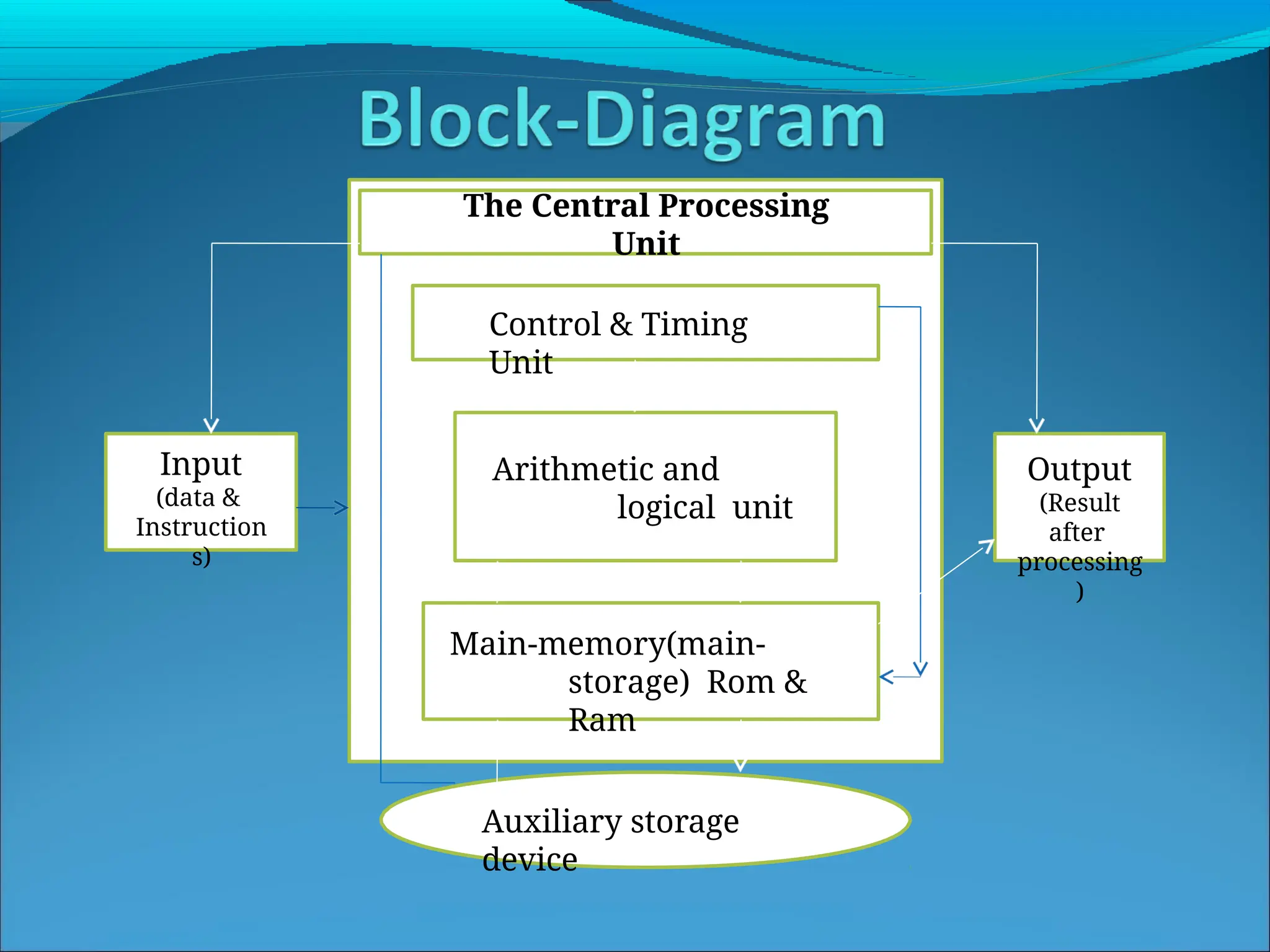
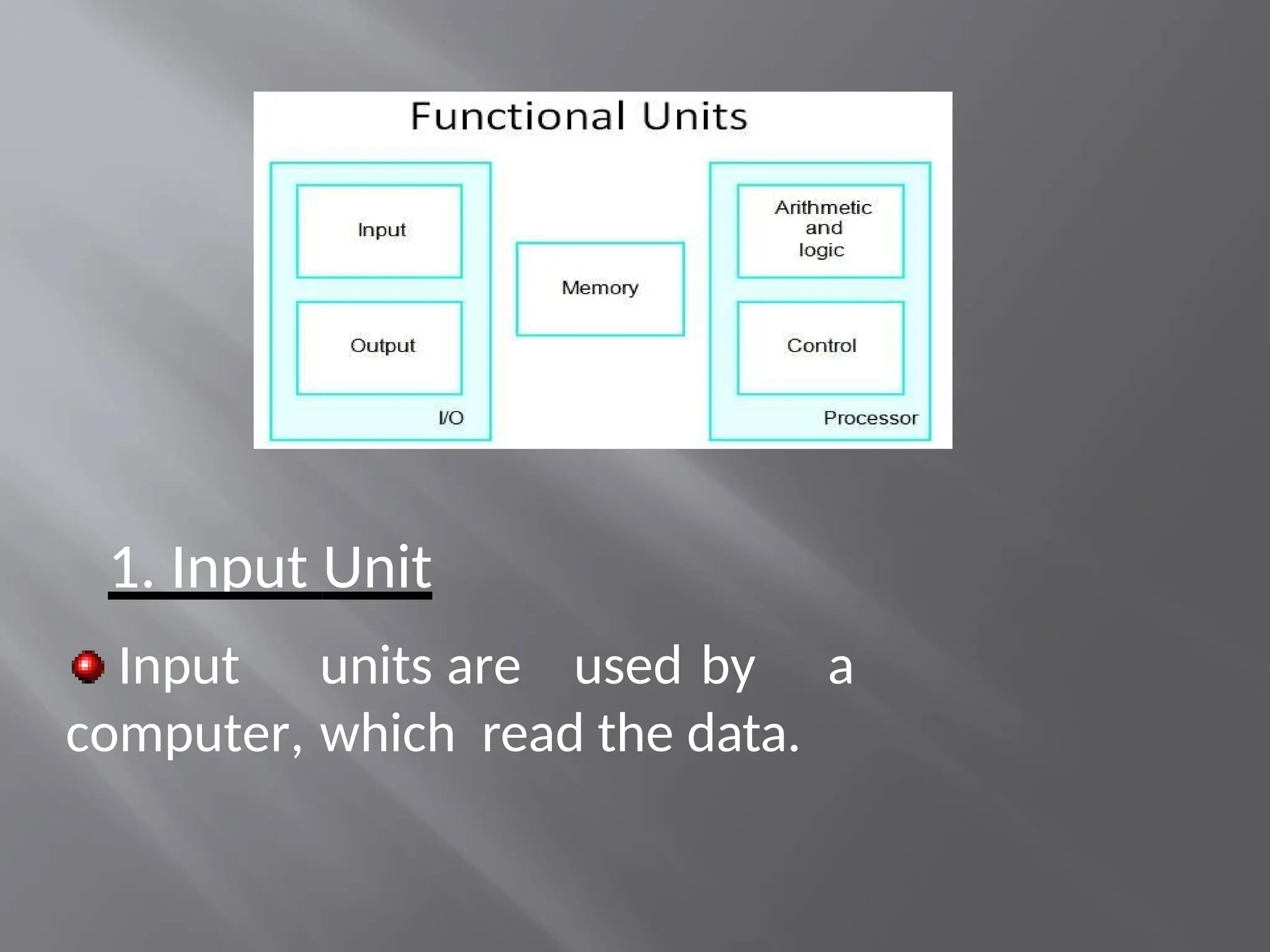
The document outlines the organization and architecture of digital computers, detailing their functional units and interconnections. Key components include the input unit, central processing unit (CPU), memory unit, arithmetic and logical unit (ALU), control unit, and output unit. It explains the role of each unit in processing data, storing information, and executing instructions.