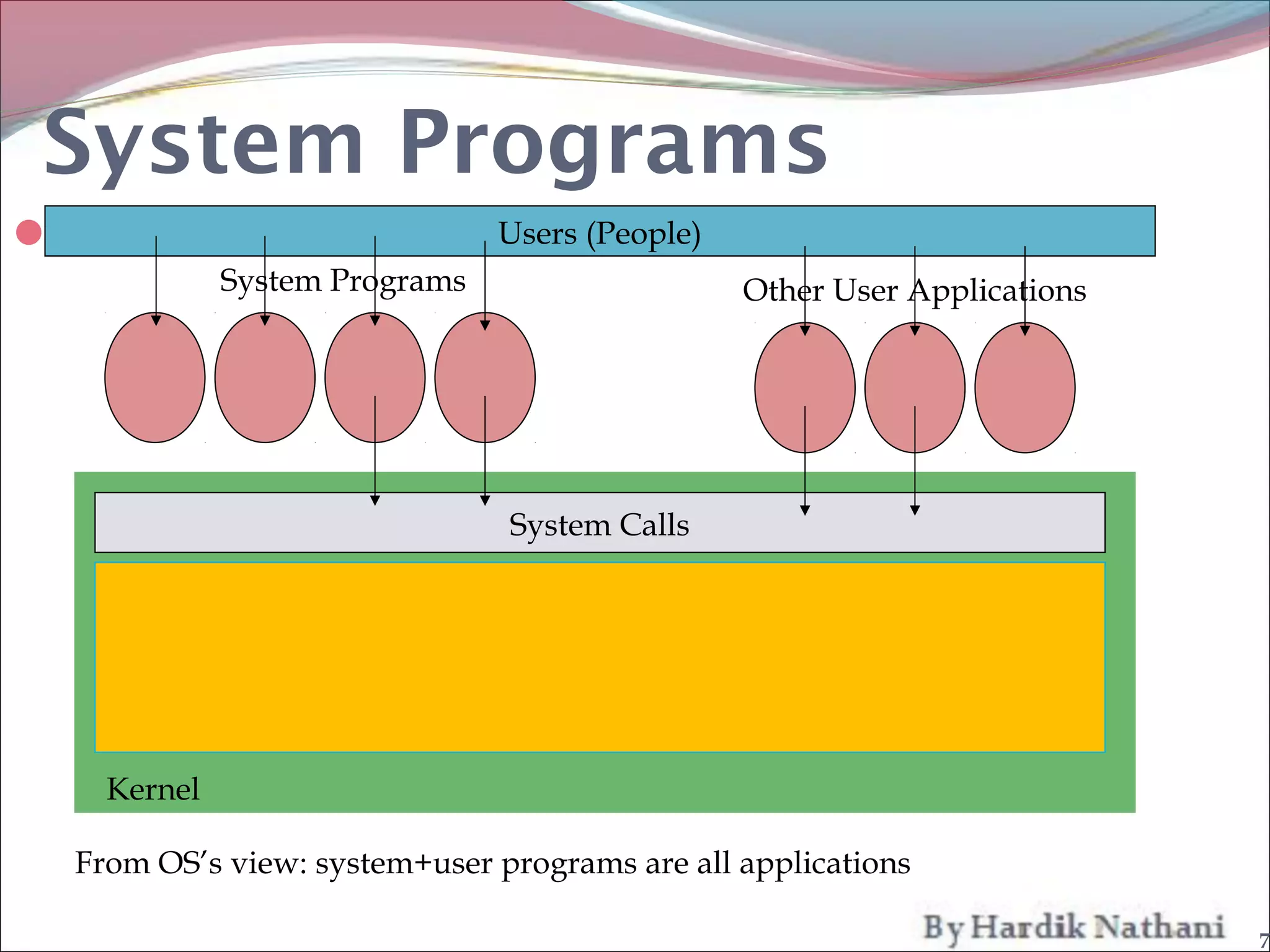
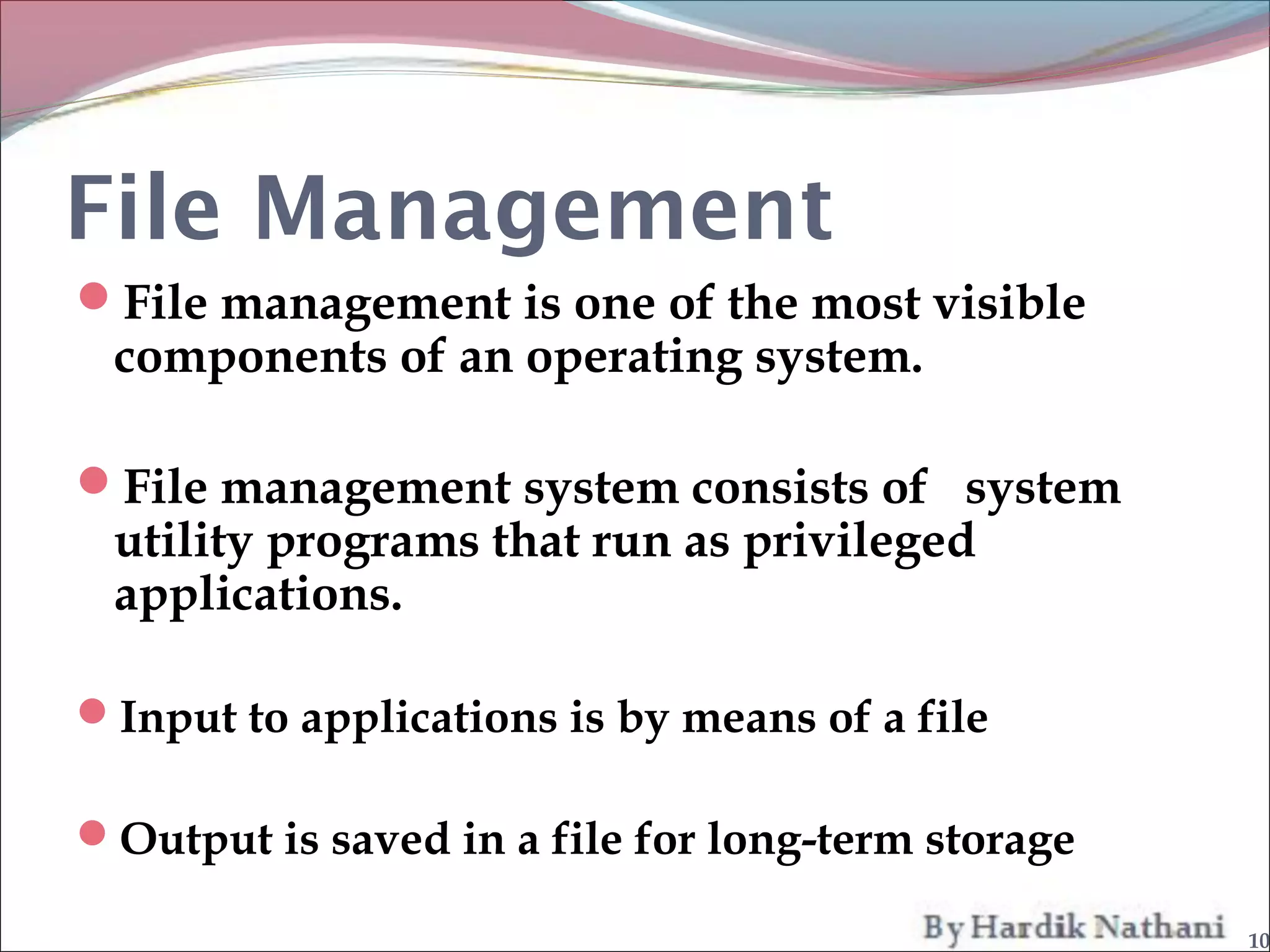
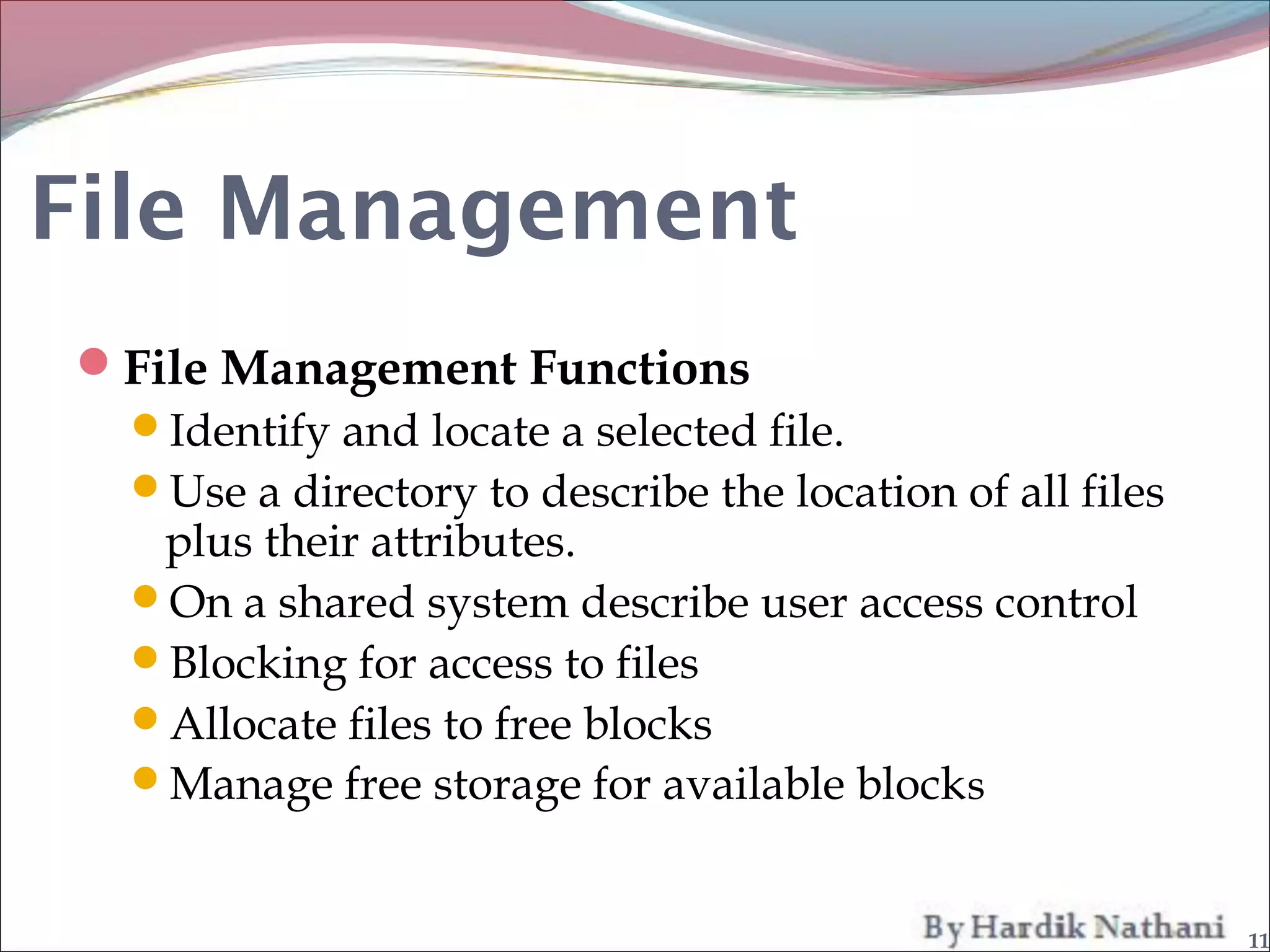
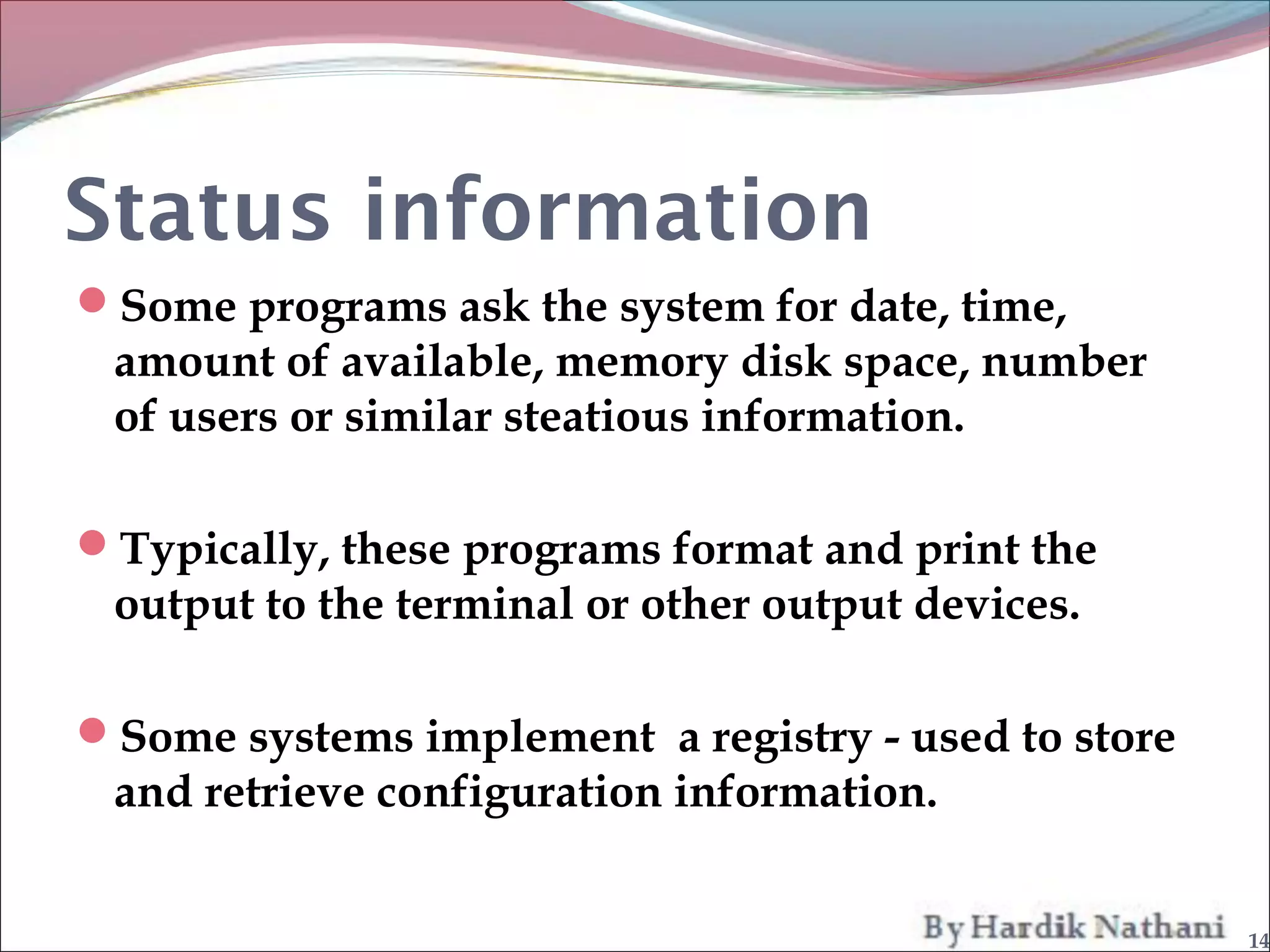
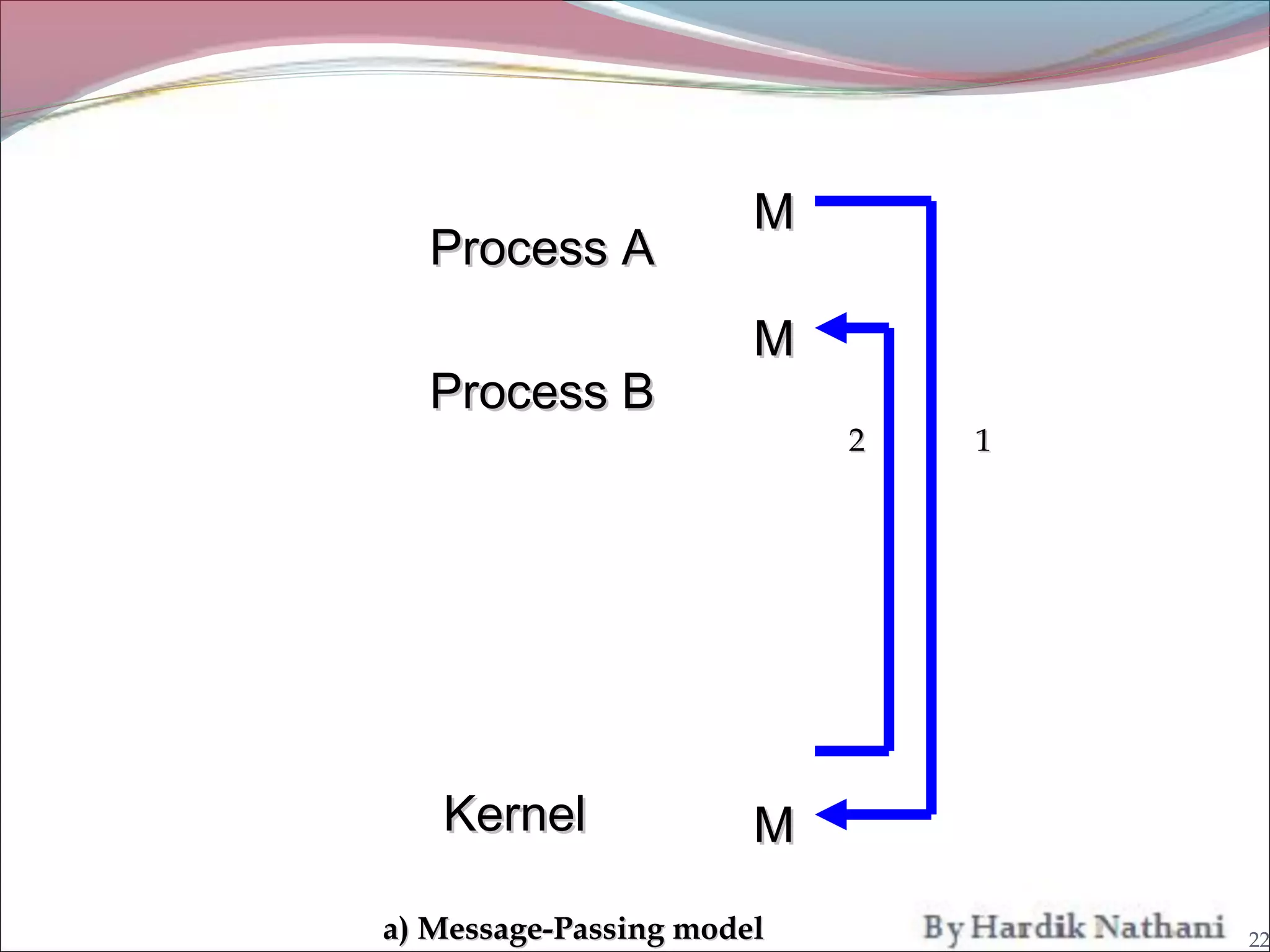
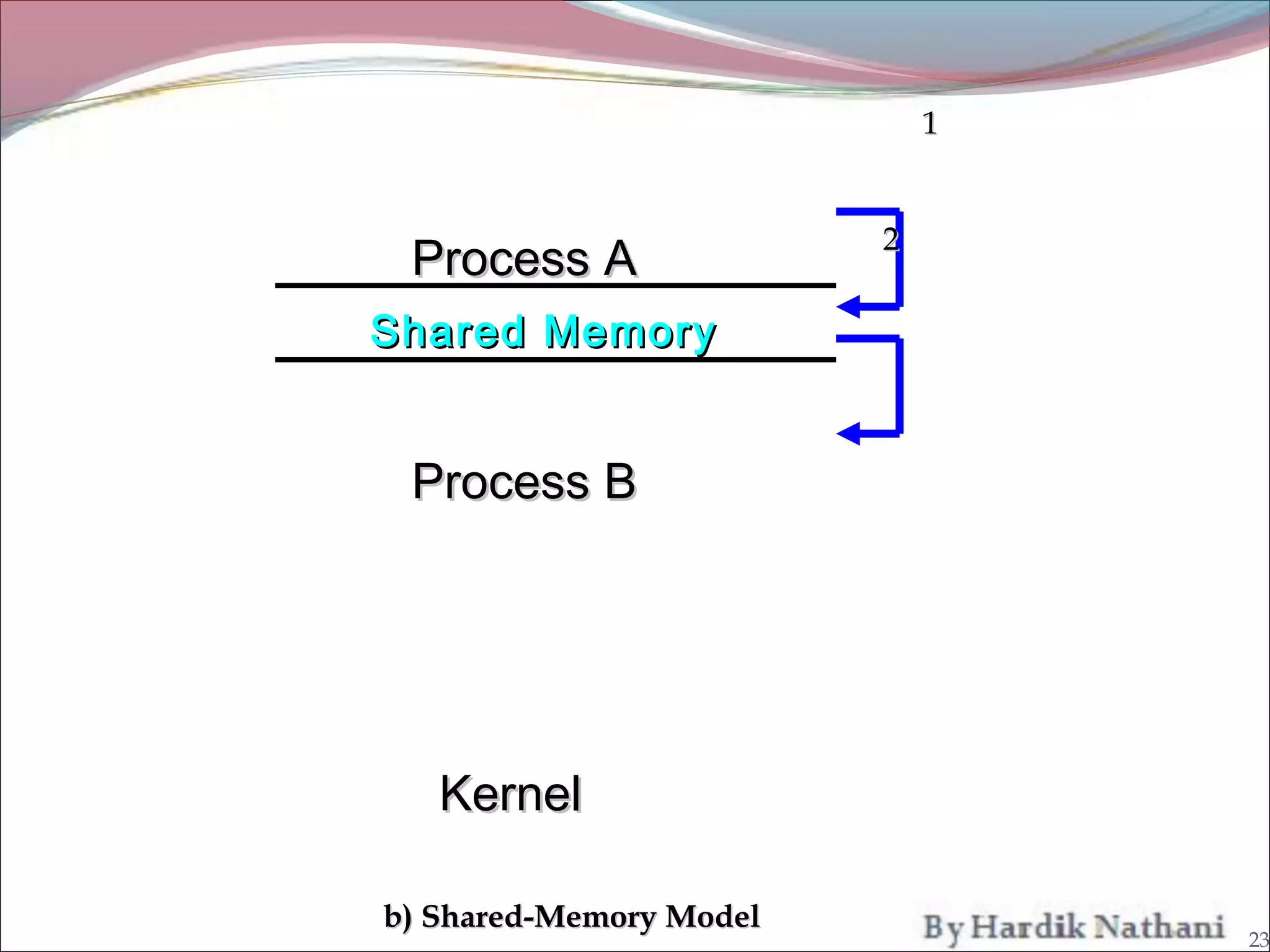
An operating system is a program that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. It acts as an intermediary between users and the computer hardware. System programs are programs that are part of an operating system and provide functions like file manipulation, status information, file modification, programming language support, program loading and execution, and communications. Common system programs include compilers, text editors, file managers, and network utilities. The operating system manages resources and coordinates the activities of other system and application programs.