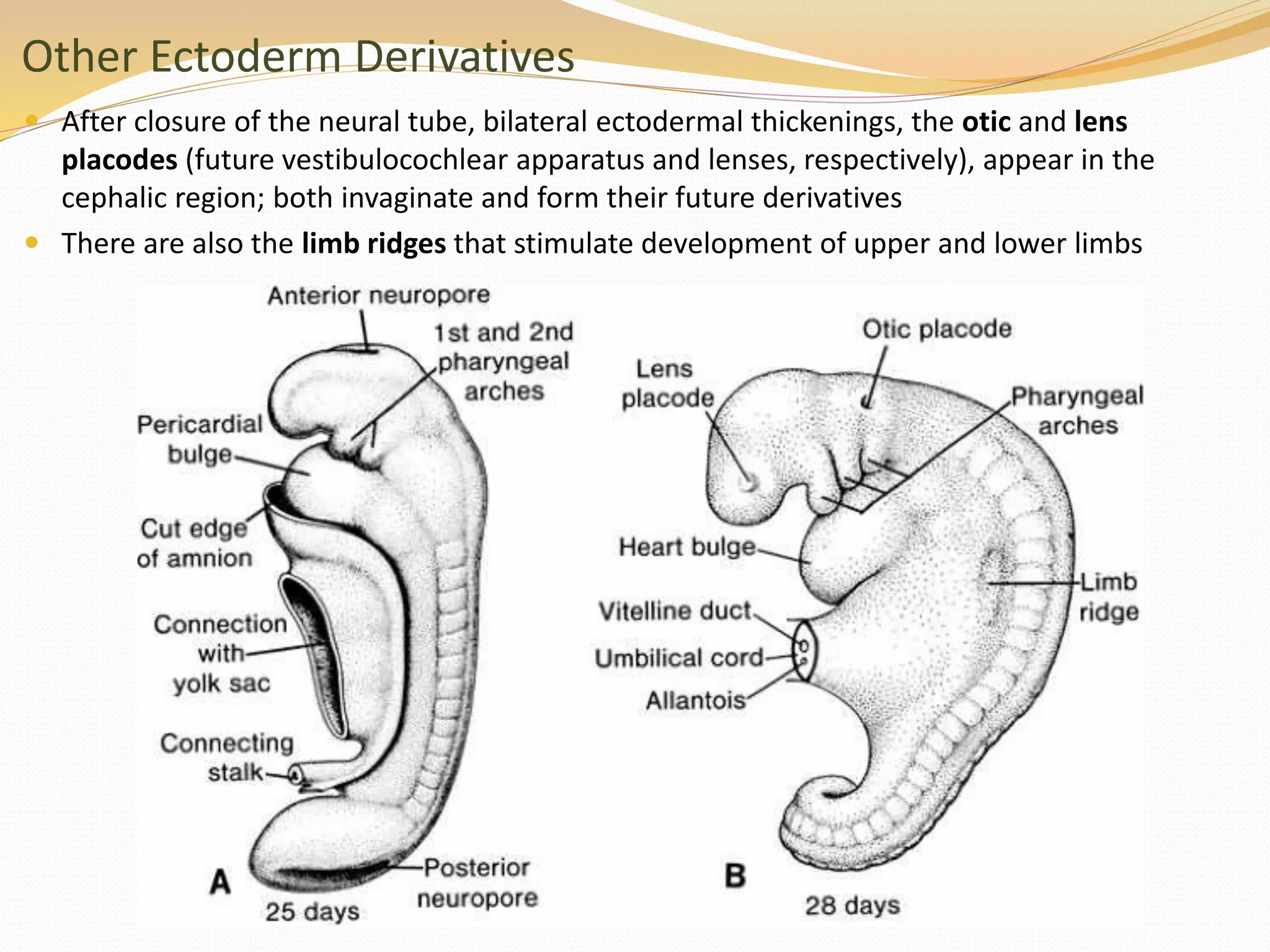
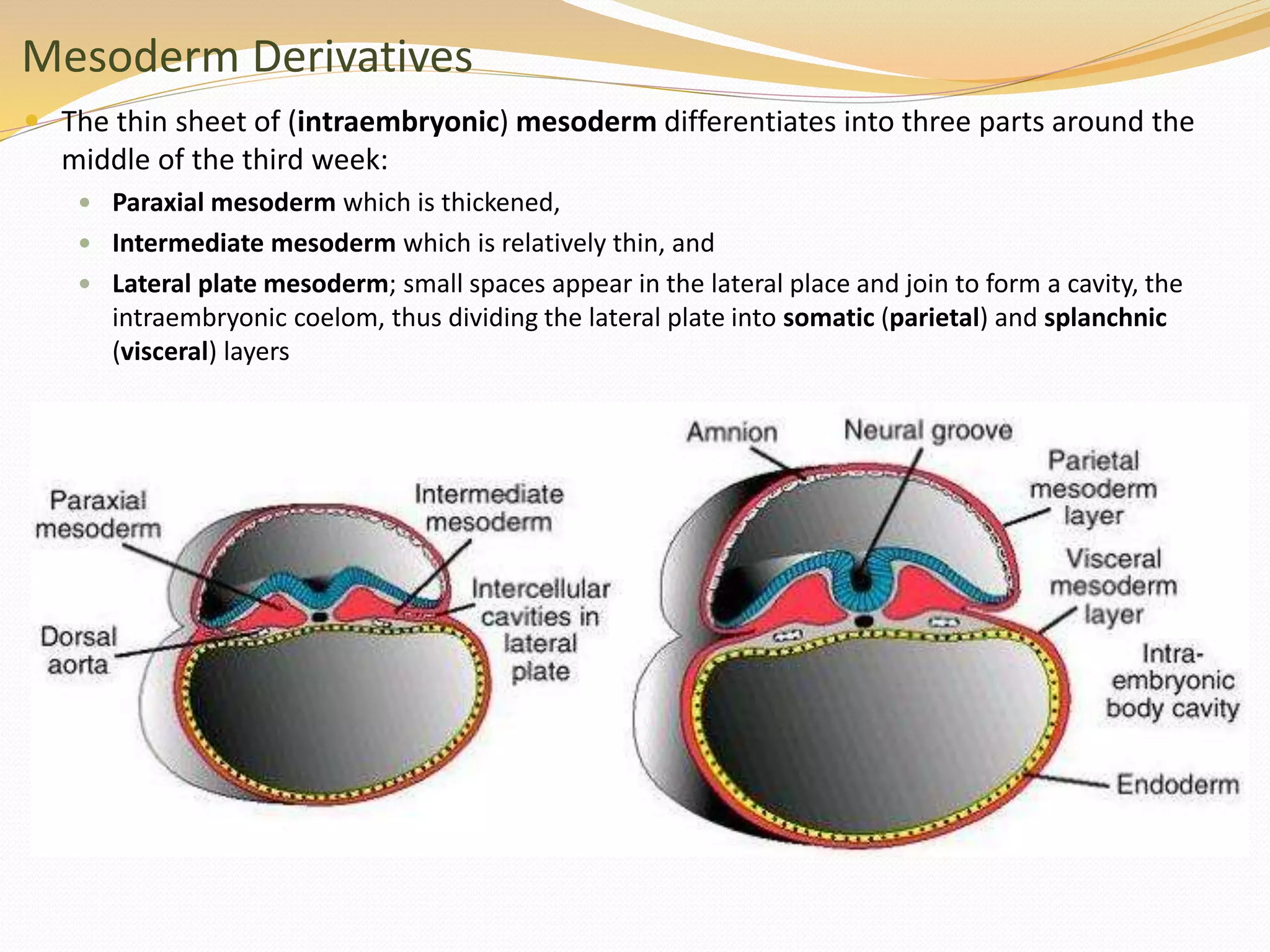
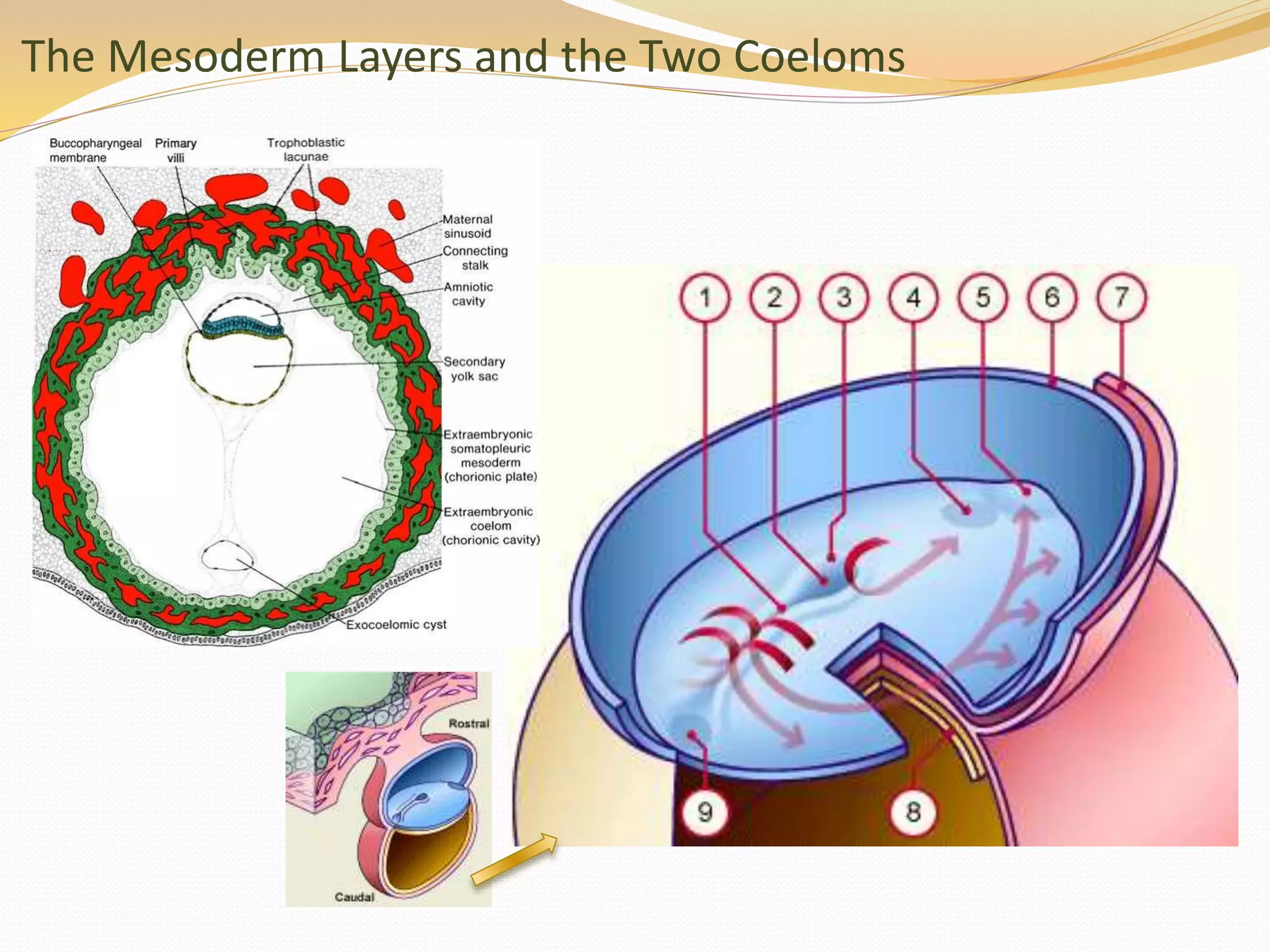
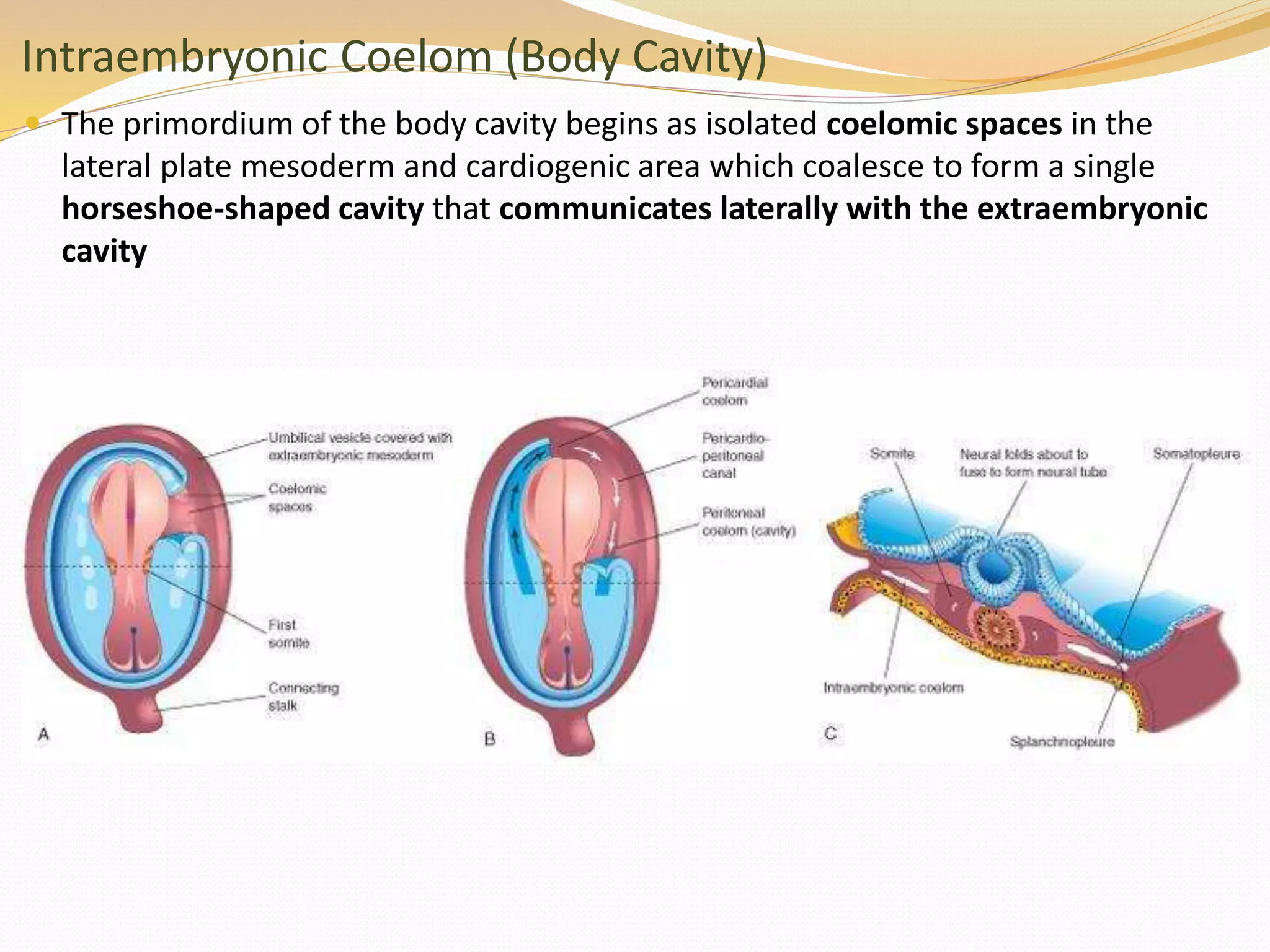
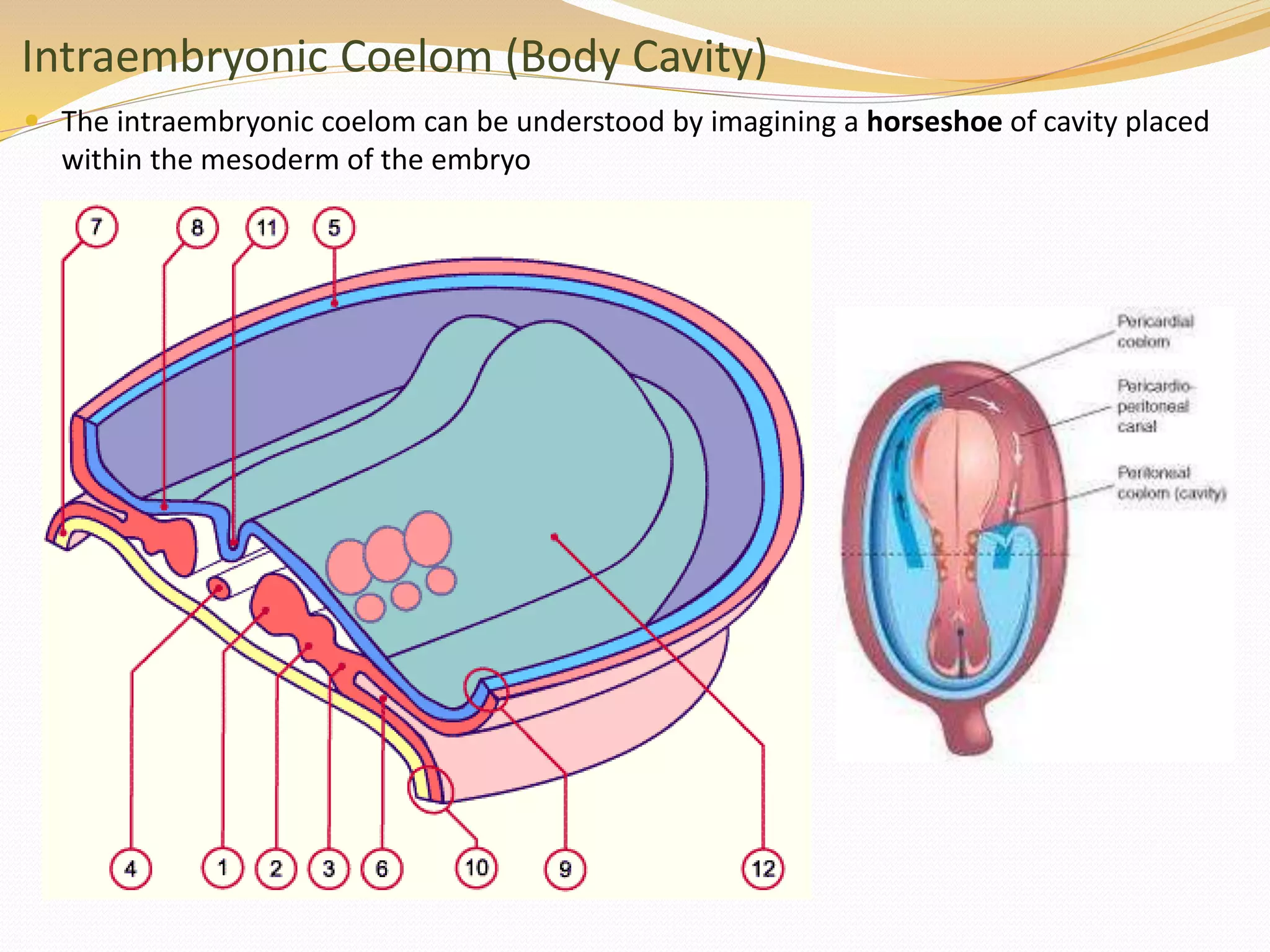
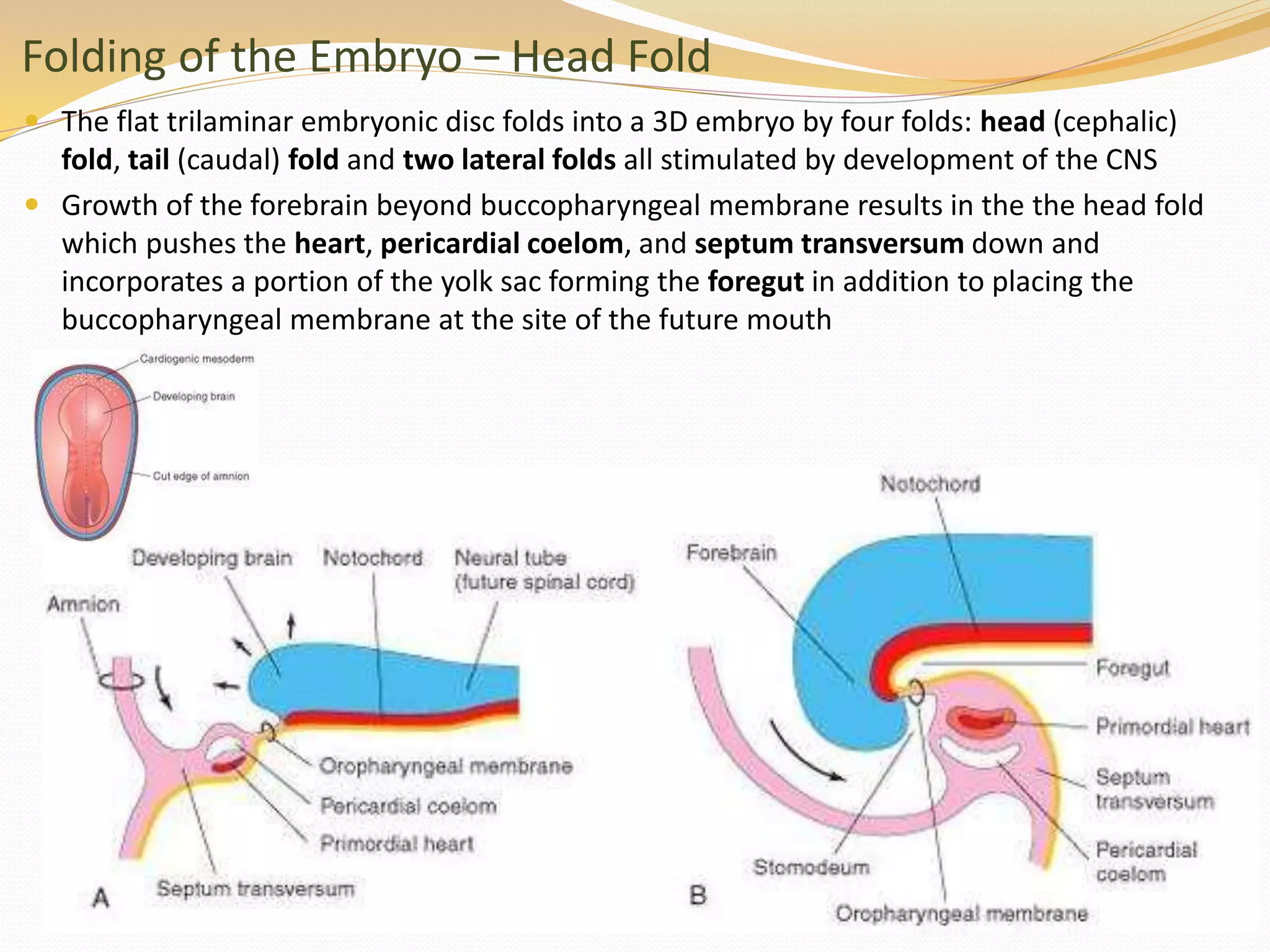
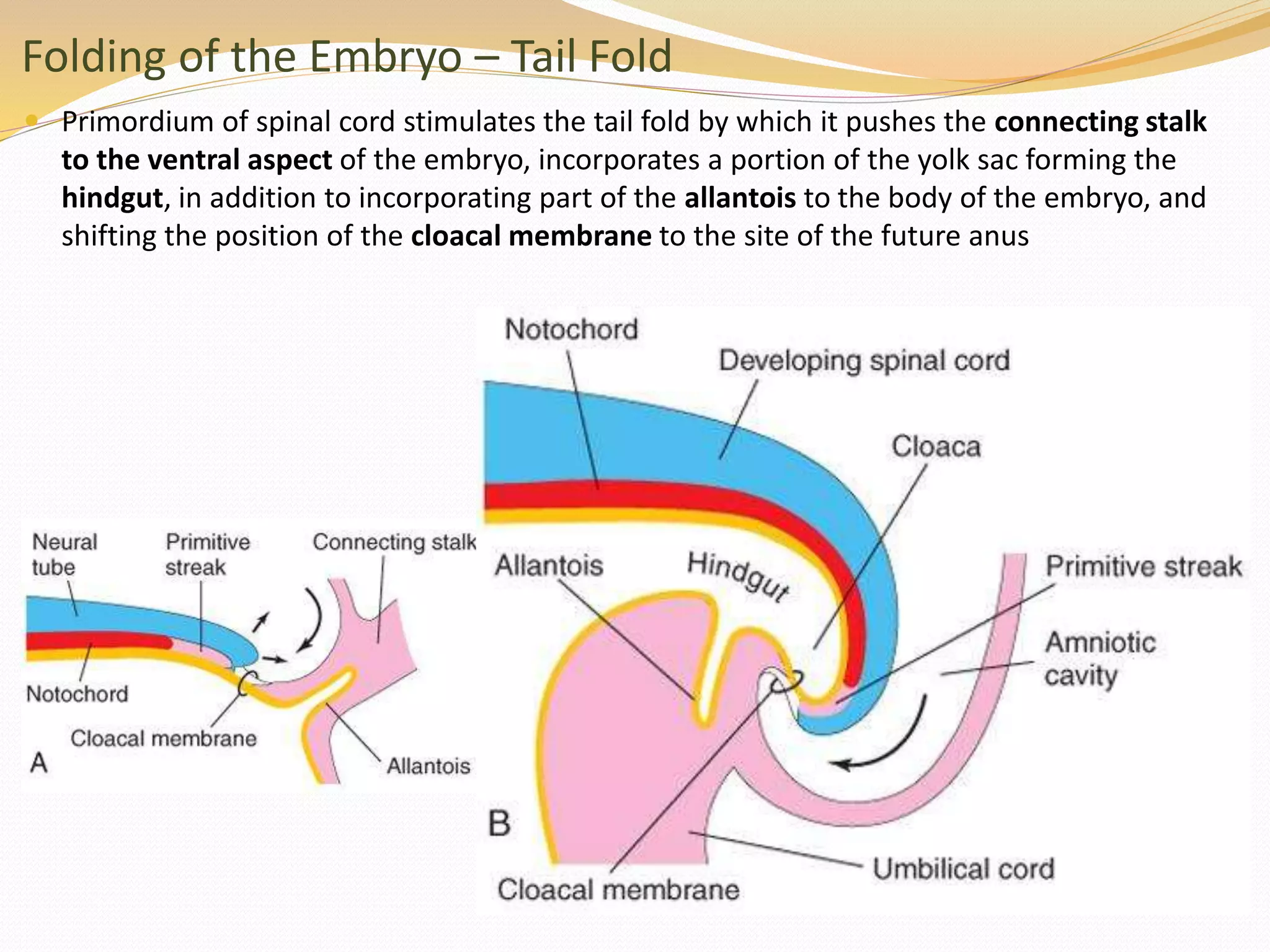
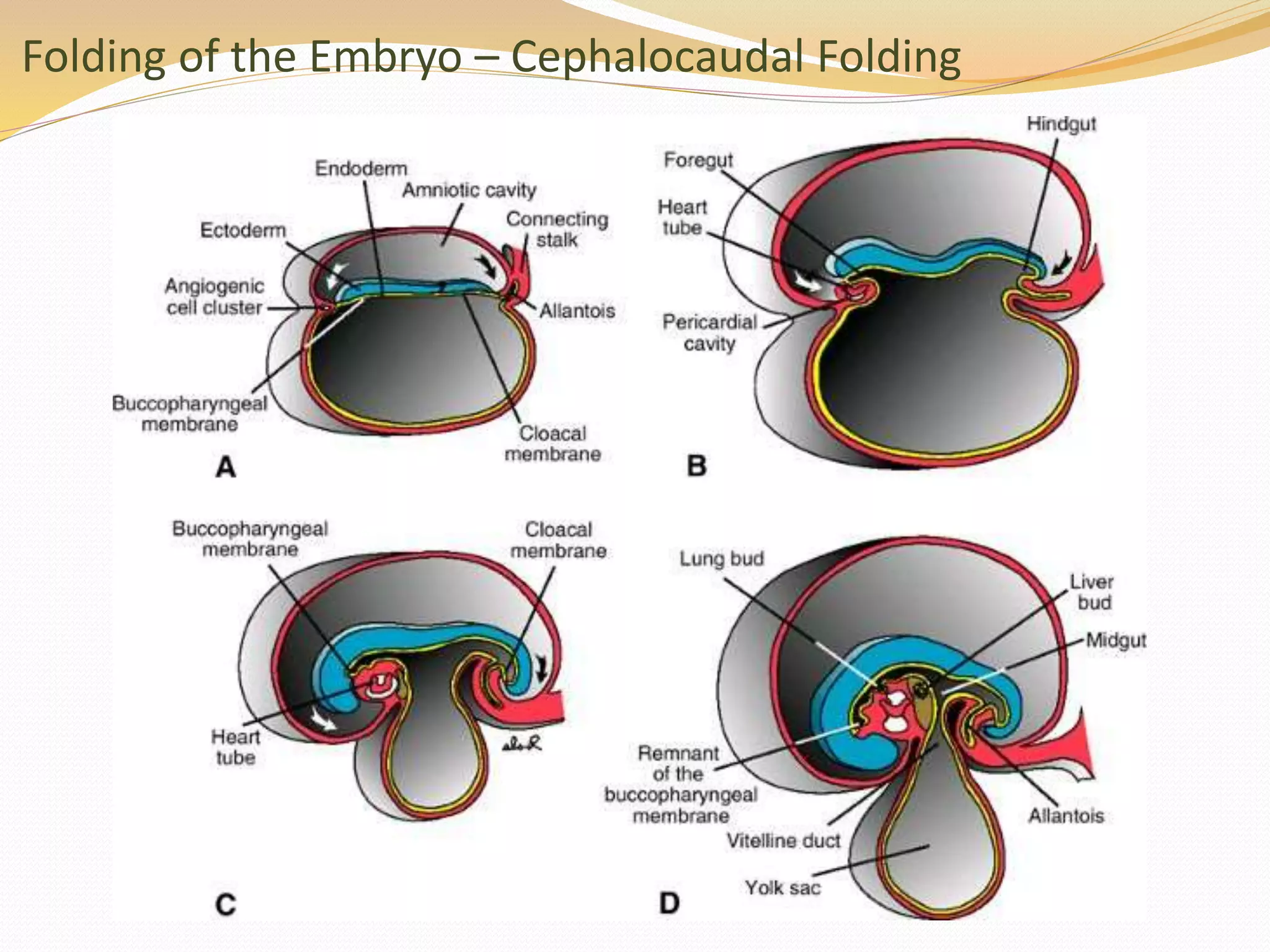
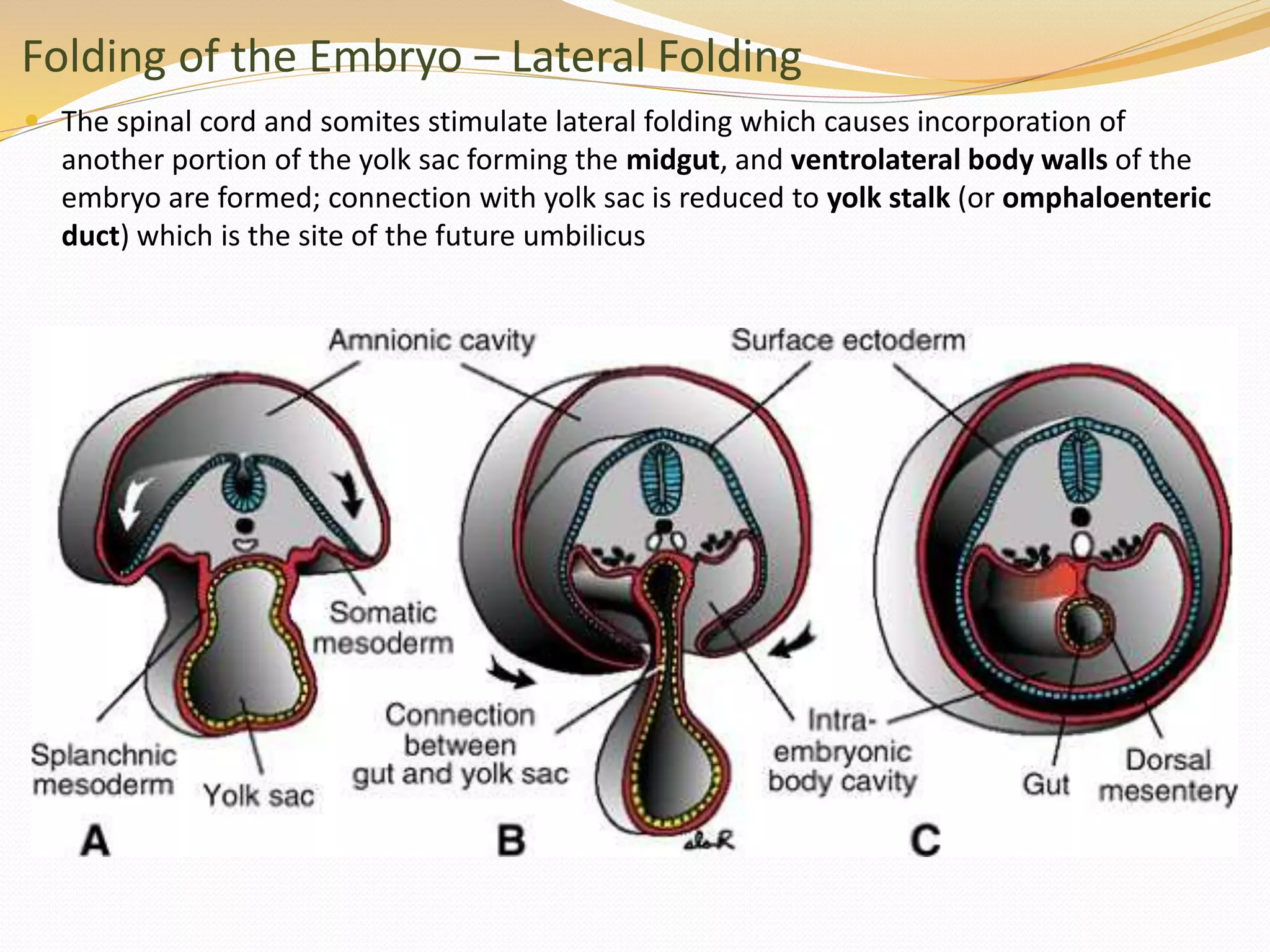
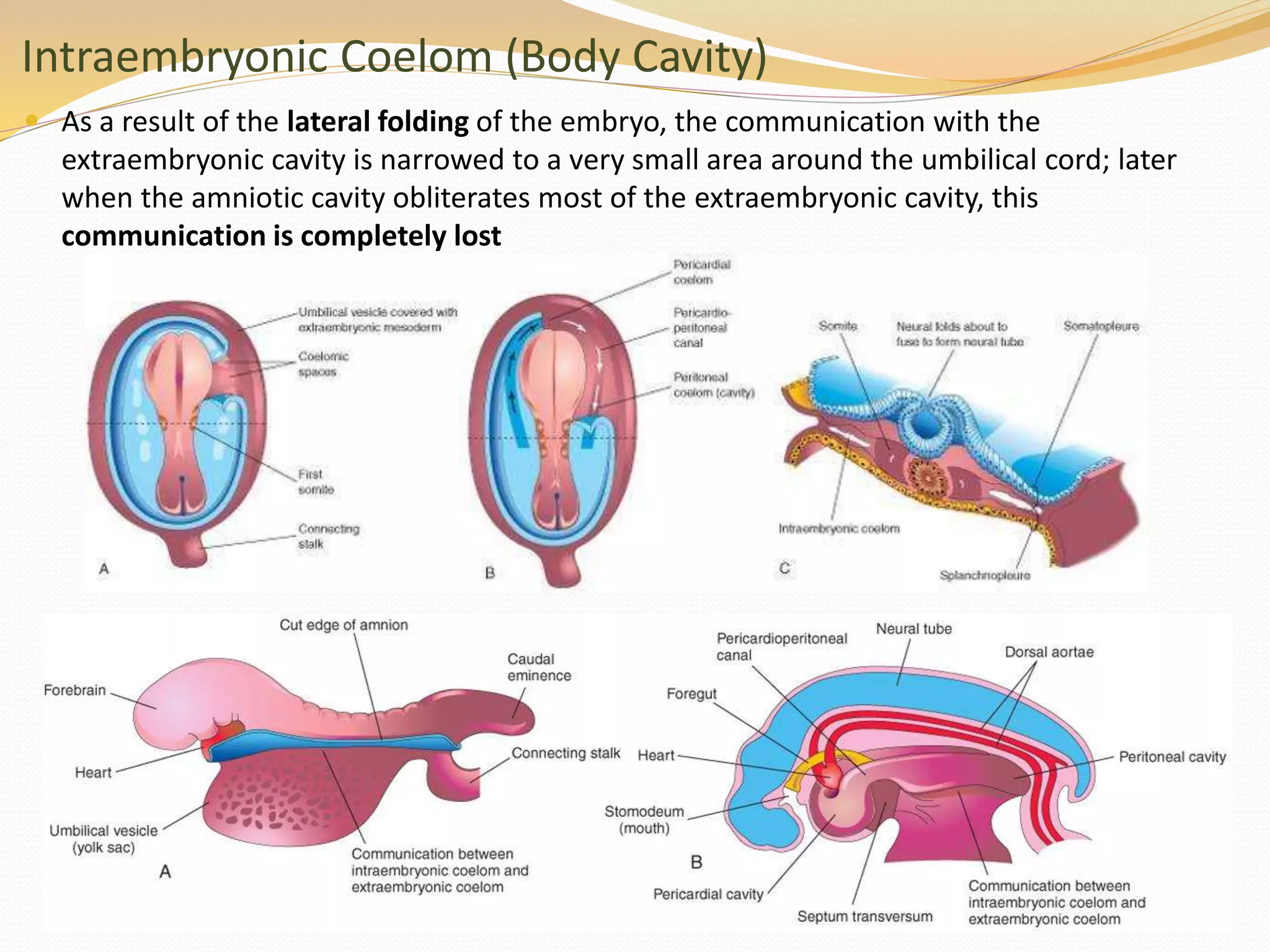
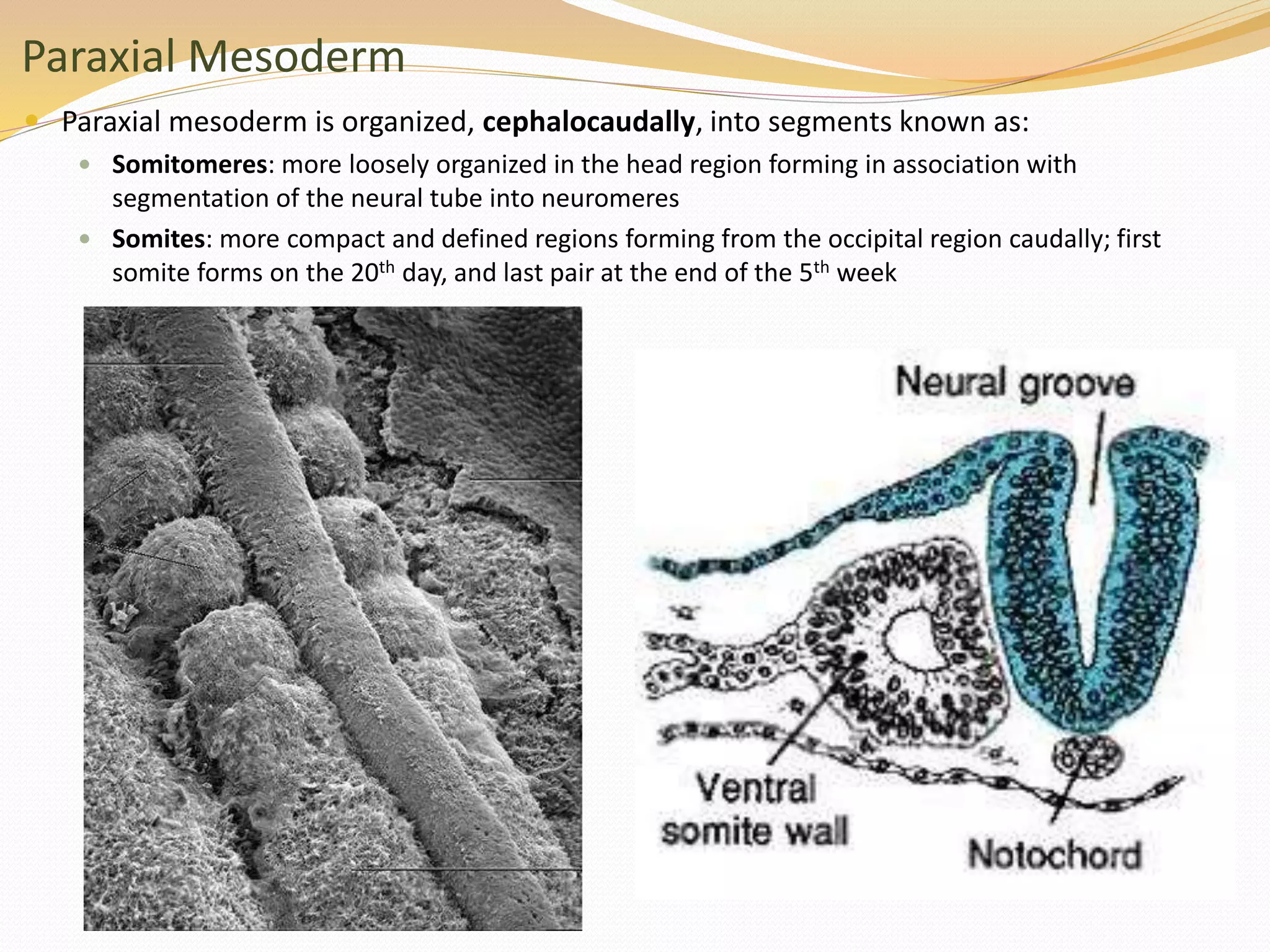
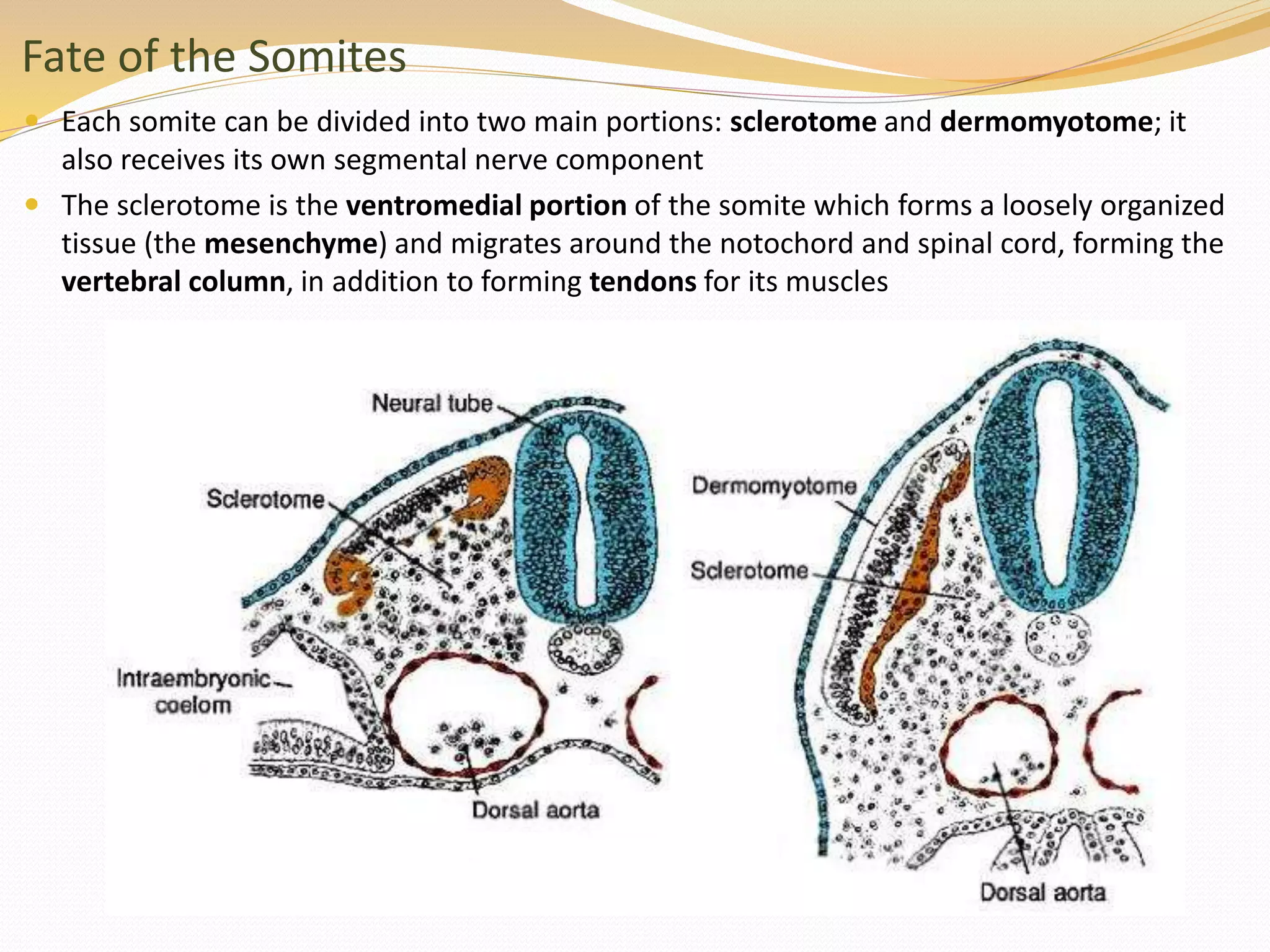
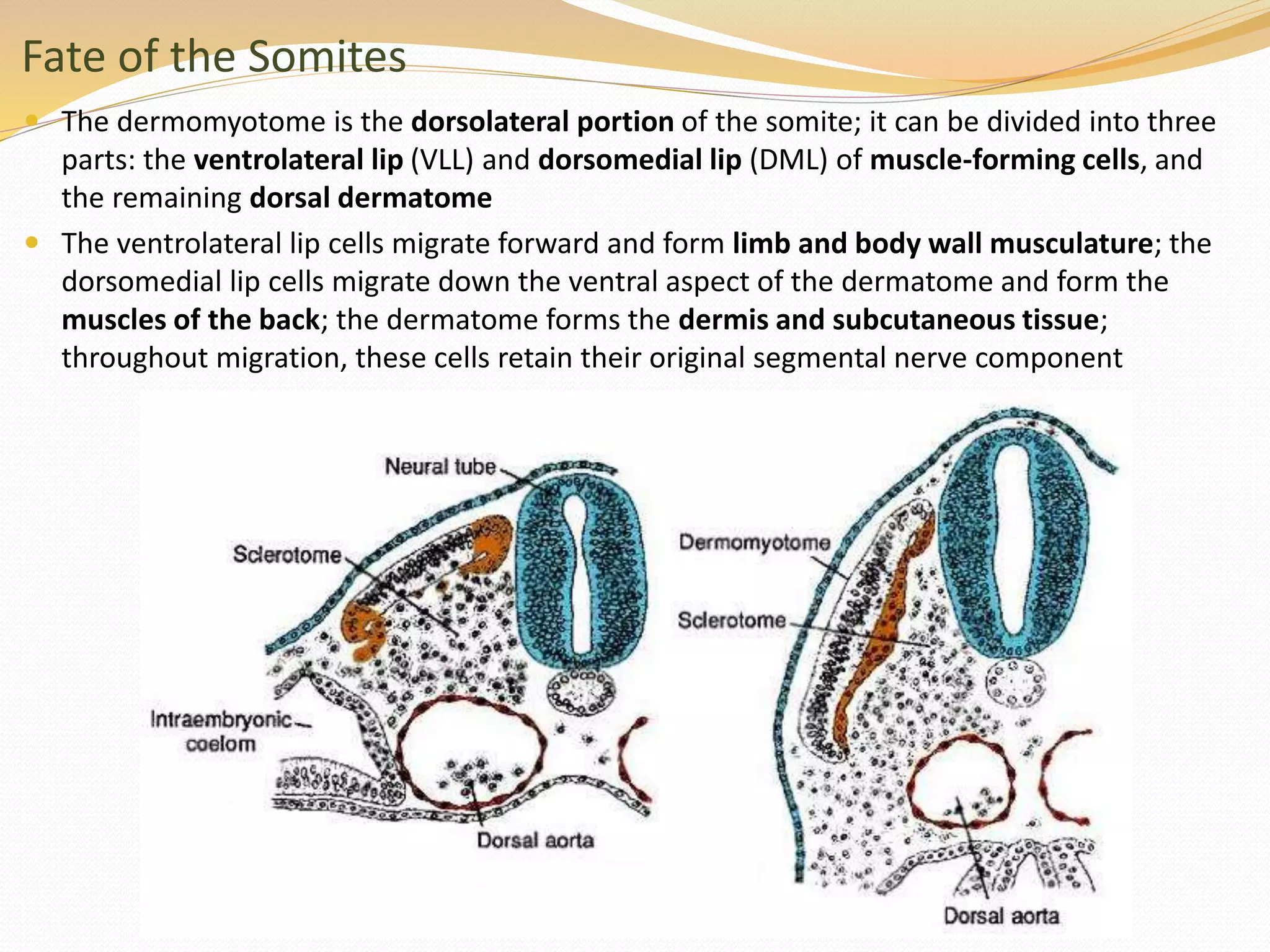
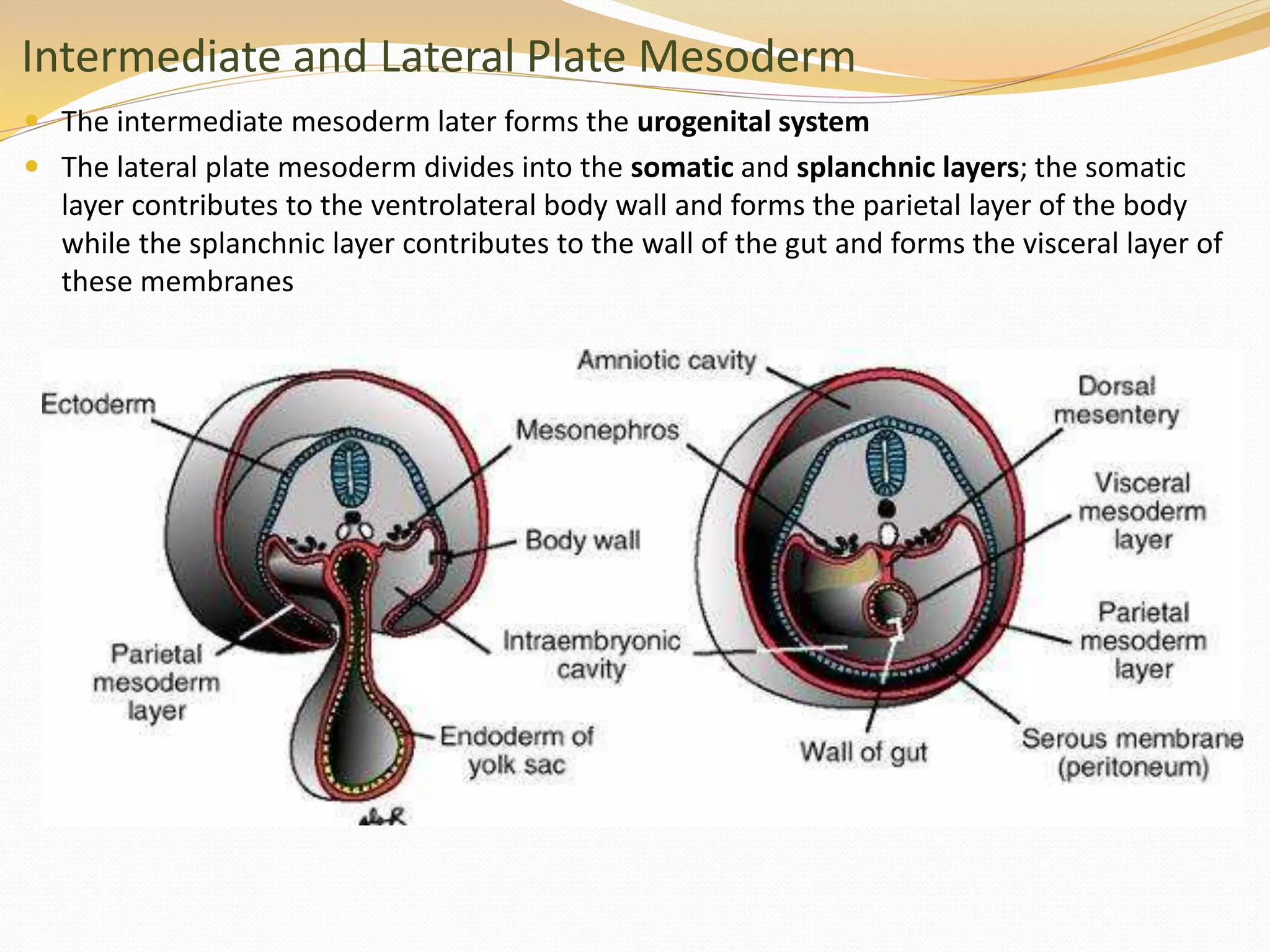
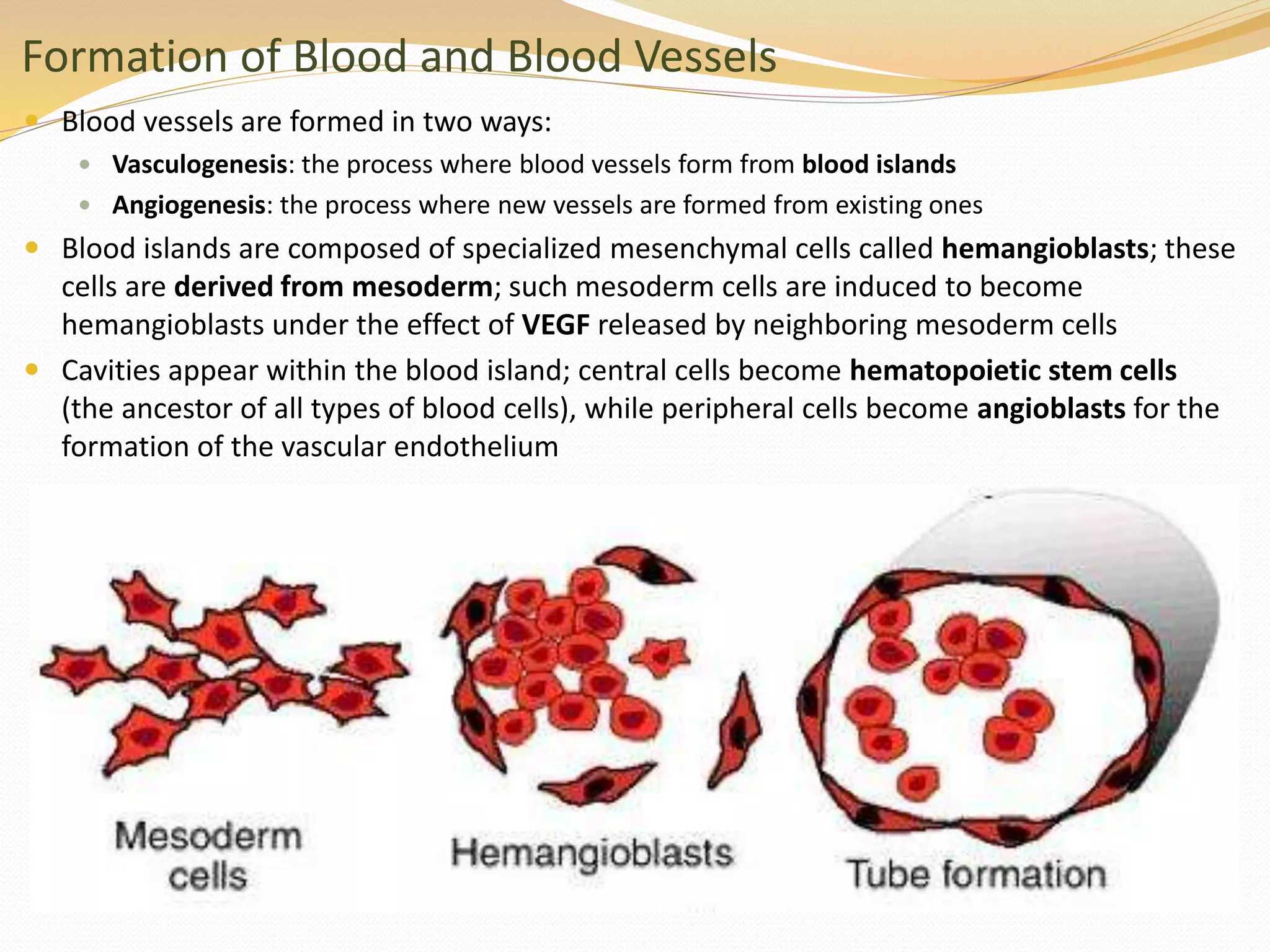
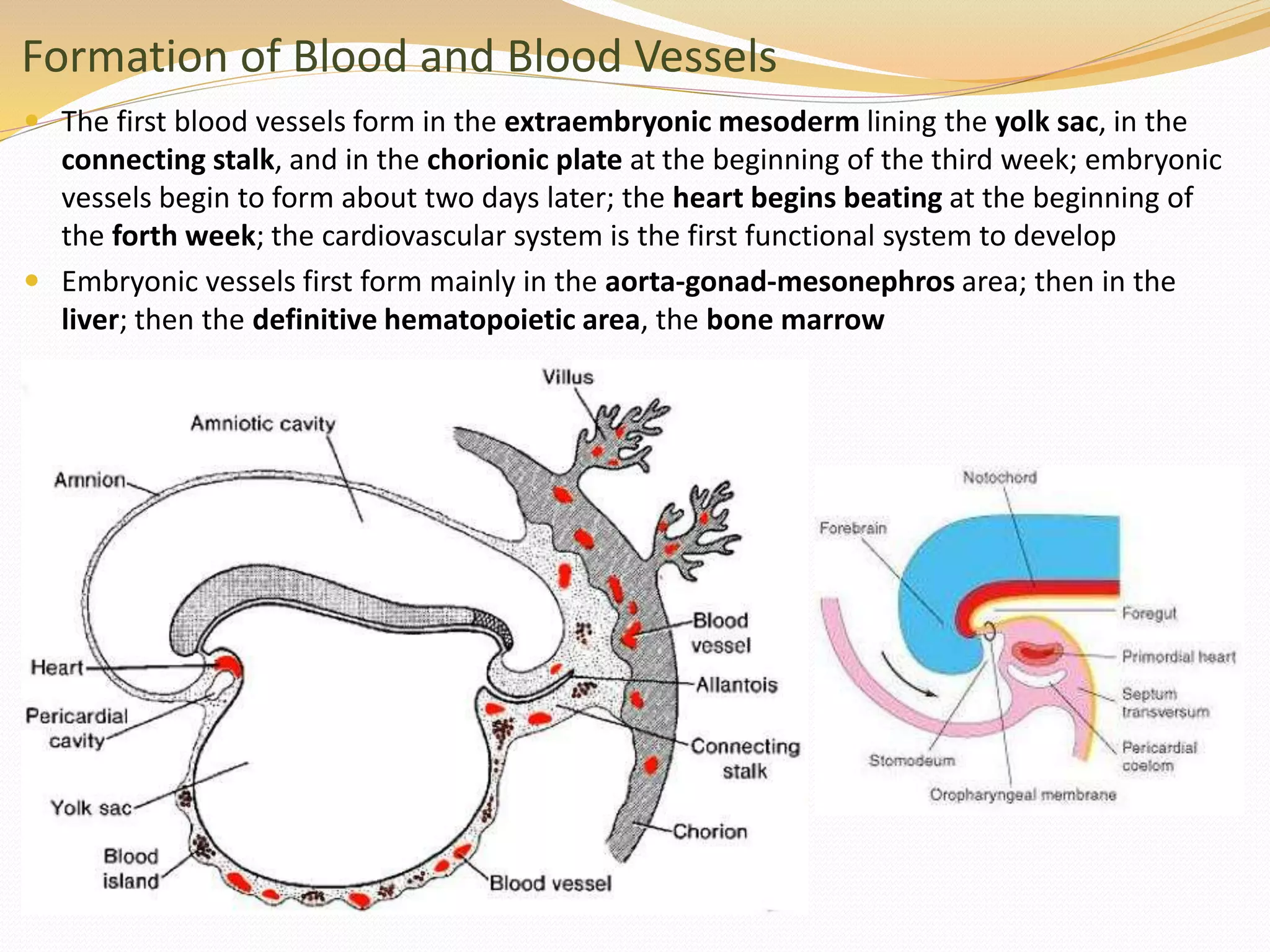
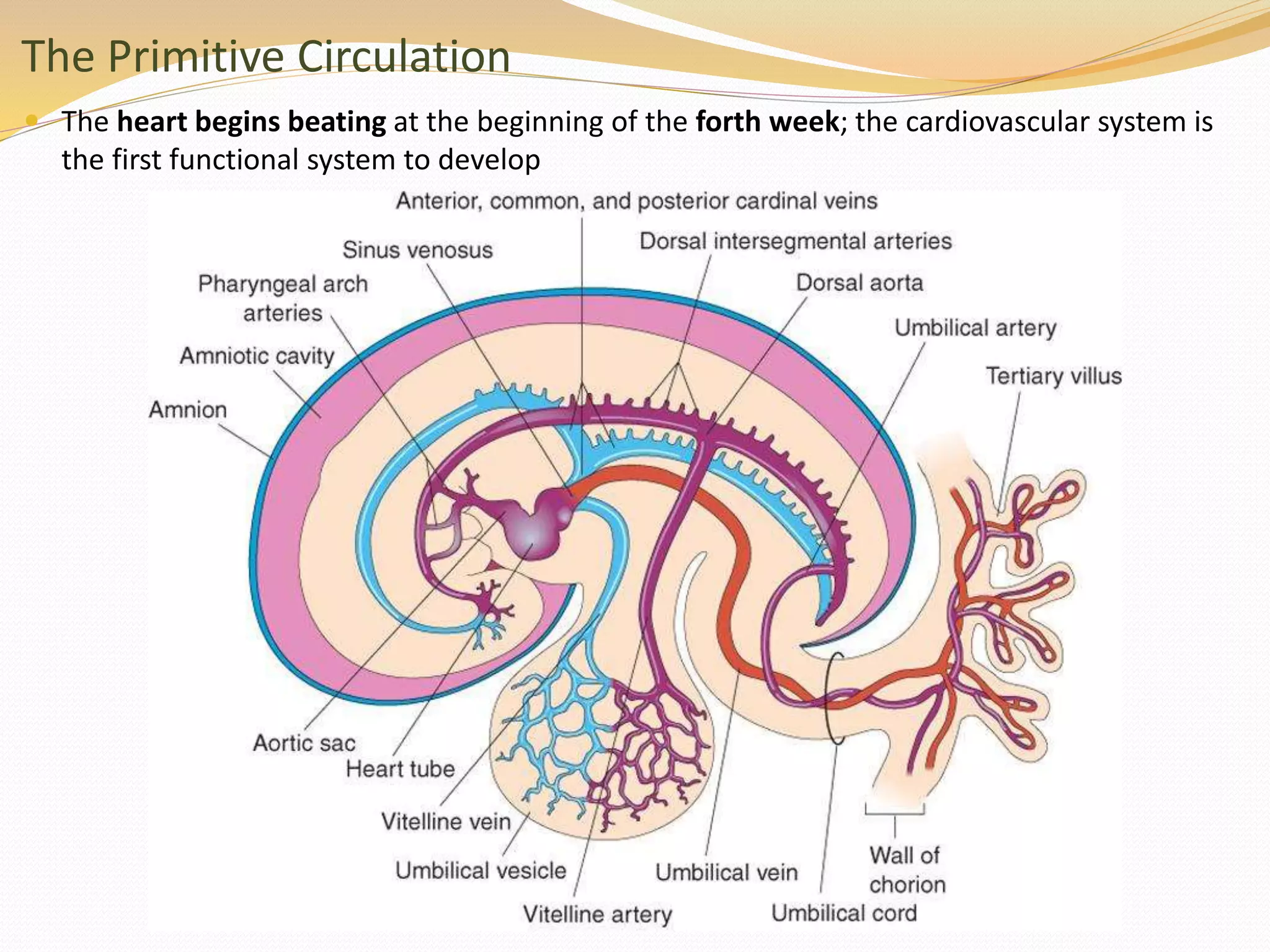
The document discusses the processes of neurulation and mesoderm differentiation in embryonic development, detailing the formation of the neural tube and the migration of neural crest cells. It describes the development of ectoderm and mesoderm derivatives, such as the formation of body cavities and the cardiovascular system. Additionally, it outlines the roles of somites and their contributions to musculature and the vertebral column.