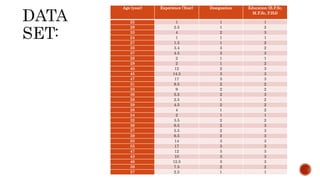
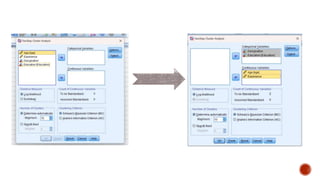
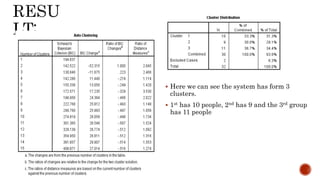
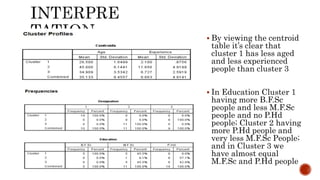
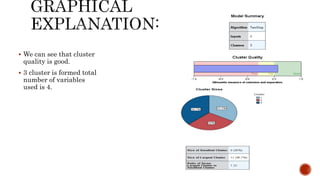
This document discusses two-step cluster analysis. It explains that two-step cluster analysis is a hybrid approach that first separates groups using a distance measure, and then chooses the optimal subgroup model using a probabilistic approach. It can handle both categorical and continuous variables by assuming variable independence within clusters. The algorithm can also automatically select the optimal number of clusters and is scalable to large datasets. The document provides an example of two-step cluster analysis using designation and education as categorical variables, and age and experience as continuous variables to cluster 30 individuals into three groups based on these characteristics.