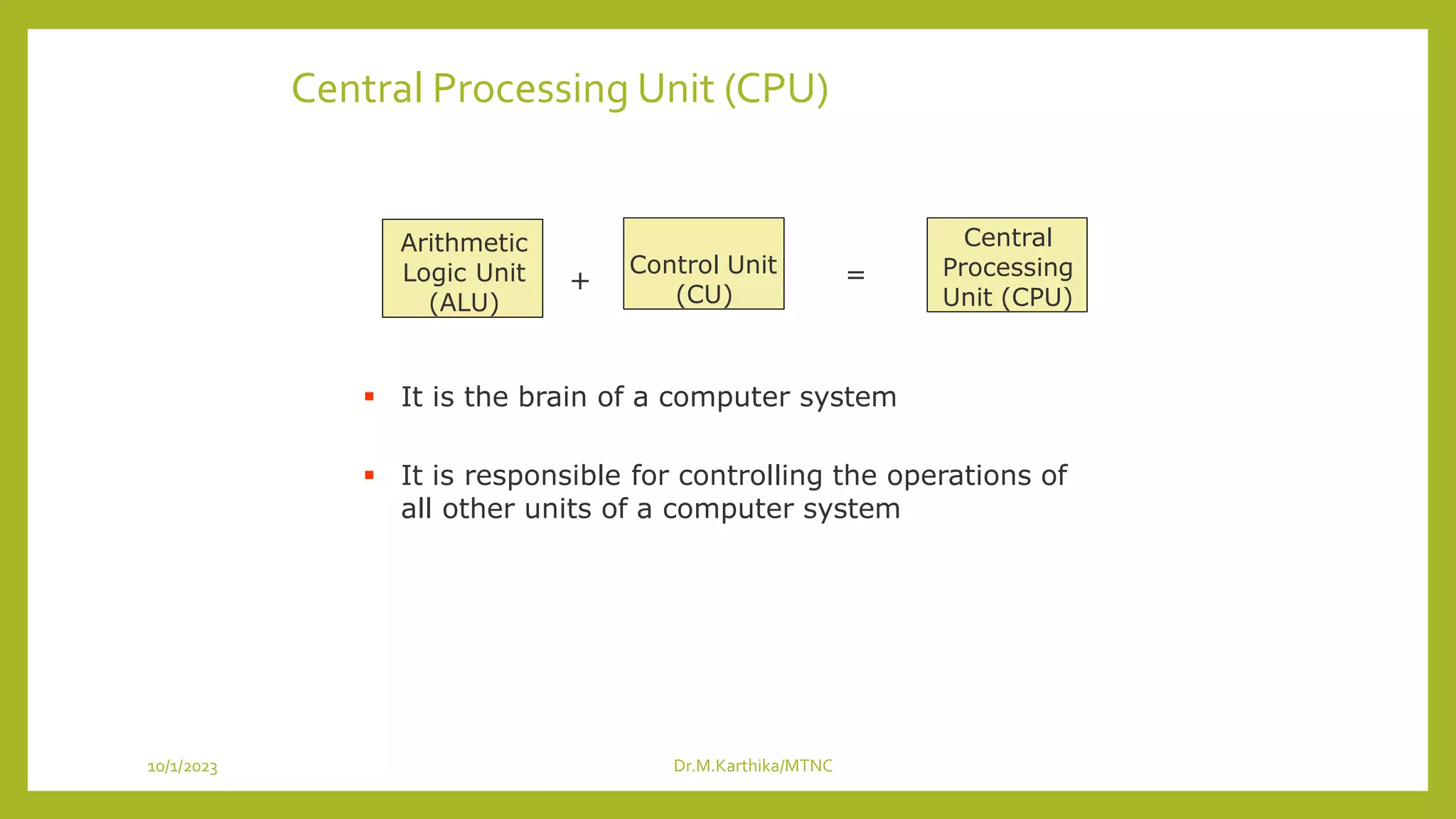
This document discusses the basic organization and functions of a computer system. It explains that a computer system consists of an input unit, output unit, storage unit, arithmetic logic unit, and control unit working together under the central processing unit. The input unit accepts and converts data for processing, the storage unit holds programs and data, the arithmetic logic unit performs calculations, and the output unit converts results to a human readable form. A computer is considered a system because its interconnected parts work together to achieve processing goals.