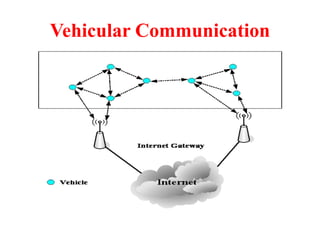
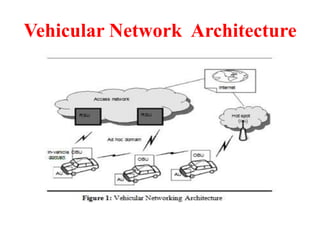
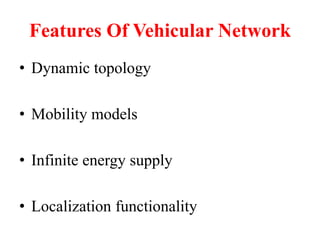
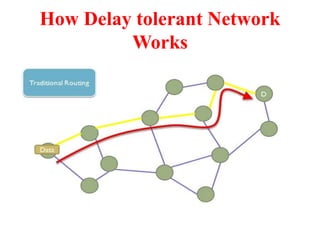
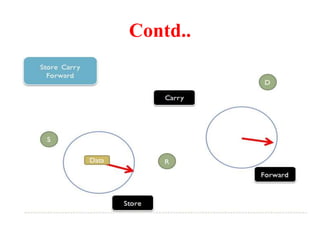
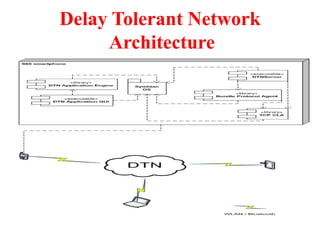
This document discusses several topics related to advanced wireless technologies, including Voice over IP networks (VoIP), vehicular networks, and delay tolerant networks. It provides overviews and definitions of each topic, describing key aspects like VoIP architecture and protocols, vehicular communication methods between vehicles and infrastructure, and the store-carry-forward approach used in delay tolerant networks to allow communication in intermittent connectivity scenarios. Application examples are also given for each such as using VoIP for voice calls over the internet, safety and traffic applications in vehicular networks, and file sharing or telemedicine over delay tolerant networks.