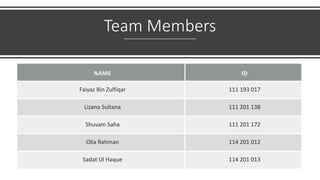
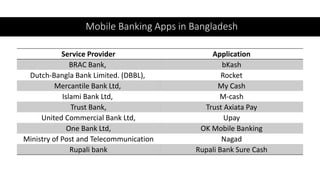
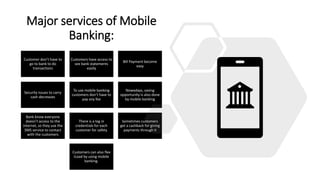
This document discusses mobile banking in Bangladesh. It provides an overview of mobile banking services in the country, including some of the first providers like Dutch Bangla Bank. It also discusses the evolution of mobile banking from SMS-based to mobile applications. The document outlines several popular mobile banking apps currently used in Bangladesh and highlights some key services offered. It notes the significant contribution of mobile banking during the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, the document discusses some challenges and future opportunities for mobile banking in Bangladesh.