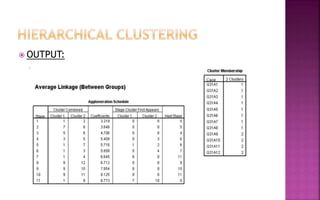
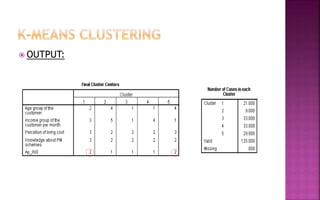
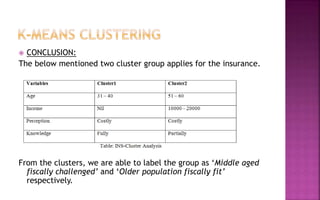
The document discusses various clustering techniques used for grouping customers and faculty based on their characteristics through cluster analysis, including hierarchical and k-means clustering methods. It describes how these techniques identify group membership and categorize data, with practical examples related to faculty's technology adaptation and banking customers' demographics. The analysis results in distinct clusters that allow for targeted marketing and interventions based on the findings.