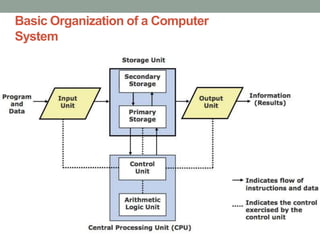
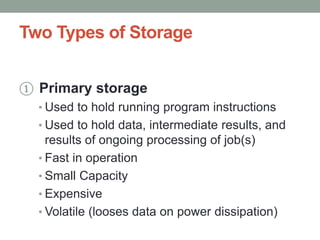
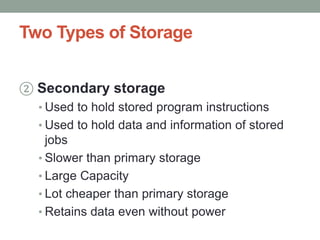
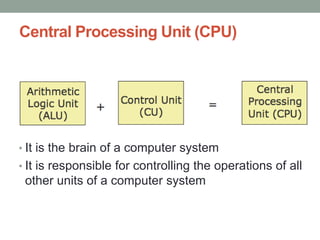
The document discusses the basic organization and operations of a computer system. It describes the five basic operations of inputting, storing, processing, outputting, and controlling. It then explains the basic components of a computer system including the input unit, output unit, storage unit, arithmetic logic unit, control unit, and central processing unit. It defines primary and secondary storage and describes the functions of the input, output, and storage units.