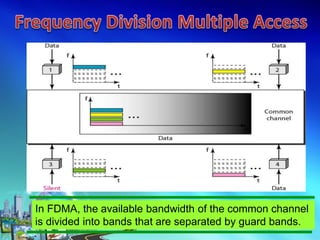
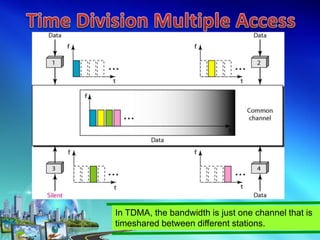
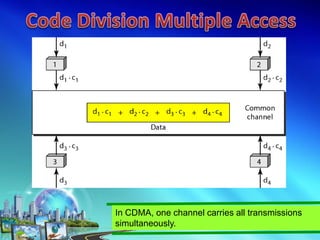
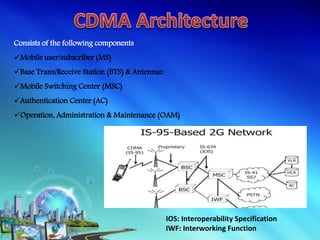
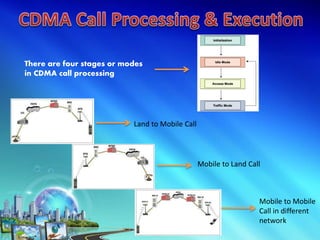
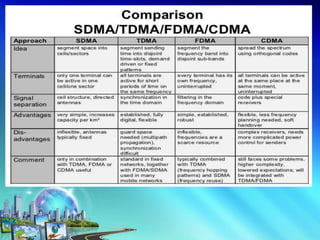
This document discusses multiple access techniques for wireless communication. It begins with an introduction to how multiple access schemes allow efficient sharing of limited radio spectrum among multiple users. It then provides a brief history of wireless communication and pioneers. The document goes on to explain various multiple access techniques in detail including FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, SDMA, and CSMA. It describes their applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Forward and reverse link power control in CDMA is also summarized.