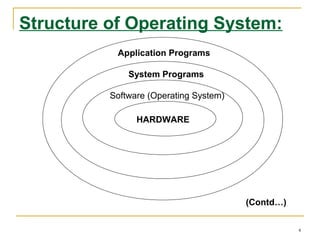
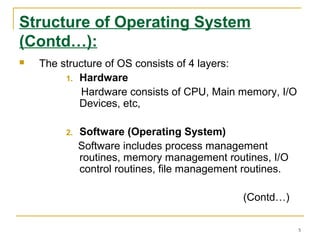
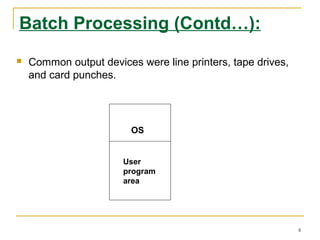
An operating system is software that enables programs to use computer hardware. It organizes and controls hardware resources and acts as an interface between programs and hardware. Operating systems perform functions like making computers more convenient to use, allowing efficient use of resources, and enabling computers to evolve without interruption. The structure of an operating system consists of four layers - hardware, the operating system software, system programs, and application programs. Early operating systems used batch processing where jobs were submitted in batches to be executed together, while later systems used multiprogramming and time sharing to allow simultaneous execution of multiple programs. Operating systems can also be classified as single-user or multi-user depending on how many users they support at once.