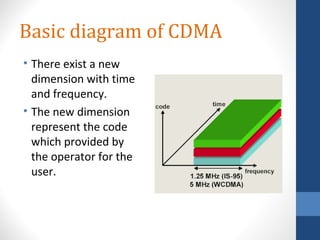
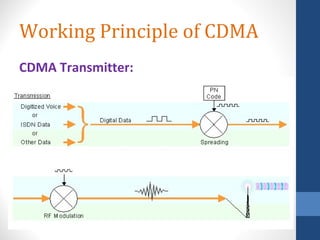
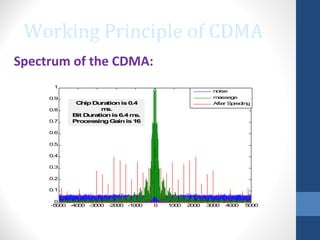
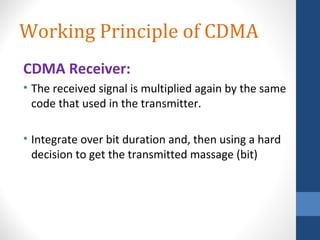
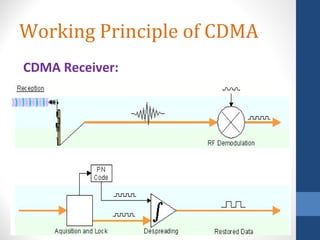
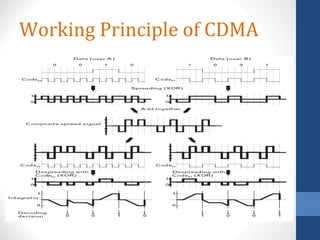
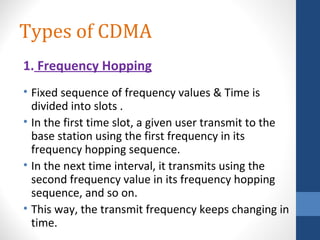
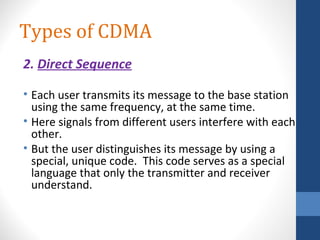
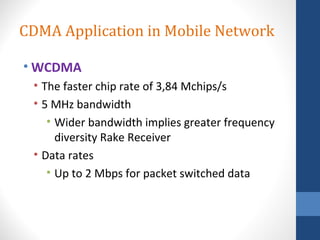
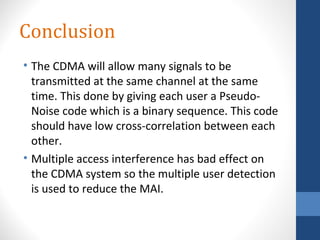
CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a digital wireless communication technology that allows multiple users to access a single channel using unique code assignments. CDMA has evolved through standards like IS-95, CDMA2000, and WCDMA. It provides benefits like increased capacity, soft handoffs, and lower power consumption compared to other technologies. While CDMA has advantages, it also faces challenges like higher licensing costs and reduced coverage area with increasing subscriber loads. Overall, CDMA remains an effective multiple access technique for wireless communications.