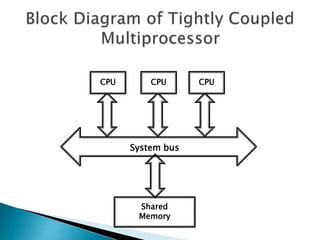
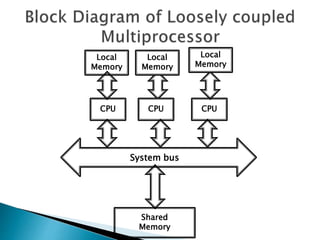
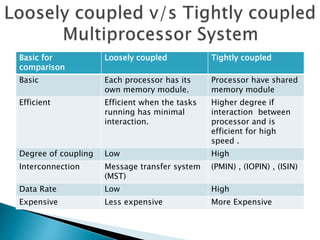
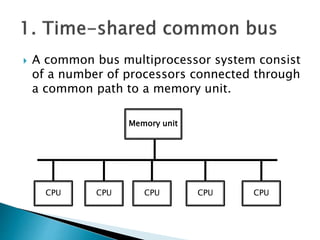
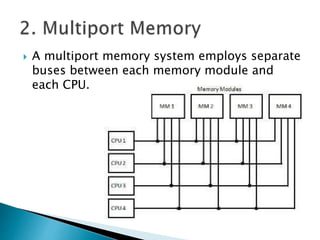
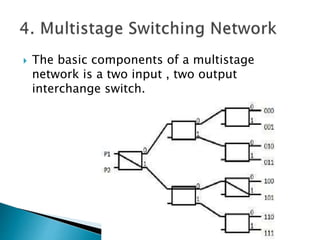
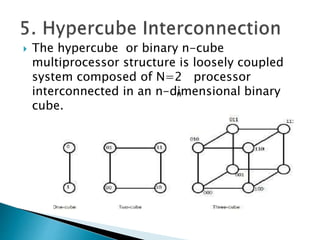
This document discusses multiprocessor systems and their classification. It defines a multiprocessor system as having two or more CPUs with shared memory and I/O. Multiprocessor systems are classified as tightly coupled, with shared memory accessible to all CPUs, or loosely coupled, with each CPU having its own local memory. The document compares tightly and loosely coupled systems and discusses various interconnection structures used in multiprocessors like common buses, multiport memory, crossbar switches, and hypercube networks.