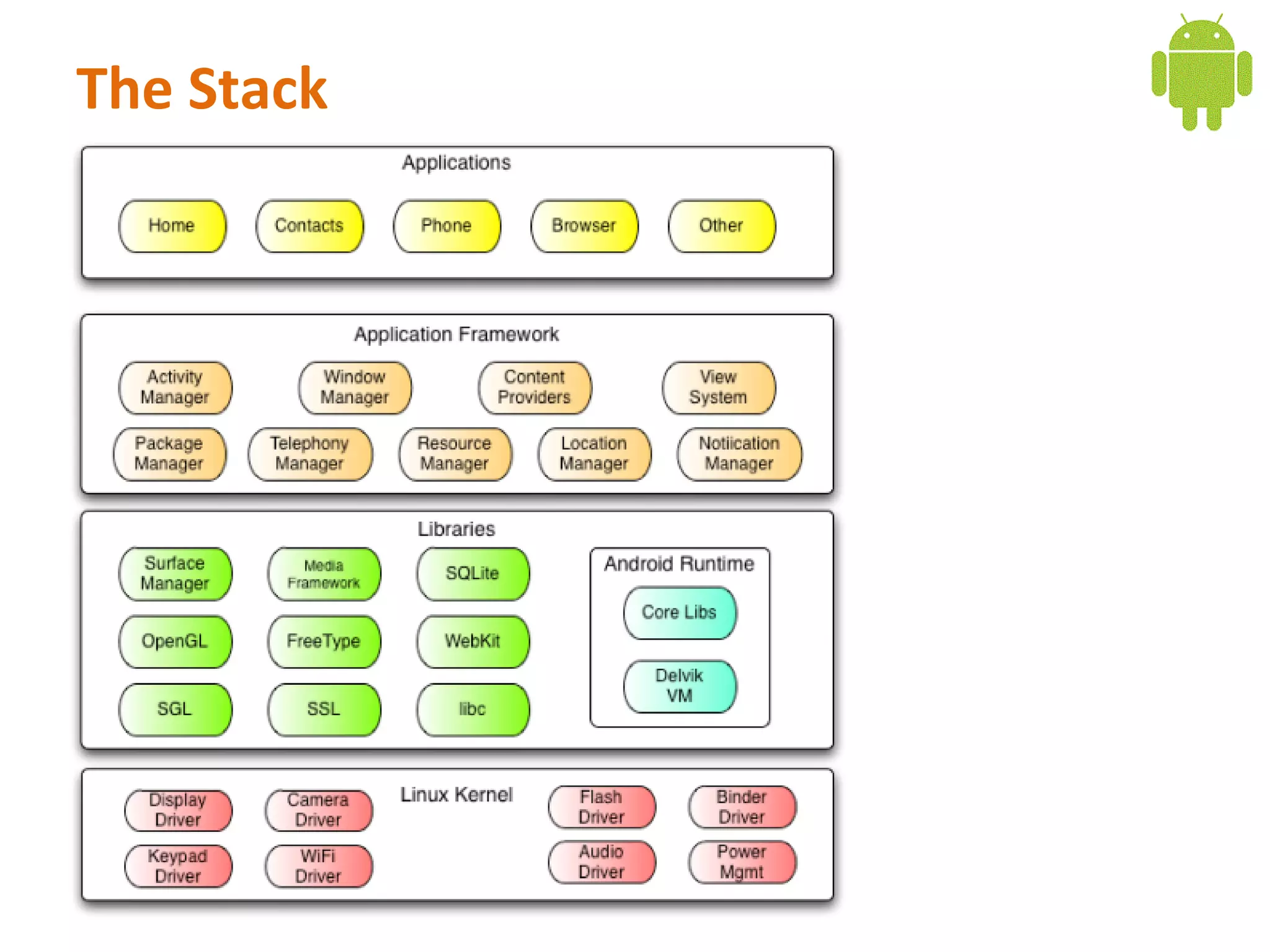
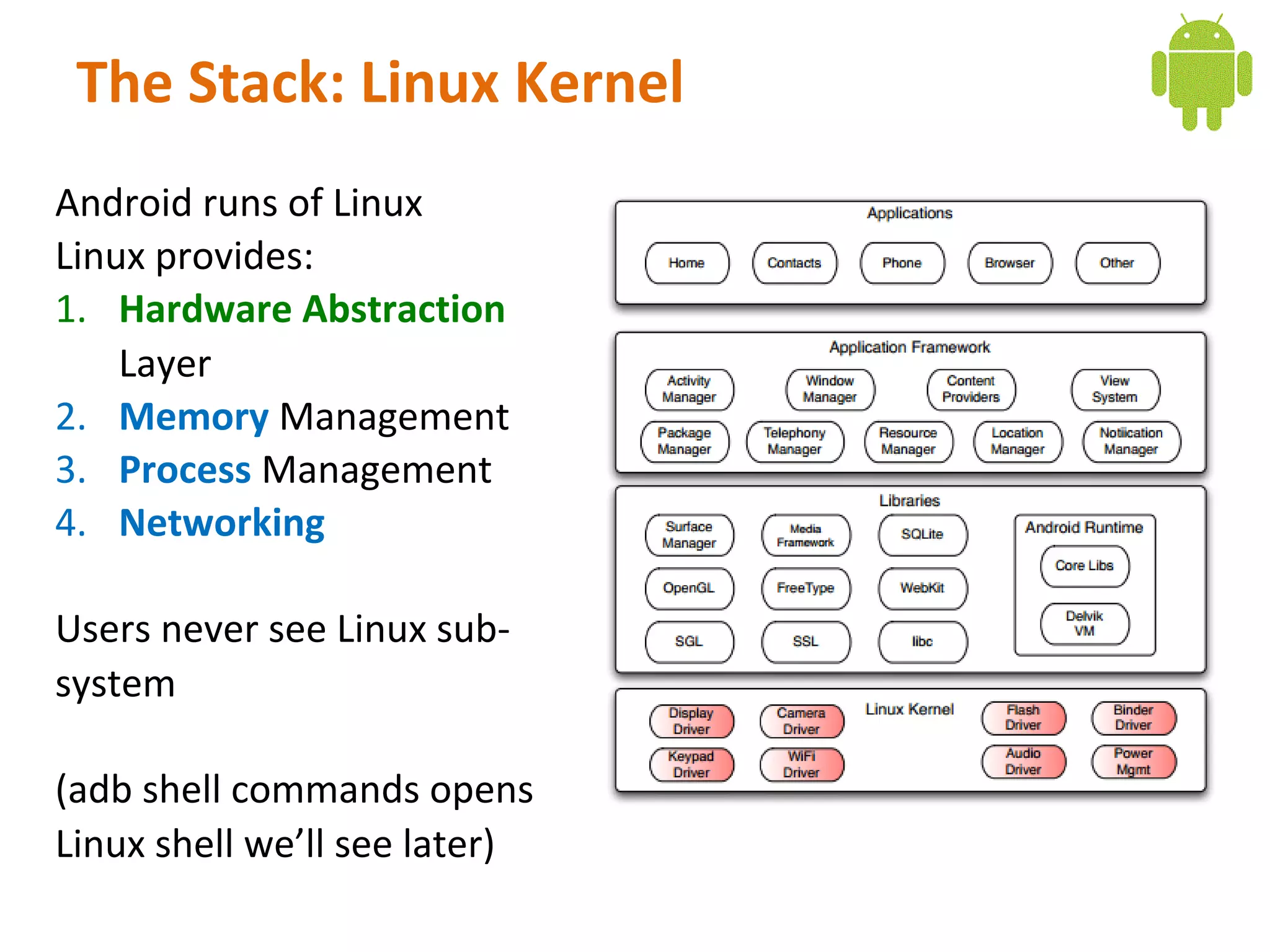
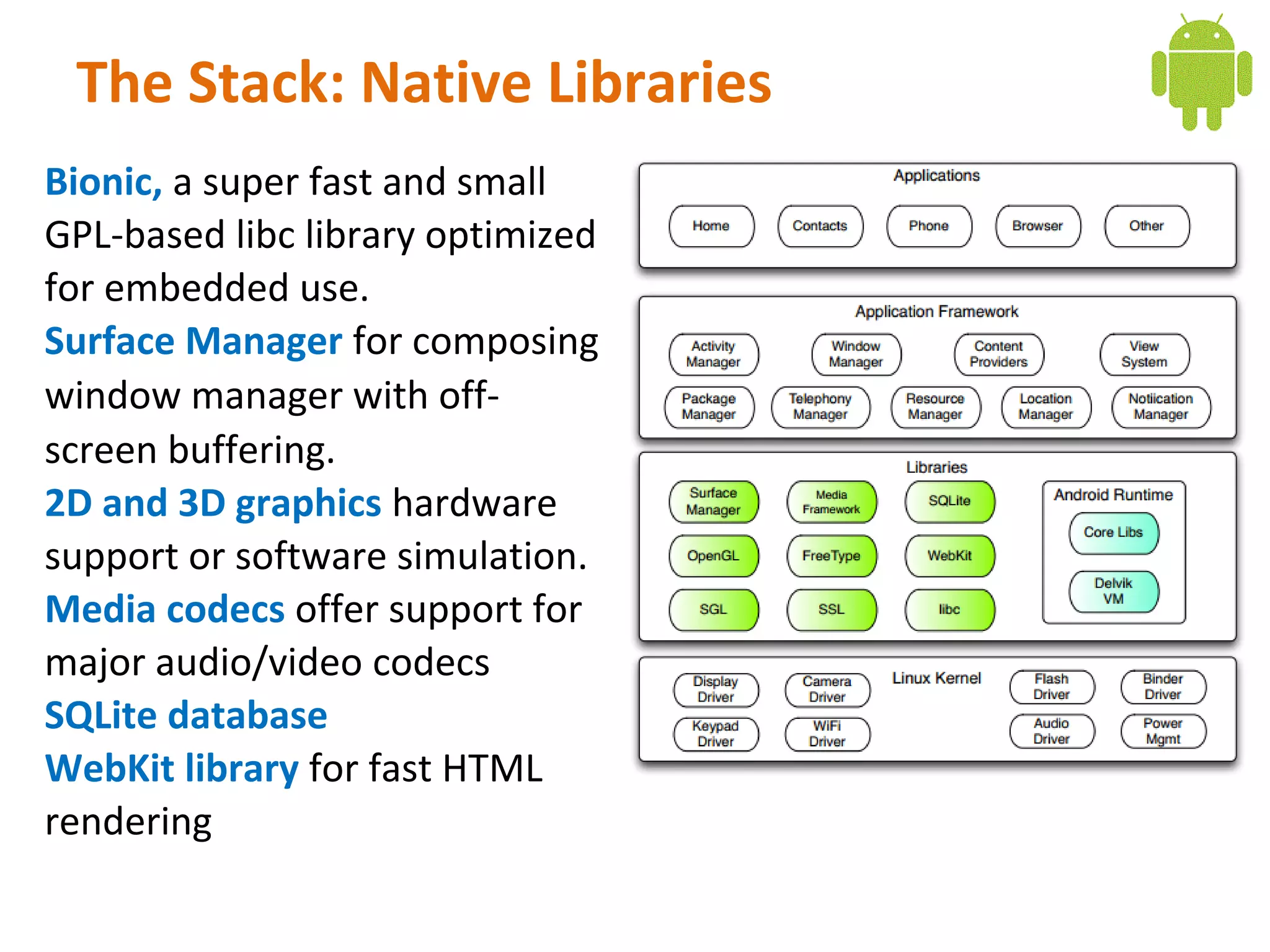
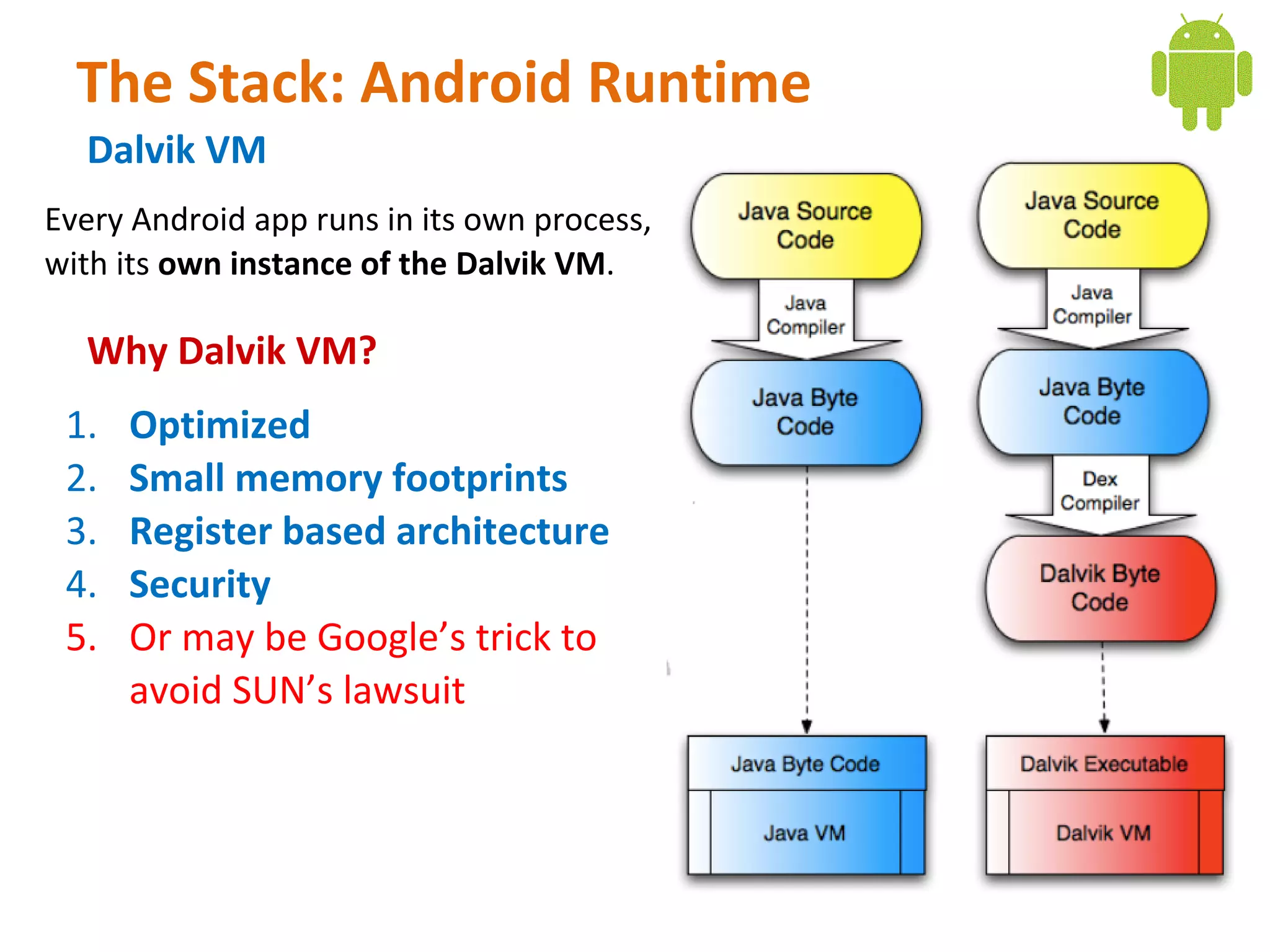
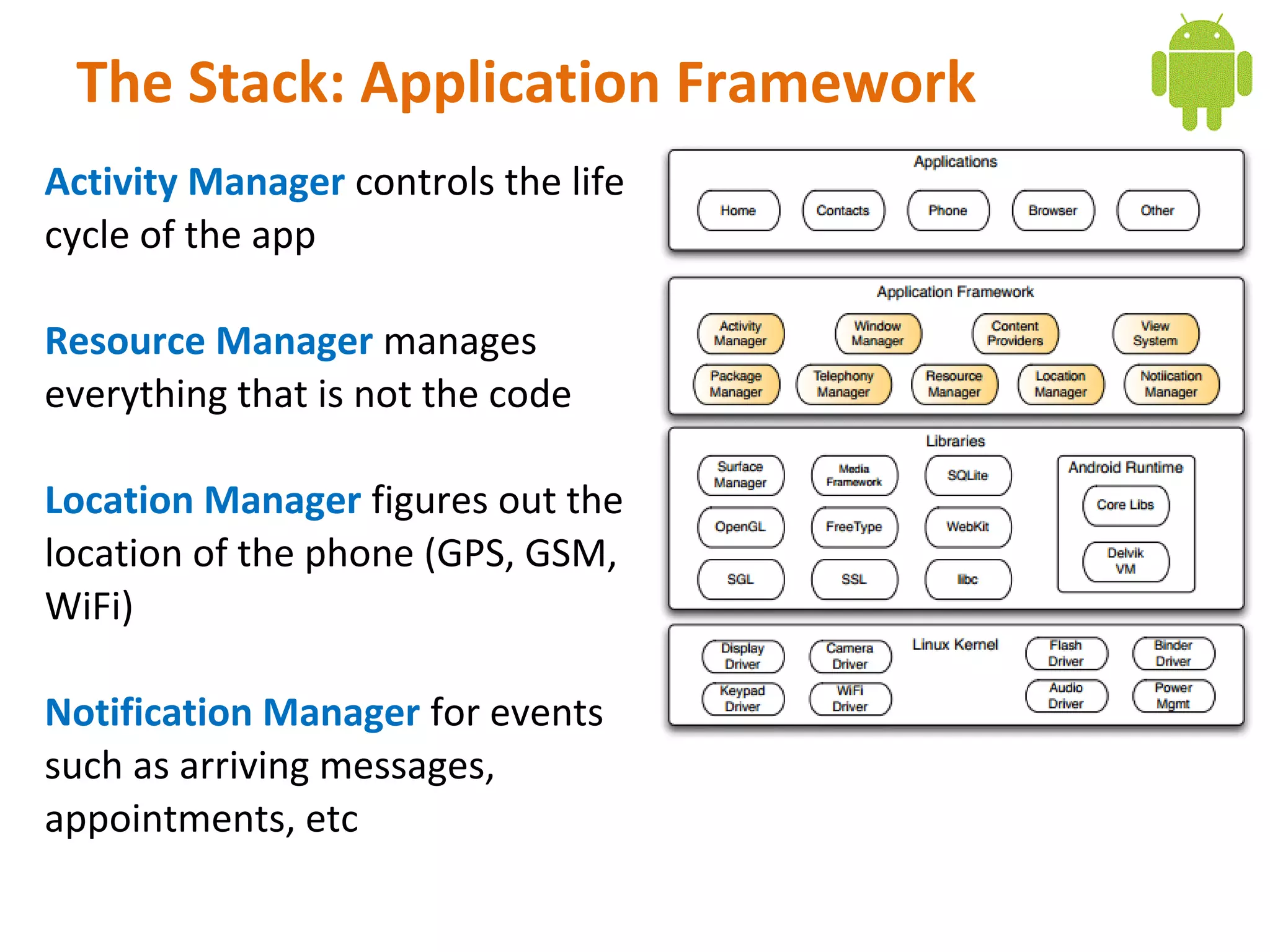
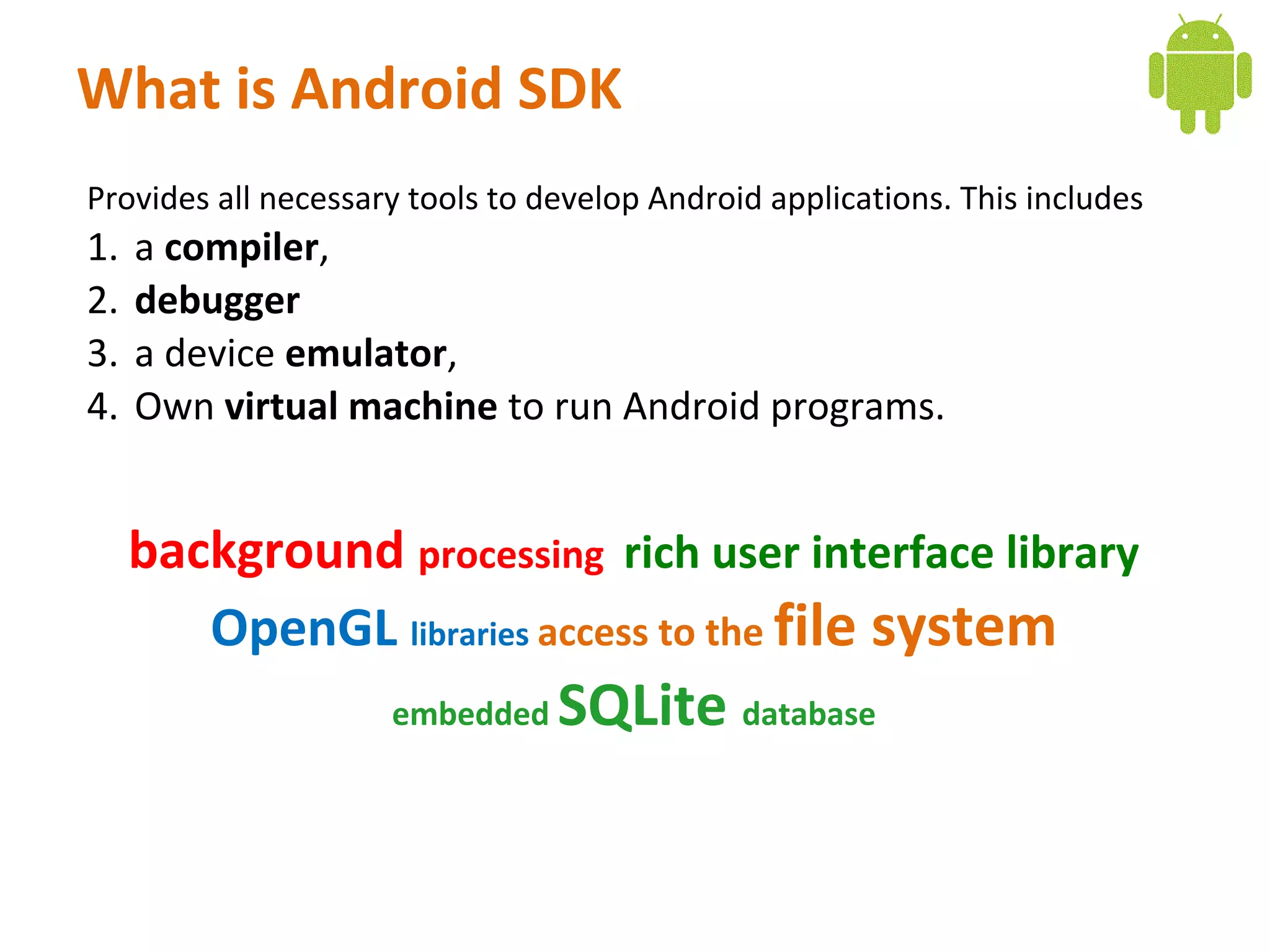
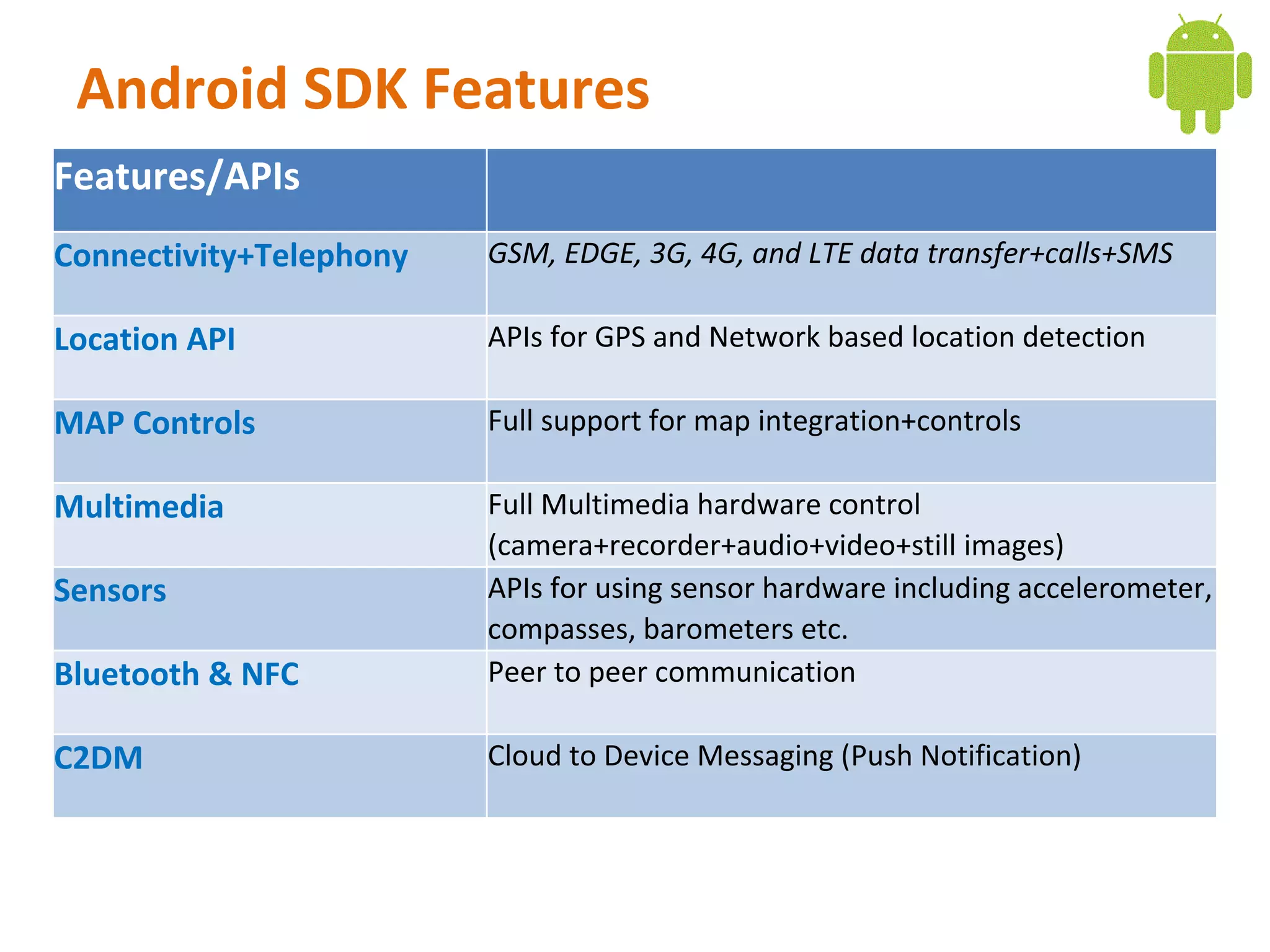
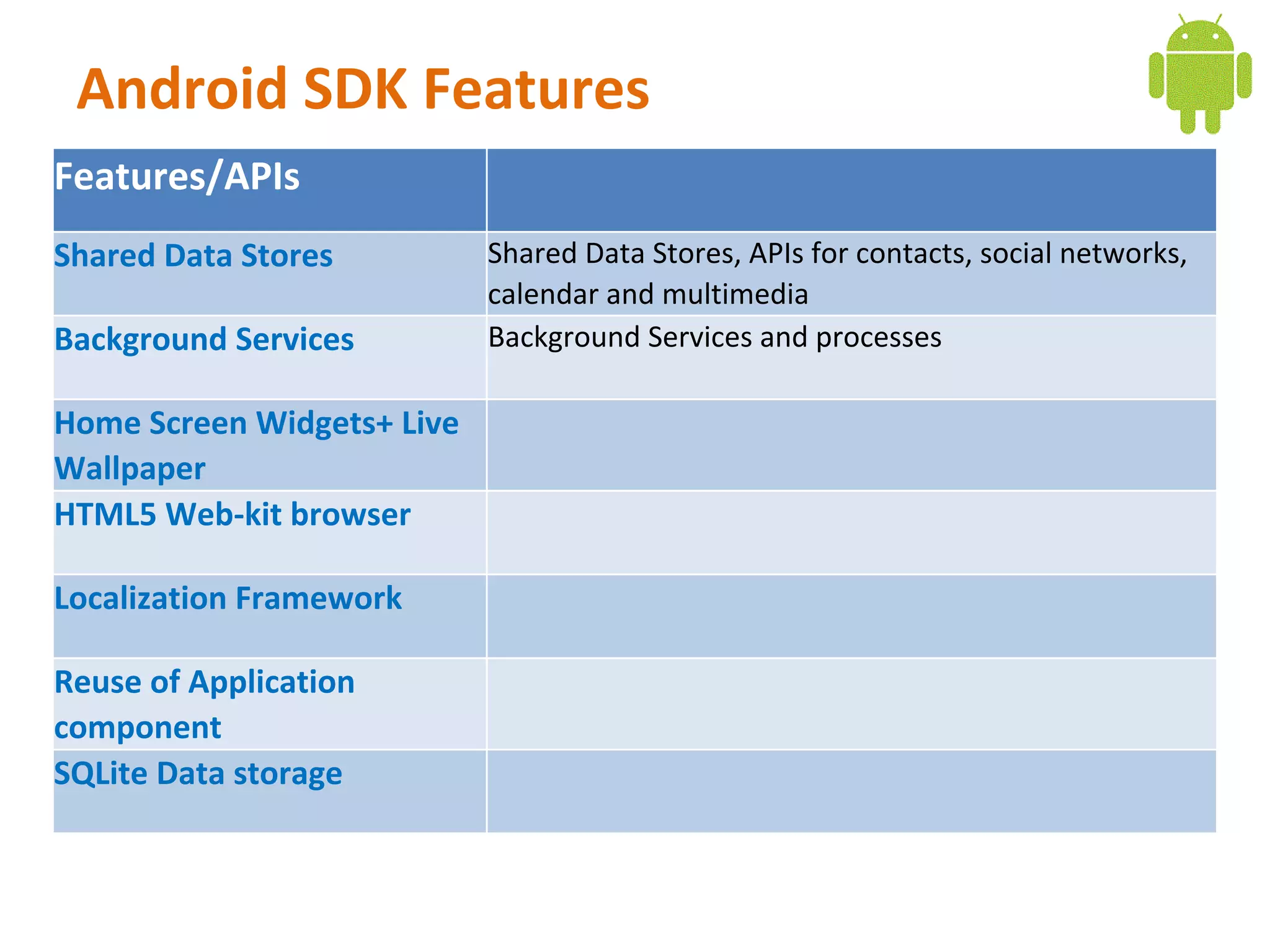
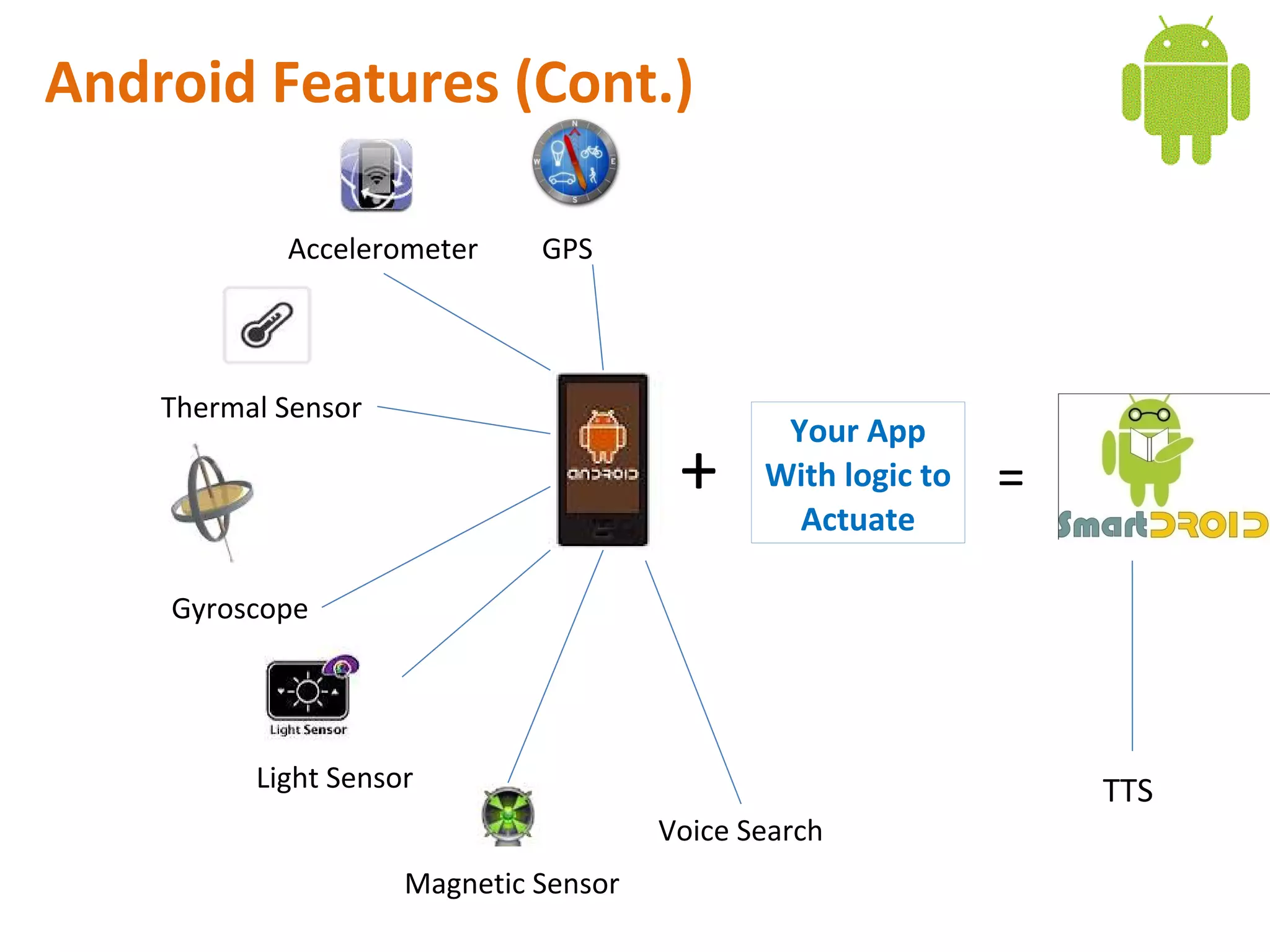
Android is an open source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware, and key applications for mobile devices. It uses the Linux kernel for core system services like memory management and process management. The Android runtime uses the Dalvik virtual machine. The application framework provides APIs for location services, connectivity, multimedia, sensors, and more. Developers can create Android applications using the Android SDK which provides tools and APIs to access device capabilities.