Embed presentation
Downloaded 805 times
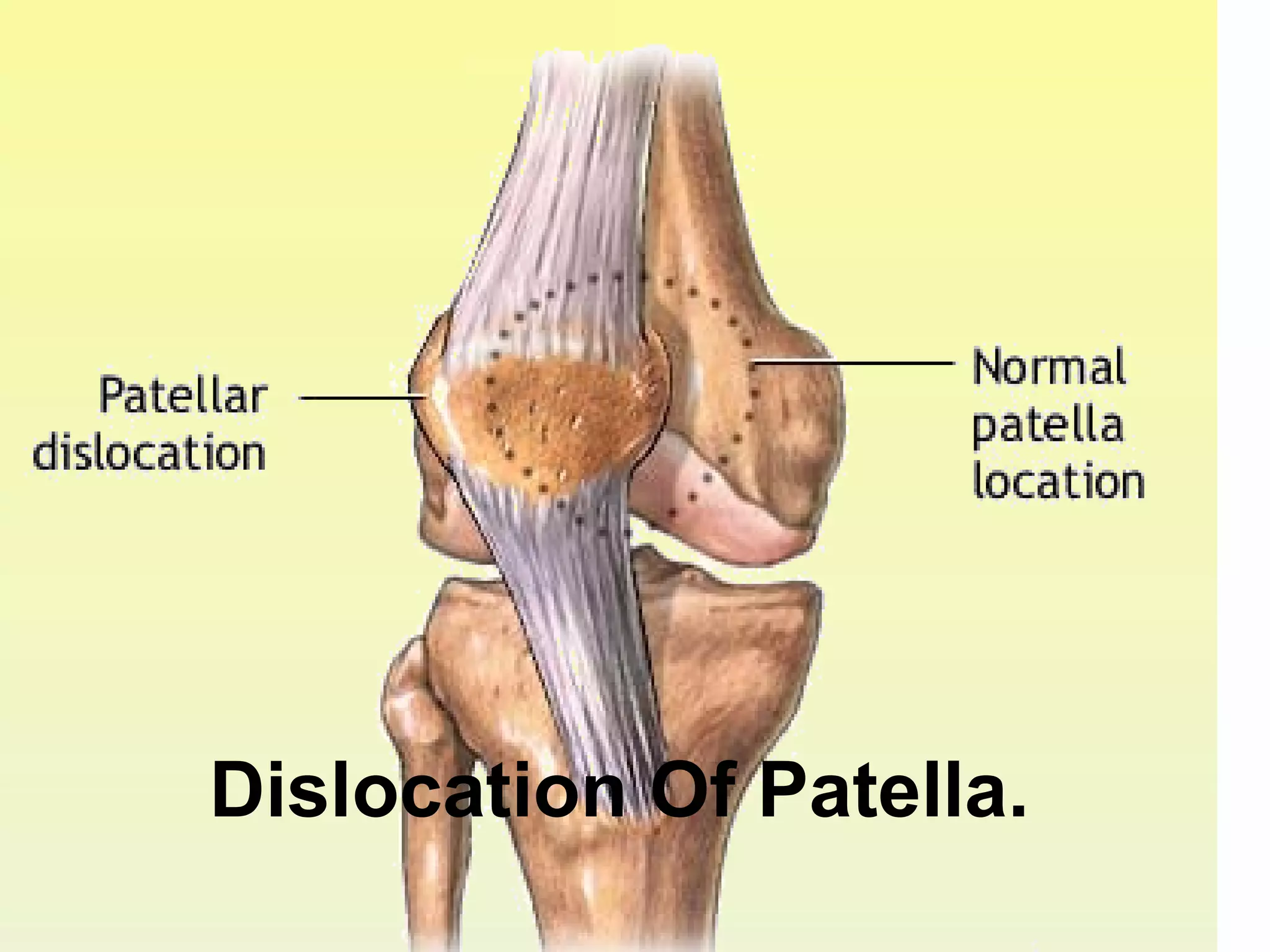

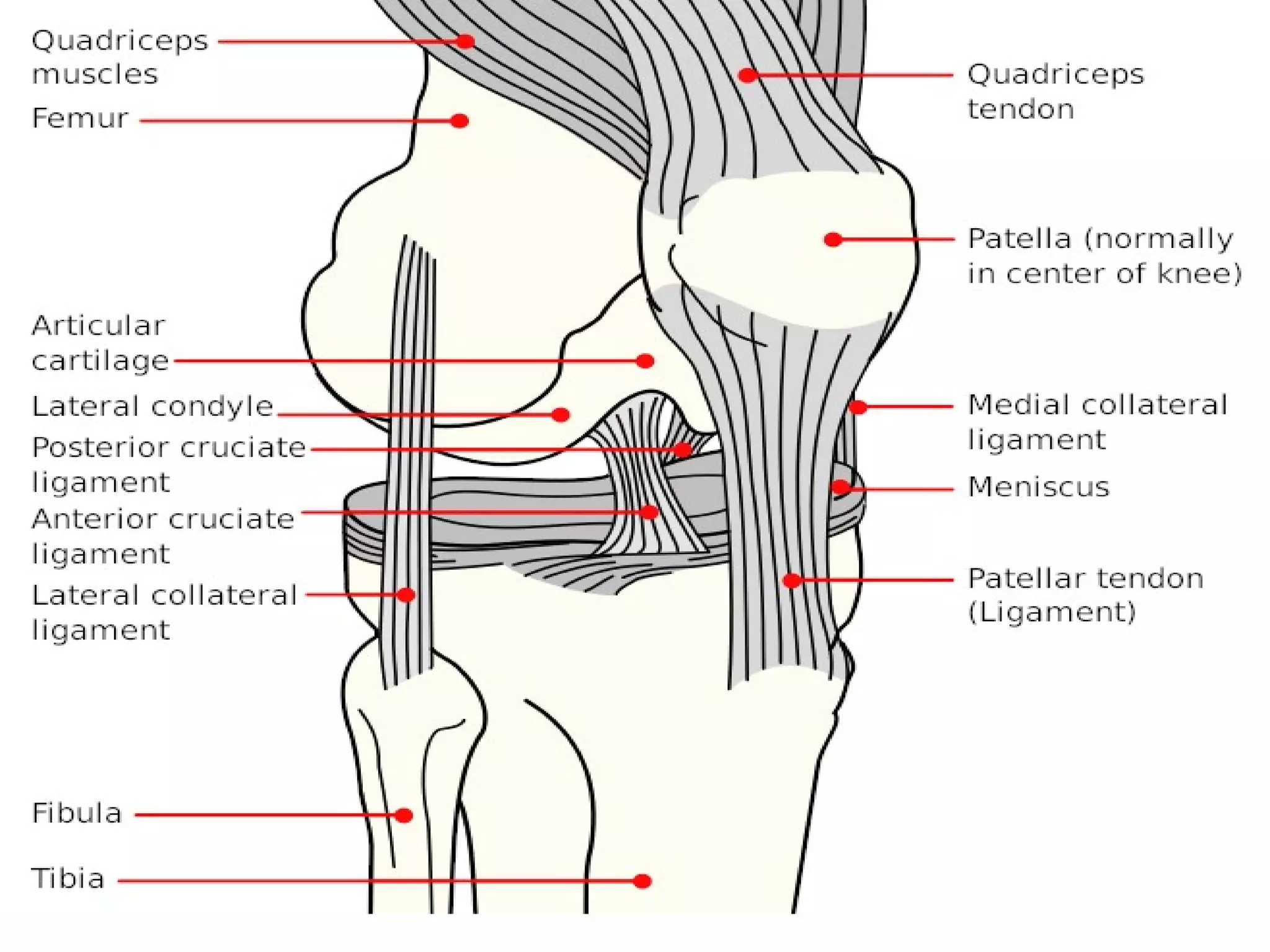
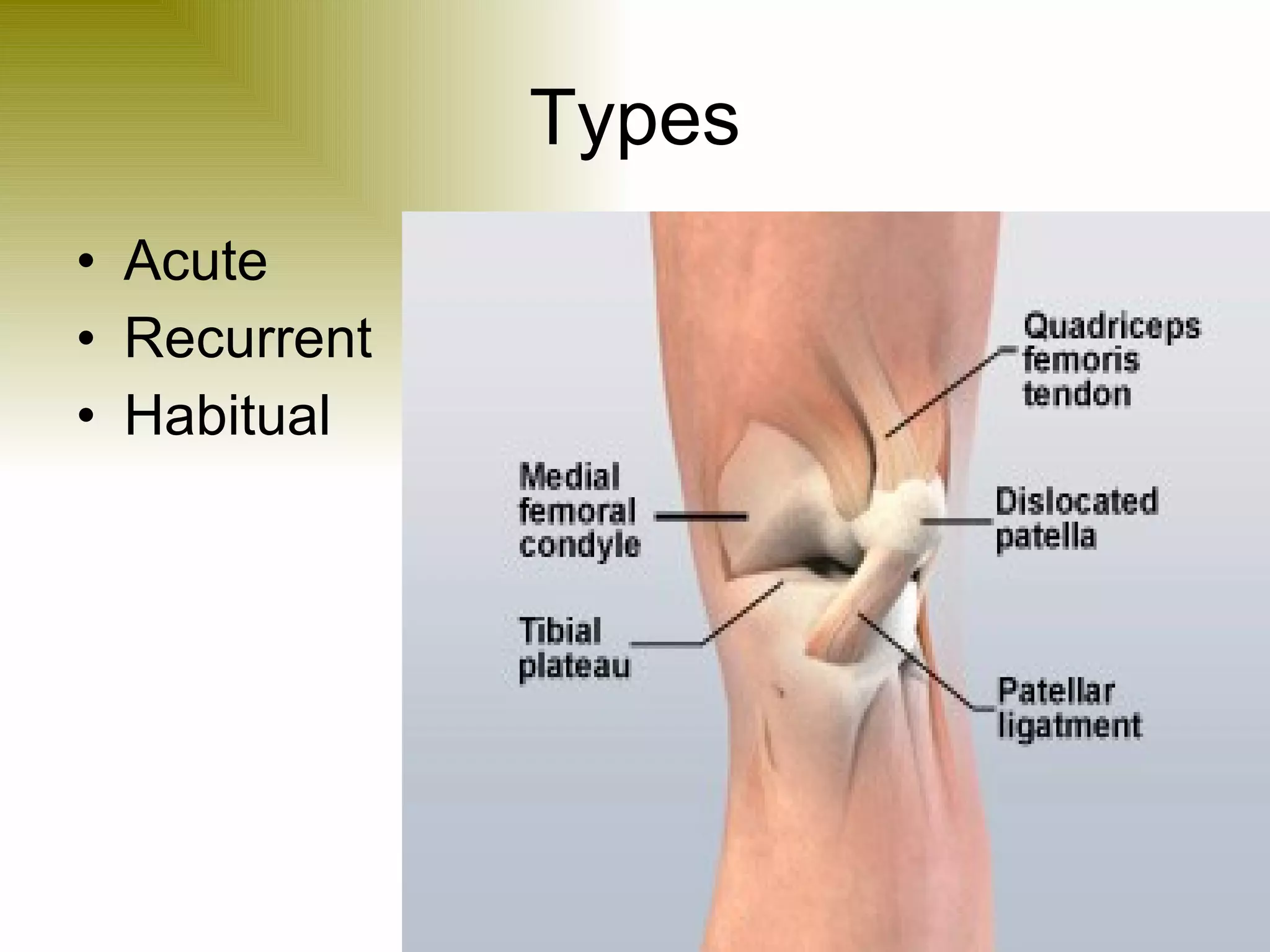



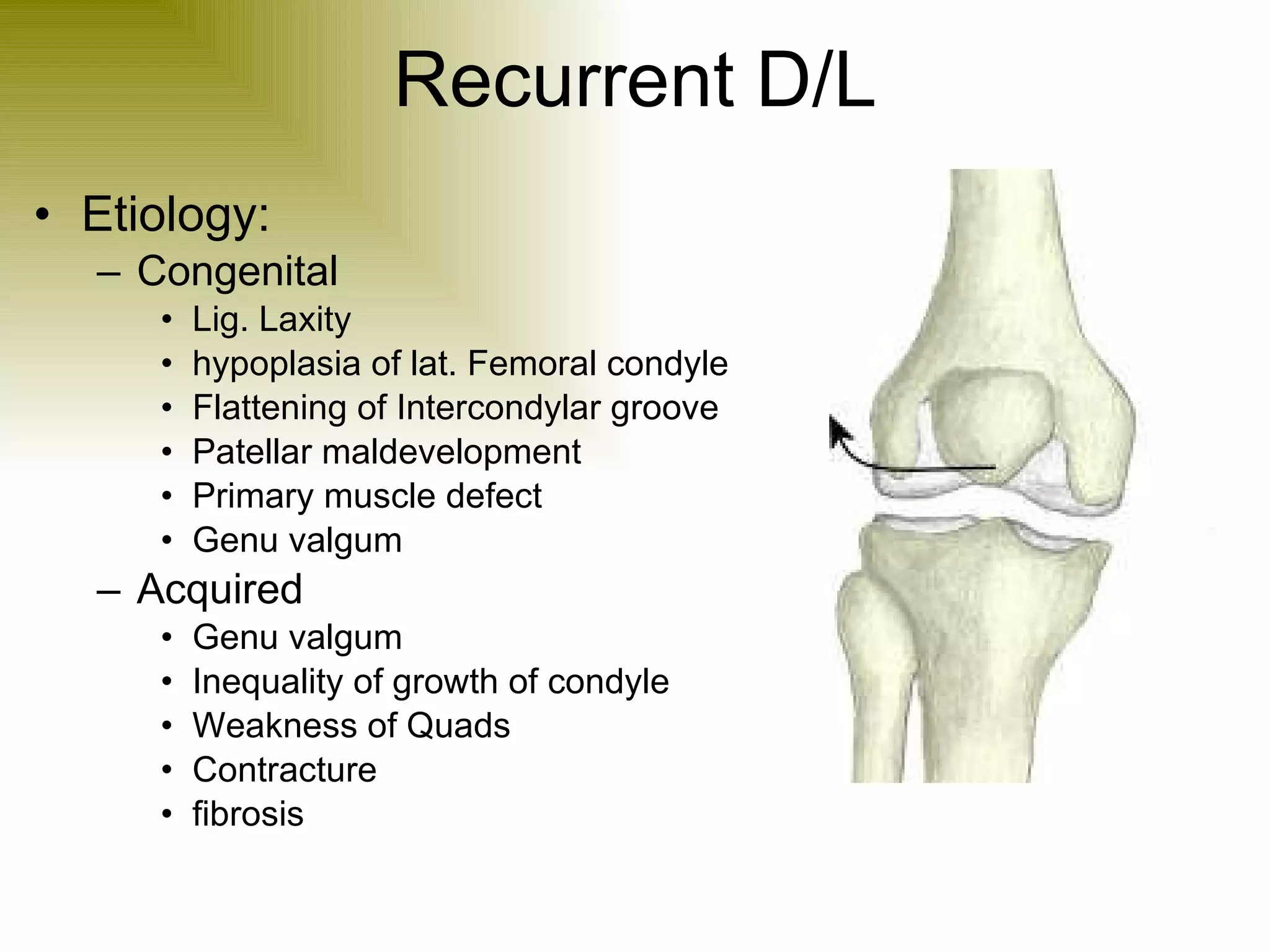
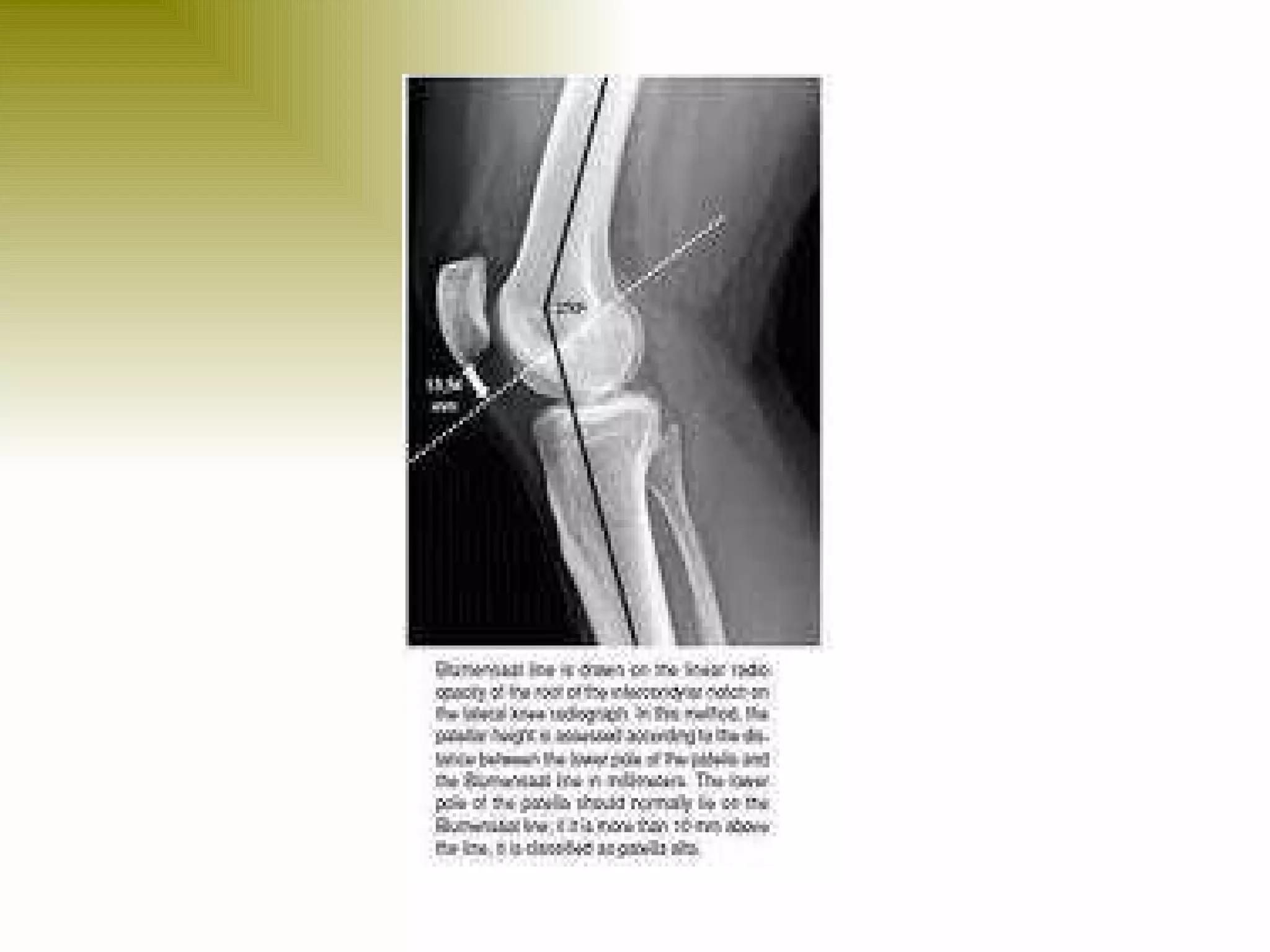
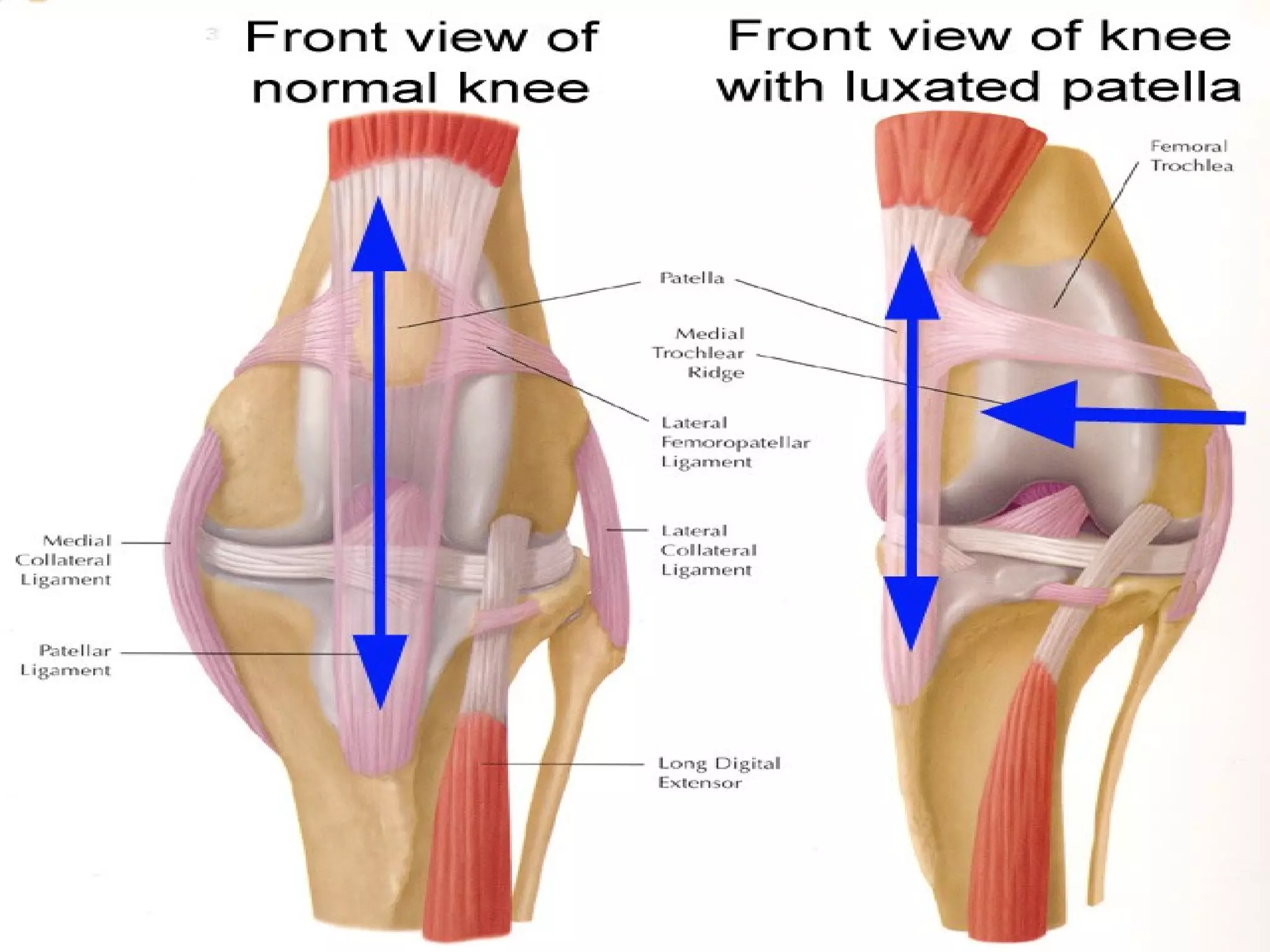



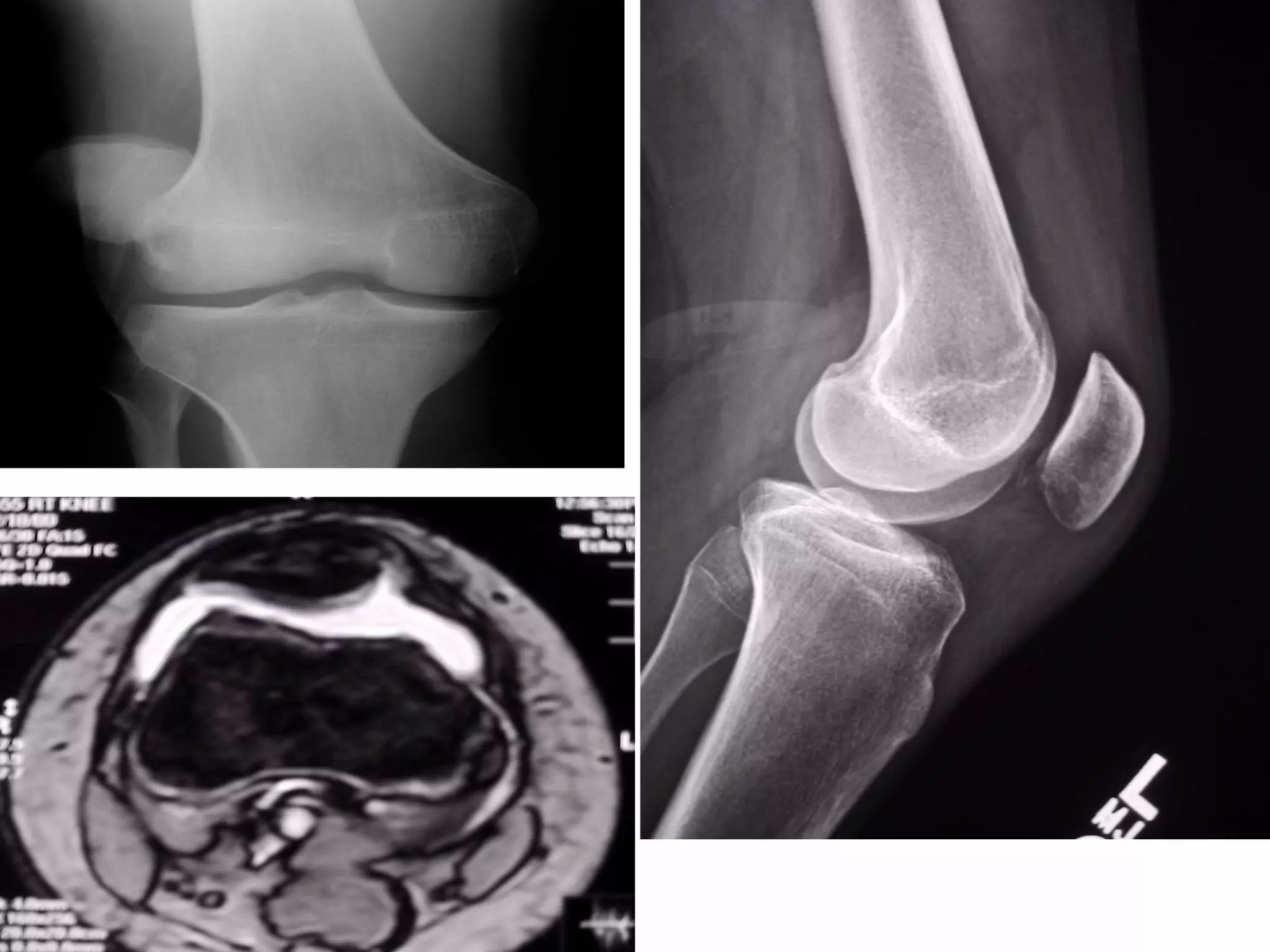
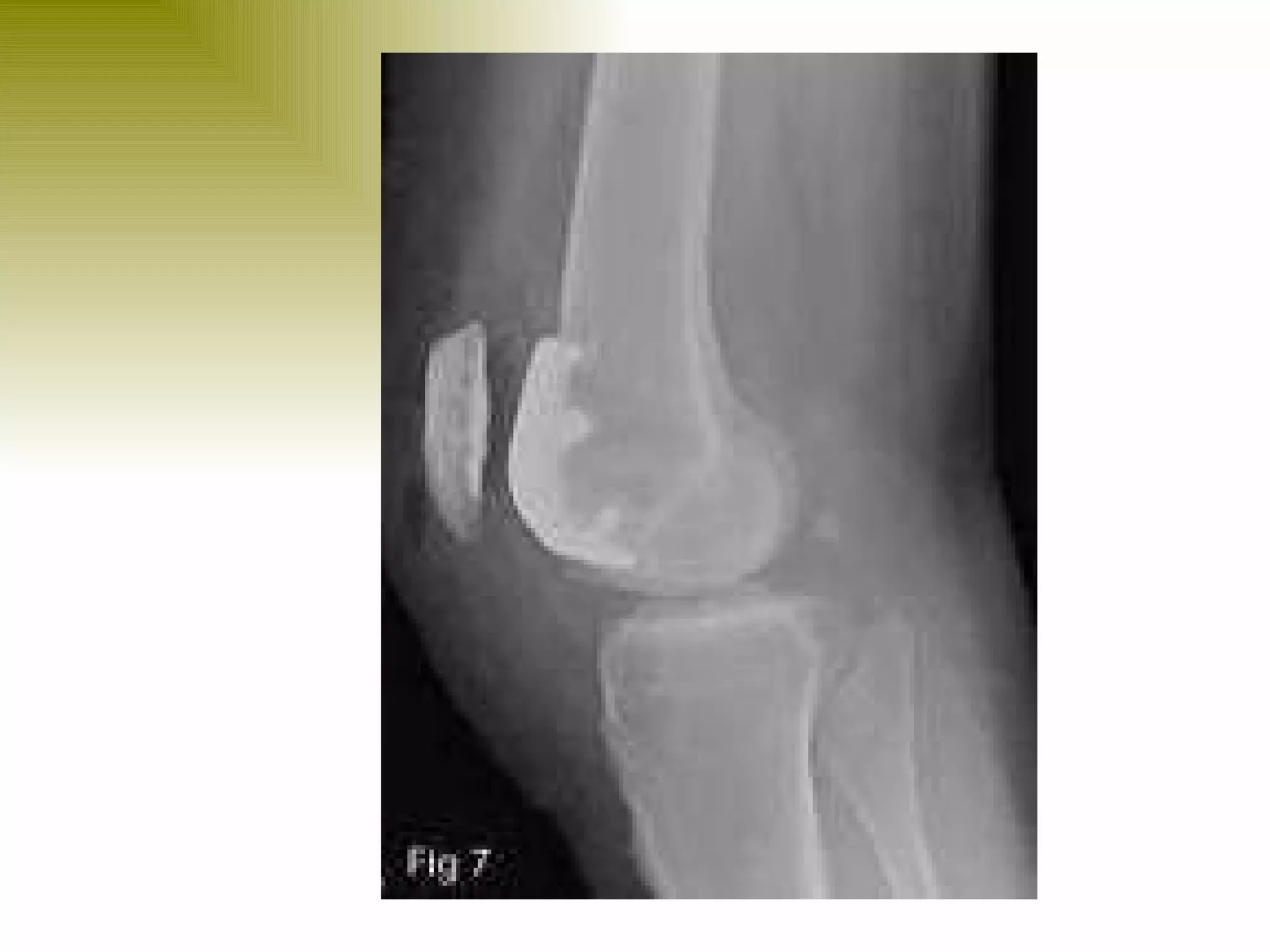
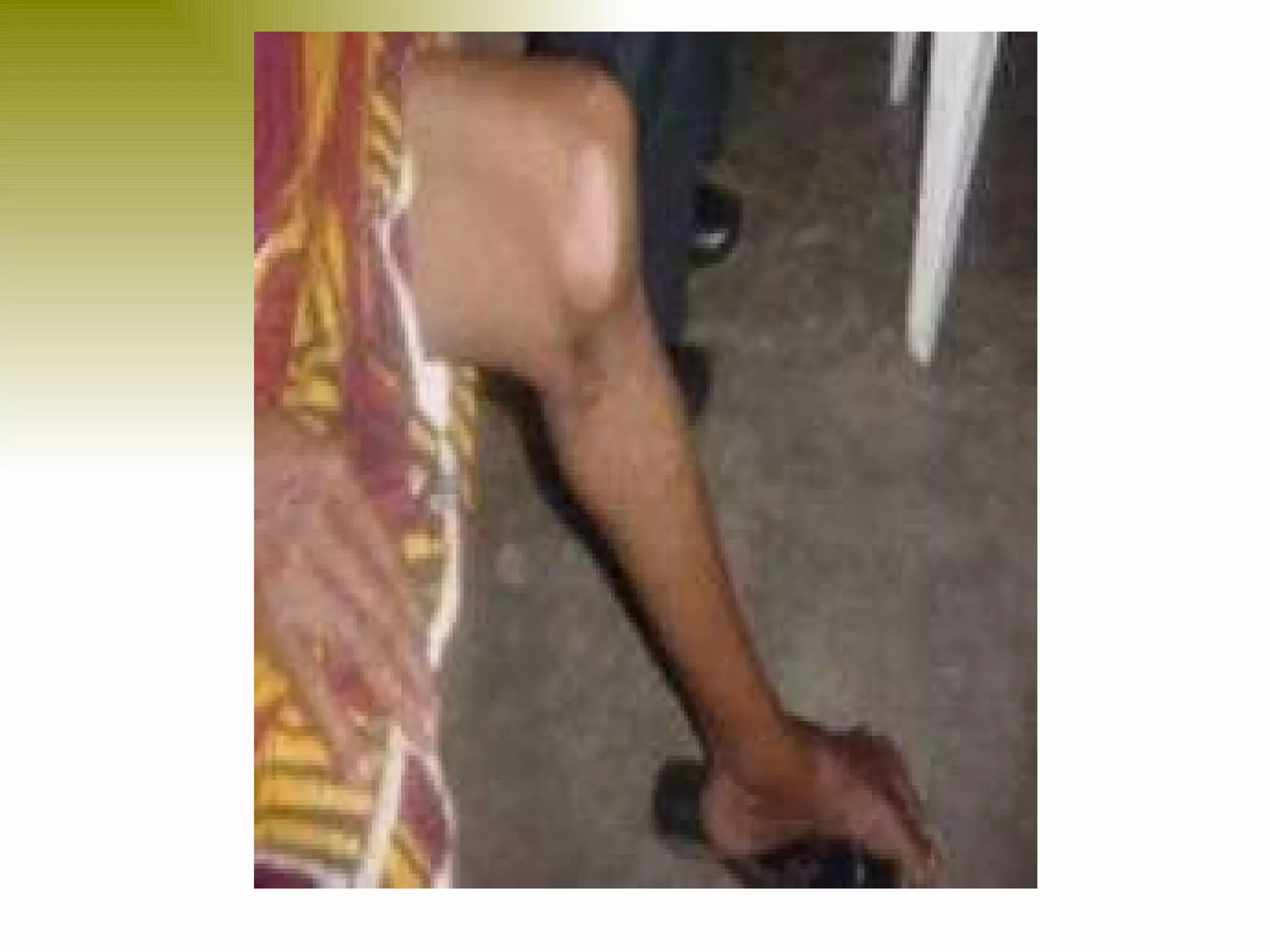

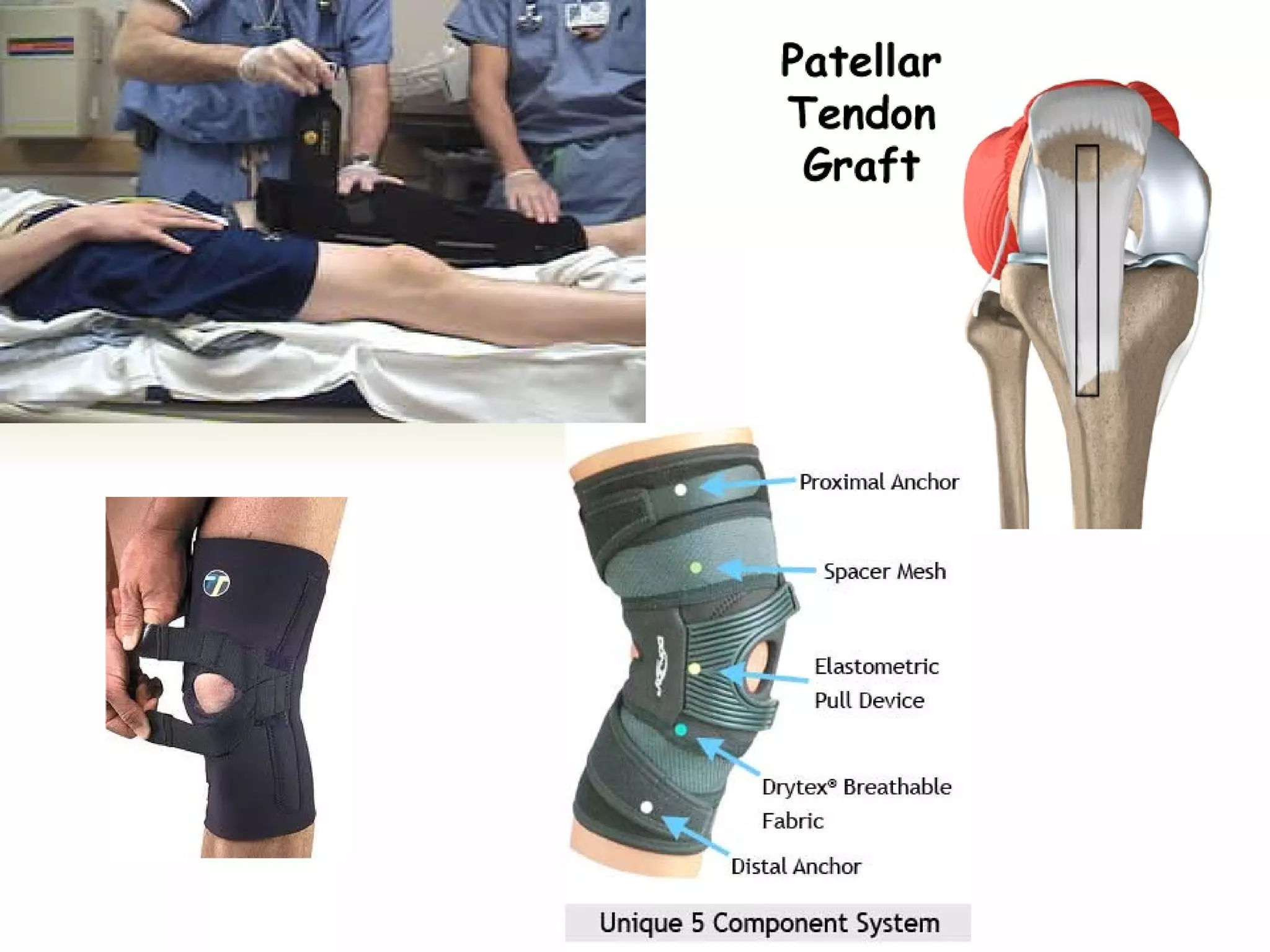
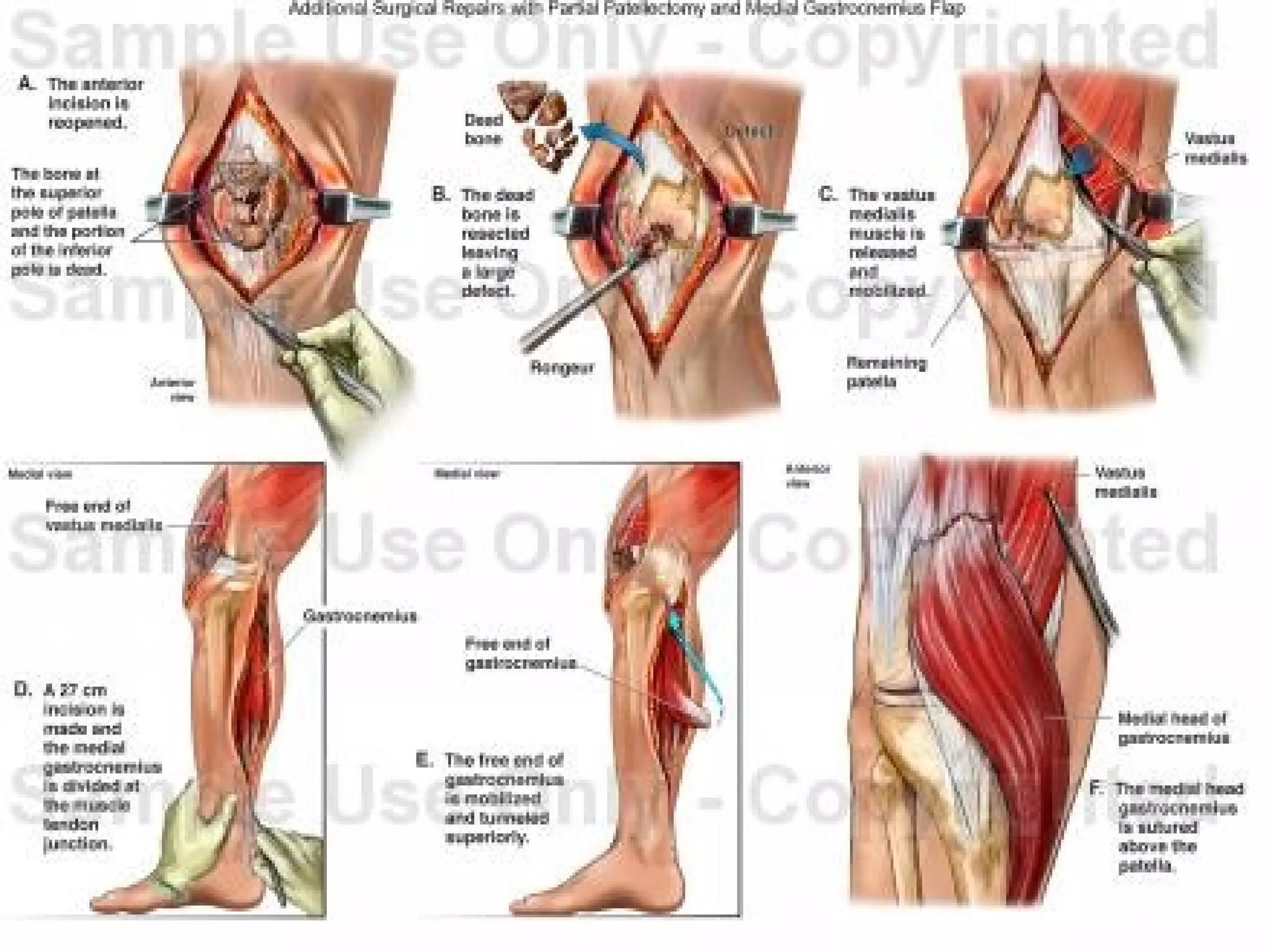



There are three types of patella dislocation: acute, recurrent, and habitual. Acute dislocation occurs suddenly due to quadriceps contraction with the knee flexed and results in the patella dislocating laterally, causing pain, swelling, and inability to straighten the knee. Recurrent dislocations are caused by ligament laxity or anatomical abnormalities and damage bones with repeated dislocations. Habitual dislocations occur every time the knee is flexed and present in early childhood.






















