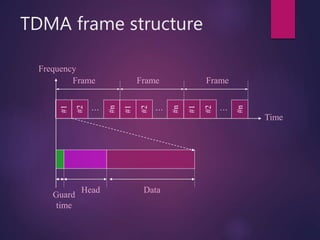
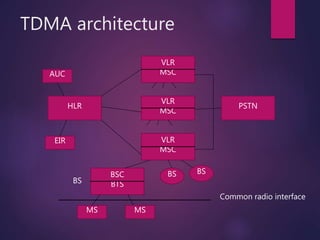
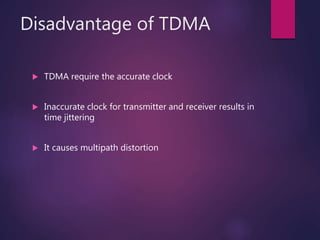
TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) is a digital wireless telephone transmission technique that allocates the given bandwidth to different users in different time slots. Each user is only allowed to transmit within their specified time interval. A TDMA frame structure divides each frequency channel into a series of time slots that are assigned to individual users. The advantages of TDMA include allowing a single channel to be used by multiple users, reducing the need for radio transceivers and allowing for smaller cell sizes. However, TDMA requires accurate clocks to avoid time jittering and multipath distortion.