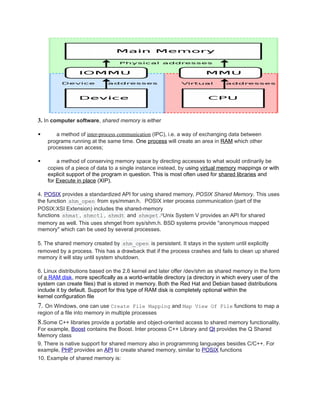
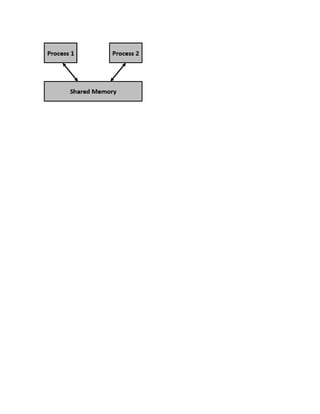
Shared memory allows multiple processes or threads to access the same block of memory concurrently. It provides an efficient means for communication between programs that is useful for reducing redundant copies of data. There are different types of shared memory architectures including uniform memory access (UMA) where all CPUs can access memory uniformly and non-uniform memory access (NUMA) where access times depend on memory location. Programming languages and operating systems provide APIs for processes to create and use shared memory regions for inter-process communication (IPC).
![Q.DESCRIBE SHARED MEMORY ?
A.1. In Computer Science, shared memory is memory that may be simultaneously accessed
by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid
redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs.
Depending on context, programs may run on a single processor or on multiple separate
processors. Using memory for communication inside a single program,
e.g. among its multiple threads, is also referred to as shared memory
2. In computer hardware, shared memory refers to a (typically large) block of random access
memory (RAM) that can be accessed by several different central processing units (CPUs) in
a multiprocessor computer system.
Shared memory systems may use:[1]
uniform memory access (UMA): all the processors share the physical memory uniformly;
non-uniform memory access (NUMA): memory access time depends on the memory
location relative to a processor;
cache-only memory architecture (COMA): the local memories for the processors at each
node is used as cache instead of as actual main memory.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sharedmemory-200511154544/75/Topic-Shared-memory-1-2048.jpg)