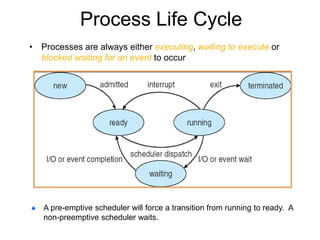
The document discusses process management in operating systems. It defines a process as a program during execution, which requires resources like memory and CPU registers. The document outlines the life cycle of a process, including the different states a process can be in like ready, running, waiting, blocked. It describes process creation and termination. The process control block (PCB) contains information needed to control and monitor each process. Context switching allows the CPU to switch between processes. Scheduling determines which process enters the running state. The document lists some common process control system calls and discusses advantages and disadvantages of process management.

![IEEE Papers Overview
Paper:1 Process Management in Distribute
System [1] represents the how one process
executing step by step in Program and Distributed
Systems at initial stage.
Paper:2 Developing Complex Systems -
Incorporating Human Variability into the Process
[2] represents the process with the comparison of
human variability.
Paper:3 Dynamic Process Migration Framework
[3] represents the process migration from one
machine to other machine , basically work on the
Distributed Systems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processmanagement-141221140008-conversion-gate02/85/Process-management-2-320.jpg)


![Process in Memory
(b, *p) - main
(a) - fun
heap (p)
(char[1000])
data (aa, buf)
text (code)
0
Process memory
Stack
Max
…
int aa;
char buf[1000];
void fun() {
int a;
…
}
main() {
int b;
char *p;
p = new char[1000];
fun();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processmanagement-141221140008-conversion-gate02/85/Process-management-5-320.jpg)