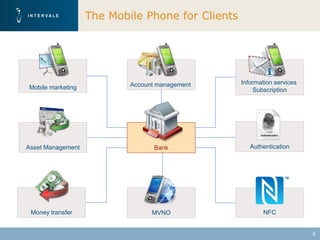
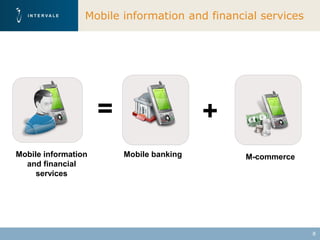
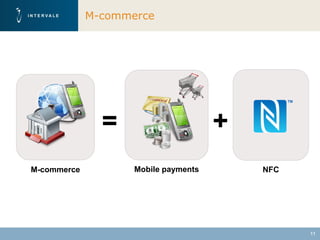
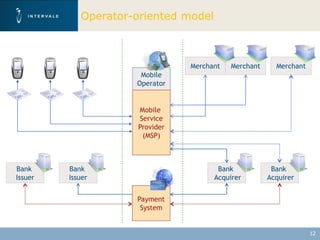
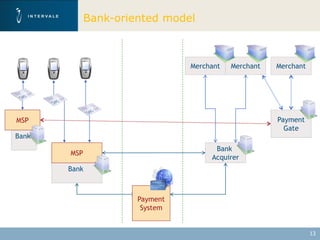
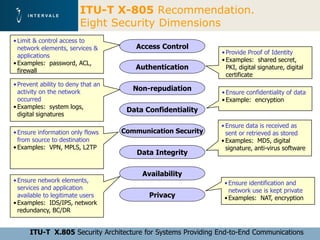
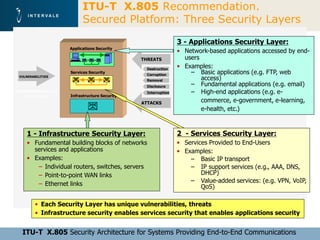
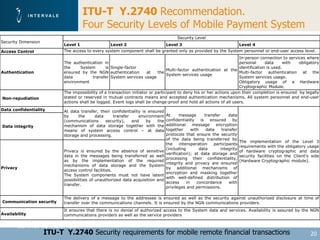
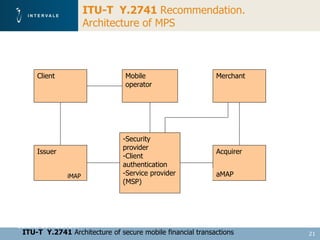
This document discusses mobile financial services and the growing use of mobile phones. It provides statistics on the rising number of mobile phone and payment card users worldwide. It then discusses how mobile phones are integrated into people's daily lives and routines. The document proposes a model for mobile information and financial services that combines mobile banking, mobile payments, and near field communication technologies. It outlines some of the security measures needed for mobile payment systems, including authentication, data integrity, and privacy.