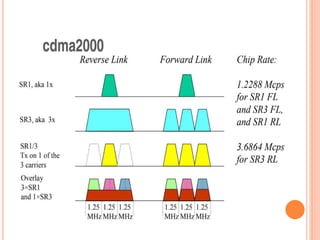
CDMA2000 is an evolution of CDMA technology that provides higher data rates and improved voice quality over CDMA. It spreads signals across a wider bandwidth and uses techniques like multicarrier modulation to support higher data rates. CDMA2000 represents a family of standards that offer both voice and high-speed data services. It provides more efficient use of spectrum and supports advanced mobile services while maintaining backward compatibility.