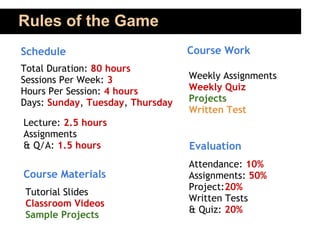
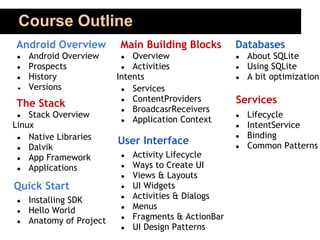
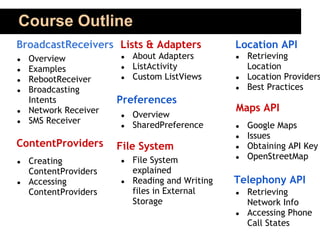
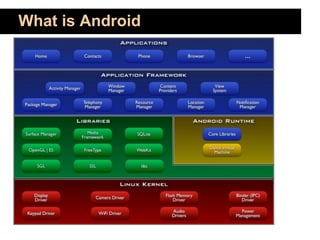
This document outlines an 80-hour course on Android application development. The course will meet 3 times per week for 4 hours of lectures, assignments, and Q&A. Topics will include the Android architecture, activities, intents, services, UI design, databases, location services, maps, and deploying apps. Students should know Java or C# fundamentals. The course aims to teach students how to build world-class mobile apps using the popular and open-source Android platform. Evaluation will be based on attendance, assignments, projects, tests, and quizzes.