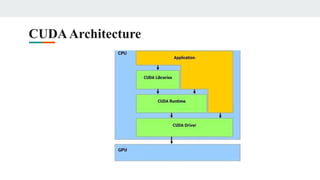
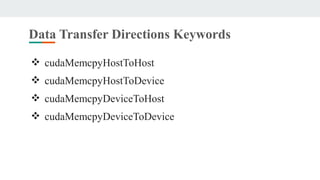
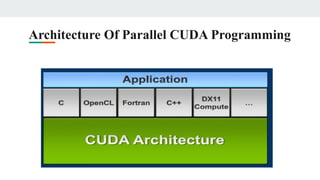
This document provides an overview of CUDA architecture and programming. It discusses key CUDA concepts like the host/device model, CUDA C extensions, GPU memory management, and parallel programming using CUDA threads and blocks. CUDA allows developers to speed up applications by offloading work to the GPU. It provides a scalable parallel programming model that maps threads to GPU threads to express data-level parallelism across thousands of lightweight threads for applications like high-bandwidth computing and visual computing.