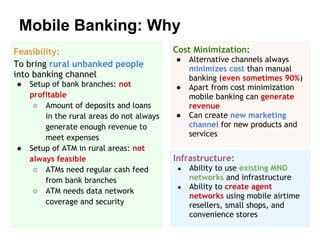
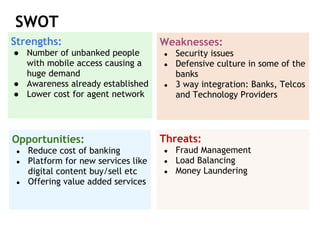
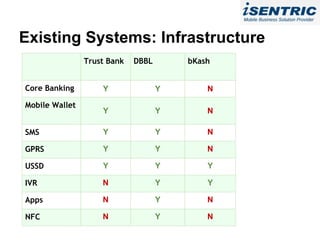
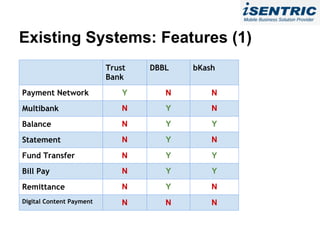
The document analyzes the state of mobile banking (MFS) in Bangladesh. It finds that MFS has grown rapidly, with over 4 million accounts opened, driven by the large unbanked population and widespread mobile phone access. Several banks have launched successful MFS programs. However, MFS is still in early stages, with opportunities to expand agent networks and offerings. Regulations by Bangladesh Bank support further growth and integration of MFS with other financial services. Security, integration challenges, and agent management remain as issues to address for MFS to become a primary banking channel in Bangladesh.






![Data Source
[1] Bangladesh Bank report on Mobile Financial Services in Bangladesh: An
Overview of Market Development. (July 2012)
[2]http://www.thedailystar.net/newDesign/news-details.php?nid=104699
[3]http://www.smbworldasia.com/en/content/dutch-bangla-bank-pioneers-
mobile-banking-banglades
[4]http://en.wikipedia.
org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_number_of_mobile_phones_in_use
[5]http://www.isentric.com/index.php?rt=page/content&page=solution-
banking&m=solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forbanks-121213071808-phpapp02/85/Mobile-Banking-in-Bangladesh-An-Incomplete-Study-15-320.jpg)