Septic shock
- 1. Topic Review Septic Shock Management Piti Niyomsirivanich, MD. 10 Jan 2013
- 2. Take home message • Adequate preload • Appropriate Antibiotic within 1 hr • Proper dose of vasopressors • Consult
- 3. Outline • Definition • Pathophysiology • Early Goal Directed Therapy • Fluid Resuscitation • Vasopressors • Steroids • Antibiotics • Glucose control • Blood product administration • Bicarbonate therapy • Stress ulcer prophylaxis
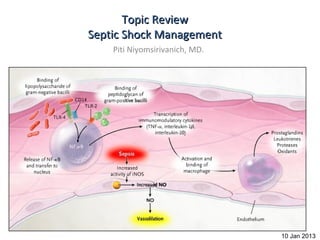
- 4. Definition • Bacteremia : Bacteria in blood • Septicemia : Bacteria + toxin in blood • SIRS : 2/4 of following conditions – 1)Temp > 38 C or < 36 C – 2) Pulse rate > 90 /min – 3) RR > 20 /min or PaCO2 < 32 mmHg – 4) WBC > 12,000/ul or < 4000 /ul and/or Band form > 10% • Sepsis = SIRS from infection • Severe sepsis = Sepsis+ end organ damage – CVS , Renal , pulmonary , Hematologic ,Metabolic acidosis • Septic Shock = Sepsis + hypotension
- 6. Guideline Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock:2008
- 7. Since 2001 10+ years ago!!!
- 9. Result of EGDT N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1368- 1377 November 8, 2001
- 10. Early goal directed therapy SIRS + SBP < 90 mmHg or MAP < 65 mmHg ONE -Or- Lactate > 4 mmol/L Hour After 20-30 ml/kg crystalloid IVF Culture Supplement oxygen Antibiotic within 1 hour Critical care consultation or ET tube (if necessary) Volume accessment < 8-12 mmHg CVP ? IVF 8-12 mmHg < 65 mmHg Five MAP ? Vasopressor (NE/dopamine) Hours >/= 65 mmHg < 70% Blood transfusion to Hct > 30% ScvO2 ? > 70% Inotropic agent Goals achieved Sedatives & muscle relaxants Resuscitation complete N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1368-1377November 8, 2001
- 12. Fluid Resusitation • Fluid therapy – crystalloids or colloids (1B) – Target a CVP of 8-12 mmHg (1C) – Give fluid challenges of 1000 mL of crystalloids • or 300–500 mL of colloids over 30 mins. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock:2008
- 14. Shock • BP = CO X TVR • CO = HR X SV • SV = EDV – ESV • BP = ( EDV- ESV ) X HR X TVR X EDV EDV • BP = EF X HR X TVR X EDV
- 15. Volume N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1368- 1377November 8, 2001
- 17. Fluid • Crystalloids – NSS – Ringer Lactate Solution • Colloids – albumin – Dextrans – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 18. Fluid • Crystalloids – NSS Low cost – Ringer Lactate Solution edema • Colloids Hemodilution Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis – albumin – Dextrans – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 19. Fluid • Crystalloids – NSS Low cost – Ringer Lactate Solution Lactate liver Acetate peripheral tissue • Colloids Potassium – albumin edema – Dextrans – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 20. Fluid • Crystalloids – NSS SAFE Study * – Ringer Lactate Solution not differrent VS NSS • Colloids hypocalcemia – albumin expensive – Dextrans – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven *A Comparison of Albumin and Saline for Fluid Resuscitation in the Intensive Care Unit N ENGL J MED 2004; 350:2247-2256 May 27, 2004
- 21. Fluid • Crystalloids Coagulopathy (inh. F VIII/ vWF) – NSS Renal damage – Ringer Lactate Solution Cross matching problem • Colloids Osmotic diuresis – albumin Anaphylaxis 0.27% – Dextrans – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 22. Fluid • Crystalloids Gelofundol Haemaccel – NSS – Ringer Lactate Solution 30,000-35,000 kDa • Colloids Renal Excretion – albumin Short half life – Dextrans Anaphylaxis 0.34% – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 23. Fluid • Crystalloids • MW 450-480 kDa Hetastarch Hespan – NSS •MW 200 kDa – Ringer Lactate Solution •HAES-Steril 6%,10% • Colloids •MW 70 kDa •HES 70/0.5 – albumin •Voluven – Dextrans Anaphylaxis 0.058% – Gelatins e.g. Haemaccel – Hydroxyethylstarch e.g. Voluven
- 24. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. CD 001319,2003
- 25. Volume Assessment • Static VS dynamic • Non-invasive – U/S IVC – Passive leg raising test – Pulse oximetry plethysmographic waveform amplitude variation • Invasive – CVP – Fluid challenge test – CVP variation – Pulse pressure variation
- 26. Volume Assessment • Require Endotracheal tube • No Endotracheal tube • W/WO Endotracheal tube
- 27. CVP measurement a= Atrial contraction c= Ventricular Contraction x= Atrial relaXation v= Venous filling y = Tr”Y”cuspids opening
- 28. CVP • CVP : poor predictor of fluid volume CHEST. July 2008;134(1):172-178.
- 29. Fluid Challenge Test for CVP Load IV fluid 200-250 ml in 10 min CVP + CVP + CVP + </=2 2-5 >/=5 Continue fluid therapy Wait Decrease rate of fluid therapy
- 30. Ultrasound IVC Caval Index = 100 x (diam expiration - diam inspiration)/diam expiration Caval Index > 50% suggest low CVP Ann Emerg Med 2010; 55:290-295.
- 31. Passive leg raising test Esophageal doppler : in cardiac output > 8% predict fluid responsiveness Critical Care 2006, 10:170
- 32. Pulse oximetry plethysmographic waveform amplitude variation
- 33. CASE A CASE B CVP =15 cmH2O CVP =5 cmH2O
- 34. Pulse oximetry plethysmographic waveform amplitude variation %POP variation POP max – POP min X 100 > 13% POP mean
- 35. Arterial Line
- 37. Vasopressor therapy • Dopamine VS Norepinephrine Kaplan–Meier Curves for 28-Day Survival in the Intention-to-Treat Population. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:779-789
- 38. Vasopressure therapy Dopamine Low dose Moderate dose (beta adrenergic receptor ) 5-10 ug/kg/min High dose (alpha adrenergic receptor) >10 ug/kg/min Maximum dose 50 ug/kg/min Norepinephrine start 0.5 mcg/min Harrison Int. Med edition 18 th
- 39. Vasopressor therapy Example ผู้หญิง 64 ปี หนัก 70 kg มาด้วย ไข้ หนาวสั่น ปัสสาวะแสบขัด CBC : WBC 25000/ul N% 85 Band 2% Hb 12 g/dl Plt 200,000/ul UA WBC 50-100 BP 80/40 mmHg PR 95/min Temp 37.8 C RR 18/min จงคำานวณ dose ของ Dopamine ให้ start 5 ug/kg/min
- 40. Vasopressor therapy Example ผู้หญิง 64 ปี หนัก 70 kg มาด้วย ไข้ หนาวสัน ปัสสาวะแสบขัด ่ CBC : WBC 25000/ul N% 85 Band 2% Hb 12 g/dl Plt 200,000/ul UA WBC 50-100 BP 80/40 mmHg PR 65/min Temp 37.8 C RR 18/min จงคำานวณ dose ของ Dopamine ให้ start 5 ug/kg/min 60 X W (kg) X D (ug/kg/min) Rate (ml/min) C Solute C= 1,000 Volume
- 41. Vasopressor therapy Example ผู้หญิง 64 ปี หนัก 70 kg มาด้วย ไข้ หนาวสัน ปัสสาวะแสบขัด ่ CBC : WBC 25000/ul N% 85 Band 2% Hb 12 g/dl Plt 200,000/ul UA WBC 50-100 BP 80/40 mmHg PR 65/min Temp 37.8 C RR 18/min จงคำานวณ dose ของ Dopamine ให้ start 5 ug/kg/min 60 X 70 X 5 Rate (ml/min) = 10.5 ml/hr 2000 1000 C= 1,000 = 2000 500 (Dopamine 1000 mg ผสม 5%D/W 500 ml)
- 42. Early goal directed therapy SIRS + SBP < 90 mmHg or MAP < 65 mmHg ONE -Or- Lactate > 4 mmol/L Hour After 20-30 ml/kg crystalloid IVF Culture Supplement oxygen Antibiotic within 1 hour Critical care consultation or ET tube (if necessary) Volume accessment < 8-12 mmHg CVP ? IVF 8-12 mmHg < 65 mmHg Five MAP Vasopressor (NE/dopamine) Hours >/= 65 mmHg < 70% Blood transfusion to Hct > 30% ScvO2 > 70% Inotropic agent Goals achieved Sedatives & muscle relaxants Resuscitation complete N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1368-1377November 8, 2001
- 43. ScvO2 ให้เงินไป โรงเรียน ขากลับ เหลือ 50 บาท แปลว่าให้เงินไปโรงเรียนพอใช้
- 44. ScvO2 O2 content O2 content เหลือ 70% แปลว่าให้ออกซิเจนไปเนือเยือพอใช้ ้ ่
- 45. ScvO2
- 46. O2 delivery • DO2 = [1.39 x Hb x SaO2 + (0.003 x PaO2)] x CO • Depend on < 70% Blood transfusion to Hct > 30 ScvO2 – Hemoglobin > 70% Inotropic agent – O2 saturation Goals achieved – Cardiac output – ScvO2 < 70% • target Hct > 30 • Inotropic drug increase cardiac output Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain (2004) 4 (4) 123-126
- 47. Alternative for ScvO2 • Lactate clearance – lactate clearance >10% or higher • 6% lower in-hospital mortality than those resuscitated to an ScvO2 of at least 70% – (95% CI, −3% to 15%) – noninferiority trial. JAMA. 2010 Feb 24;303(8):739-46.
- 48. Antimicrobial Therapy • administration of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy within 1 hr of diagnosis of septic shock (1B) and severe sepsis without septic shock (1D); • reassessment of antibiotic therapy with microbiology and clinical data to narrow coverage, when appropriate (1C); • a usual 7–10 days of antibiotic therapy guided by clinical response (1D); • source control with attention to the balance of risks and benefits of the chosen method (1C); Survival Sepsis Guideline .Crit Care Med 2008
- 49. Empirical Antibiotic • Host – Immunocompetent – Neutropenia – IVDU – Post Splenectomy – AIDS • Risk factors & exposures • Site of infection • Antibiotics of choice ?? Antibiotic therapy in patients with septic shock European Journal of Anaesthesiology (EJA). 28(5):318-324, May 2011
- 50. Tips • every 10 min, survival is decreased by 1%.* • First dose Full dose – Then renal adjustment * Antibiotic therapy in patients with septic shock European Journal of Anaesthesiology (EJA). 28(5):318-324, May 2011
- 51. De-escalate Therapy • De-escalate Empirical antimicrobial therapy in life-threatening situations – Start with Broad Spectrum • ‘Broad-spectrum antibiotics’ refers to antibiotics with activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including imipenem-cilastatin, piperacillin-tazobactam, ceftazidime or ciprofloxacin. • Limited-spectrum antibiotics will only refer to β-lactam antibiotics without activity against P. aeruginosa (essentially, ceftriaxone and amoxicillin-clavulanate). Antibiotic therapy in patients with septic shock European Journal of Anaesthesiology (EJA). 28(5):318-324, May 2011
- 52. De-escalate Therapy : Life Threatening • "สันๆ แต่ aggressive" แล้วปรับลงมา ้ – Recurrent infections were more common in Group No De-escalate (19% versus 5%, P = 0.01) – An inadequate empiric antibiotic therapy was more frequent in Group No De-escalate (27.5% versus 7.7% P = 0.02) – Mortality between the two groups 18.3% (D) vs 24.6% (ND) Critical Care 2010, 14:R225
- 53. Antibiotic therapy in patients with septic shock European Journal of Anaesthesiology (EJA). 28(5):318-324, May 2011
- 55. Steroids in CIRCI (critical illness related corticosteroid insufficiency) •stress-dose steroid therapy given only in septic shock after blood pressure is identified to be poorly responsive to fluid and vasopressor therapy (2C) •Survival Sepsis Guideline 2008 Serum cortisol •< 15 ug/dl definite adrenal insufficiency •13-35 ug/dl Suspected •>35 ug/dl no benefit •สมาคมเวชบำาบัดวิกฤติแห่งประเทศไทย
- 56. Steroids in CIRCI Surge in cortisol (> 9 ug/dl) response to ACTH 250 ug stimulation Benefit from steroids JAMA. 2002 Aug 21;288(7):862-71
- 57. CIRCI Baseline cortisol level < or = 35 microg/dl is a useful diagnostic threshold for diagnosis of steroid responsiveness in Thai patients with septic shock ACTH stimulation test should not be used sensitivity was 85%, the specificity was 62% J Med Assoc Thai 2010 Jan;93 Suppl 1:S187-95
- 58. CIRCI • Hydrocortisone 100 mg bolus then 200 mg V drip in 24 hr • OR • Hydrocortisone bolus q 4-6 hr NOT q 8 hr – e.g. Hydrocortisone 50 mg V q 6 hr • Then taper off
- 60. Blood Sugar control • NICE-SUGAR study – 3050 patients – Medicine & Surgery Ward – Multicenter randomized open label study – ICU & non ICU – Intensive control 81-108 mg% – Conventional control 144-180 mg% The NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators N Engl J Med 2009; 360:1283-1297March 26, 2009
- 61. NICE-SUGAR Study The NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators N Engl J Med 2009; 360:1283-1297March 26, 2009
- 65. Basal Insulin with Scheduled Insulin (prandial insulin) with Correctional dose
- 67. • CBG (ก่อนอาหาร) เช้า กลางวัน เย็น ก่อนนอน
- 68. Somchai Pathanaangkul ,Royal Thai Army Medica Vol 57 No.4 Oct.-Dec. 2004
- 69. Blood Transfusion ● Give red blood cells when hemoglobin decreases to 7.0 g/dL (70 g/L) to target a hemoglobin of 7.0–9.0 g/dL in adults (1B). A higher hemoglobin lev el may be required in special circumstances (e.g., myocardial ischaemia, se vere hypoxemia, acute hemorrhage, cyanotic heart disease, or lactic acidosi s) ● Do not use erythropoietin to treat sepsis-related anemia. Erythropoietin may be used for other accepted reasons (1B) Do not use fresh frozen plasma to correct laboratory clotting abnormalities unless there is bleeding or planned i nvasive procedures (2D) ● Do not use antithrombin therapy (1B) Administer platelets when (2D) Counts are 5000/mm3 (5 109/L) regardless of bleeding Counts are 5000–30,000/mm3 (5–30 109/L) and there is significant bleeding risk Higher platelet counts (50,000/mm3 [50 109/L]) are required for surgery or invasive procedures
- 70. Blood Transfusion • TRICC Study – Study design: Multicenter RCT – Setting: 25 ICUs across Canada – Hb • 7-9 g/dl (Restrictive Strategy) • 10-12 g/dl (Liberal Strategy) – Primary Outcome : mortality rate 30 days – Results • Hb 7-9 g/dl group mortality rate 22.2% • Hb 10-12 g/dl mortality rate 28.1% • (P=0.05)
- 71. TRICC Study Hb 7-9 g/dl Hb 10-12 g/dl
- 72. Bicarbonate Therapy • We recommend against the use of sodium bicarbonate therapy for the purpost of improving hemodynamics or reducing vasopressure requirement with hypoperfusion-induced lactic acidemia with pH > 7.15 (1B) Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock:2008
- 73. Hb O2 Dissociation curve
- 74. Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis • We recommend that stress ulcer prophylaxis using H2 blocker (1A) • Or PPI (1B) be given to patients with severe sepsis to prevent upper GI bleed. • Weighted aginst the potential effect of an increased stomach pH on development of VAP Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock:2008
- 75. Other • Sucralfate* – Not associated with an increase in stress ulceration. – Less impact gastric colonization Less VAP – Increase aspiration • Enteral Feeding *EAST Practice Management Guidelines Committee
- 76. Take home message • Adequate preload • Antibiotic within 1 hr • Proper dose of vasopressors. • Consult
- 77. Thank you
